Abstract
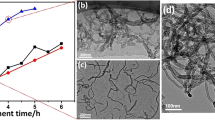
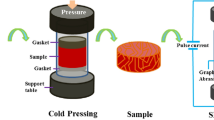
Carbon nanotube-reinforced copper matrix (CNT/Cu) composites were prepared by a method involving solution-aging treatment, in situ chemical vapor deposition (CVD), and spark plasma sintering (SPS). The tribological properties of the CNT/Cu composites were greatly improved, and the friction stability was better than that of Cu. These performance improvements were attributed to the uniform distribution of the CNTs without agglomeration and the strong interfacial bonding between the Cu matrix and CNTs. The coefficient of friction was 0.2, which was lower than that of pure copper (0.55), and the wear rate of the CNT/Cu composites was 2 times lower than that of pure copper. The wear mechanism was also discussed from the perspective of the wear morphology and interface structure. Furthermore, the electrical conductivity remained at a high level. The preparation technique is simple and easy to be controlled and can be used to synthesize CNT/Cu composites with excellent tribological properties and electrical conductivity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Kato, I.Y. TakamaM, K. Washida and Y. Sasaki, Wear and Mechanical Properties of Sintered Copper-tin Composites Containing Graphite or Molybdenum Disulfide, Wear, 2003, 255, p 573–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(03)00072-3
A.P. Zhilyaev, A. Morozova, J.M. Cabrera, R. Kaibyshev and T.G. Langdon, Wear Resistance and Electroconductivity in a Cu-0.3Cr-0.5Zr Alloy Processed by ECAP, J. Mater. Sci., 2017, 52(1), p 305–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0331-8
D.B. Miracle, Metal Matrix Composites–From Science to Technological Significance, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2005, 65(15), p 2526–2540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2005.05.027
A. Azarniya, A. Azarniya, S. Sovizi, H.R.M. Hosseini, T. Varol, A. Kawasaki and S. Ramakrishnad, Physicomechanical Properties of Spark Plasma Sintered Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced Metal Matrix Nanocomposites, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2017, 90, p 276–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2017.07.007
Z.D. Shi, J. Sheng, Z.Y. Yang, Z.Y. Liu, S. Chen, M. Wang, L.D. Wang and W.D. Fei, Facile Synthesis of High-Performance Carbon Nanosheet/Cu Composites from Copper Formate, Carbon, 2020, 165, p 349–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.04.061
F. Daneshvar, S. Tagliaferri, H. Chen, T. Zhang, C. Liu and H.J. Sue, Ultralong Electrospun Copper−Carbon Nanotube Composite Fibers for Transparent Conductive Electrodes with High Operational Stability, ACS Appl. Electron. Mater., 2020, 2, p 2692–2698. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaelm.0c00466
R. Shu, X.S. Jiang, H.L. Sun, Z.Y. Shao, T.F. Song and Z.P. Luo, Recent Researches of the Bio-Inspired Nano-Carbon Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites, Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf., 2020, 131, p 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2020.105816
S. Iijima, Helical Microtubules of Graphitic Carbon, Nature, 1991, 354(6348), p 56–58. https://doi.org/10.1038/354056a0
S.S. Xie, W.Z. Li, Z.W. Pan, B.H. Chang and L.F. Sun, Mechanical and Physical Properties on Carbon Nanotube, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 2000, 61(7), p 1153–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3697(99)00376-5
C. Laurent, E. Flahaut and A. Peigney, The Weight and Density of Carbon Nanotubes versus the Number of Walls and Diameter, Carbon, 2010, 48(10), p 2994–2996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2010.04.010
M.F. Yu, O. Lourie, M.J. Dyer, K. Moloni, T.F. Kelly and R.S. Ruoff, Strength and Breaking Mechanism of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes under Tensile Load, Science, 2000, 287(5453), p 637–640. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.287.5453.637
F. Akhlaghi and A. Zare-Bidaki, Influence of Graphite Content on the Dry Sliding and Oil Impregnated Sliding Wear Behavior of Al 2024 – Graphite Composites Produced by in situ Powder Metallurgy Method, Wear, 2009, 266(1), p 37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2008.05.013
A.D. Moghadam, E. Omrani, P.L. Menezes and P.K. Rohatgi, Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Self-Lubricating Metal Matrix Nanocomposites Reinforced by Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) and Graphene–A Review, Compos. B Eng., 2015, 77, p 402–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.03.014
A.D. Moghadam, B.F. Schultz, J.B. Ferguson, E. Omrani, P.K. Rohatgi and N. Gupta, Functional Metal Matrix Composites: Self-lubricating, Self-healing, and Nanocomposites-An Outlook, Jom, 2014, 66(6), p 872–881. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-0948-5
X. Gao, H.Y. Yue, E.J. Guo, S.L. Zhang, L.H. Yao, X.Y. Lin, B. Wang and E.H. Guan, Tribological Properties of Copper Matrix Composites Reinforced with Homogeneously Dispersed graphene Nanosheets, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2018, 34(10), p 1925–1931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2018.02.010
W. Xu, R. Hu, J.S. Li and H.Z. Fu, Effect of Electrical Current on Tribological Property of Cu matrix Composite Reinforced by Carbon Nanotubes, Trans. Nonferrous Metals Soc. China, 2011, 21(10), p 2237–2241. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61001-7
W.X. Chen, J.P. Tu, L.Y. Wang, H.Y. Gan, Z.D. Xu and X.B. Zhang, Tribological Application of Carbon Nanotubes in a Metal-based Composite Coating and Composites, Carbon, 2003, 41(2), p 215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(02)00265-8
W.Z. Zhai, N. Srikanth, L.B. Kong and K. Zhou, Carbon Nanomaterials in Tribology, Carbon, 2017, 119, p 150–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.04.027
M.Y. Zhou, X.N. Qu, L.B. Ren, L.L. Fan, Y.W.X. Zhang, Y.Y. Guo, G.F. Quan, Q. Tang et al., The Effects of Carbon Nanotubes on the Mechanical and Wear Properties of AZ31 Alloy, Materials, 2017, 10(12), p 1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121385
S.R. Dong, J.P. Tu and X.B. Zhang, An Investigation of the Sliding wear Behavior of Cu-Matrix Composite Reinforced by Carbon Nanotubes, Mater. Sci. Eng. Struct. Mater. Properties Microstruct. Process., 2001, 313(1–2), p 83–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(01)00963-7
K.T. Kim, S. Cha and S.H. Hong, Hardness and Wear Resistance of Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Cu Matrix Nanocomposites, Mater. Sci. Eng. Struct. Mater. Properties Microstruct. Process., 2007, 449, p 46–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.02.310
W. Xu, R. Hu, J.S. Li, Y.Z. Zhang and H.Z. Fu, Tribological Behavior of CNTs-Cu and Graphite-Cu Composites with Electric Current, Trans. Nonferrous Metals Soc. China, 2012, 22(1), p 78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61143-6
H.Y. Yue, L.H. Yao, X. Gao, S.L. Zhang, E.J. Guo, H. Zhang, X.Y. Lin and B. Wang, Effect of Ball-Milling and Graphene Contents on the Mechanical Properties and Fracture Mechanisms of Graphene Nanosheets Reinforced Copper Matrix Composites, J. Alloy. Compd., 2017, 691, p 755–762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.08.303
Ch. Guiderdoni, E. Pavlenko, V. Turq, A. Weibel, P. Puech, C. Estournès, A. Peigney, W. Bacsa et al., The Preparation of Carbon Nanotube (CNT)/Copper Composites and the Effect of the Number of CNT Walls on Their Hardness, Friction and Wear Properties, Carbon, 2013, 58, p 185–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.02.049
Z.X. Huang, Z. Zheng, S. Zhao, S.J. Dong, P. Luo and L. Chen, Copper Matrix Composites Reinforced by Aligned Carbon Nanotubes: Mechanical and Tribological Properties, Mater. Des., 2017, 133, p 570–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.08.021
R. Murugesan, M. Gopal and G. Murali, Effect of Cu, Ni Addition on the CNTs Dispersion, Wear and Thermal Expansion Behavior of Al-CNT Composites by Molecular Mixing and Mechanical Alloying, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2019, 495, 143542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143542
Z.Y. Hu, Z.H. Zhang, X.W. Cheng, F.C. Wang, Y.F. Zhang and S.L. Li, A Review of Multi-Physicalfields Induced Phenomena and Effects in Spark Plasma Sintering: Fundamentals and Applications, Mater. Des., 2020, 191, p 1–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108662
H. Wang, Z.H. Zhang, Z.Y. Hu, Q. Song, S.P. Yin and Z. Kang, Improvement of Interfacial Interaction and Mechanical Properties in Copper Matrix Composites Reinforced with Copper Coated Carbon Nanotubes, Mater. Sci. Eng. Struct. Mater. Properties Microstruct. Process., 2018, 715, p 163–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.01.005
H. Wang, Z.H. Zhang, H.M. Zhang, Z.Y. Hu, S.L. Li and X.W. Cheng, Novel Synthesizing and Characterization of Copper Matrix Composites Reinforced with Carbon Nanotubes, Mater. Sci. Eng. Struct. Mater. Properties Microstruct. Process., 2017, 696, p 80–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.04.055
T. Rodriguez-Suarez, J.F. Bartolome, A. Smirnov, S. Lopez-Esteban, R. Torrecillas and J.S. Moya, Sliding Wear Behaviour of Alumina/Nickel Nanocomposites Processed by a Conventional Sintering Route, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2011, 31(8), p 1389–1395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2011.02.011
D. Nayak, N. Ray, R. Sahoo and M. Debata, Analysis of Tribological Performance of Cu Hybrid Composites Reinforced with Graphite and TiC Using Factorial Techniques, Tribol. Trans., 2014, 57(5), p 908–918. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2014.923079
S.M. Javadhesari, S. Alipour and M.R. Akbarpour, Microstructural Characterization and Enhanced Hardness, Wear and Antibacterial Properties of a Powder Metallurgy SiC/Ti-Cu Nanocomposite as a Potential Material for Biomedical Applications, Ceram. Int., 2019, 45(8), p 10603–10611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.02.127
S.L. Fu, X.H. Chen and P. Liu, Preparation of CNTs/Cu Composites with Good Electrical Conductivity and Excellent Mechanical Properties, Mater. Sci. Eng. Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process., 2020, 771, 138656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.138656
H.J. Choi, S.M. Lee and D.H. Bae, Wear Characteristic of Aluminum-Based Composites Containing Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Wear, 2010, 270(1), p 12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2010.08.024
G.Y. Lee, C.K.H. Dharan and R.O. Ritchie, A Physically-Based Abrasive Wear Model for Composite Materials, Wear, 2002, 252(3–4), p 322–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(01)00896-1
M.A. Shaik and B.R. Golla, Development of Highly Wear Resistant Cu-Al Alloys Processed via Powder Metallurgy, Tribol. Int., 2019, 136, p 127–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2019.03.055
Y.M. Li, Q.B. Yue, H.Y. Li and H.B. He, Friction and Wear Characteristics of 20Cr Steel Substrate and TiAlN Coating under Different Lubrication Conditions, Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., 2018, 19(10), p 1521–1528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-018-0179-8
P.C. Tsai, Y.R. Jeng, J.T. Lee, I. Stachiv and P. Sittner, Effects of Carbon Nanotube Reinforcement and Grain Size Refinement Mechanical Properties and Wear Behaviors of Carbon Nanotube/Copper Composites, Diam. Relat. Mater., 2017, 74, p 197–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2017.03.012
N.S. Shaari, J.M. Said, A. Jumahat and M.H. Ismail, Wear Behaviour of Copper/Carbon Nanotubes, Ind. Lubr. Tribol., 2017, 69(3), p 342–347. https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-09-2016-0198
J.L. Li, L.J. Wang, T. He and W. Jiang, Surface Graphitization and Mechanical Properties of Hot-Pressed Bulk Carbon Nanotubes Compacted by Spark Plasma Sintering, Carbon, 2007, 45(13), p 2636–2642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2007.08.023
A.K. Behera, R. Chandran, S. Das and A. Mallik, Wear Performance and Nanomechanical Behavior of Sonoelectroplated Cu-Graphene Nanocomposite Thin Films, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2021, 30(2), p 1398–1410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05355-y
V. Testa, S. Morelli, G. Bolelli, L. Lusvarghi, S. Björklund and S. Joshi, Micromechanical Behaviour and Wear Resistance of Hybrid Plasma-Sprayed TiC Reinforced Tribaloy-400, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2021, 425, p 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127682
F. Daneshvar, T. Zhang, A. Aziz, H.J. Sue and M.E. Welland, Tuning the Composition and Morphology of Carbon Nanotube-Copper Interface, Carbon, 2020, 157, p 583–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.10.084
X.F. Chen, J.M. Tao, J.H. Yi, C.J. Li, R. Bao, Y.C. Liu, X. You and S.L. Tan, Balancing the Strength and Ductility of Carbon Nanotubes Reinforced Copper Matrix Composites with Microlaminated Structure and Interdiffusion Interface, Mater. Sci. Eng. Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process., 2018, 712, p 790–793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.12.044
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2017YFB0306405), the State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks (Grant No. 2018GZKF03007), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51201107).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, S., Chen, X., Liu, P. et al. Tribological Properties and Electrical Conductivity of Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced Copper Matrix Composites. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 4955–4962 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-06596-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-06596-9