Abstract
Objective
To detect absorbed bioactive compounds of the water extract whose pharmacodynamic effect was craniocerebral protection for quality control assessment.
Methods
Anthraquinones in water extract of rhubarb (WER), in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI) and in ipsilateral cortex of TBI rats following oral WER were respectively explored by ultra performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array detector (UPLC-PDA) method developed in the present study. The effects of anthraquinones absorbed into injured cortex on superoxidase dismutase (SOD) activity in TBI rats were detected. The antioxidative anthraquinones absorbed into target organ were evaluated for quality control of WER.
Results
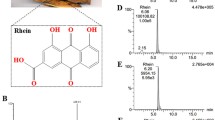
Anthraquinones in WER were aloe-emodin, rhein, emodin, chrysophanol, and physcion. Only the last anthraquinone was found in CSF and in ipsilateral cortex under this chromatographic condition. Physcion increased SOD activity in TBI rats significantly.
Conclusions
Physcion was the main active compound of rhubarb against craniocerebral injury via antioxidant pathway. According to our strategy, the exploration of physcion suggested the possibility of a novel quality control of WER in treating TBI injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peter AGM. Herbal remedies. New Engl J Med 2002;347:2046–2056.
Dennis N. The new face of traditional Chinese medicine. Science 2003;299:188–190.
Yan SK, Xin WF, Luo GA, Wang YM, Cheng YY. An approach to develop two-dimensional fingerprint for the quality control of Qingkailing injection by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection. J Chromatogr A 2005;1090:90–97.
Huang X. Idea, background and significance of traditional Chinese medicine research according to bioethnopharmaceutical analyses. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2002;22:251–252.
Drasar P, Moravcova J. Recent advances in analysis of Chinese medical plants and traditional medicines. J Chromatogr B 2004;812:3–21.
Mao Y, Li Y, Yao N. Simultaneous determination of salidroside and tyrosol in extracts of Rhodiola L. by microwave assisted extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2007;45:510–515.
Ding L, Luo XB, Tang F, Yuan JB, Guo ML, Yao SZ. Quality control of medicinal herbs Fructus gardeniae, common andrographis herb and their preparations for their active constituents by high-performance liquid chromatography photodiode array detection-electro spray mass spectrometry. Talanta 2008;74:1344–1349.
Wang ZJ, Wo SK, Wang L, Lau CBS, Lee VHL, Chow MSS, et al. Simultaneous quantification of active components in herbs and products of Si-Wu-Tang by high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2009;50:232–244.
Xie PS, Leung AY. Understanding the traditional aspect of Chinese medicine in order to achieve meaningful quality control of Chinese materia medica. J Chromatogr A 2009;1216:1933–1940.
Huang X, Qin F, Zhang HM, Xiao HB, Wang LX, Zhang XY, et al. Cardioprotection by Guanxin II in rats with acute myocardial infarction is related to its three compounds. J Ethnopharmacol 2009;121:268–273.
Wang Y, Huang Xi, Qin F, Ren P, Zhu ZY, Fan R, et al. A strategy for detecting optimal ratio of cardioprotetiondependent three compounds as quality control of Guan-Xin-Er-Hao formula. J Ethnopharmacol 2011;133:735–742.
Wang FX, Zhang ZY, Cui XJ, Peter BH. Identification of rhubarbs by using NIR spectrometry and temperature-constrained cascade correlation networks. Talanta 2006;70:1170–1176.
Liu LH, Fan LY, Chen HL, Chen XG, Hu ZD. Separation and determination of four active anthraquinones in Chinese herbal preparations by flow injection-capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2005;26:2999–3006.
Gu JW, Hiroshi H, Mitsue T, Takashi A. Effects of emodin on synaptic transmission in rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons in vitro. Neuropharmacology 2005;49:103–111.
Gu JW, Zhang X, Zhou F, Wen AD, Qin SY, Yi SY, et al. Rhubarb extracts in treating complications of severe cerebral injury. Chin Med J 2000;113:529–531.
Eileen MW, Vicente G, Arthur I, Katherine H, Stephanie B, Yang W, et al. Brain tissue oxygen and outcome after severe traumatic brain injury: a systematic review. Crit Care Med 2009;37:2057–2063.
Memduh K, Bayram C, Fehmi O, Ahmet D, Recep S, Irfan A, et al. Does melatonin protect or treat brain damage from traumatic oxidative stress? Exp Brain Res 2005;163:406–410.
Shadi H, Fabiola F, Nicole C, Bruno P, Michel P, Catherine ML, et al. Minocycline effects on cerebral edema: Relations with inflammatory and oxidative stress markers following traumatic brain injury in mice. Brain Res 2009;1291:122–132.
He DX, Chen B, Tian QQ, Yao SZ. Simultaneous determination of five anthraquinones in medicinal plants and pharmaceutical preparations by HPLC with fluorescence detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2009;49:1123–1127.
Jin W, Wang YF, Ge RL, Shi HM, Jia CQ, Tu PF. Simultaneous analysis of multiple bioactive constituents in Rheum tanguticum Maxim. ex Balf. by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2007;21:2351–2360.
Lin CC, Wu C, Lin TC, Sheu SJ. Determination of 19 rhubarb constituents by high-performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet-mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 2006;29:2584–2593.
Junko K, Izumi M, Norihiro K. Simultaneous determination of anthraquinones in rhubarb by high-performance liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A 2007;1145:183–189.
Wang JB, Li HF, Jin C, Qu Y, Xiao XH. Development and validation of a UPLC method for quality control of rhubarb-based medicine: fast simultaneous determination of five anthraquinone derivatives. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2008;47:765–770.
Subash CV, Narendra PS, Arun KS. Determination and locational variations in the quantity of hydroxyanthraquinones and their glycosides in rhizomes of Rheum emodi using high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 2005;1097:59–65.
Singh NP, Gupta AP, Sinha AK. High-performance thin layer chromatography method for quantitative determination of four major anthraquinone derivatives in Rheum emodi. J Chromatogr A 2005;1077:202–206.
Ye M, Han J, Chen HB, Zheng JH, Guo DA. Analysis of phenolic compounds in rhubarbs using liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray Ionization mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 2007;18:82–91.
Wang YS, Chen FQ. The influence of ten decoction methods on active components in rhubarb decoction. Chin Tradit Patent Med (Chin) 1990;12:5–7.
Gao GW, Zhang B, Liu YH, Liu QF. The application of rhubarb in several brain injury. Central Plains Med J (Chin) 2002;29(4):8–9.
Feeney DM, Boyeson MG, Linn RT, Murray HM, Dail WG. Responses to cortical injury: methodology and local effects of contusions in the rat. Brain Res 1981;211:67–77.
Ding MY, Ma SW, Liu DL. Simultaneous determination of hydroxyanthraquinones in rhubarb and experimental animal bodies by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Sci 2003;19:1163–1165.
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. The Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Vol.I. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press; 2005:17–18.
Lee JH, Kim JM, Kim C. Pharmacokinetic analysis of rhein in Rheum undulatum L. J Ethnopharmacol 2003;84:5–9.
Lai YL, Smith PM, Lamm WJE, Hildebrandt J. Sampling and analysis of cerebrospinal fluid for chronic studies in awake rats. J Appl Physiol 1983;54:1754–1757.
Vladimir AT, Yulia YT, Grigory GB, Tatiana VS, Vladimir BR, Peter JQ, et al. Oxidative stress following traumatic brain injury in rats: quantitation of biomarkers and detection of free radical intermediates. J Neurochem 2000;75:2178–2189.
Chong ZZ, Li F, Kenneth M. Oxidative stress in the brain: novel cellular targets that govern survival during neurodegenerative disease. Prog Neurobiol 2005;75:207–246.
Klaus A, Heribert H. Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 2004;55:373–399.
Niklas M, Tommy L, Fredrik C, Lars H. Effects of the nitrone radical scavengers PBN and S-PBN on in vivo trapping of reactive oxygen species after traumatic brain injury in rats. J Cerebr Blood F Met 2001;21:1259–1267.
Mubeen AA, Kelly NR, Stephen WS. Oxidative stress and modification of synaptic proteins in hippocampus after traumatic brain injury. Free Radical Bio Med 2008;45:443–452.
Marian V, Dieter L, Jan M, Mark TDC, Milan M, Joshua T. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell B 2007;39:44–84.
Anna IB, Enoch PW, Yuji U, Milton MS, Hermes AK, John TP. Cerebral vascular responsiveness after experimental traumatic brain injury: the beneficial effects of delayed hypothermia combined with superoxide dismutase administration. J Neurosurg 2008;109:502–509.
Akira I, Osamu TI, Kazuo K, Hiroshige I, Fumihiko Y, Hiroko M, et al. Evaluation of Rhubarb using antioxidative activity as an index of pharmacological usefulness. J Ethnopharmacol 2004;91:89–94.
Hisashi M, Toshio M, Iwao T, Park JY, Shoichi H, Masayuki Y. Antioxidant constituents from rhubarb: structural requirements of stilbenes for the activity and structures of two new anthraquinone glucosides. Bioorgan Med Chem 2001;9:41–50.
Ren P, Qin F, Huang X, Zhu ZY. Simultaneous LC analysis of aloe-emodin, rhein, emodin, and chrysophanol in Rhizoma Rhei-type preparations. Chromatographia 2009;70:1515–1517.
Wu T, Wang C, Wang X, Xiao HQ, Ma Q, Zhang Q. Comparison of UPLC and HPLC for analysis of 12 phthalates. Chromatographia 2008;68:803–806.
Gao XY, Jiang Y, Lu JQ, Tu PF. One single standard substance for the determination of multiple anthraquinone derivatives in rhubarb using high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection. J Chromatogr A 2009;1216:2118–2123.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Fund for Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Gan of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, the Major Research Plan of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 90409010), and was partly supported by the Huge Project to Boost Chinese Drug Development (No. 2009ZX09304-003)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Huang, X., Liang, Qh. et al. A strategy for detecting absorbed bioactive compounds for quality control in the water extract of rhubarb by ultra performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array detector. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 18, 690–698 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-012-1053-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-012-1053-7