Abstract
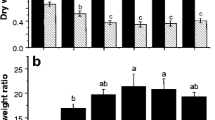
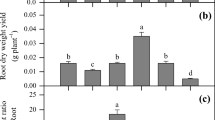
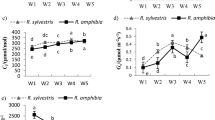
This experiment was used to explore whether the 11 nitrogenous nutrients affect the hyperaccumulation of Rorippa globosa (Turcz.) Thell. to Cd. Pot culture experiments using soil spiked with Cd as CdCl2·2.5H2O and 11 nitrogen-containing chemicals were conducted to determine the efficiency of the accumulation of Cd by R. globosa. Application of all 11 nitrogenous nutrients significantly (p < 0.05) enhanced Cd accumulation by R. globosa (Turcz.) Thell. Two major modes of Cd accumulation were observed: (i) through increase of biomass yield without reduction of Cd uptake and (ii) through increase of Cd uptake efficiency in parallel with increase of biomass yield. Bicarbonate > phosphate > chloride compounds of NH4 enhanced the biomass yield to the greatest extent, while oxalate > nitrate > chloride > and bicarbonate caused a significant increase of Cd uptake by R. globosa. Competition between N and Cd translocation caused either significant reduction of Cd translocation factor or decrease of biomass yield. Of studied nutrients, ammonium bicarbonate NH4HCO3 and ammonium chloride NH4Cl exerted the best joint effect of these two processes on the efficiency of R. globosa as a Cd hyperaccumulator. Application of these chemicals caused increase of Cd concentrations in roots of R. globosa by 35.1 and 41.1 %, and in shoots by 13.9 and 56.4 %, while biomasses of roots increased by 5.8- and 3.8-fold and in shoots by 7.4-fold, and 6.4-fold, respectively, compared to the control. As a result, accumulated load (μg pot−1) of Cd in roots increased by 8.2- and 5.8-fold and in shoots by 8.6- and 10.6-fold in both pots. Consequently, chemicals (NH4HCO3 and NH4Cl) that enhanced both Cd enrichment and biomass yield had the greatest effect on the bioaccumulation capacity of R. globosa.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano DC, Wenzel WW, Vangronsveld J, Bolan NS (2004) Role of assisted natural remediation in environmental cleanup. Geoderma 122:121–142
Carrasco-Gil S, Estebaranz-Yubero M, Medel-Cuesta D, Millana R, Hernandez L (2012) Influence of nitrate fertilization on Hg uptake and oxidative stress parameters in alfalfa plants cultivated in a Hg-polluted soil. Environ Exp Bot 75:16–24
Chang YS, Chang YJ, Lin CT, Lee MC, Wu CW, Lai YH (2013) Nitrogen fertilization promotes the phytoremediation of cadmium in Pentas lanceolata. I. Biodeteri. Biodegrad. In Press, Corrected proof
Evangelou MWH, Bauer U, Ebel M, Schaeffer A (2007) The influence of EDDS and EDTA on the uptake of heavy metals of Cd and Cu from soil with tobacco Nicotiana tabacum. Chemosphere 68:345–353
Giansoldati V, Tassi E, Morelli E, Gabellieri E, Pedron F, Barbafieri M (2012) Nitrogen fertilizer improves boron phytoextraction by Brassica juncea grown in contaminated sediments and alleviates plant stress. Chemosphere 87:1119–1125
Jalloh M, Chen J, Zhen F, Zhang G (2009) Effect of different N fertilizer forms on antioxidant capacity and grain yield of rice growing under Cd stress. J Hazard Mater 162:1081–1085
Li S, Liu R, Wang M, Wang X, Shan H, Wang H (2006) Phytoavailability of cadmium to cherry-red radish in soils applied composted chicken or pig manure. Geoderma 136:260–271
Li TQ, Yang XE, Lu LL, Islam E, He ZL (2009) Effects of zinc and cadmium interactions on root morphology and metal translocation in a hyperaccumulating species under hydroponic conditions. J Hazard Mater 169:734–741
Liu L, Chen HS, Cai P, Liang W, Huang QY (2009) Immobilization and phytotoxicity of Cd in contaminated soil amended with chicken manure compost. J Hazard Mater 163:563–567
Luo BF, Du ST, Lu KX, Liu WX, Lin XY, Jin CW (2012) Iron uptake system mediates nitrate-facilitated cadmium accumulation in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) plants. J Exp Bot 63(8):3127–3136
Lux A, Martinka M, Vaculik M, White PJ (2011) Root responses to cadmium in the rhizosphere: a review. J Exp Bot 52(1):21–37
Marques APGC, Oliveira RS, Samardjieva KA, Pissarra J, Rangel AOSS, Castro PML (2008) EDDS and EDTA- enhanced zinc accumulation by Solanum nigrum inoculated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi grown in contaminated soil. Chemosphere 70:1002–1014
Martha L (2005) Enhancement of lead uptake by alfalfa (Medicago sativa) using EDTA and a plant growth promoter. Chemosphere 61:595–598
Monsant AC, Tang C, Baker AJM (2010a) The effect of nitrogen form on rhizosphere soil pH and zinc phytoextraction by Thlaspi caerulescens. Chemosphere 73:635–642
Monsant AC, Wang YD, Tang CX (2010b) Nitrate nutrition enhances zinc hyperaccumulation in Noccaea caerulescens (Prayon). Plant Soil 336:391–404
Salati S, Quadri G, Tambone F, Adani F (2010) Fresh inorganic matter of municipal solid waste enhances phytoextraction of heavy metals from contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 158(5):1899–1906
Srivastava M, Santos J, Srivastava P, Ma LQ (2010) Comparison of arsenic accumulation in 18 fern species and four Pteris vittata accessions. Bioresour Technol 101:2691–2699
Tessier A, Campbell PGC, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51:844–851
Thayalakumaran T (2003) Plant uptake and leaching of copper during EDTA-enhanced phytoremediation of repacked and undisturbed soil. Plant Soil 254:415–423
Uraguchi S, Mort S, Kuramata M, Kawasami A, Arao T, Ishikawa S (2009) Root-to-shoot Cd translocation via the xylem is the major process determining shoot and grain cadmium accumulation in rice. J Exp Bot 60:2677–2688
Wei SH, Twardowska I (2013) Main rhizosphere characteristics of the Cd hyperaccumulator Rorippa globosa (Turcz.) Thell. Plant Soil 372:669–681
Wei SH, Zhu JG, Zhou QX, Zhan J (2011) Fertilizer amendment for improving the phytoextraction of cadmium by a hyperaccumulator Rorippa globosa (Turcz.) Thell. J. Soils Sediments 11:915–922
Willey N, Tang S (2006) Some effects of nitrogen nutrition on cesium uptake and translocation by species in the Poaceae, Asteraceae and Caryophyllidae. Environ Exp Bot 58:114–122
Zaier H, Ghnaya T, Ben RK, Lakhdar A, Rejeb S, Jemal F (2010) Effects of EDTA on phytoextraction of heavy metals (Zn, Mn and Pb) from sludge-amended soil with Brassica napus. Bioresour Technol 101:3978–3983
Zhuang P, Shu W, Li Z, Liao B, Li J, Shao J (2009) Removal of metals by sorghum plants from contaminated land. J Environ Sci 21(10):1432–1437
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31270540, 31070455 and 40971184), the National Science & Technology Pillar Program (2012BAC17B04), Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (2012AA06A202), Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, China (201102224), and Polish-Chinese Joint Research Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, S., Ji, D., Twardowska, I. et al. Effect of different nitrogenous nutrients on the cadmium hyperaccumulation efficiency of Rorippa globosa (Turcz.) Thell.. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 1999–2007 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3448-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3448-9