Abstract
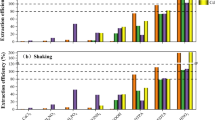
Soil washing is one of the effective methods for permanent removal of heavy metals from farmland soil, and selection of washing agents determines heavy metal removal efficiency. However, there is still a lack of cost-efficient and eco-friendly washing agents. In this study, three residues of traditional Chinese herbal medicine (RTCHM) extracts: residues of Prunus mume (Sieb.) Sieb. et Zucc. (RPM), residues of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. (RSC), and residues of Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge (RCP), were tested for their potential of Cd removal. The variations in amounts and compositions of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and citric acid were responsible for the difference in Cd removal efficiencies of RTCHM extracts. Fourier-transform infrared spectrophotometer (FTIR) analysis showed that hydroxyl, carboxyl, and amine were the main functional groups of RTCHM extracts to chelate with heavy metals. The optimum conditions for RTCHM extracts were 100 g L−1 concentration, solid–liquid ratio 1:10, pH 2.50, and contact time of 1 h, and the highest Cd removal efficiencies of RPM, RSC, and RCP extracts reached 35%, 11%, and 15%, respectively. The ecological risk of Cd decreased significantly due to the decrease of exchangeable and reducible Cd fractions. RTCHM extracts washing alleviated soil alkalinity and had little effect on soil cation exchange capacity. Meanwhile, the concentrations of soil organic matter and nitrogen were enhanced significantly by RPM extracts and the activities of soil catalase and urease were also improved. Overall, among the tested extracts, RPM extracts was a much more feasible and environment-friendly washing agent for the remediation of Cd-contaminated farmland soil.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current research are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
Abdolali A, Ngo HH, Guo WS, Lu SY, Chen SS, Nguyen NC, Zhang XB, Wang J, Wu Y (2016) A breakthrough biosorbent in removing heavy metals: equilibrium, kinetic, thermodynamic and mechanism analyses in a lab-scale study. Sci Total Environ 542:603–611
Ali R, Hamad HA, Hussein MM, Malash GF (2016) Potential of using green adsorbent of heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions: adsorption kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic, mechanism and economic analysis. Ecol Eng 91:317–332
Beiyuan JZ, Tsang DCW, Valix M, Zhang WH, Yang X, Ok YS, Li XD (2017) Selective dissolution followed by EDDS washing of an e-waste contaminated soil: extraction efficiency, fate of residual metals, and impact on soil environment. Chemosphere 166:489–496
Cao YR, Zhang SR, Wang GY, Huang QL, Li T, Xu XX (2017a) Removal of Pb, Zn, and Cd from contaminated soil by new washing agent from plant material. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:8525–8533
Cao YR, Zhang SR, Wang GY, Li T, Xu XX (2017b) Enhancing the soil heavy metals removal efficiency by adding HPMA and PBTCA along with plant washing agents. J Hazard Mater 339:33–42
Chao HP, Chang CC, Nieva A (2014) Biosorption of heavy metals on Citrus maxima peel, passion fruit shell, and sugarcane bagasse in a fixed-bed column. J Ind Eng Chem 20:3408–3414
Chae Y, Cui R, Kim SW, An G, Jeong SW, An YJ (2017) Exoenzyme activity in contaminated soils before and after soil washing: ß-glucosidase activity as a biological indicator of soil health. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 135:368–374
Chen Q, Zheng JW, Wen LY, Yang C, Zhang LJ (2019) A multi-functional-group modified cellulose for enhanced heavy metal cadmium adsorption: performance and quantum chemical mechanism. Chemosphere 224:509–518
Chen YM, Lin WH, Lin YA, Liu CC, Wang MK (2014) Remediation of lead-contaminated soil using dissolved organic carbon solutions prepared by wine-processing waste sludge. Geoderma 235–236:233–239
Chien SWC, Wang HH, Chen YM, Wang MK, Liu CC (2021) Removal of heavy metals from contaminated paddy soils using chemical reductants coupled with dissolved organic carbon solutions. J Hazard Mater 403:123549
Dresler S, Hawrylak-Nowak B, Kováčik J, Woźniak M, Gałazka A, Staniak M, Wójciak M, Sowa I (2021) Organic nitrogenmodulates not only cadmium toxicity but also micr-bial activity in plants. J Hazard Mater 402:123887
Feng C, Chen Y, Zhang SR, Li LX, Wang GY, Xu XX, Li T, Zhong QM (2020) Removal of lead, zinc and cadmium from contaminated soils with two plant extracts: Mechanism and potential risks. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 187:109829
Feng C, Zhang SR, Li LX, Wang GY, Xu XX, Li T, Zhong QM (2018) Feasibility of four wastes to remove heavy metals from contaminated soils. J Environ Manage 212:258–265
Gluhar S, Kaurin A, Finžgar N, Gerl M, Kastelec D, Lestan D (2021) Demonstrational gardens with EDTA-washed soil. Part I: remediation efficiency, effect on soil properties and toxicity hazards. Sci Total Environ 792:149060
Guo XF, Zhao GH, He QS, Wei ZB, Zheng W, Qian TW, Wu QT (2018) Effect of mixed chelators of EDTA, GLDA, and citric acid on bioavailability of residual heavy metals in soils and soil properties. Chemosphere 209:776–782
Gusiatin ZM, Klimiuk E (2012) Metal (Cu, Cd and Zn) removal and stabilization during multiple soil washing by saponin. Chemosphere 86:383–391
Gusiatin ZM, Radziemska M (2018) Saponin versus rhamnolipids for remediation of Cd contaminated soils. Clean: Soil Air Water 46:1700071
Hkanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res 975–1001
Ho HH, Swennen R, Cappuyns V, Vassilieva E, Van Gerven T, Tran TV (2012) Potential release of selected trace elements (As, Cd, Cu, Mn, Pb and Zn) from sediments in Cam River-mouth (Vietnam) under influence of pH and oxidation. Sci Total Environ 435–436:487–498
Hu W, Niu YL, Zhu H, Dong K, Wang DQ, Liu F (2021) Remediation of zinc-contaminated soils by using the two-step washing with citric acid and water-soluble chitosan. Chemosphere 282:131092
Jelusic M, Lestan D (2014) Effect of EDTA washing of metal polluted garden soils. Part I: toxicity hazards and impact on soil properties. Sci Total Environ 475:132–141
Kulikowska D, Gusiatin ZM, Bulkowska K, Kierklo K (2015a) Humic substances from sewage sludge compost as washing agent effectively remove Cu and Cd from soil. Chemosphere 136:42–49
Kulikowska D, Gusiatin ZM, Bulkowska K, Klik B (2015b) Feasibility of using humic substances from compost to remove heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn) from contaminated soil aged for different periods of time. J Hazard Mater 300:882–891
Lasheen MR, Ammar NS, Ibrahim HS (2012) Adsorption/desorption of Cd(II), Cu(II) and Pb(II) using chemically modified orange peel: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Solid State Sci 14:202–210
Li HJ, Che P, Wei XP, Qi YD, Yin Z, Liu HT (2019) Decipherment of herb medicine Nanwuweizi and Wuweizi in Chinese ancient literature. China J Chin Mater Med 44:4053–4059 ((in Chinese with English abstract))
Li Y, Zhang HB, Tu C, Song F, Luo YM (2017) Occurrence of red clay horizon in soil profiles of the Yellow River Delta: implications for accumulation of heavy metals. J Geochem Explor 176:120–127
Liu BH, Wang SX, Wang J, Zhang XZ, Shen ZG, Shi L, Chen YH (2020) The great potential for phytoremediation of abandoned tailings pond using ectomycorrhizal Pinus sylvestris. Sci Total Environ 719:137475
Liu CC, Chen GB (2013) Reclamation of cadmium-contaminated soil using dissolved organic matter solution originating from wine-processing waste sludge. J Hazard Mater 244–245:645–653
Mao XH, Jiang R, Xiao W, Yu JG (2015) Use of surfactants for the remediation of contaminated soils: a review. J Hazard Mater 285:419–435
Marrugo-Negrete J, Pinedo-Hernandez J, Diez S (2017) Assessment of heavy metal pollution, spatial distribution and origin in agricultural soils along the Sinú River Basin, Colombia. Environ Res 154:380–388
Meng F, Yuan G, Wei J, Bi D, Ok YS, Wang H (2017) Humic substances as a washing agent for Cd-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 181:461–467
Ministry of Environmental Protection and the Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China (MEP and MLR) 2014. Bulletin on National Survey of Soil Contamination (2014). China Environmental Protection Industry Beijing (10–11 pp. in Chinese)
Nemati K, Abu Bakar NK, Abas MR, Sobhanzadeh E (2011) Speciation of heavy metals by modified BCR sequential extraction procedure in different depths of sediments from Sungai Buloh, Selangor, Malaysia. J Hazard Mater 192:402–410
Pan JH, Lee KY, Kim JH, Shin H, Lee JH, Kim YJ (2016) Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc. fruit ameliorates alcoholic liver injury in mice by inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation through oxidative stress. J Funct Foods 25:135–148
Ren XH, Yan R, Wang HC, Kou YY, Chae KJ, Kim IS, Park YJ, Wang AJ (2015) Citric acid and ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid as effective washing agents to treat sewage sludge for agricultural reuse. Waste Manage 46:440–448
Sankararaman S, Velayuthan S, Chen YQ, Robertson J, Sferra TJ (2022) Role of traditional Chinese herbal medicines in functional gastrointestinal and motility disorders. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 24:43–51
Tao WY, Jin JJ, Zheng YP, Li S (2021) Current advances of resource utilization of herbal extraction residues in China. Waste Biomass Valorziation 12:5853–5868
Wang GY, Zhang SR, Xu XX, Li T, Li Y, Deng OP, Gong GS (2014) Efficiency of nanoscale zero-valent iron on the enhanced low molecular weight organic acid removal Pb from contaminated soil. Chemosphere 117:617–624
Wang GY, Zhang SR, Xu XX, Zhong QM, Zhang CE, Jia YX, Li T, Deng OP, Li Y (2016) Heavy metal removal by GLDA washing: optimization, redistribution, recycling, and changes in soil fertility. Sci Total Environ 569–570:557–568
Wang GY, Zhang SR, Zhong QM, Peijinenburg WJGM, Vijver MG (2018) Feasibility of Chinese cabbage (Brassica bara) and lettuce (Lactuca sativa) cultivation in heavily metals-contaminated soil after washing with biodegradable chelators. J Clean Prod 197:479–490
Wang L, Zhang HY, Wang L (2010) Comparison of pharmacological effects of Fructus Mume and its processed products. J Chin Med Mater 33:353–356 ((in Chinese with English abstract))
Wei M, Chen JJ, Wang XW (2016) Removal of arsenic and cadmium with sequential soil washing techniques using Na2EDTA, oxalic and phosphoric acid: Optimization conditions, removal effectiveness and ecological risks. Chemosphere 156:252–261
Xia ZH, Zhang SR, Cao Y, Zhong QM, Wang GY, Li T, Xu XX (2019) Remediation of cadmium, lead and zinc in contaminated soil with CETSA and MA/AA. J Hazard Mater 366:177–183
Xu XX, Yang Y, Wang GY, Zhang SR, Cheng Z, Li T, Yang ZB, Xian JR, Yang YX, Zhou W (2020) Removal of heavy metals from industrial sludge with new plant-based washing agents. Chemosphere 246:125816
Yan RY, Wei JL, Yang B (2013) Chemical constituents of Crataegus pinnatifida Bge. var. major N. E Br Lishizhen. Med Mater Med Res 26:42–43 ((in Chinese with English abstract))
Yang RC, Liu H, Bai C, Wang YC, Zhang XH, Guo R, Wu SY, Wang JX, Leung E, Chang H, Li P, Liu TG, Wang Y (2020) Chemical composition and pharmacological mechanism of Qingfei Paidu Decoction and Ma Xing Shi Gan Decoction against Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): In silico and experimental study. Pharmacol Res 157:104820
Yang S, Li Y, Liu GM, Si SC, Zhu X, Tu C, Li LZ, Luo YM (2022a) Sequential washing and eluent regeneration with agricultural waste extracts and residues for facile remediation of meta-contaminated agricultural soils. Sci Total Environ 835:155548
Yang S, Li Y, Si SC, Liu GM, Yun H, Tu C, Li LZ, Luo YM (2022b) Feasibility of a combined solubilization and eluent drainage system to remove Cd and Cu from agricultural soil. Sci Total Environ 807:150733
Yang ZH, Zhang Z, Chai LY, Wang Y, Liu Y, Xiao RY (2016) Bioleaching remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils using Burkholderia sp. Z-90. J Hazard Mater 301:145–152
Yoo J, Lee C, Lee J, Baek K (2017) Simultaneous application of chemical oxidation and extraction processes is effective at remediating soil Co-contaminated with petroleum and heavy metals. J Environ Manag 186:314–319
Zhang H, Gao YT, Xiong HB (2017) Removal of heavy metals from polluted soil using the citric acid fermentation broth: a promising washing agent. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:9506–9514
Zhang QW, Lin LG, Ye WC (2018) Techniques for extraction and isolation of natural products: a comprehensive review. Chin Med 13(1):20 ((in Chinese with English abstract))
Zhang SY, Wen J, Hu Y, Fang Y, Zhang HB, Xing L, Wang YX, Zeng GM (2019) Humic substances from green waste compost: an effective washing agent for heavy metal (Cd, Ni) removal from contaminated sediments. J Hazard Mater 366:210–218
Zhang Y, Wu CF, Deng SP, Zhang JL, Hou JY, Wang C, Fu ZC (2022) Effect of diferent washing solutions on soil enzyme activity and microbial community in agricultural soil severely contaminated with cadmium. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(36):54641–54651
Zhu HN, Yuan XZ, Zeng GM, Jiang M, Liang J, Zhang C, Yin J, Huang HJ, Liu ZF, Jiang HW (2012) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port based on modified potential ecological risk index. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 22:1470–1477 ((in Chinese with English abstract))
Zou Z, Qiu RL, Zhang WH, Dong HY, Zhao ZH, Zhang T, Wei MG, Cai XD (2009) The study of operating variables in soil washing with EDTA. Environ Pollut 157:229–236
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation of China (41991335).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yi Wang: data curation, methodology, writing original draft, visualization, formal analysis. Yuan Li: data curation, investigation, methodology, writing — review and editing. Shuai Yang: data curation, methodology, writing — review and editing. Qihao Wang: investigation, methodology. Shaocheng Si: investigation, methodology. Hanyi Mei: investigation, validation. Guoming Liu: investigation, validation. Xiangliang Pan: methodology, writing — review and editing. Yongming Luo: conceptualization, supervision, methodology, writing — review and editing, dunding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kitae Baek.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Li, Y., Yang, S. et al. Removal of Cd from contaminated farmland soil by washing with residues of traditional Chinese herbal medicine extracts. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 31461–31470 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24409-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24409-3