Abstract
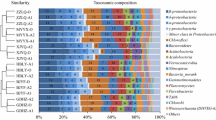
Discharging waste water from the bauxite desilication process will bring potential environmental risk from the residual ions and organic compounds, especially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide. Characterization of the microbial community diversity in waste water plays an important role in the biological treatment of waste water. In this study, eight waste water samples from five flotation plants in China were investigated. The microbial community and functional profiles within the waste water were analyzed by a metagenomic sequencing method and associated with geochemical properties. The results revealed that Proteobacteria and Firmicutes were the dominant bacterial phyla. Both phylogenetical and clusters of orthologous groups’ analyses indicated that Tepidicella, Paracoccus, Pseudomonas, and Exiguobacterium could be the dominant bacterial genera in the waste water from bauxite desilication process for their abilities to biodegrade complex organic compounds. The results of the microbial community diversity and functional gene compositions analyses provided a beneficial orientation for the biotreatment of waste water, as well as regenerative using of water resources. Besides, this study revealed that waste water from bauxite desilication process was an ideal ecosystem to find novel microorganisms, such as efficient strains for bio-desilication and bio-desulfurization of bauxite.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed RM, Al-Fori M, Al-Sabahi J, Prigent S, Headley T (2021) Impacts of partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide (HPAM) on microbial mats from a constructed wetland treating oilfield produced water. Chemosphere 285:131421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131421
Al-Sabahi J, Bora T, Claereboudt M, Al-Abri M, Dutta J (2018) Visible light photocatalytic degradation of HPAM polymer in oil produced water using supported zinc oxide nanorods. Chem Eng J 351:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.071
Anders HJ, Kaetzke A, Kämpfer P, Ludwig W, Fuchs G (1995) Taxonomic position of aromatic- degrading denitrifying pseudomonad strains K 172 and KB 740 and their description as new members of the genera Thauera, as Thauera aromatica sp. nov., and Azoarcus, as Azoarcus evansii sp. nov., respectively, members of the beta subclass of the Proteobacteria. Int J System Bacteriol 45(2). https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-45-2-327
Beals EW (1984) Bray-Curtis ordination: an effective strategy for analysis of multivariate ecological data. Adv Ecol Res Elsevier 14:1–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2504(08)60168-3
Bueche M, Junier P (2016) Effect of organic carbon and metal accumulation on the bacterial communities in sulphidogenic sediments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(11):10443–10456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6056-z
Chang ZY, Feng QM, Ou LM (2014) Study on the impact of flocculants in backwater on bauxite flotation [J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mineral Processing Section) 6:88–91. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-9492.2014.06.022
Cho JC, Tiedje JM (2001) Bacterial species determination from DNA-DNA hybridization by using genome fragments and DNA microarrays. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(8):3677–3682. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.67.8.3677-3682.2001
Claesson MJ, O'Sullivan O, Wang Q, Nikkilä J, Marchesi JR, Smidt H, de Vos WM, Ross RP, O'Toole PW (2009) Comparative analysis of pyrosequencing and a phylogenetic microarray for exploring microbial community structures in the human distal intestine. PLoS One 4(8):e6669. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006669
Cytryn E, van Rijn J, Andreas S, Armin G, de Beer D, Dror M (2005) Identification of bacteria potentially responsible for oxic and anoxic sulfide oxidation in biofilters of a recirculating mariculture system. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:10. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.10.6134-6141.2005
Delegan Y, Kocharovskaya Y, Bogun A, Sizova A, Solomentsev V, Iminova L, Nikita L, Alina Z, Mikhail G, Solyanikova I (2021) Characterization and genomic analysis of Exiguobacterium alkaliphilum B-3531D, an efficient crude oil degrading strain. Biotechnol Reports 32:e00678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2021.e00678
Du R, Cao S, Li B, Zhang H, Li X, Zhang Q, Peng Y (2019) Step-feeding organic carbon enhances high-strength nitrate and ammonia removal via DEAMOX process. Chem Eng J 501-510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.12.011
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26(19):2460–2461. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq461
Ellis RJ, Morgan P, Weightman AJ, Fry JC (2003) Cultivation-dependent and -independent approaches for determining bacterial diversity in heavy-metal- contaminated soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(6):3223–3230. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.6.3223-3230.2003
Feng G, Zhong H, Liu GY, Zhao SG, Xia LY (2009) Flotation of aluminosilicate minerals using alkylguanidine collectors. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 19(1):228–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(08)60257-5
Furmanczyk EM, Kaminski MA, Lipinski L, Dziembowski A, Sobczak A (2018) Pseudomonas laurylsulfatovorans sp. nov., sodium dodecyl sulfate degrading bacteria, isolated from the peaty soil of a wastewater treatment plant. Syst Appl Microbiol 41(4):348–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2018.03.009
Gibson B, Wonyen D, Chelgani SC (2017) A review of pretreatment of diasporic bauxite ores by flotation separation. Miner Eng 114:64–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2017.09.009
Huo Q, Liu X, Chen L, Wu Y, Wu H, Xie J, Liu X, Qiu G (2019) Treatment of backwater in bauxite flotation plant and optimization by using Box-Behnken design. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 29(4):821–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(19)64992-7
Ihaka R, Gentleman R (1996) R: a language for data analysis and graphics. J Comput Graph Stat 5(3):299–314. https://doi.org/10.1080/10618600.1996.10474713
Ji G, Tan Y, Zhang L (2011) Bacterial and granular sludge characteristics in an ultrahigh-temperature upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor treating super heavy oil-containing wastewater. Environ Eng Sci 28(2):129–137. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2010.0166
Ji B, Yang K, Zhu L, Jiang Y, Wang H, Zhou J, Zhang H (2015) Aerobic denitrification: a review of important advances of the last 30 years. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 20(4):643–651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-015-0009-0
Ji F, Yuan Y, Lai B (2017) Microbial community dynamics in aerated biological fluidized bed (ABFB) with continuously increased p-nitrophenol loads. Process Biochem 63:185–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2017.07.033
Ji H, Zhang Y, Bararunyeretse P, Li H (2018) Characterization of microbial communities of soils from gold mine tailings and identification of mercury-resistant strain. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 165:182–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.011
Jiang X, Mingchao MA, Jun LI, Anhuai LU, Zhong Z (2008) Bacterial diversity of active sludge in wastewater treatment plant. Earth Sci Front 15(6). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5791(09)60015-4
Joshi SJ, Abed RM (2017) Biodegradation of polyacrylamide and its derivatives. Environ Processes 4(2):463–476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-017-0224-0
Khan ST, Takaichi S, Harayama S (2008) Paracoccus marinus sp. nov., an adonixanthin diglucoside-producing bacterium isolated from coastal seawater in Tokyo Bay. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58(2):383–386. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65103-0
Kulshreshtha NM, Kumar A, Dhall P, Gupta S, Bisht G, Pasha S, Singh V, Kumar R (2010) Neutralization of alkaline industrial wastewaters using Exiguobacterium sp. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 64(3):191–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2010.01.003
Kulshreshtha NM, Kumar RN, Begum Z, Shivaji S, Kumar A (2013) Exiguobacterium alkaliphilum sp. nov. isolated from alkaline wastewater drained sludge of a beverage factory. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63(12):4374–4379. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.039123-0
Kwon SW, Kim JS, Park IC, Yoon SH, Park DH, Lim CK, Go SJ (2003) Pseudomonas koreensis sp. nov., Pseudomonas umsongensis sp. nov. and Pseudomonas jinjuensis sp. nov., novel species from farm soils in Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53(1):21–27. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02326-0
Langille MG, Zaneveld J, Caporaso JG, McDonald D, Knights D, Reyes JA, Clemente JC, Burkepile DE, Thurber RLV, Knight R (2013) Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat Biotechnol 31(9):814. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2676
Levin BD, Walsh KA, Sullivan K, Bren KL, Elliott SJ (2015) Methionine ligand lability of homologous monoheme cytochromes c. Inorg Chem 54(1):38–46. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic501186h
Li S, Wang R, Guo Y, Guo Y, Wang G, Liu X, Qiu G (2016) Bio-desulfurization of high-sulfur bauxite by designed moderately thermophilic consortia. Nonferr Metal Soc 11:2393–2402. https://doi.org/10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2016.11.016
Liu B, Mao Y, Bergaust L, Bakken LR, Frostegard A (2013) Strains in the genus Thauera exhibit remarkably different denitrification regulatory phenotypes. Environ Microbiol 15(10):2816–2828. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12142
Long T, Liu X, Ai C, Wang C, Huo Q (2022) Treatment technique for wastewater from bauxite flotation and an application for its reuse. J Cleaner Prod 130321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130321
Luo YL, Yang ZH, Xu ZY, Zhou LJ, Zeng GM, Huang J, Xiao Y, Wang LK (2011) Effect of trace amounts of polyacrylamide (PAM) on long-term performance of activated sludge. J Hazard Mater 189(1-2):69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.01.115
Mechichi T, Erko S, Nasser G'o, Georg F (2002) Phylogenetic and metabolic diversity of bacteria degrading aromatic compounds under denitrifying conditions, and description of Thauera phenylacetica sp. nov., Thauera aminoaromaticasp. nov., and Azoarcus buckelii sp. nov. Arch Microbiol 178(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-002-0422-6
Meng X, Wu J, Kang J, Gao J, Liu R, Gao Y, Wang R, Fan R, Khoso SA, Sun W (2018) Comparison of the reduction of chemical oxygen demand in wastewater from mineral processing using the coagulation–flocculation, adsorption and Fenton processes. Miner Eng 128:275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2018.09.009
Ojewumi ME, Okeniyi JO, Ikotun JO, Okeniyi ET, Ejemen VA, Popoola AP (2018) Bioremediation: data on Pseudomonas aeruginosa effects on the bioremediation of crude oil polluted soil. Data in Brief 101-113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2018.04.102
Peix A, Valverde A, Rivas R, Igual JM, Ramírez-Bahena M-H, Mateos Pedro F, Santa-Regina I, Rodríguez-Barrueco C, Martínez-Molina E, Velázquez E (2007) Reclassification of Pseudomonas aurantiaca as a synonym of Pseudomonas chlororaphis and proposal of three subspecies, P. chlororaphis subsp. chlororaphis subsp. nov., P. chlororaphis subsp. aureofaciens subsp. nov., comb. nov. and P. chlororaphis subsp. aurantiaca subsp. nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:6. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64621-0
Romanenko Lyudmila A, Masataka U, Tebo Bradley M, Naoto T, Frolova Galina M, Mikhailov Valery V (eds) (2008) Pseudomonas marincola sp. nov., isolated from marine environments. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:3. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65406-0
Shi Z, Zhang Y, Zhou J, Chen M, Wang X (2013) Biological removal of nitrate and ammonium under aerobic atmosphere by Paracoccus versutus LYM. Bioresour Technol 148:144–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.08.052
Smith P (2009) The processing of high silica bauxites-review of existing and potential processes. Hydrometallurgy 98(1–2):162–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2009.04.015
Song T, Li S, Ding W, Li H, Bao M, Li Y (2018) Biodegradation of hydrolyzed polyacrylamide by the combined expanded granular sludge bed reactor-aerobic biofilm reactor biosystem and key microorganisms involved in this bioprocess. Bioresour Technol 263:153–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.04.121
Song T, Li S, Yin Z, Bao M, Lu J, Li Y (2021) Hydrolyzed polyacrylamide-containing wastewater treatment using ozone reactor-upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor-aerobic biofilm reactor multistage treatment system. Environ Pollut 269:116111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116111
Wang Q, He J (2020) Complete nitrogen removal via simultaneous nitrification and denitrification by a novel phosphate accumulating Thauera sp. strain SND5. Water Res 185:116300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116300
Wang MQ, Sun L (2016) Pseudomonas oceani sp. nov., isolated from deep seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:10. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001343
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(16):5261–5267. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00062-07
Wang L, Qiao N, Sun F, Shao Z (2008a) Isolation, gene detection and solvent tolerance of benzene, toluene and xylene degrading bacteria from nearshore surface water and Pacific Ocean sediment. Extremophiles: Life Under Extreme Conditions 12:3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-007-0136-4
Wang Y, Huang C, Hu Y, Hu Y, Lan Y (2008b) Beneficiation of diasporic- bauxite ore by selective flocculation with a polyacrylate flocculant. Miner Eng 21(9):664–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2008.01.001
Wang Z, Pan F, Hesham AE, Gao Y, Zhang Y, Yang M (2015) Impacts of produced water origin on bacterial community structures of activated sludge. J Environ Sci-China 37(11):192–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2015.04.030
Wang X, Wu J, Kumari D (2018) Composition and functional genes analysis of bacterial communities from urban parks of Shanghai, China and their role in ecosystem functionality. Landsc Urban Plan 177:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2018.05.003
Yang B, Qin Y, He X, Li H, Ma J (2021) The removal of ammonia nitrogen via heterotrophic assimilation by a novel Paracoccus sp. FDN-02 under anoxic condition. Sci Total Environ 152236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152236
Yoo W, Lee CW, Kim B, Le LT, Park SH, Kim HW, Kim TD (2019) Structural and functional analysis of a dimeric fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (EaFAH) from psychrophilic Exiguobacterium antarcticum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 509(3):773–778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.183
You J, Li Y, Hong S, Wang J, Yu J, Mu B, Xue Y (2019) Tepidicella baoligensis sp. nov., a novel member of Betaproteobacterium isolated from an oil reservoir. Curr Microbiol 76(4):410–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-018-1604-z
Yu XY, Wang HL, Wang QQ, Bo F, Zhong H (2016) Flotation of low-grade bauxite using organosilicon cationic collector and starch depressant. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 26(4):1112–1117. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64209-7
Zhang C, Zhao L, Bao M, Lu J (2018a) Potential of hydrolyzed polyacrylamide biodegradation to final products through regulating its own nitrogen transformation in different dissolved oxygen systems. Bioresour Technol 61-68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.01.143
Zhang H, Zhao Z, Chen S, Kang P, Wang Y, Feng J, Jia J, Yan M, Wang Y, Xu L (2018b) Paracoccus versutus KS293 adaptation to aerobic and anaerobic denitrification: insights from nitrogen removal, functional gene abundance, and proteomic profiling analysis. Bioresour Technol 260:321–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.123
Zhang Y, Zhao L, Song T, Cheng Y, Bao M, Li Y (2020) Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in an aerobic biofilm biosystem with loofah sponges as carriers for biodegrading hydrolyzed polyacrylamide-containing wastewater. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 43(3):529–540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02247-x
Zhao J, Wu W, Zhang X, Zhu M, Tan W (2017) Characteristics of bio-desilication and bio-flotation of Paenibacillus mucilaginosus BM-4 on aluminosilicate minerals. Int J Miner Process 168:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2017.09.002
Zhao L, Xiao D, Liu Y, Xu H, Nan H, Li D, Cao X (2020a) Biochar as simultaneous shelter, adsorbent, pH buffer, and substrate of Pseudomonas citronellolis to promote biodegradation of high concentrations of phenol in wastewater. Water Res 239:124708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115494
Zhao L, Zhang C, Lu Z, Bao M, Lu J (2020b) Key role of different levels of dissolved oxygen in hydrolyzed polyacrylamide bioconversion: focusing on metabolic products, key enzymes and functional microorganisms. Bioresour Technol 306:123089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123089
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Funding
This work was supported by the research fund of Key Laboratory of Ecology of Rare and Endangered Species and Environmental Protection (Guangxi Normal University), Ministry of Education, China (ERESEP2022Z15); the research fund of Guangxi Key Research and Development Program (AB21220057); the research fund of the Guangxi Key Laboratory of Landscape Resources Conservation and Sustainable Utilization in Lijiang River Basin, Guangxi Normal University (grant no.: LRCSU21Z0213); and the research funds of the Scientific Research and Technology Development Program of Guangxi (Guike AD 20159040); Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (2020JJA120007) and Foundation for S&T Achievements Transformation of GXNU (2019PY003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Sampling and material preparation were performed by Qiang Huo, Ruoyang Li, and Chenquan Wang. Measurements were performed by Chunqiang Chen, Ruoyang Li, and Chenquan Wang. Investigation and funding acquisition were performed by Qiang Huo, Tengfa Long, and Xi Liu. Visualization were performed by Qiang Huo and Tengfa Long. Writing (review and editing) were performed by Qiang Huo, Ruoyang Li, and Xi Liu.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Robert Duran
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huo, Q., Li, R., Chen, C. et al. Study on potential microbial community to the waste water treatment from bauxite desilication process. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 15438–15453 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23150-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23150-1