Abstract
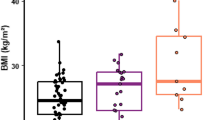
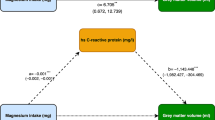
It was recently discovered that bisphenol A (BPA) and phthalates are cardiovascular disruptors. Inflammation is central to the initiation and progression of cardiovascular disease (CVD). This study evaluated whether BPA and different phthalate metabolites are associated with the inflammation marker high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) in healthy Korean adults. This research is part of an ongoing, population-based study of Korean adults (30–64 years of age) conducted at the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center (CMERC). The study enrolled 200 healthy volunteers (96 men, 104 women). Plasma hs-CRP was measured as an inflammation marker. BPA and five phthalate metabolites in urine were analyzed by using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. BPA and monobenzyl phthalate (MBzP) differed significantly between the low-hs-CRP (<2 mg/L) and high-hs-CRP (≥2 mg/L) groups. BPA and MBzP were related to hs-CRP in an inverted L-shaped manner. High BPA levels (≥75th percentile) had significant odd ratios (ORs) for high hs-CRP even after adjusting for confounding factors related to obesity and insulin resistance, such as visceral fat volume, body mass index (BMI), adiponectin, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) (OR = 2.85; 95 % CI, 1.16–6.97). However, there was no significant association for MBzP ≥75th percentile. BPA was significantly related to high hs-CRP, even after adjusting for factors related to obesity and insulin resistance. Therefore, BPA could have a direct relationship with systemic inflammation regardless of obesity or insulin resistance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chevalier N, Fénichel P (2015) Endocrine disruptors: new players in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes? Diabetes Metab 41:107–115
Dekant W, Volkel W (2008) Human exposure to bisphenol a by biomonitoring: methods, results and assessment of environmental exposures. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 228:114–134
Glass CK, Witztum JL (2001) Atherosclerosis. The road ahead. Cell 104:503–516
Gore AC, Chappell VA, Fenton SE, Flaws JA, Nadal A, Prins GS, Toppari J, Zoeller RT (2015) EDC-2: the Endocrine Society’s second scientific statement on endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Endocr Rev 36:E1–E150
Han SJ, Ha KH, Jeon JY, Kim HJ, Lee KW, Kim DJ (2015) Impact of cadmium exposure on the association between lipopolysaccharide and metabolic syndrome. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:11396–11409
Hansen JF, Bendtzen K, Boas M, Frederiksen H, Nielsen CH, Rasmussen ÅK, Feldt-Rasmussen U (2015) Influence of phthalates on cytokine production in monocytes and macrophages: a systematic review of experimental trials. PLoS One 10:e0120083
Hong YC, Park EY, Park MS, Ko JA, Oh SY, Kim H, Lee KH, Leem JH, Ha EH (2009) Community level exposure to chemicals and oxidative stress in adult population. Toxicol Lett 184:139–144
Jeon JY, Ha KH, Kim DJ (2015) New risk factors for obesity and diabetes: environmental chemicals. J Diabetes Investig 6:109–111
Kaptoge S, Di Angelantonio E, Lowe G, Pepys MB, Thompson SG, Collins R, Danesh J (2010) C-reactive protein concentration and risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and mortality: an individual participant meta-analysis. Lancet 375:132–140
Kavlock RJ, Daston GP, DeRosa C, Fenner-Crisp P, Gray LE, Kaattari S, Lucier G, Luster M, Mac MJ, Maczka C, Miller R, Moore J, Rolland R, Scott G, Sheehan DM, Sinks T, Tilson HA (1996) Research needs for the assessment of health and environmental effects of endocrine disruptors: a report of the U.S. EPA-sponsored workshop. Environ Health Perspect 104:715–740
Lakind JS, Goodman M, Mattison DR (2014) Bisphenol a and indicators of obesity, glucose metabolism/type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease: a systematic review of epidemiologic research. Crit Rev Toxicol 44:121–150
Lang IA, Galloway TS, Scarlett A, Henley WE, Depledge M, Wallace RB, Melzer D (2008) Association of urinary bisphenol a concentration with medical disorders and laboratory abnormalities in adults. JAMA 300:1303–1310
Libby P, Ridker PM (2004) Inflammation and atherosclerosis: role of C-reactive protein in risk assessment. Am J Med 116(Suppl 6A):9S–16S
Liu Y, Mei C, Liu H, Wang H, Zeng G, Lin J, Xu M (2014) Modulation of cytokine expression in human macrophages by endocrine-disrupting chemical bisphenol-a. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 451:592–598
Lusis AJ (2000) Atherosclerosis. Nature 407:233–241
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
Maury E, Brichard SM (2010) Adipokine dysregulation, adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic syndrome. Mol Cell Endocrinol 314:1–16
Meeker JD, Ferguson KK (2011) Relationship between urinary phthalate and bisphenol a concentrations and serum thyroid measures in U.S. adults and adolescents from the National Health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES) 2007–2008. Environ Health Perspect 119:1396–1402
Melzer D, Rice NE, Lewis C, Henley WE, Galloway TS (2010) Association of urinary bisphenol a concentration with heart disease: evidence from NHANES 2003/06. PLoS One 5:e8673
Melzer D, Osborne NJ, Henley WE, Cipelli R, Young A, Money C, McCormack P, Luben R, Khaw KT, Wareham NJ, Galloway TS (2012) Urinary bisphenol a concentration and risk of future coronary artery disease in apparently healthy men and women. Circulation 125:1482–1490
Olsén L, Lind L, Lind PM (2012) Associations between circulating levels of bisphenol a and phthalate metabolites and coronary risk in the elderly. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 80:179–183
Pepys MB, Hirschfield GM (2003) C-reactive protein: a critical update. J Clin Invest 111:1805–1812
Ridker PM, Danielson E, Fonseca FA, Genest J, Gotto AM Jr, Kastelein JJ, Koenig W, Libby P, Lorenzatti AJ, MacFadyen JG, Nordestgaard BG, Shepherd J, Willerson JT, Glynn RJ, JUPITER Study Group (2008) Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C-reactive protein. N Engl J Med 359:2195–2207
Rogers JA, Metz L, Yong VW (2013) Review: endocrine disrupting chemicals and immune responses: a focus on bisphenol-a and its potential mechanisms. Mol Immunol 53:421–430
Sargis RM (2014) The hijacking of cellular signaling and the diabetes epidemic: mechanisms of environmental disruption of insulin action and glucose homeostasis. Diabetes Metab J 38:13–24
Shoelson AE, Lee J, Goldfine AB (2006) Inflammation and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 116:1793–1801
Singh S, Li SS (2011) Phthalates: toxicogenomics and inferred human diseases. Genomics 97:148–157
Singh S, Li SS (2012) Bisphenol a and phthalates exhibit similar toxicogenomics and health effects. Gene 494:85–91
Sun Q, Cornelis MC, Townsend MK, Tobias DK, Eliassen AH, Franke AA, Hauser R, Hu FB (2014) Association of urinary concentrations of bisphenol a and phthalate metabolites with risk of type 2 diabetes: a prospective investigation in the nurses’ health study (NHS) and NHSII cohorts. Environ Health Perspect 122:616–623
Talsness CE, Andrade AJ, Kuriyama SN, Taylor JA, vom Saal FS (2009) Components of plastic: experimental studies in animals and relevance for human health. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 364:2079–2096
Teitelbaum SL, Li Q, Lambertini L, Belpoggi F, Manservisi F, Falcioni L, Bua L, Silva MJ, Ye X, Calafat AM, Chen J (2016) Paired serum and urine concentrations of biomarkers of diethyl phthalate, methyl paraben, and Triclosan in rats. Environ Health Perspect 124:39–45
Trasande L, Attina TM, Sathyanarayana S, Spanier AJ, Blustein J (2013) Race/ethnicity-specific associations of urinary phthalates with childhood body mass in a nationally representative sample. Environ Health Perspect 121:501–506
vom Saal FS, Akingbemi BT, Belcher SM, Birnbaum LS, Crain DA, Eriksen M, Farabollini F, Guillette LJ Jr, Hauser R, Heindel JJ, Ho SM, Hunt PA, Iguchi T, Jobling S, Kanno J, Keri RA, Knudsen KE, Laufer H, LeBlanc GA, Marcus M, McLachlan JA, Myers JP, Nadal A, Newbold RR, Olea N, Prins GS, Richter CA, Rubin BS, Sonnenschein C, Soto AM, Talsness CE, Vandenbergh JG, Vandenberg LN, Walser-Kuntz DR, Watson CS, Welshons WV, Wetherill Y, Zoeller RT (2007) Chapel Hill bisphenol a expert panel consensus statement: integration of mechanisms, effects in animals and potential to impact human health at current levels of exposure. Reprod Toxicol 24:131–138
Wang T, Li M, Chen B, Xu M, Xu Y, Huang Y, Lu J, Chen Y, Wang W, Li X, Liu Y, Bi Y, Lai S, Ning G (2012) Urinary bisphenol a(BPA) concentration associates with obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:E223–E227
Wang T, Xu M, Xu Y, Lu J, Li M, Chen Y, Wang W, Lai S, Bi Y, Ning G (2015) Association of Bisphenol a Exposure with Hypertension and Early Macrovascular Diseases in Chinese adults: a cross-sectional study. Medicine (Baltimore) 94:e1814
Wiberg B, Lind PM, Lind L (2014) Serum levels of monobenzylphthalate (MBzP) is related to carotid atherosclerosis in the elderly. Environ Res 133:348–352
Wolstenholme JT, Rissman EF, Connelly JJ (2011) The role of bisphenol a in shaping the brain, epigenome and behavior. Horm Behav 59:296–305
Zhu J, Jiang L, Liu Y, Qian W, Liu J, Zhou J, Gao R, Xiao H, Wang J (2015) MAPK and NF-κB pathways are involved in bisphenol A-induced TNF-α and IL-6 production in BV2 microglial cells. Inflammation 38:637–648
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea (No. HI13C0715).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, Y.J., Ha, K.H. & Kim, D.J. Exposure to bisphenol A is directly associated with inflammation in healthy Korean adults. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 284–290 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7806-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7806-7