Abstract
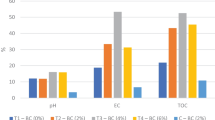
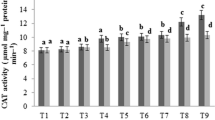
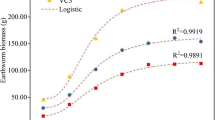
Vermicomposting is an eco-friendly technology, where earthworms are introduced in the waste, inter alia sewage sludge, to cooperate with microorganisms and enhance decomposition of organic matter. The main aims of the present study was to determine the influence of two different earthworm species, Eisenia fetida and Eisenia andrei, on the changes of selected metallic trace elements content in substratum during vermicomposting process using three different sewage sludge mainly differentiated by their metal contents. Final vermicompost has shown a slight reduction in Cd, Cu, Ni, and Pb, while the Zn concentration tends to increase. Accumulation of particular heavy metals in earthworms’ bodies was assessed. Both species revealed high tendency to accumulate Cd and Zn, but not Cu, Ni, and Pb, but E. andrei has higher capabilities to accumulate some metals. Riboflavin content, which content varies depending on metal pollution in several earthworms species, was measured supravitaly in extruded coelomocytes. Riboflavin content decreased slightly during the first 6 weeks of exposure and subsequently restored till the end of the 9-week experiment. Selected agronomic parameters have also been measured in the final product (vermicompost) to assess the influence of earthworms on substratum.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1999) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. APHA, Washington DC
Bernard F, Brulle F, Douay F, Lemiere S, Demuynck S, Vandenbulcke F (2010) Metallic trace element body burdens and gene expression analysis of biomarker candidates in Eisenia fetida, using an “exposure/depuration” experimental scheme with field soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1034–45
Brulle F, Mitta G, Leroux R, Lemiere S, Lepretre A, Vandenbulcke F (2007) The strong induction of metallothionein gene following cadmium exposure transiently affects the expression of many genes in Eisenia fetida: a trade-off mechanism? comparative biochemistry and physiology. Toxicol Pharmacol : CBP 144:334–41
Dai J (2004) Heavy metal accumulation by two earthworm species and its relationship to total and DTPA-extractable metals in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 36:91–98
Demuynck S, Grumiaux F, Mottier V, Schikorski D, Lemiere S, Lepretre A (2007) Cd/Zn exposure interactions on metallothionein response in Eisenia fetida (Annelida, Oligochaeta). Comp Biochem Physiol Toxicol Pharmacol : CBP 145:658–68
Dominguez J, Edwards CA (2011) Biology and ecology of earthworm species used for vermicomposting. In: Edwards CA, Sherman RL (eds) Vermiculture technology: earthworms, organic wastes, and environmental management. CRC Press, USA
Domínguez-Crespo MA, Sánchez-Hernández ZE, Torres-Huerta AM, Negrete-Rodríguez MLX, Conde-Barajas E, Flores-Vela A (2011) Effect of the heavy metals Cu, Ni, Cd and Zn on the growth and reproduction of epigeic earthworms (E. Fetida) during the vermistabilization of municipal sewage sludge. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:915–931
Edwards CA (1988) Examines the earthworm through morphology, taxonomy, biology and look at its environmental role. In: Neuhauser CAEEF (ed) Earthworms in waste and environmental management. SPB Academic Publ. Co, The Hague, pp 21–31
Edwards CA, Bater JE (1992) The use of earthworms in environmental management. Soil Biol Biochem 24:1683–1689
Elvira C, Sampedro L, Benítez E, Nogales R (1998) Vermicomposting of sludges from paper mill and dairy industries with Eisenia Andrei: a pilot-scale study. Bioresour Technol 63:205–211
Fritsch C, Giraudoux P, Cœurdassier M, Douay F, Raoul F, Pruvot C, Waterlot C, Ad V, Scheifler R (2010) Spatial distribution of metals in smelter-impacted soils of woody habitats: influence of landscape and soil properties, and risk for wildlife. Chemosphere 81:141–155
Garg P, Gupta A, Satya S (2006) Vermicomposting of different types of waste using Eisenia foetida: a comparative study. Bioresour Technol 97:391–5
Gogoi A, Biswas S, Bora J, Bhattacharya SS, Kumar M (2015) Effect of vermicomposting on copper and zinc removal in activated sludge with special emphasis on temporal variation. Ecohydrol Hydrobiol 15:101–107
Hait S, Tare V (2011) Vermistabilization of primary sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 102:2812–20
Hernstein R (1981) Utilization of earthworms and microorganisms in stabilization, decontamination and detoxification of residual sludges from treatment of wastewater. National Science Foundation, Washington, DC
Homa J, Rorat A, Kruk J, Cocquerelle C, Plytycz B, Vandenbulcke F (2015) Dermal exposure of Eisenia Andrei earthworms: effects of heavy metals on metallothionein and phytochelatin synthase gene expressions in coelomocytes. Environ Toxicol Chem 34:1397–1404
ISO (6878:2004) Water quality -- Determination of phosphorus -- Ammonium molybdate spectrometric method
Koziol B, Markowicz M, Kruk J, Plytycz B (2006) Riboflavin as a source of autofluorescence in Eisenia fetida coelomocytes. Photochem Photobiol 82:570–3
Lavelle P, Spain AV (2001) Soil ecology. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, p 654
Liu X, Hu C, Zhang S (2005) Effects of earthworm activity on fertility and heavy metal bioavailability in sewage sludge. Environ Int 31:874–879
Maboeta MS, Rensburg LV (2003) Vermicomposting of industrially produced woodchips and sewage sludge utilizing Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 56:265–270
Manna MC, Jha S, Ghosh PK, Acharya CL (2003) Comparative efficacy of three epigeic earthworms under different deciduous forest litters decomposition. Bioresour Technol 88:197–206
Mazur AI, Klimek M, Morgan AJ, Plytycz B (2011) Riboflavin storage in earthworm chloragocytes and chloragocyte-derived eleocytes and its putative role as chemoattractant for immunocompetent cells. Pedobiologia 54:S37–S42
Mitchell MJ, Mulligan RM, Hartenstein R, Neuhauser EF (1977) Conversion of sludges into “topsoils” by earthworms. Compost Sci 18:28–32
Mitchell MJ, Hornor SG, Abrams BI (1980) Decomposition of sewage sludge in drying beds and the potential role of the earthworm, Eisenia foetida1. J Environ Qual 9:373–378
Mohee R, Soobhany N (2014) Comparison of heavy metals content in compost against vermicompost of organic solid waste: past and present. Resour Conserv Recycl 92:206–213
Morgan JE, Morgan AJ (1992) Heavy metal concentrations in the tissues, ingesta and faeces of ecophysiologically different earthworm species. Soil Biol Biochem 24:1691–1697
Morgan JE, Morgan AJ (1998) The distribution and intracellular compartmentation of metals in the endogeic earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa sampled from an unpolluted and a metal-contaminated site. Environ Pollut 99:167–75
Ndegwa PM, Thompson SA (2000) Effects of C-to-N ratio on vermicomposting of biosolids. Bioresour Technol 75:7–12
Neuhauser EF, Cukic ZV, Malecki MR, Loehr RC, Durkin PR (1994) Bioconcentration and biokinetics of heavy metals in the earthworm. Environ Pollut 89:293–301
OECD (1984) OECD guideline for testing chemicals. Section 2: effects on biotic systems, Method, 207, Earthworm, acute toxicity tests, Paris, France
OECD (2007) OECD Annual Report 2007, OECD Publishing
Olchawa E, Bzowska M, Sturzenbaum SR, Morgan AJ, Plytycz B (2006) Heavy metals affect the coelomocyte-bacteria balance in earthworms: environmental interactions between abiotic and biotic stressors. Environ Pollut 142:373–81
Pattnaik S, Reddy MV (2011) Heavy metals remediation from urban wastes using three species of earthworm (Eudrilus eugeniae, Eisenia fetida and Perionyx excavatus). J Environ Chem Ecotoxicol 3:345–356
Pauwels M, Frérot H, Souleman D, Vandenbulcke F (2013) Using biomarkers in an evolutionary context: lessons from the analysis of biological responses of oligochaete annelids to metal exposure. Environ Pollut 179:343–350
Peijnenburg WJGM, Baerselman R, de Groot AC, Jager T, Posthuma L, Van Veen RPM (1999) Relating environmental availability to bioavailability: soil-type-dependent metal accumulation in the oligochaete Eisenia Andrei. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 44:294–310
Plytycz B, Lis-Molenda U, Cygal M, Kielbasa E, Grebosz A, Duchnowski M, Andre J, Morgan AJ (2009) Riboflavin content of coelomocytes in earthworm (Dendrodrilus rubidus) field populations as a molecular biomarker of soil metal pollution. Environ Pollut 157:3042–50
Plytycz B, Kielbasa E, Grebosz A, Duchnowski M, Morgan AJ (2010) Riboflavin mobilization from eleocyte stores in the earthworm dendrodrilus rubidus inhabiting aerially-contaminated Ni smelter soil. Chemosphere 81:199–205
Plytycz B, Klimek M, Klimek BA, Szymanski W, Kruk J, Morgan AJ (2011) Riboflavin content in the coelomocytes of contrasting earthworm species is differentially affected by edaphic variables including organic matter and metal content. Pedobiologia 54:S43–S48
PN-ISO (10694:2002) Soil quality - determination of organic and total carbon after dry combustion (‘elementary analysis’)
PN-ISO (11261:2002) Soil quality - determination of total nitrogen - modified Kjeldahl method
Prakash M, Karmegam N (2010) Vermistabilization of pressmud using perionyx ceylanensis Mich. Bioresour Technol 101:8464–8468
Reynolds JW, Wetzel MJ (2004) Nomenclatura oligochaetologica. Supplementum quartum, A catalogue of names, descriptions and type specimens of the Oligochaeta. Illinois Natural History Survey Special Publication, Illinois
Roodbergen M, Klok C, van der Hout A (2008) Transfer of heavy metals in the food chain earthworm black-tailed godwit (limosa limosa): comparison of a polluted and a reference site in the Netherlands. Sci Total Environ 406:407–12
Rorat A, Kacprzak M, Vandenbulcke F, Płytycz B (2013) Soil amendment with municipal sewage sludge affects the immune system of earthworms Dendrobaena veneta. Appl Soil Ecol 64:237–244
Rorat A, Kachamakova-Trojanowska N, Jozkowicz A, Kruk J, Cocquerelle C, Vandenbulcke F, Santocki M, Plytycz B (2014) Coelomocyte-derived fluorescence and DNA markers of composting earthworm species. Journal of experimental zoology. A Ecol Genet Physiol 321:28–40
Singh RP, Embrandiri A, Ibrahim MH, Esa N (2011) Management of biomass residues generated from palm oil mill: vermicomposting a sustainable option. Resour Conserv Recycl 55:423–434
Soobhany N, Mohee R, Garg VK (2015) Comparative assessment of heavy metals content during the composting and vermicomposting of municipal solid waste employing eudrilus eugeniae. Waste Manag 39:130–145
Spurgeon DJ, Hopkin SP (1996) Risk assessment of the threat of secondary poisoning by metals to predators of earthworms in the vicinity of a primary smelting works. Sci Total Environ 187:167–183
Spurgeon DJ, Hopkin SP (1999) Comparisons of metal accumulation and excretion kinetics in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to contaminated field and laboratory soils. Appl Soil Ecol 11:227–243
Suthar S, Singh S (2008) Vermicomposting of domestic waste by using two epigeic earthworms (Perionyx excavatus and Perionyx sansibaricus). Int J Environ Sci Technol 5:99–106
Suthar S, Singh S (2009) Bioconcentrations of metals (Fe, Cu, Zn, Pb) in earthworms (Eisenia fetida), inoculated in municipal sewage sludge: do earthworms pose a possible risk of terrestrial food chain contamination? Environ Toxicol 24:25–32
Wang L, Hung Y-T, Li K (2009) Vermicomposting process. In: Wang L, Pereira N, Hung Y-T (eds) Biological treatment processes. Handbook of environmental engineering. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 715–732
Yadav A, Garg VK (2009) Feasibility of nutrient recovery from industrial sludge by vermicomposting technology. J Hazard Mater 168:262–8
Acknowledgements
The project was financed with National Center for Science grant based on DEC-2013/09/N/NZ9/01937, by K/ZDS/001955 from the Jagiellonian University, the French Agence National de la Recherche, and by BS PB/401/304/11 and BS MN/401/304/12 from Czestochowa University of Technology (CUT). H. Suleiman was supported by Syrian Ministry of Higher Education. A. Rorat was supported by a doctoral fellowship from Lille 1 University and CUT. Agnieszka Rorat is a beneficient of the project “DoktoRIS – Scholarship Program for Innovative Silesia” funded by the European Union.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rorat, A., Suleiman, H., Grobelak, A. et al. Interactions between sewage sludge-amended soil and earthworms—comparison between Eisenia fetida and Eisenia andrei composting species. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 3026–3035 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5635-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5635-8