Abstract
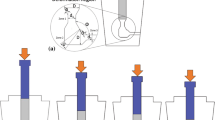
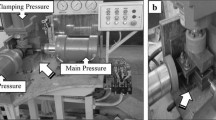
Pure Mg particles were consolidated by equal-channel angular pressing (ECAP) with back pressure at 423 K. Fully dense bulk Mg with a homogeneous grain structure was obtained. After multiple passes, grains were significantly refined to below 2 µm, resulting in much enhanced yield strength and enhanced ductility. The intense \(\left(10\stackrel{-}{1}1\right)\langle \stackrel{-}{1}2\stackrel{-}{1}0\rangle \) texture was developed during ECAP, leading to texture softening. The oxide layer on the surface of Mg particles was broken into nano-sized pieces distributed in the matrix, hindering the movement of dislocations and providing dispersion strengthening.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.L. Mordike and T. Ebert, Magnesium: Properties-Applications-Potential, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2001, 302, p 37-45.
M. Mabuchi, Y. Chino, H. Iwasaki et al., The Grain Size and Texture Dependence of Tensile Properties in Extruded Mg-9Al-1Zn, Mater. Trans., 2001, 42, p 1182-1118.
J.H. Lee, T. Lee, S.W. Song et al., Enhancing Yield Strength by Suppressing Detwinning in a Rolled Mg-3Al-1Zn Alloy with 10-12 Twins, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2014, 612, p 328-333.
J. Zhang, Q. Ma and F.S. Pan, Effects of trace Er Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Mg–Zn–Zr alloy, Mater. Des., 2010, 31, p 4043-4049.
G.D. Fan, M.Y. Zheng, X.S. Hu et al., Improved Mechanical Property and Internal Friction of Pure Mg Processed by ECAP, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2012, 556, p 588-594.
B.J. Bonarski, E. Schafler, B. Mikulowski and M.J. Zehetbauer, Effects of Recrystallization on Texture, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in HPT-Deformed Pure Mg, J. Phys: Conf. Ser., 2010, 240, p 012133.
P. W. J. Mckenzie, R. Lapovok, ECAP with back pressure for optimum strength and ductility in aluminium alloy 6016. Part 1: Microstructure, Acta Materialia. 58 (2010) 3198-3211.
T.G. Langdon, Twenty-Five Years of Ultrafine-Grained Materials: Achieving Exceptional Properties Through Grain Refinement, Acta Mater., 2013, 61, p 7035-7059.
H. Liu, J. Ju, X.W. Yang et al., J. Alloy. Compd., 2017, 704, p 509-517.
H. Liu, C. Sun, C. Wang et al., J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2020, 59, p 61-71.
W.C. Su, L. Lu and M.O. Lai, A Model for the Grain Refinement Mechanism in Equal Channel Angular Pressing of Mg alloy from Microstructural Studies, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2006, 434, p 227-236.
F.M. Lu, A.B. Ma, J.H. Jiang et al., Enhanced Mechanical Properties and Rolling Formability of Fine-Grained Mg–Gd–Zn–Zr Alloy Produced by Equal-Channel Angular Pressing, J. Alloy. Compd., 2015, 643, p 28-33.
E. Mostaed, A. Fabrizi, D. Dellasega, F. Bonollo and M. Vedani, Microstructure, Mechanical Behavior and Low Temperature Superplasticity of ECAP Processed ZM21 Mg Alloy, J. Alloy. Compd., 2015, 638, p 267-276.
W.B. Fang, W. Fang and H.F. Sun, Preparation of High-Strength Mg–3Al–Zn Alloy with Ultrafine-Grained Microstructure by Powder Metallurgy, Powder Technol., 2011, 212, p 161–165.
A. Mogucheva, E. Babich, B. Ovsyannikov et al., Microstructural Evolution in a 5024 Aluminum Alloy Processed by ECAP with and Without Back Pressure, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2013, 560, p 178-192.
J. Li, W. Xu, X. Wu, H. Ding and K. Xia, Effects of Grain Size on Compressive Behaviour in Ultrafine Grained Pure Mg Processed by Equal Channel Angular Pressing at Room Temperature, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2011, 528, p 5993-5998.
K. Xia, J.T. Wang, X. Wu et al., Equal Channel Angular Pressing of Magnesium Alloy AZ31, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2005, 410, p 324-327.
K. Xia and X. Wu, Back Pressure Equal Channel Angular Consolidation of Pure Al Particles, Scripta Mater., 2005, 53, p 1225-1229.
K. Xia, X. Wu, T. Honma et al., Ultrafine Pure Aluminum Through Back Pressure Equal Channel Angular Consolidation (BP-ECAC) of Particles, J. Mater. Sci., 2007, 42, p 1551-1560.
P. Minarik, J. Vesely, R. Kral et al., Exceptional Mechanical Properties of Ultra-Fine Grain Mg-4Y-3RE Alloy Processed by ECAP, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2017, 708, p 193-198.
M. Cabibbo, C. Paoletti, P. Minarik et al., Secondary Phase Precipitation and Thermally Stable Microstructure Refinement Induced by ECAP on Mg-Y-Nd (WN43) Alloy, Mater. Lett., 2019, 237, p 5-8.
J.Y. Zhang, Z.X. Kang and L.L. Zhou, Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Mg–Gd–Nd–Zn–Zr Alloy Processed by Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2015, 647, p 184-190.
E. Dogan, S. Wang, M.W. Vaughan et al., Dynamic Precipitation in Mg-3Al-1Zn Alloy During Different Plastic Deformation Modes, Acta Mater., 2016, 116, p 1-13.
A.K. Chaubey, S. Scudino and M.S. Khoshkho, High-Strength Ultrafine Grain Mg–7.4%Al Alloy Synthesized by Consolidation of Mechanically Alloyed Powders, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 610, p 456-461.
J.Z. Li, H. Ding, X.L. Wu, W. Xu and K. Xia, The Influence of Texture and Grain Size on Compressive Deformation Behavior of Pure Mg Through Equal-Channel Angular Processing, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2010, 667-669, p 385-390.
W.J. Kim, C.W. An, Y.S. Kim, S.I. Hong et al., Mechanical Properties and Microstructures of an AZ61 Mg Alloy Produced by Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Scripta Mater., 2002, 47, p 39-44.
C.P. Wang, F.G. Li, B. Chen et al., Severe Plastic Deformation Techniques for Bulk Ultrafine-Grained Materials, Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2012, 41, p 941-946.
Y. Kim, S. Lee, J.B. Jeon et al., Effect of a High Angle Grain Boundary on Deformation Behavior of Al Nanopillars, Scripta Mater., 2015, 107, p 5-9.
G.H. Zahid, Y. Huang and P.B. Prangnell, Microstructure and Texture Evolution During Annealing a Cryogenic-SPD Processed Al-Alloy with a Nanoscale Lamellar HAGB Grain Structure, Acta Mater., 2009, 57, p 3509-3521.
Y.D. Qiao, X. Wang, Z.Y. Liu and E.D. Wang, Effects of Grain Size, Texture and Twinning on Mechanical Properties and Work-Hardening Behaviors of Pure Mg, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2013, 578, p 240-246.
W. Lei, W. Liang, H. Wang and Y. Sun, Evolution of Texture and Mechanical Properties of Pure Mg Processed by ECAP at Room Temperature, J. The Miner. Metals Mater. Soc., 2017, 69, p 2297-2301.
X.G. Qiao, Y.W. Zhao, W.M. Gan et al., Hardening Mechanism of Commercially Pure Mg Processed by High Pressure Torsion at Room Temperature, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2014, 619, p 95-106.
K. Mathis, K. Nyilas, A. Axt et al., The Evolution of Non-basal Dislocations as a Function of Deformation Temperature in Pure Magnesium Determined by X-ray Diffraction, Acta Mater., 2004, 52, p 2889-2894.
I. Dragomir and T. Ungar, Contrast Factors of Dislocations in the Hexagonal Crystal System, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2002, 35, p 556-564.
R. Verma, A. Srinivasan, R. Jayaganthan, S.K. Nath and S. Goel, Studies on Tensile Behaviour and Microstructural Evolution of UFG Mg-4Zn-4Gd Alloy Processed Through Hot Rolling, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2017, 704, p 412-426.
D. Liu, M.Z. Bian, S.M. Zhu et al., Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Mg-3Al-1Zn Sheets Produced by Hot-Roller-Cold-Material Rolling, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2017, 706, p 304-310.
K. Mathism, G. Farkas, G. Garces and J. Gubicza, Evolution of Dislocation Density During Compression of a Mg-Zn-Y Alloy with Long Period Stacking Ordered Structure, Mater. Lett., 2017, 190, p 86-89.
L. Balogh, R.B. Figueiredo, T. Ungar and T.G. Langdon, The Contributions of Grain Size, Dislocation Density and Twinning to the Strength of a Magnesium Alloy Processed by ECAP, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2010, 528, p 533-538.
T. Krajnak, P. Minarik, J. Straska, J. Gubicza, K. Mathis and M. Janecek, Influence of Equal Channel Angular Pressing Temperature on Texture, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Extruded AX41 Magnesium, J. Alloy. Compd., 2017, 705, p 273-282.
X.J. Wang, X.S. Hu, W.Q. Liu et al., Ageing Behavior of As-cast SiCp/AZ91 Mg Matrix Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2017, 682, p 491-500.
P. Xiao, Y.M. Gao, X.R. Yang et al., Processing, Microstructure and Ageing Behavior of In-situ Submicron TiB2 Particles Reinforced AZ91 Mg Matrix Composites, J. Alloy. Compd., 2018, 764, p 96-106.
W.M. Gan, K. Wu, M.Y. Zheng et al., Microstructure and Mechanical Property of the ECAPed Mg2Si/Mg Composite, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2009, 516, p 283-289.
H.K. Lin, J.C. Huang and T.G. Langdon, Relationship Between Texture and Low Temperature Superplasticity in an Extruded AZ31 Mg Alloy Processed by ECAP, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2005, 402, p 250-257.
W.J. Kim, S.I. Hong, Y.S. Kim et al., Texture Development and its Effect on Mechanical Properties of an AZ61 Mg Alloy Fabricated by Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Acta Mater., 2003, 51, p 3293-3307.
W.J. Kim, H.W. Lee, S.J. Yoo and Y.B. Park, Texture and Mechanical Properties of Ultrafine-Grained Mg–3Al–1Zn Alloy Sheets Prepared by High-Ratio Differential Speed Rolling, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2011, 528, p 874-879.
E.O. Hall, The Deformation and Aging of Mild Steel, Proc. Phys. Soc. Section B, 1951, 64, p 747-753.
N.J. Petch, The Cleavage Strength of Polycrystals, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1953, 174, p 25-28.
J.E. Bailey and P.B. Hirsch, The Dislocation Distribution, Flow Stress, and Stored Energy in Cold-Worked Polycrystalline Silver, Philos. Mag. A J. Theor. Exp. Appl. Phys., 1960, 5, p 485-497.
A. Sanaty-Zadeh, Comparison Between Current Models for the Strength of Particulate-Reinforced Metal Matrix Nanocomposites with Emphasis on Consideration of Hall-Petch Effect, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2012, 531, p 112-118.
T.S. Srivatsan, Book Review: Dispersion Strengthened Aluminum Alloys, Mater. Manuf. Processes, 1991, 6, p 565-568.
Y.D. Qiao, X. Wang, Z.Y. Liu and E.D. Wang, Effect of Temperature on Microstructures, Texture and Mechanical Properties of hot Rolled Pure Mg Sheets, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2012, 568, p 202-205.
F.E. Hauser, P.R. Landon and J.E. Dorn, Fracture of Magnesium Alloys at Low Temperature, Trans. Am. Inst. Min. Metall. Eng., 1956, 206, p 589-593.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Xia, K. & Ding, H. Consolidation of Pure Magnesium Powder by Equal-Channel Angular Pressing with Back Pressure. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 30, 2213–2219 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05479-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05479-9