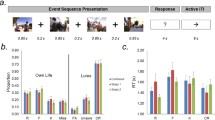
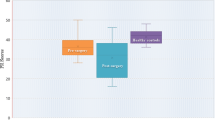
Abstract
The human hippocampus is believed to be a crucial node in the neural network supporting autobiographical memory retrieval. Structural mesial temporal damage associated with temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) provides an opportunity to systematically investigate and better understand the local and distal functional consequences of mesial temporal damage in the engagement of the autobiographical memory network. We examined 19 TLE patients (49.21 ± 11.55 years; 12 females) with unilateral mesial TLE (MTLE; 12 with anterior temporal lobe resection: 6 right MTLE, 6 left MTLE) or bilateral mesial TLE (7 BMTLE) and 18 matched healthy subjects. We used functional MRI (fMRI) with an adapted autobiographical memory paradigm and a specific neuropsychological test (Autobiographical Memory Interview, AMI). While engaged in the fMRI autobiographical memory paradigm, all groups activated a large fronto-temporo-parietal network. However, while this network was left lateralized for healthy participants and right MTLE patients, left MTLE and patients with BMTLE also showed strong activation in right temporal and frontal regions. Moreover, BMTLE and left MTLE patients also showed significant mild deficits in episodic autobiographical memory performance measured with the AMI test. The right temporal and extra-temporal fMRI activation, along with the impairment in autobiographical memory retrieval found in left MTLE and BMTLE patients suggest that alternate brain areas—other than the hippocampus—may also support this process, possibly due to neuroplastic effects.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addis, D. R., McIntosh, A. R., Moscovitch, M., Crawley, A. P., & McAndrews, M. P. (2004). Characterizing spatial and temporal features of autobiographical memory retrieval networks: A partial least squares approach. Neuroimage, 23(4), 1460–1471.
Addis, D. R., Moscovitch, M., & McAndrews, M. P. (2007). Consequences of hippocampal damage across the autobiographical memory network in left temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain, 130(Pt 9), 2327–2342.
Andreasen, N. C., O’Leary, D. S., Cizadlo, T., Arndt, S., Rezai, K., Watkins, G. L., et al. (1995). Remembering the past: Two facets of episodic memory explored with positron emission tomography. American Journal of Psychiatry, 152, 1576–1585.
Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. (2005). Unified segmentation. Neuroimage, 26, 839–851.
Bonelli, S. B., Powell, R. H., Yogaraiah, M., Samson, R. S., Symms, M. R., Thompson, P. J., Koepp, M. J., & Duncan, J. S. (2010). Imaging memory in temporal lobe epilepsy: Predicting the effects of temporal lobe resection. Brain, 133(Pt4), 1186–1199.
Cendes, F., Li, L. M., Watson, C., Andermann, F., Dubeau, F., & Arnold, D. L. (2000). Is ictal recording mandatory in temporal lobe epilepsy? Not when the interictal electroencephalogram and hippocampal atrophy coincide. Archives of Neurology, 57(4), 497–500.
Denkova. E., Botzung, A., Scheiber, C., Manning, L. (2006). Material-independent cerebral network of re-experiencing personal events: evidence from two parallel fMRI experiments. Neurosci Lett, 16,407(1),32–6.
Gilboa, A. (2004). Autobiographical and episodic memory—One and the same? Evidence from prefrontal activation in neuroimaging studies. Neuropsychologia, 42, 1336–1349.
Gilboa, A., Ramirez, J., Köhler, S., Westmacott, R., Black, S. E., & Moscovitch, M. (2005). Retrieval of autobiographical memory in Alzheimer’s disease: Relation to volumes of medial temporal lobe and other structures. Hippocampus, 15(4), 535–550.
Herfurth, K., Kapr, B., Schwarz, M., Stefan, H., & Pauli, E. (2010). Autobiographical memory in temporal lobe epilepsy: Role of hippocampal and temporal lateral structures. Epilepsy & Behavior, 19(3), 365–371.
Hermann, B. P., Wyler, A. R., Somes, G., Dohan, F. C., Jr., Berry, A. D., 3rd, & Clement, L. (1994). Declarative memory following anterior temporal lobectomy in humans. Behavioral Neuroscience, 108, 3–10.
Kaplan, E., Goodglass, H., & Weintraub, S. (1983). Boston naming test. Philadelphia. Lea & Febiger.
Kopelman, M. D., Wilson, B. A., & Baddeley, A. D. (1989). The autobiographical memory interview: A new assessment of autobiographical and personal semantic memory in amnesic patients. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 11, 724–744.
Lambon, R. M. A., Cipolotti, L., Manes, F., & Patterson, K. (2010). Taking both sides: Do unilateral anterior temporal lobe lesions disrupt semantic memory? Brain, 133(11), 3243–3255.
Lancaster, J. L., Woldorff, M. G., Parsons, L. M., Liotti, M., Freitas, C. S., Rainey, L., Kochunov, P. V., Nickerson, D., Mikiten, S. A., & Fox, P. T. (2000). Automated Talairach atlas labels for functional brain mapping. Human Brain Mapping, 10, 120–131.
Levine, B., Turner, G. R., Tisserand, D. J., Hevenor, S. J., Graham, S. J., & McIntosh, A. R. (2004). The functional neuroanatomy of episodic and semantic autobiographical remembering: A prospective functional fMRI study. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 16(9), 1633–1646.
Lieberman, M. D., & Cunningham, W. A. (2009). Type I and type II error concerns in fMRI research: Re-balancing the scale. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 4, 423–428.
Maguire, E. A. (2001). Neuroimaging studies of autobiographical event memory. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London B Biol Sci, 356, 1441–1451.
Maguire, E. A., & Frith, C. D. (2003). Lateral asymmetry in the hippocampal response to the remoteness of autobiographical memories. The Journal of Neuroscience, 23(12), 5302–5307.
Maguire, E. A., Vargha-Khadem, F., & Mishkin, M. (2001). The effects of bilateral hippocampal damage on fMRI regional activations and interactions during memory retrieval. Brain, 124(Pt 6), 1156–1170.
Markowitsch, H. J., Thiel, A., Reinkemeier, M., Kessler, J., Koyuncu, A., & Heiss, W. D. (2000). Right amygdalar and temporofrontal activation during autobiographic, but not during fictitious memory retrieval. Behavioural Neurology, 12(4), 181–190.
Markowitsch, H. J., Vandekerckhove, M. M. P., Lanfermann, H., & Russ, M. O. (2003). Engagement of lateral and medial prefrontal areas in the ecphory of sad and happy autobiographical memories. Cortex, 39, 1–23.
Mc Cormick, C., Moscovitch, M., Valiante, T. A., Cohn, M., & McAndrews, M. P. (2018). Different neural routes to autobiographical memory recall in healthy people and individuals with left medial temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurpsychologia, Epub.
Milner, B., & Klein, D. (2016). Loss of recent memory after bilateral hippocampal lesions: Memory and memories-looking back and looking forward. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 87(3), 230.
Moscovitch, M., & Nadel, L. (1998). Consolidation and the hippocampal complex revisited: In defense of the multiple-trace model. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 8(2), 297–300.
Neisser, U., Winograd, E., Bergman, E. T., Schreiber, C. A., Palmer, S. E., & Weldon, M. S. (1996). Remembering the earthquake: Direct experience vs hearing new. Memory, 4(4), 337–357.
Noulhiane, M., Piolino, P., Hasboun, D., Clemenceau, S., Baulac, M., & Samson, S. (2007). Autobiographical memory after temporal lobe resection: Neuropsychological and MRI volumetric findings. Brain, 120, 3184–3199.
Oldfield, R. C. (1971). The assessment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia, 9, 97–113.
Peña-Casanova, J. (2005). Integrated neuropsychological exploration program Barcelona test revised. Barcelona: Masson.
Piefke, M., Weiss, P. H., Zilles, K., Markowitsch, H. J., & Fink, G. R. (2003). Differential remoteness and emotional tone modulate the neural correlates of autobiographical memory. Brain, 126, 650–668.
Reitan, R. M. (1992). Trail making test: Manual for administration and scoring. Tucson: Reitan Neuropsychology Laboratory.
Renoult, L., Davidson, P. S., Palomobo, D. J., Moscovitch, M., & Levine, B. (2012). Personal semantics: At the crossroads of semantic and episodic memory. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 16(11), 550–558.
Ripollés, P., Marco-Pallares, J., de Diego-Balaguer, R., Miró, J., Falip, M., Juncadella, M., Rubio, F., & Rodríguez-Fornells, A. (2012). Analysis of automated methods for spatial normalization of lesioned brains. Neuroimage, 60, 1296–1306.
Rudie, J. D., Colby, J. B., & Salamon, N. (2015). Machine learning classification of mesial temporal sclerosis in epilepsy patients. Epilepsy Research, 117, 63–39.
Ryan, L., Nadel, L., Keil, K., Putnam, K., Schnyer, D., Trouard, T., & Moscovitch, M. (2001). The hippocampus complex and retrieval of recent and very remote AMs: Evidence from functional magnetic resonance imaging in neurologically intact people. Hippocampus, 11, 707–714.
Scoville, W. B., & Milner, B. (1957). Loss of recent memory after bilateral hippocampal lesions. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 20, 11–26.
So, N., Gloor, P., Quesney, L. F., Jones-Gotman, M., Olivier, A., & Andermann, F. (1989). Depth electrode investigations in patients with bitemporal epileptiform abnormalities. Annals of Neurology, 25(5), 423–431.
Spiers, H. J., Burgess, N., Maguire, E. A., Baxendale, S. A., Hartley, T., Thompson, P. J., & O’Keefe, J. (2001). Unilateral temporal lobectomy patients show lateralized topographical and episodic memory deficits in a virtual town. Brain, 124(Pt 12), 2476–2489.
Squire, L. R. (1992). Memory and the hippocampus: A synthesis from findings with rats, monkeys and humans. Psychological Review, 99, 195–231.
St. Jacques, P. L., & Levine, B. (2007). Ageing and autobiographical memory for emotional and neutral events. Memory, 15(2), 129–144.
Steinvorth, S., Levine, B., & Corkin, S. (2005). Medial temporal lobe structures are needed to reexperience remote autobiographical memories: Evidence from H.M and W.R. Neuropsychologia, 43(4), 479–496.
St-Laurent, M., Moscovitch, M., Levine, B., & McAndrews, M. P. (2009). Determinants of autobiographical memory narratives in patients with unilateral temporal lobe epilepsy or excisions. Neuropsychologia, 47, 2211–2221.
St-Laurent, M., Moscovitch, M., Tau, M., & McAndrews, M. P. (2011). The temporal unraveling of autobiographical memory narratives in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy or excisions. Hippocampus, 21(4), 409–421.
Svoboda, E., McKinnon, M. C., & Levine, B. (2006). The functional neuroanatomy of autobiographical memory: A meta-analysis. Neuropsychologia, 44(12), 2189–2208.
Tulving, E. (2002). Episodic memory: From mind to brain. Annual Review of Psychology, 53, 1–25.
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N., Mazoyer, B., & Joliot, M. (2002). Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage, 15, 273–289.
Vilà-Balló, A., Mas-Herrero, E., Ripollés, P., Simó, M., Miró, J., López-Barroso, D., Cucurell, D., Juncadella, M., Marco-Pallarés, J., Falip, M., & Rodríguez-Fornells, A. (2017). Unravelling the role of the hippocampus in reversal learning. The Journal of Neuroscience, 37(28), 6686–6697.
Viskontas, I. V., McAndrews, M. P., & Moscovitch, M. (2000). Remote episodic memory deficits in patients with unilateral temporal lobe epilepsy and excisions. The Journal of Neuroscience, 20, 5853–5857.
Wechsler, D. (1997). Wechsler adult intelligence scale third edition (WAIS-III): Administration and scoring manual. San Antonio. In TX. USA: The Psychological Corp.
Wechsler, D. (2004). WMS III. Escala de memoria de Wechsler-III. Madrid: TEA.
Wiebe, S., Blume, W. T., Girvin, J. P., & Eliasziw, M. (2001). Effectiveness and Efficienciy source of surgery for temporal lobe epilepsy study group. A randomized, controlled trial of surgery for temporal-lobe epilepsy. The New England Journal of Medicine, 345, 311–318.
Wieser, H. G. (2004). ILAE commission report. Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis. Epilepsia, 45, 695–714.
Acknowledgments
This project was partially supported by a grant from the Spanish Government (Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, PSI2011-29219), by Instituto de Salud Carlos III through the project PI16/00392 (Co-funded by European Regional Development Fund. ERDF, a way to build Europe), and by the FPU program awarded to PR (AP2010-4179) and JS (12/04117). Júlia Miró is the recipient of a research contract (code: JR14/0031) from the Carlos III National Health Institute (Spanish Government).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests relevant to the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miró, J., Ripollés, P., Sierpowska, J. et al. Autobiographical memory in epileptic patients after temporal lobe resection or bitemporal hippocampal sclerosis. Brain Imaging and Behavior 14, 1074–1088 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00113-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00113-8