Abstract
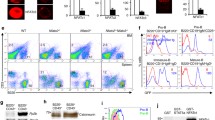
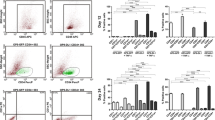
Zfyve16 (a.k.a. endofin or endosome-associated FYVE-domain protein), a member of the FYVE-domain protein family, is involved in endosomal trafficking and in TGF-β, BMP, and EGFR signaling. The FYVE protein SARA regulates the TGF-β signaling pathway by recruiting Smad2/3 and accelerating their phosphorylation, thereby altering their susceptibility to TGF-β-mediated T cell suppression. Zfyve16 binds to Smad4 and their binding affects the formation of Smad2/3-Smad4 complex in TGF-β signaling. However, the in vivo function of Zfyve16 remains unknown. In this study, we generated a Zfyve16 knockout mouse strain (Zfyve16KO) and examined its hematopoietic phenotypes and hematopoietic reconstruction ability. The proportion of Tcells in the peripheral blood of Zfyve16KO mice increases compared with that in wild-type mice. This finding is consistent with the role of Zfyve16 in facilitating TGF-β signaling. Unpredictably, B cell proliferation is inhibited in Zfyve16KO mice. The proliferation potential of Zfyve16KO B-lymphoid cells also significantly decreases in vitro. These results suggest that Zfyve16 inhibits the proliferation of T cells, possibly through the TGF-β signaling, but upregulates the proliferation of B-lymphoid cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seet LF, Hong W. Endofin, an endosomal FYVE domain protein. J Biol Chem 2001; 276(45): 42445–42454
Michel SL, Berg JM. Building a metal binding domain, one half at a time. Chem Biol 2002; 9(6): 667–668
Stenmark H, Aasland R, Toh BH, D’Arrigo A. Endosomal localization of the autoantigen EEA1 is mediated by a zinc-binding FYVE finger. J Biol Chem 1996; 271(39): 24048–24054
Stenmark H, Aasland R. FYVE-finger proteins—effectors of an inositol lipid. J Cell Sci 1999; 112(Pt 23): 4175–4183
Gillooly DJ, Simonsen A, Stenmark H. Cellular functions of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and FYVE domain proteins. Biochem J 2001; 355(2): 249–258
Chen YG, Wang Z, Ma J, Zhang L, Lu Z. Endofin, a FYVE domain protein, interacts with Smad4 and facilitates transforming growth factor-β signaling. J Biol Chem 2007; 282(13): 9688–9695
Dong M, Blobe GC. Role of transforming growth factor-β in hematologic malignancies. Blood 2006; 107(12): 4589–4596
Huang F, Chen YG. Regulation of TGF-b receptor activity. Cell Biosci 2012; 2(1): 9
Toy W, Lim SK, Loh MC, Lim YP. EGF-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of endofin is dependent on PI3K activity and proper localization to endosomes. Cell Signal 2010; 22(3): 437–446
Blobe GC, Schiemann WP, Lodish HF. Role of transforming growth factor β in human disease. N Engl J Med 2000; 342(18): 1350–1358
Khalil N. TGF-β: from latent to active. Microbes Infect 1999; 1(15): 1255–1263
Hμger M, Pedersen CC, Larsen MT, Andersen MK, Hother C, Grønbæk K, Jarmer H, Borregaard N, Cowland JB. MicroRNA- 130a-mediated down-regulation of Smad4 contributes to reduced sensitivity to TGF-β1 stimulation in granulocytic precursors. Blood 2011; 118(25): 6649–6659
Derynck R, Zhang YE. Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-β family signalling. Nature 2003; 425(6958): 577–584
Letterio JJ. TGF-β signaling in T cells: roles in lymphoid and epithelial neoplasia. Oncogene 2005; 24(37): 5701–5712
Zhang N, Bevan MJ. TGF-β signaling to T cells inhibits autoimmunity during lymphopenia-driven proliferation. Nat Immunol 2012; 13(7): 667–673
Cottrez F, Groux H. Regulation of TGF-β response during T cell activation is modulated by IL-10. J Immunol 2001; 167(2): 773–778
Letterio JJ, Geiser AG, Kulkarni AB, Dang H, Kong L, Nakabayashi T, Mackall CL, Gress RE, Roberts AB. Autoimmunity associated with TGF-β1-deficiency in mice is dependent on MHC class II antigen expression. J Clin Invest 1996; 98(9): 2109–2119
Wolfraim LA, Fernandez TM, Mamura M, Fuller WL, Kumar R, Cole DE, Byfield S, Felici A, Flanders KC, Walz TM, Roberts AB, Aplan PD, Balis FM, Letterio JJ. Loss of Smad3 in acute T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2004; 351(6): 552–559
Bakkebø M, Huse K, Hilden VI, Smeland EB, Oksvold MP. TGF-β-induced growth inhibition in B-cell lymphoma correlates with Smad1/5 signalling and constitutively active p38 MAPK. BMC Immunol 2010; 11(1): 57
Tsukazaki T, Chiang TA, Davison AF, Attisano L, Wrana JL. SARA, a FYVE domain protein that recruits Smad2 to the TGFβ receptor. Cell 1998; 95(6): 779–791
Itoh F, Divecha N, Brocks L, Oomen L, Janssen H, Calafat J, Itoh S, Dijke P. The FYVE domain in Smad anchor for receptor activation (SARA) is sufficient for localization of SARA in early endosomes and regulates TGF-β/Smad signalling. Genes Cells 2002; 7(3): 321–331
Seet LF, Hong W. Endofin recruits clathrin to early endosomes via TOM1. J Cell Sci 2005; 118(3): 575–587
Seet LF, Liu N, Hanson BJ, Hong W. Endofin recruits TOM1 to endosomes. J Biol Chem 2004; 279(6): 4670–4679
Goh JB, Wallace DF, Hong W, Subramaniam VN. Endofin, a novel BMP-SMAD regulator of the iron-regulatory hormone, hepcidin. Sci Rep 2015; 5(1): 13986
Shi W, Chang C, Nie S, Xie S, Wan M, Cao X. Endofin acts as a Smad anchor for receptor activation in BMP signaling. J Cell Sci 2007; 120(7): 1216–1224
Li MO, Wan YY, Flavell RA. T cell-produced transforming growth factor-β1 controls T cell tolerance and regulates Th1- and Th17-cell differentiation. Immunity 2007; 26(5): 579–591
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFC0902800), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81230055 and 81530006 to Ruibao Ren), and the Samuel Waxman Cancer Research Foudation Co-PI Program. We thank Huanbin Zhao, Min Wu, Chun Zhang, Mingzhu Liu, Zhangsen Huang, and Lingyun Tang for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Li, D., Qiu, Q. et al. Zfyve16 regulates the proliferation of B-lymphoid cells. Front. Med. 12, 559–565 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-017-0562-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-017-0562-3