Abstract
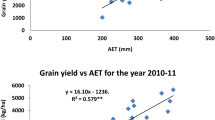
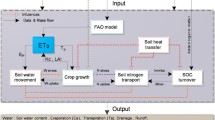
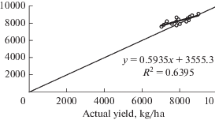
The test on the model with data collected from two years’ field experiments revealed an ability to satisfactorily simulate crop parameters such as LAI, biomass accumulation and partitioning, yield, and variables influencing crop growth and development as nitrogen uptake by crops and partitioning in different organs, and dynamics of soil water and nitrogen including infiltration and leaching. With the model, crop yield, water use efficiency (WUE), nitrogen use efficiency (NYE) and water-nitrogen leaching at specific soil layers under various water and nitrogen management practices were simulated to provide data used as references for designing sustainable nitrogen and water management practices.
The outputs of the simulated experiment with various treatments of irrigation and nitrogen application indicated that crop yield was closely related to water and nitrogen application, crop water use was positively related to irrigation amount, and nitrogen fertilization could improve the crop water use and WUE within certain limits. This is a valuable evidence to be considered in water-saving farming. Nitrogen uptake had a positive relation to nitrogen application, while irrigation to some extent improved its uptake by crops and hence increased NYE. Additionally, irrigation and fertilization had great effects on nitrogen leaching. Thus, in order to improve WUE and NYE, the model showed how nitrogen application and irrigation should be well coordinated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu C S (2005). Farmland ecosystem at the piedmont of Taihang. In: Sun H L, ed. Chinese Ecosystem. Beijing: Science Press, 1052–1085 (in Chinese)
Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences (1978). Physical and Chemical Analysis of Soil. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press (in Chinese)
Liang W L, Lü H Z, Xia A P (2006). A preliminary analysis on the yield gap of winter wheat between demonstration plots and farmers’ fields. Journal of Food, Agriculture & Environment, 4(3 & 4): 143–146
Liang W L, Lü H Z, Wang G Y, Connor D J, Rimmington G M (2007). A simulation model assisted study on water and nitrogen dynamics and their effects on crop performance in the wheat-maize system I: The Model. Front Agric China, 1(2):155–165
Liu X H (2005). Science of Farming System. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 247–255 (in Chinese)
Lü H Z (2001). Simulation of water and nitrogen behavior and their effects on yield and sustainability of wheat-maize double cropping system. Dissertation for the Master Degree. Baoding: Agricultural University of Hebei (in Chinese)
Sun Y H, Li R Q, Dang H K, Zhang X W, Li H L, Li Y M (2007). Population and individual characteristics of growth and development and yield components of super-high-yielding winter wheat in Hebei Province. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei, 30(3):1–8 (in Chinese)
Tong P Y, Cheng Y N (1997). Model of Maize Growth and Yield. Beijing: China Agricultural Technology Press (in Chinese)
Wang G Y (1999). Simulation of crop yield-water relationship of wheatmaize system. Dissertation for the Master Degree. Baoding: Agricultural University of Hebei (in Chinese)
Zhang F X, Zhou M Y, Xu H P, Guo K Q (2005). Effects of water and fertilizer coupling on growing and yield of winter wheat. Jorunal of Water Resources and Architectural Engingeering, 3(2):22–24 (in Chinese)
Zhao G C, Liu L H, Yang Y S, Zhang Y, Yang Z S (2002). Effect of fertilizer application on population quality, root system distribution, grain yield and quality in super-high-yielding wheat. Acta Agriculturae Boreall-sinica, 17(4):82–87 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Lü, H., Liang, W., Wang, G. et al. A simulation model assisted study on water and nitrogen dynamics and their effects on crop performance in the wheat-maize system: (II) model calibration, evaluation and simulated experimentation. Front. Agric. China 3, 109–121 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-009-0025-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-009-0025-y