Abstract
Objectives
This study aimed to determine the role of ONSD measurement by US for diagnosis of high ICP in TBI patients.
Methods
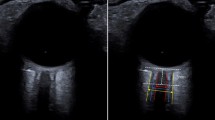
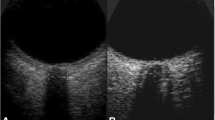
ONSD measurement by US was performed in adult TBI patients within 1 h of planned CT brain, while CT signs of high ICP were determined. Invasive ICP measurement was performed simultaneously in patients who had intraventricular device in situ. High ICP was determined as ICP > 22 mmHg.
Results
A total of 48 patients were enrolled. Twenty-eight patients had positive CT criteria for high ICP, while 20 patients were negative. The mean value of ONSD was 0.63 ± 0.06 cm in positive group compared with 0.55 ± 0.07 cm in negative one with significant difference (p < 0.001). A total of 22 patients had intraventricular device. Thirteen patients had high ICP, while 9 patients had normal ICP. The mean value of ONSD was 0.66 ± 0.05 cm in high ICP group compared with 0.58 ± 0.08 cm in normal one with significant difference (p = 0.004). ONSD with cut-off value > 0.61 cm predicted high ICP with sensitivity of 84.62% and specificity of 66.67% with significant AUC of 0.85 (p = 0.006).
Conclusion
ONSD measurement by ultrasound is a good screening tool for high ICP in traumatic brain injury patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dunn LT (2002) Raised intracranial pressure. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 73:23–27
Joseph B, Haider AA, Pandit V et al (2015) Changing paradigms in the management of 2184 patients with traumatic brain injury. Ann Surg 262:440–448
Mayhall CG, Archer NH, Lamb VA et al (1984) Ventriculostomy-related infections. N Engl J Med 310:553–559
Wang L, Feng L, Yao Y et al (2015) Optimal optic nerve sheath diameter threshold for the identification of elevated opening pressure on lumbar puncture in a Chinese population. PLoS One 10:1–10
Chen L, Wang L, Hu Y et al (2019) Ultrasonic measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter: a non-invasive surrogate approach for dynamic, real-time evaluation of intracranial pressure. Br J Ophthalmol 103(4):437–441
Golshani K (2015) Diagnostic accuracy of optic nerve ultrasonography and ophthalmoscopy in prediction of elevated intracranial pressure. Emergency 3(2):54
Carney N, Totten AM, O'Reilly C et al (2017) Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. Neurosurgery 80(1):6–15
Hansen HC, Helmke K (1996) The subarachnoid space surrounding the optic nerves. An ultrasound study of the optic nerve sheath. Surg Radiol Anat 18:323–328
Blaivas M, Theodoro D, Sierzenski PR (2003) Elevated intracranial pressure detected by bedside emergency ultrasonography of the optic nerve sheath. Acad Emerg Med 10:376–381
Geeraerts T, Launey Y, Martin L et al (2007) Ultrasonography of the optic nerve sheath may be useful for detecting raised intracranial pressure after severe brain injury. Intensive Care Med 33(10):1704–1711
Soldatos T, Karakitsos D, Chatzimichail K et al (2008) Optic nerve sonography in the diagnostic evaluation of adult brain injury. Crit Care 12(3):150–156
Kim SE, Hong EP, Kim HC et al (2019) Ultrasonographic optic nerve sheath diameter to detect increased intracranial pressure in adults: a meta-analysis. Acta Radiol 60(2):221–229
Robba C, Santori G, Czosnyka M et al (2018) Optic nerve sheath diameter measured sonographically as non-invasive estimator of intracranial pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med 44:1284–1294
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author Ashraf S Altayar declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Amr Z Abouelela declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Eslam E Abdelshafey declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Khaled SS Mohammed declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Ahmed A Hassan declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Mohammed A Khattab declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Walid Alhabashy declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Wael Gomaa declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Amr F Mohammed declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Muhammad S Umerani declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the local and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
After approval of local ethics and research committee, informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study or their families.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This study was done at King Fahd Military Medical Complex, Dahran, KSA
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altayar, A.S., Abouelela, A.Z., Abdelshafey, E.E. et al. Optic nerve sheath diameter by ultrasound is a good screening tool for high intracranial pressure in traumatic brain injury. Ir J Med Sci 190, 387–393 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-020-02242-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-020-02242-2