Abstract
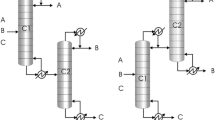
dividing wall column (DWC) is a thermally coupled distillation system with a high energy efficiency that requires lower space and investment compared to the conventional column system. The design of a DWC involves a number of structural and process parameters that need to be optimized simultaneously to improve energetic and economic potential and reduce space requirement. We used response surface methodology (RSM) to optimize DWC nonlinearly and to figure out the effect of parameters and their interactions on energy consumption, product quality, and dimensions of a DWC. Results demonstrate that process variables have significant effects on the energy efficiency of a DWC as compared to the effect of structural variables. The optimum DWC parameters can be found by RSM with minimal simulation runs and the prediction results of RSM agree well with the rigorous simulation results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Harmsen, Chem. Eng. Processing: Process Intensification, 49, 70 (2010).
R. Taylor, R. Krishna and H. Kooijman, Chem. Eng. Prog., 98, 28 (2003).
P. Proios, N. F. Goula and E. N. Pistikopoulos, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 44, 4656 (2005).
A. Harwardt, S. Kossack and W. Marquardt, Comput.-Aided Chem. Eng., 25, 91 (2008).
O. Yildirim, A. A. Kiss and E. Y. Kenig, Sep. Purif. Technol., 80, 403 (2011).
F. B. Petlyuk, Int. Chem. Eng., 5, 555 (1965).
Y. H. Kim, M. Nakaiwa and K. S. Hwang, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 19, 383 (2002).
Y. H. Kim, K. S. Hwang and M. Nakaiwa, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 21, 1098 (2004)
G. Kaibel, Chem. Ing. Tech., 59, 533 (1987).
M. A. Schultz, D. G. Stewart, J. M. Harris, J. M. S. P. Rosenblum, M. S. Shakur and D. E. O’Brien, Chem. Eng. Prog., 98, 64 (2002).
I. Dejanovi, Lj. Matijaševi and Ž. Oluji, Chem. Eng. Process., 49, 559 (2010).
B. G. Rong, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 89, 1281 (2011).
N. V. D. Long, S. H. Lee and M. Y. Lee, Chem. Eng. Process, 49, 825 (2010).
C. Triantafyllou and R. Smith, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 70, 118 (1992).
F. Z. Seihoub, H. Benyounes, W. Shen and V. Gerbaud, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 56, 9710 (2017).
C. E. Torres-Ortega and B. G. Rong, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 55, 7411 (2016).
G. Madenoor Ramapriya, M. Tawarmalani and R. Agrawal, AIChE J., 64, 649 (2018).
G. Madenoor Ramapriya, M. Tawarmalani and R. Agrawal, AIChE J., 64, 660 (2018).
W. L. Luyben, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 123, 152 (2017).
Y. H. Kim, Chem. Eng. Commun., 205, 134 (2018).
I. J. Halvorsen and S. Skogestad, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 42, 596 (2003).
Z. Fidkowski and L. Krolikowski, AIChE J., 32, 537 (1986).
N. A. Carlberg and A. W. Westerberg, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 28, 1379 (1989).
N. A. Carlberg and A. W. Westerberg, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 28, 1386 (1989).
N. Ramírez-Corona, A. Jiménez-Gutiérrez, A. Castro-Agüero and V. Rico-Ramírez, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 88, 1405 (2010).
S. H. Lee, M. Shamsuzzoha, M. Han, Y. H. Kim and M. Y. Lee, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 28, 348 (2011).
N. V. D. Long and M. Y. Lee, Asia Pac. J. Chem. Eng., 6, 338 (2011).
R. Premkumar and G. P. Rangaiah, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 87, 47 (2009).
Dejanovic, L. Matijasevic, H. Jansen and Z. Olujic, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 50, 5680 (2011).
G. P. Rangaiah, E. L. Ooi and R. Premkumar, Chem. Prod. Process Model., 4, 7 (2009).
J. G. S. Herna´ndez, S. Herna´ndez and A. Jime´nez, Inst. Chem. Eng., 80, 783 (2002).
M. Serra, A. Espun˜a and L. Puigjaner, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 42, 1773 (2003).
S. Herna´ ndez and J. S. Me´ndez, Chem. Eng. Commun., 192, 1085 (2005).
S. Wenzel and H. J. Röhm, Chem. Ing. Technol., 27, 484 (2004).
A. A. Kiss and J. P. S. David, Comput. Chem. Eng., 38, 74 (2012).
J. A. Caballero and I. E. Grossmann, Comput. Chem. Eng., 61, 118 (2014).
C. Guitérrez-Antonio and A. Briones-Ramírez, Comput. Chem. Eng., 33, 454 (2009).
N. V. D. Long and M. Lee, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 29, 567 (2012).
V. K. Sangal, V. Kumar and I. M. Mishra, Comput. Chem. Eng., 40, 33 (2012).
W. L. Luyben, Distillation design and control using Aspen simulation, Wiley, New York (2013).
T. D. Nguyen, Conceptual design, simulation and experimental validation of divided wall column: application for non-reactive and reactive mixture, PhD diss (2015).
D. C. Montgomery, Design and Analysis of Experiments, Wiley, New York (2001).
R. Myers, Response Surface Methodology. Boston: Allyn and Bacon, Inc. (1971).
R. L. Mason, R. F. Gunst and J. L. Hess, Statistical design and analysis of experiments: with applications to engineering and science, Wiley, New York (2003).
T. W. Anderson and D. A. Darling, Ann. Math. Statist., 23, 2 (1952)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lavasani, M.S., Rahimi, R. & Zivdar, M. Response surface methodology in optimization of a divided wall column. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 35, 1414–1422 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-018-0048-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-018-0048-2