Abstract
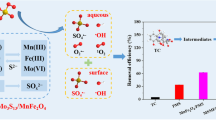
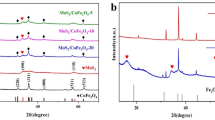
Co-doped magnetic Mn3O4 was synthesized by the solvothermal method and adopted as an effective catalyst for the degradation of oxytetracycline (OTC) in water. Synergistic interactions between Co-Mn3O4 and Fe3O4 not only resulted in the enhanced catalytic activity through the activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) to degrade OTC but also made Fe3O4/Co-Mn3O4 easy to be separated and recovered from aqueous solution. 94.2% of OTC could be degraded within 60 min at an initial OTC concentration of 10 mg L−1, catalyst dosage of 0.2 g L−1, and PMS concentration of 10 mM. The high efficiency of OTC removal was achieved in a wider pH range of 3.0–10.0. Co (II), Co (III), Fe (II), Fe (III), Mn (II), Mn (III), and Mn (IV) on Fe3O4/Co-Mn3O4 were identified as catalytic sites based on XPS analysis. The free radical quenching experiments showed that O2•− radicals and 1O2 played the main role in the degradation process and the catalytic degradation of OTC involved both free radical and non-free radical reactions. Eventually, the intermediates of OTC degradation were examined, and the possible decomposition pathways were proposed. The excellent catalytic performances of Fe3O4/Co-Mn3O4 came from the fact that the large specific surface area could provide abundant active sites for the activation of PMS and the redistribution of inter-atomic charges accelerated the redox reactions of metal ions. The high degradation efficiency and rate constant of OTC in actual water samples indicated that Fe3O4/Co-Mn3O4 had a good practical application potential.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Extra data are available from the authors (lixiaoli@lzu.edu.cn) upon reasonable request.
References
Ali J, Shahzad A, Wang J, Ifthikar J, Lei W, Aregay GG, Chen Z, Chen Z (2021) Modulating the redox cycles of homogenous Fe(III)/PMS system through constructing electron rich thiomolybdate centres in confined layered double hydroxides. Chem Eng J 408:127242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127242
Blair-González J, Contreras-Villacura E, Guevara AC, Toloza CP (2021) Oxytetracycline removal by biological/chemical activated mesoporous carbon. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111384
Cai C, Zhang H, Zhong X, Hou L (2015) Ultrasound enhanced heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by a bimetallic Fe-Co/SBA-15 catalyst for the degradation of Orange II in water. J Hazard Mater 283:70–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.08.053
Chen C, Xie M, Kong L, Lu W, Feng Z, Zhan J (2020a) Mn3O4 nanodots loaded g-C3N4 nanosheets for catalytic membrane degradation of organic contaminants. J Hazard Mater 390:122146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122146
Chen P, Gou Y, Ni J, Liang Y, Yang B, Jia F (2020b) Efficient Ofloxacin degradation with Co(II)-doped MoS2 nano-flowers as PMS activator under visible-light irradiation. Chem Eng J 401:125978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125978
Chen S, Deng J, Ye C, Xu C, Huai L, Li J, Li X (2020c) Simultaneous removal of para-arsanilic acid and the released inorganic arsenic species by CuFe2O4 activated peroxymonosulfate process. Sci Total Environ 742:140587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140587
Chen H, Liu S, Xu XR, Diao ZH, Sun KF, Hao QW, Liu SS, Ying GG (2018) Tissue distribution, bioaccumulation characteristics and health risk of antibiotics in cultured fish from a typical aquaculture area. J Hazard Mater 343:140–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.09.017
Chen X, Chen J, Qiao X, Wang D, Cai X (2008) Performance of nano-Co3O4/peroxymonosulfate system: kinetics and mechanism study using Acid Orange 7 as a model compound. Appl Catal B Environ 80:116–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.11.009
Deng J, Cheng YQ, Lu YA, Crittenden JC, Zhou SQ, Gao NY, Li J (2017) Mesoporous manganese Cobaltite nanocages as effective and reusable heterogeneous peroxymonosulfate activators for Carbamazepine degradation. Chem Eng J 330:505–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.149
Ferrari B, Mons R, Vollat B, Fraysse B, Paxeus N, Giudice RL, Pollio A, Garric J (2004) Environmental risk assessment of six human pharmaceuticals: are the current environmental risk assessment procedures sufficient for the protection of the aquatic environment? Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1344–1354. https://doi.org/10.1897/03-246
Guan Y, Ma J, Ren Y, Liu Y, Xiao J, Lin L, Zhang C (2013) Efficient degradation of atrazine by magnetic porous copper ferrite catalyzed peroxymonosulfate oxidation via the formation of hydroxyl and sulfate radicals. Water Res 47:5431–5438https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.06.023
Guo ZY, Li CX, Gao M, Han X, Zhang YJ, Zhang WJ, Li WW (2021) Mn−O Covalency governs the intrinsic activity of Co-Mn spinel oxides for boosted peroxymonosulfate activation. Angew Chemie - Int Ed 60:274–280. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202010828
Hagedorn CH, Alpers DH (1977) Biodegradability of some antibiotics, elimination of the genotoxicity and affection of wastewater bacteria in a simple test. Gastroenterology 73:1019–1022. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-5085(19)31851-7
Han CH, Park HD, Kim SB, Yargeau V, Choi JW, Lee SH, Park JA (2020) Oxidation of tetracycline and oxytetracycline for the photo-Fenton process: their transformation products and toxicity assessment. Water Res 172:115514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115514
He W, Li Z, Lv S, Niu M, Zhou W, Li J, Lu R, Gao H, Pan C, Zhang S (2021) Facile synthesis of Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) towards enhancing photo-Fenton like degradation of levofloxacin via a synergistic effect between Fe3O4 and MIL-100(Fe). Chem Eng J 409:128274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.128274
He X, O’Shea KE (2020a) Rapid transformation of H1-antihistamines cetirizine (CET) and diphenhydramine (DPH) by direct peroxymonosulfate (PMS) oxidation. J Hazard Mater 398:123219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123219
He X, O’Shea KE (2020b) Selective oxidation of H1-antihistamines by unactivated peroxymonosulfate (PMS): influence of inorganic anions and organic compounds. Water Res 186:116401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116401
Hong JS, Seo H, Lee YH, Cho KH, Ko C, Park S, Nam KT (2020) Nickel-doping effect on Mn3O4 nanoparticles for electrochemical water oxidation under neutral condition. Small Methods 4:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.201900733
Hu H, Li X, Wu S, Lou W, Yang C (2021) Effects of long-term exposure to oxytetracycline on phytoremediation of swine wastewater via duckweed systems. J Hazard Mater 414:125508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125508
Hu P, Long M (2016) Cobalt-catalyzed sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation: a review on heterogeneous catalysts and applications. Appl Catal B Environ 181:103–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.07.024
Hu X, Li C, Song J, Zheng S, Sun Z (2020) Multidimensional assembly of oxygen vacancy-rich amorphous TiO2-BiOBr-sepiolite composite for rapid elimination of formaldehyde and oxytetracycline under visible light. J Colloid Interface Sci 574:61–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.04.035
Hutchings M, Truman A, Wilkinson B (2019) Antibiotics: past, present and future. Curr Opin Microbiol 51:72–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2019.10.008
Isidori M, Lavorgna M, Nardelli A, Pascarella L, Parrella A (2005) Toxic and genotoxic evaluation of six antibiotics on non-target organisms. Sci Total Environ 346:87–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.11.017
Jaafarzadeh N, Ghanbari F, Ahmadi M (2017) Efficient degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by peroxymonosulfate/magnetic copper ferrite nanoparticles/ozone: a novel combination of advanced oxidation processes. Chem Eng J 320:436–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.03.036
Jawad A, Zhan K, Wang H, Shahzad A, Zeng Z, Wang J, Zhou X, Ullah H, Chen Z, Chen Z (2020) Tuning of persulfate activation from a free radical to a nonradical pathway through the incorporation of non-redox magnesium oxide. Environ Sci Technol 54:2476–2488. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b04696
Jiang J, Wang X, Zhang C, Li T, Lin Y, Xie T, Dong S (2020) Porous 0D/3D NiCo2O4/g-C3N4 accelerate emerging pollutant degradation in PMS/vis system: degradation mechanism, pathway and toxicity assessment. Chem Eng J 397:125356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125356
Karimian S, Moussavi G, Fanaei F, Mohammadi S, Shekoohiyan GS (2020) Shedding light on the catalytic synergies between Fe(II) and PMS in vacuum UV (VUV/Fe/PMS) photoreactors for accelerated elimination of pharmaceuticals: The case of metformin. Chem Eng J 400:125896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125896
Kohantorabi M, Moussavi G, Giannakis S (2020) A review of the innovations in metal- and carbon-based catalysts explored for heterogeneous peroxymonosulfate (PMS) activation, with focus on radical vs. non-radical degradation pathways of organic contaminants. Chem Eng J 411:127957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127957
Lai X, Ning X, Chen J, Li Y, Zhang Y, Yuan Y (2020) Comparison of the Fe2+/H2O2 and Fe2+/PMS systems in simulated sludge: removal of PAHs, migration of elements and formation of chlorination by-products. J Hazard Mater 398:122826 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122826
Li C, Wu J, Peng W, Fang Z, Liu J (2019) Peroxymonosulfate activation for efficient sulfamethoxazole degradation by Fe3O4/β-FeOOH nanocomposites: coexistence of radical and non-radical reactions. Chem Eng J 356:904–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.064
Li H, Wan J, Ma Y, Wang Y (2016) Synthesis of novel core–shell Fe0@Fe3O4 as heterogeneous activator of persulfate for oxidation of dibutyl phthalate under neutral conditions. Chem Eng J 301:315–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.147
Li J, Dong T, Keerthisinghe TP, Chen H, Li M, Chu W, Yang J, Hu Z, Snyder SA, Dong Wu, Fang M (2020) Long-term oxytetracycline exposure potentially alters brain thyroid hormone and serotonin homeostasis in zebrafish. J Hazard Mater 399:123061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123061
Li Y, Deng M, Wang X, Wang Y, Li J, Xia S, Zhao J (2021a) In-situ remediation of oxytetracycline and Cr(VI) co-contaminated soil and groundwater by using blast furnace slag-supported nanosized Fe0/FeSx. Chem Eng J 412:128706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128706
Li L, Liu S, Cheng M, Lai C, Zeng G, Qin L, Liu X, Li B, Zhang W, Yi Y, Zhang M, Fu Y, Li M, Long M (2021b) Improving the Fenton-like catalytic performance of MnOx-Fe3O4/biochar using reducing agents: a comparative study. J Hazard Mater 406:124333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124333
Li ZY, Wang L, Liu YL, He PN, Zhang X, Chen J, Gu HT, Zhang HC, Ma J (2021c) Overlooked enhancement of chloride ion on the transformation of reactive species in peroxymonosulfate/Fe(II)/NH2OH system. Water Res 195:116973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.116973
Li N, Tian Y, Zhao J, Zhang J, Zhang J, Zuo W, Ding Y (2017) Efficient removal of chromium from water by Mn3O4@ZnO/Mn3O4 composite under simulated sunlight irradiation: synergy of photocatalytic reduction and adsorption. Appl Catal B Environ 214:126–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.05.041
Lin H, Wu J, Zhang H (2014) Degradation of clofibric acid in aqueous solution by an EC/Fe3+/PMS process. Chem Eng J 244:514–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.01.099
Liu N, Lu N, Yu HT, Chen S, Quan X (2021a) Degradation of aqueous bisphenol A in the CoCN/Vis/PMS system: catalyst design, reaction kinetic and mechanism analysis. Chem Eng J 407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127228
Liu S, Zhang Z, Huang F, Liu Y, Feng L, Jiang J, Zhang L, Qi F, Liu C (2021b) Carbonized polyaniline activated peroxymonosulfate (PMS) for phenol degradation: role of PMS adsorption and singlet oxygen generation. Appl Catal B Environ 286:119921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.119921
Liu Y, He X, Fu Y, Dionysiou DD (2016) Degradation kinetics and mechanism of oxytetracycline by hydroxyl radical-based advanced oxidation processes. Chem Eng J 284:1317–1327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.09.034
Liu Y, Luo J, Tang L, Feng C, Wang J, Deng Y, Liu H, Yu J, Feng H, Wang J (2020) Origin of the enhanced reusability and electron transfer of the carbon-coated Mn3O4 nanocube for persulfate activation. ACS Catal 10:14857–14870. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.0c04049
Luo J, Bo S, Qin Y, An Q, Xiao Z, Zhai S (2020) Transforming goat manure into surface-loaded cobalt/biochar as PMS activator for highly efficient ciprofloxacin degradation. Chem Eng J 395:125063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125063
Ma W, Yao B, Zhang W, He Y, Niu J (2021) Fabrication of PVDF-based piezocatalytic active membrane with enhanced oxytetracycline degradation efficiency through embedding few-layer E-MoS2 nanosheets. Chem Eng J 415:129000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129000
Martins N, Pereira R, Abrantes N, Pereira J, Goncalnes F, Marques CR (2012) Ecotoxicological effects of ciprofloxacin on freshwater species: data integration and derivation of toxicity thresholds for risk assessment. Ecotoxicology 21:1167–1176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0871-x
Nie M, Yang Y, Zhang Z, Yan C, Wang X, Li H, Dong W (2014) Degradation of chloramphenicol by thermally activated persulfate in aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 246:373–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.02.047
Oh WD, Dong Z, Lim TT (2016) Generation of sulfate radical through heterogeneous catalysis for organic contaminants removal: current development, challenges and prospects. Appl Catal B Environ 194:169–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.04.003
Peng B, Song T, Wang T, Chai L, Yang W, Li X, Li C, Wang H (2016) Facile synthesis of Fe3O4@Cu(OH)2 composites and their arsenic adsorption application. Chem Eng J 299:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.03.135
Peroti L, Huoviven P, Orellana S, Munoz M, Fuentes R, Gomez I (2021) Uptake of microalgae as sublethal biomarker reveals phototoxicity of oxytetracycline to the crustacean Daphnia magna. Water Res 188:116556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116556
Persaud RR, Azad MB, Chari RS, Sears MR, Becker AB, Kozyrskyj AL, Investigators CS (2015) Perinatal antibiotic exposure of neonates in Canada and associated risk factors: a population-based study. J Matern Neonatal Med 28:1190–1195. https://doi.org/10.3109/14767058.2014.947578
Ren Y, Lin L, Ma J, Yang J, Feng J, Fan Z (2015) Sulfate radicals induced from peroxymonosulfate by magnetic ferrospinel MFe2O4 (M=Co, Cu, Mn, and Zn) as heterogeneous catalysts in the water. Appl Catal B Environ 165:572–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.10.051
Saputra E, Muhammad S, Sun H, Ang HM, Tade MO, Wang S (2013) Manganese oxides at different oxidation states for heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate for phenol degradation in aqueous solutions. Appl Catal B Environ 142–143:729–735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.06.004
Shao P, Tian J, Yang F, Duan X, Gao S, Shi W, Luo X, Cui F, Luo S, Wang S (2018a) Identification and regulation of active sites on nanodiamonds: establishing a highly efficient catalytic system for oxidation of organic contaminants. Adv Funct Mater 28:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201705295
Shao S, Hu Y, Cheng J, Chen Y (2018b) Research progress on distribution, migration, transformation of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in aquatic environment. Crit Rev Biotechnol 38:1195–1208. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2018.1471038
Shokoohi R, Salari M, Shabanloo A, Shabanloo N, Marofi S, Faraji H, Tabar MV, Moradnia M (2020) Catalytic activation of persulphate with Mn3O4 nanoparticles for degradation of acid blue 113: process optimisation and degradation pathway. Int J Environ Anal Chem 00:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1773810
Sun QT, Xu BD, Yang J, Qian TT, Jiang H (2020) Layered oxides supported Co-Fe bimetal catalyst for carbamazepine degradation via the catalytic activation of peroxymonosulfate. Chem Eng J 400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125899
Wang F, Xiao M, Ma X, Wu S, Ge M, Yu X (2021) Insights into the transformations of Mn species for peroxymonosulfate activation by tuning the Mn3O4 shapes. Chem Eng J 404:127097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127097
Wang G, Cheng C, Zhu J, Wang L, Gao S, Xia X (2019a) Enhanced degradation of atrazine by nanoscale LaFe1-xCuxO3-δ perovskite activated peroxymonosulfate: performance and mechanism. Sci Total Environ 673:565–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.098
Wang X, Shen J, Kang J, Zhao X, Chen Z (2019b) Mechanism of oxytetracycline removal by aerobic granular sludge in SBR. Water Res 161:308–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.06.014
Wang G, Zhou S, Han X, Zhang L, Ding S, Li Y, Zhang D, Zarin K (2020a) Occurrence, distribution, and source track of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in the main rivers of Chongqing city, southwest China. J Hazard Mater 389:122110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122110
Wang W, Niu Q, Zeng G, Zhang C, Huang D, Shao B, Zhou C, Yang Y, Liu Y, Guo H, Xiong W, Lei L, Liu S, Yi H, Chen S, Tang X (2020b) 1D porous tubular g-C3N4 capture black phosphorus quantum dots as 1D/0D metal-free photocatalysts for oxytetracycline hydrochloride degradation and hexavalent chromium reduction. Appl Catal B Environ 273:119051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119051
Xie Z, Lu G, Liu J, Yan Z, Ma B, Zhang Z, Chen W (2015) Occurrence, bioaccumulation, and trophic magnification of pharmaceutically active compounds in Taihu Lake, China. Chemosphere 138:140–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.05.086
Xu Y, Ai J, Zhang H (2016) The mechanism of degradation of bisphenol A using the magnetically separable CuFe2O4/peroxymonosulfate heterogeneous oxidation process. J Hazard Mater 309:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.01.023
Yang Y, Banerijee G, Brudvig GW, Kim JH, Pignatello JJ (2018) Oxidation of organic compounds in water by unactivated peroxymonosulfate. Environ Sci Technol 52:5911–5919. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b00735
Yang Y, Zeng G, Huang D, Zhang C, He D, Zhou C, Wang W, Xiong W, Li X, Li B, Dong W, Zhou Y (2020) Molecular engineering of polymeric carbon nitride for highly efficient photocatalytic oxytetracycline degradation and H2O2 production. Appl Catal B Environ 272:118970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118970
Zeng Z, Khan A, Wang Z, Zhao M, Mo W, Chen Z (2020) Elimination of atrazine through radical/non-radical combined processes by manganese nano-catalysts/PMS and implications to the structure-performance relationship. Chem Eng J 397:125425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125425
Zhang C, He D, Fu S, Zeng G, Liang Q, Yang Y, Huang D, Wang W, Zhou Y (2021a) Silver iodide decorated ZnSn (OH)6 hollow cube : room-temperature preparation and application for highly efficient photocatalytic oxytetracycline degradation. Chem Eng J 421:129810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129810
Zhang Y, Zhang BT, Teng Y, Zhao J, Sun X (2021b) Heterogeneous activation of persulfate by carbon nanofiber supported Fe3O4@carbon composites for efficient ibuprofen degradation. J Hazard Mater 401:123428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123428
Zhang S, Gao H, Xu X, Cao R, Yang H, Xu X, Li J (2020) MOF-derived CoN/N-C@SiO2 yolk-shell nanoreactor with dual active sites for highly efficient catalytic advanced oxidation processes. Chem Eng J 381:122670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122670
Zhang QQ, Ying GG, Pan CG, Liu YS, Zhao JL (2015) A comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environ Sci Technol 49:6772–6782. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00729
Zhao J, Li F, Wei H, Ai H, Gu L, Chen J, Zhang L, Chi M, Zhai J (2021) Superior performance of ZnCoOx/peroxymonosulfate system for organic pollutants removal by enhancing singlet oxygen generation: the effect of oxygen vacancies. Chem Eng J 409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.128150
Zhao J, Nan J, Zhao Z, Li N, Liu J, Cui F (2017) Energy-efficient fabrication of a novel multivalence Mn3O4-MnO2 heterojunction for dye degradation under visible light irradiation. Appl Catal B Environ 202:509–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.09.065
Zimmermann P, Curtis N (2019) Effect of intrapartum antibiotics on the intestinal microbiota of infants: a systematic review. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2018-316659
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province (No. 20JR10RA631) and the Open Project of Key Laboratory of Green Chemical Engineering Process of Ministry of Education (No. GCP20200207).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaoli Li proposed the project and provided the funds. Liyan He designed the experiments and synthesized the materials. Liyan He did the series of experiments and prepared the first draft of this manuscript. Hui Li, Jianzhi Wang, and Qifei Gao revised the manuscript. All co-authors contributed to this work.
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
No animal studies are presented in this manuscript. No human studies are presented in this manuscript. No potentially identifiable human images or data are presented in this study.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Santiago V. Luis.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, L., Li, H., Wang, J. et al. Peroxymonosulfate activation by Co-doped magnetic Mn3O4 for degradation of oxytetracycline in water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 39249–39265 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18929-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18929-1