Abstract
Purpose of Review
The goal of this review is to provide an update on current thinking regarding herpes simplex encephalitis (HSE), emphasizing new information about pathogenesis, diagnosis, and immune responses. Specific questions to be addressed are the following: (1) Is there a genetic predisposition to HSE? (2) What clinical approaches have the greatest impact on improving the long-term outcomes in patients with HSE? And (3) are there immune-mediated mechanisms that may account for relapsing HSE?
Recent Findings
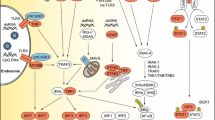
Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR 3) plays an important role in innate immune responses, including generation of interferons. Multiple single-gene errors in TLR 3 interferon pathways have recently been described in children that result in increased susceptibility to HSE. Conversely, studies in both animal models and humans indicate that both cytolytic viral replication and immune-mediated responses (including cytotoxic T lymphocytes and immune mechanisms mediated by TLR 2) contribute to the pathology of HSV, suggesting possible new therapeutic approaches. In terms of treatment, data clearly indicate that a longer duration between onset of symptoms and initiation of effective antiviral therapy correlates directly with less favorable clinical outcome. Recurrent or relapsing HSE may occasionally occur, but recent observations indicate that many instances of “relapsing HSE”, especially in children, are more often anti-N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) encephalitis triggered by the antecedent HSV infection.
Summary
Innate immune responses are critical for defense against HSV; genetic defects in this system may predispose patients to HSE. During acute HSE, exuberant immune responses may contribute to the CNS pathology, suggesting that selective immunosuppressive therapy, coupled with potent antiviral drugs, may eventually play a role in the therapeutic management of HSV. While overall clinical outcomes of HSE remain suboptimal, the initiation of high-dose acyclovir therapy as early as possible in the course of the illness provides the best chance for a patient to survive with minimal neurologic damage. Distinguishing relapsing HSE from autoimmune anti-NMDAR antibody encephalitis is critically important because therapeutic approaches will be very different.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Hjalmarsson A, Blomqvist P, Skoldenberg B. Herpes simplex encephalitis in Sweden, 1990–2001: incidence, morbidity, and mortality. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45:875–80.
Puchhammer-Stockl E, Presterl E, Croy C, et al. Screening for possible failure of herpes simplex virus PCR in cerebrospinal fluid for the diagnosis of herpes simplex encephalitis. J Med Virol. 2001;64:531–6.
Skoldenberg B, Forsgren M, Alestig K, et al. Acyclovir versus vidarabine in herpes simplex encephalitis. Randomised multicentre study in consecutive Swedish patients. Lancet. 1984;2:707–11.
Whitley RJ, Alford CA, Hirsch MS, et al. Vidarabine versus acyclovir therapy in herpes simplex encephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1986;314:144–9.
Kennedy PG, Steiner I. Recent issues in herpes simplex encephalitis. J Neurovirol. 2013;19:346–50.
Olson LC, Buescher EL, Artenstein MS, Parkman PD. Herpesvirus infections of the human central nervous system. N Engl J Med. 1967;277:1271–7.
Skoldenberg B. Herpes simplex encephalitis. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1991;80:40–6.
Skoldenberg B. Herpes simplex encephalitis. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1996;100:8–13.
Studahl M, Lindquist L, Eriksson BM, et al. Acute viral infections of the central nervous system in immunocompetent adults: diagnosis and management. Drugs. 2013;73:131–58.
Tyler KL. Update on herpes simplex encephalitis. Rev Neurol Dis. 2004;1:169–78.
Aurelius E, Johansson B, Skoldenberg B, Forsgren M. Encephalitis in immunocompetent patients due to herpes simplex virus type 1 or 2 as determined by type-specific polymerase chain reaction and antibody assays of cerebrospinal fluid. J Med Virol. 1993;39:179–86.
Mateen FJ, Miller SA, Aksamit Jr AJ. Herpes simplex virus 2 encephalitis in adults. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014;89:274–5.
Singh TD, Fugate JE, Hocker S, Wijdicks EF, Aksamit Jr AJ, Rabinstein AA. Predictors of outcome in HSV encephalitis. J Neurol. 2016;263:277–89.
George BP, Schneider EB, Venkatesan A. Encephalitis hospitalization rates and inpatient mortality in the United States, 2000–2010. PLoS One. 2014;9, e104169.
Whitley RJ, Soong SJ, Linneman Jr C, Liu C, Pazin G, Alford CA. Herpes simplex encephalitis. Clinical assessment. JAMA. 1982;247:317–20.
Dagsdottir HM, Sigurethardottir B, Gottfreethsson M, et al. Herpes simplex encephalitis in Iceland 1987–2011. SpringerPlus. 2014;3:524.
Riancho J, Delgado-Alvarado M, Sedano MJ, Polo JM, Berciano J. Herpes simplex encephalitis: clinical presentation, neurological sequelae and new prognostic factors. Ten years of experience. Neurol Sci. 2013;34:1879–81.
Riera-Mestre A, Gubieras L, Martinez-Yelamos S, Cabellos C, Fernandez-Viladrich P. Adult herpes simplex encephalitis: fifteen years’ experience. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2009;27:143–7.
Sili U, Kaya A, Mert A. Herpes simplex virus encephalitis: clinical manifestations, diagnosis and outcome in 106 adult patients. J Clin Virol. 2014;60:112–8.
Stahl JP, Mailles A, De Broucker T. Herpes simplex encephalitis and management of acyclovir in encephalitis patients in France. Epidemiol Infect. 2012;140:372–81.
Jennische E, Eriksson CE, Lange S, Trybala E, Bergstrom T. The anterior commissure is a pathway for contralateral spread of herpes simplex virus type 1 after olfactory tract infection. J Neurovirol. 2015;21:129–47.
Menasria R, Canivet C, Piret J, Boivin G. Infiltration pattern of blood monocytes into the central nervous system during experimental herpes simplex virus encephalitis. PLoS One. 2015;10, e0145773.
Whitley R, Lakeman AD, Nahmias A, Roizman B. Dna restriction-enzyme analysis of herpes simplex virus isolates obtained from patients with encephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1982;307:1060–2.
Baringer JR, Pisani P. Herpes simplex virus genomes in human nervous system tissue analyzed by polymerase chain reaction. Ann Neurol. 1994;36:823–9.
Taylor SW, Smith RM, Pari G, Wobeser W, Rossiter JP, Jackson AC. Herpes simplex encephalitis. Can J Neurol Sci. 2005;32:246–7.
Wang JP, Bowen GN, Zhou S, et al. Role of specific innate immune responses in herpes simplex virus infection of the central nervous system. J Virol. 2012;86:2273–81.
Aurelius E, Andersson B, Forsgren M, Skoldenberg B, Strannegard O. Cytokines and other markers of intrathecal immune response in patients with herpes simplex encephalitis. J Infect Dis. 1994;170:678–81.
Conrady CD, Drevets DA, Carr DJ. Herpes simplex type I (HSV-1) infection of the nervous system: is an immune response a good thing? J Neuroimmunol. 2010;220:1–9.
Piret J, Boivin G. Innate immune response during herpes simplex virus encephalitis and development of immunomodulatory strategies. Rev Med Virol. 2015;25:300–19.
Domingues RB, Tsanaclis AM, Pannuti CS, Mayo MS, Lakeman FD. Evaluation of the range of clinical presentations of herpes simplex encephalitis by using polymerase chain reaction assay of cerebrospinal fluid samples. Clin Infect Dis. 1997;25:86–91.
Fisher CM. Hypomanic symptoms caused by herpes simplex encephalitis. Neurology. 1996;47:1374–8.
Hart RP, Kwentus JA, Frazier RB, Hormel TL. Natural history of Kluver-Bucy syndrome after treated herpes encephalitis. South Med J. 1986;79:1376–8.
• Fine AJ, Sorbello A, Kortepeter C, Scarazzini L. Central nervous system herpes simplex and varicella zoster virus infections in natalizumab-treated patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57:849–52. Case series that emphasizes the potential for immunomodulatory drug therapies to increase the risk for HSE.
Kwiatkowski A, Gallois J, Bilbault N, Calais G, Mackowiak A, Hautecoeur P. Herpes encephalitis during natalizumab treatment in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2012;18:909–11.
Sharma K, Ballham SA, Inglis KE, Renowden S, Cottrell DA. Does natalizumab treatment increase the risk of herpes simplex encephalitis in multiple sclerosis? Case and discussion. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2013;2:385–7.
Bradford RD, Pettit AC, Wright PW, et al. Herpes simplex encephalitis during treatment with tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49:924–7.
Crusio RH, Singson SV, Haroun F, Mehta HH, Parenti DM. Herpes simplex virus encephalitis during treatment with etanercept. Scand J Infect Dis. 2014;46:152–4.
Schepers K, Hernandez A, Andrei G, et al. Acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex encephalitis in a patient treated with anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Virol. 2014;59:67–70.
Jakob NJ, Lenhard T, Schnitzler P, et al. Herpes simplex virus encephalitis despite normal cell count in the cerebrospinal fluid. Crit Care Med. 2012;40:1304–8.
Tan IL, McArthur JC, Venkatesan A, Nath A. Atypical manifestations and poor outcome of herpes simplex encephalitis in the immunocompromised. Neurology. 2012;79:2125–32.
Alonso-Vanegas MA, Quintero-Lopez E, Martinez-Albarran AA, Moreira-Holguin JC. Recurrent Herpes simplex virus encephalitis after neurologic surgery. World Neurosurg. 2016.
Berger A, Shahar T, Margalit N. Herpes simplex type 2 encephalitis after craniotomy: case report and literature review. World Neurosurg. 2015.
de Almeida SM, Crippa A, Cruz C, et al. Reactivation of herpes simplex virus-1 following epilepsy surgery. Epilepsy Behav Case Rep. 2015;4:76–8.
Kim SH, Lee SG, Kim SH, Kim DS, Kim HD. Relapsed herpes simplex virus encephalitis after epilepsy surgery. J Epilepsy Res. 2013;3:28–31.
Matikas A, Kontopodis E, Nintos G, et al. A case of herpes simplex-associated encephalitis after brain irradiation for lung cancer metastases. Anticancer Res. 2014;34:4411–4.
Saito M, Kiyozaki H, Obitsu T, et al. Herpes simplex virus-1 encephalitis induced by chemoradiotherapy and steroids in an esophageal cancer patient: a case report. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:233.
Berzero G, Di Stefano AL, Dehais C, et al. Herpes simplex encephalitis in glioma patients: a challenging diagnosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015;86:374–7.
Abel L, Plancoulaine S, Jouanguy E, et al. Age-dependent Mendelian predisposition to herpes simplex virus type 1 encephalitis in childhood. J Pediatr. 2010;157:623–9. 9.e1.
Andersen LL, Mork N, Reinert LS, et al. Functional IRF3 deficiency in a patient with herpes simplex encephalitis. J Exp Med. 2015;212:1371–9.
Guo Y, Audry M, Ciancanelli M, et al. Herpes simplex virus encephalitis in a patient with complete TLR3 deficiency: TLR3 is otherwise redundant in protective immunity. J Exp Med. 2011;208:2083–98.
Herman M, Ciancanelli M, Ou YH, et al. Heterozygous TBK1 mutations impair TLR3 immunity and underlie herpes simplex encephalitis of childhood. J Exp Med. 2012;209:1567–82.
Perez de Diego R, Mulvey C, Crawford M, et al. The proteome of Toll-like receptor 3-stimulated human immortalized fibroblasts: implications for susceptibility to herpes simplex virus encephalitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131:1157–66.
Sancho-Shimizu V, Perez de Diego R, Lorenzo L, et al. Herpes simplex encephalitis in children with autosomal recessive and dominant TRIF deficiency. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:4889–902.
Zhang SY, Abel L, Casanova JL. Mendelian predisposition to herpes simplex encephalitis. Handb Clin Neurol. 2013;112:1091–7.
•• Lim HK, Seppanen M, Hautala T, et al. TLR3 deficiency in herpes simplex encephalitis: high allelic heterogeneity and recurrence risk. Neurology. 2014;83:1888–97. Extends our understanding of genetic deficiencies in the TLR3 pathway that predispose children to the development of HSE.
Mork N, Kofod-Olsen E, Sorensen KB, et al. Mutations in the TLR3 signaling pathway and beyond in adult patients with herpes simplex encephalitis. Genes Immun. 2015;16:552–66.
Lopez Roa P, Alonso R, de Egea V, Usubillaga R, Munoz P, Bouza E. PCR for detection of herpes simplex virus in cerebrospinal fluid: alternative acceptance criteria for diagnostic workup. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51:2880–3.
Rawal G, Yadav S, Wani UR, Ambastha AK. HSV encephalitis with normal CSF—a case report with review of literature. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015;9:Od06–7.
Razavi B, Razavi M. Herpes simplex encephalitis—an atypical case. Infection. 2001;29:357–8.
Davis R, Jeffery K, Atkins BL. Hypoglycorrhachia in herpes simplex encephalitis. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:1506–7.
Aurelius E, Johansson B, Skoldenberg B, Staland A, Forsgren M. Rapid diagnosis of herpes simplex encephalitis by nested polymerase chain reaction assay of cerebrospinal fluid. Lancet. 1991;337:189–92.
Lakeman FD, Whitley RJ. Diagnosis of herpes simplex encephalitis: application of polymerase chain reaction to cerebrospinal fluid from brain-biopsied patients and correlation with disease. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Collaborative Antiviral Study Group. J Infect Dis. 1995;171:857–63.
Steiner I, Budka H, Chaudhuri A, et al. Viral meningoencephalitis: a review of diagnostic methods and guidelines for management. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17:999–e57.
Binnicker MJ, Espy MJ, Irish CL. Rapid and direct detection of herpes simplex virus in cerebrospinal fluid by use of a commercial real-time PCR assay. J Clin Microbiol. 2014;52:4361–2.
Adler AC, Kadimi S, Apaloo C, Marcu C. Herpes simplex encephalitis with two false-negative cerebrospinal fluid PCR tests and review of negative PCR results in the clinical setting. Case Rep Neurol. 2011;3:172–8.
Weil AA, Glaser CA, Amad Z, Forghani B. Patients with suspected herpes simplex encephalitis: rethinking an initial negative polymerase chain reaction result. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34:1154–7.
Wildemann B, Ehrhart K, Storch-Hagenlocher B, et al. Quantitation of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA in cells of cerebrospinal fluid of patients with herpes simplex virus encephalitis. Neurology. 1997;48:1341–6.
Schloss L, Falk KI, Skoog E, Brytting M, Linde A, Aurelius E. Monitoring of herpes simplex virus DNA types 1 and 2 viral load in cerebrospinal fluid by real-time PCR in patients with herpes simplex encephalitis. J Med Virol. 2009;81:1432–7.
Bhullar SS, Chandak NH, Baheti NN, et al. Diagnosis of herpes simplex encephalitis by ELISA using antipeptide antibodies against type-common epitopes of glycoprotein B of herpes simplex viruses. J Immunoass Immunochem. 2016;37:217–27.
Denes E, Labach C, Durox H, et al. Intrathecal synthesis of specific antibodies as a marker of herpes simplex encephalitis in patients with negative PCR. Swiss Med Wkly. 2010;140:w13107.
Domingues RB, Lakeman FD, Mayo MS, Whitley RJ. Application of competitive PCR to cerebrospinal fluid samples from patients with herpes simplex encephalitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36:2229–34.
Hjalmarsson A, Granath F, Forsgren M, Brytting M, Blomqvist P, Skoldenberg B. Prognostic value of intrathecal antibody production and DNA viral load in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with herpes simplex encephalitis. J Neurol. 2009;256:1243–51.
Poissy J, Champenois K, Dewilde A, et al. Impact of herpes simplex virus load and red blood cells in cerebrospinal fluid upon herpes simplex meningo-encephalitis outcome. BMC Infect Dis. 2012;12:356.
Revello MG, Baldanti F, Sarasini A, Zella D, Zavattoni M, Gerna G. Quantitation of herpes simplex virus DNA in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with herpes simplex encephalitis by the polymerase chain reaction. Clin Diagn Virol. 1997;7:183–91.
Bhullar SS, Chandak NH, Purohit HJ, Taori GM, Daginawala HF, Kashyap RS. Determination of viral load by quantitative real-time PCR in herpes simplex encephalitis patients. Intervirology. 2014;57:1–7.
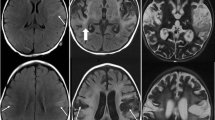
McCabe K, Tyler K, Tanabe J. Diffusion-weighted MRI abnormalities as a clue to the diagnosis of herpes simplex encephalitis. Neurology. 2003;61:1015–6.
Mekan SF, Wasay M, Khelaeni B, Saeed Z, Hassan A, Sheerani M. Herpes simplex encephalitis: analysis of 68 cases from a tertiary care hospital in Karachi, Pakistan. JPMA J Pak Med Assoc. 2005;55:146–8.
Aksamit AJ. Herpes simplex encephalitis in adults and older children. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2005;7:145–50.
Renard D, Nerrant E, Lechiche C. DWI and FLAIR imaging in herpes simplex encephalitis: a comparative and topographical analysis. J Neurol. 2015;262:2101–5.
Baringer JR. Herpes simplex infections of the nervous system. Neurol Clin. 2008;26:657–74. viii.
Hatipoglu HG, Sakman B, Yuksel E. Magnetic resonance and diffusion-weighted imaging findings of herpes simplex encephalitis. Herpes. 2008;15:13–7.
To TM, Soldatos A, Sheriff H, et al. Insights into pediatric herpes simplex encephalitis from a cohort of 21 children from the California Encephalitis Project, 1998–2011. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014;33:1287–8.
Kataoka H, Inoue M, Shinkai T, Ueno S. Early dynamic SPECT imaging in acute viral encephalitis. J Neuroimaging. 2007;17:304–10.
Kim YS, Jung KH, Lee ST, et al. Prognostic value of initial standard EEG and MRI in patients with herpes simplex encephalitis. J Clin Neurol. 2016.
Townend BS, Hanson JA, Sturm JW, Whyte S. Stroke or encephalitis? Emerg Med Australas. 2005;17:401–4.
Studahl M, Bergstrom T, Hagberg L. Acute viral encephalitis in adults—a prospective study. Scand J Infect Dis. 1998;30:215–20.
Whitley RJ, Gnann JW. Viral encephalitis: familiar infections and emerging pathogens. Lancet. 2002;359:507–13.
• Chow FC, Glaser CA, Sheriff H, et al. Use of clinical and neuroimaging characteristics to distinguish temporal lobe herpes simplex encephalitis from its mimics. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;60:1377–83. Discussion of the differential diagnosis of HSE.
Jarrin I, Sellier P, Lopes A, et al. Etiologies and management of aseptic meningitis in patients admitted to an internal medicine department. Medicine. 2016;95, e2372.
Sellner J, Trinka E. Seizures and epilepsy in herpes simplex virus encephalitis: current concepts and future directions of pathogenesis and management. J Neurol. 2012;259:2019–30.
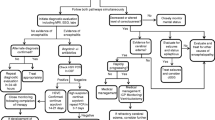
Tunkel AR, Glaser CA, Bloch KC, et al. The management of encephalitis: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47:303–27.
Hughes PS, Jackson AC. Delays in initiation of acyclovir therapy in herpes simplex encephalitis. Can J Neurol Sci. 2012;39:644–8.
Solomon T, Michael BD, Smith PE, et al. Management of suspected viral encephalitis in adults—Association of British Neurologists and British Infection Association National Guidelines. J Infect. 2012;64:347–73.
Jouan Y, Grammatico-Guillon L, Espitalier F, Cazals X, Francois P, Guillon A. Long-term outcome of severe herpes simplex encephalitis: a population-based observational study. Crit Care. 2015;19:345.
Maraite N, Mataigne F, Pieri V, Dang T, Diederich NJ. Early decompressive hemicraniectomy in fulminant herpes simplex encephalitis. Bull Soc Sci Med Grand Duche Luxemb. 2010:279–82.
Safain MG, Roguski M, Kryzanski JT, Weller SJ. A review of the combined medical and surgical management in patients with herpes simplex encephalitis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015;128:10–6.
Singhi P, Saini AG, Sahu JK, et al. Unusual clinical presentation and role of decompressive craniectomy in herpes simplex encephalitis. J Child Neurol. 2015;30:1204–7.
Kimberlin DW, Lakeman FD, Arvin AM, et al. Application of the polymerase chain reaction to the diagnosis and management of neonatal herpes simplex virus disease. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Collaborative Antiviral Study Group. J Infect Dis. 1996;174:1162–7.
Gnann Jr JW, Skoldenberg B, Hart J, et al. Herpes simplex encephalitis: lack of clinical benefit of long-term valacyclovir therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;61:683–91.
Pouplin T, Pouplin JN, Van Toi P, et al. Valacyclovir for herpes simplex encephalitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55:3624–6.
Schulte EC, Sauerbrei A, Hoffmann D, Zimmer C, Hemmer B, Muhlau M. Acyclovir resistance in herpes simplex encephalitis. Ann Neurol. 2010;67:830–3.
Stranska R, Schuurman R, Nienhuis E, et al. Survey of acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus in the Netherlands: prevalence and characterization. J Clin Virol. 2005;32:7–18.
Meyding-Lamade UK, Oberlinner C, Rau PR, et al. Experimental herpes simplex virus encephalitis: a combination therapy of acyclovir and glucocorticoids reduces long-term magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities. J Neurovirol. 2003;9:118–25.
Thompson KA, Blessing WW, Wesselingh SL. Herpes simplex replication and dissemination is not increased by corticosteroid treatment in a rat model of focal Herpes encephalitis. J Neurovirol. 2000;6:25–32.
Kamei S, Sekizawa T, Shiota H, et al. Evaluation of combination therapy using aciclovir and corticosteroid in adult patients with herpes simplex virus encephalitis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005;76:1544–9.
Lizarraga KJ, Alexandre LC, Ramos-Estebanez C, Merenda A. Are steroids a beneficial adjunctive therapy in the immunosuppressed patient with herpes simplex virus encephalitis? Case Rep Neurol. 2013;5:52–5.
Ramos-Estebanez C, Lizarraga KJ, Merenda A. A systematic review on the role of adjunctive corticosteroids in herpes simplex virus encephalitis: is timing critical for safety and efficacy? Antivir Ther. 2014;19:133–9.
Martinez-Torres F, Menon S, Pritsch M, et al. Protocol for German trial of Acyclovir and corticosteroids in Herpes-simplex-virus-encephalitis (GACHE): a multicenter, multinational, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled German, Austrian and Dutch trial [ISRCTN45122933]. BMC Neurol. 2008;8:40.
Prichard MN, Kern ER, Hartline CB, Lanier ER, Quenelle DC. CMX001 potentiates the efficacy of acyclovir in herpes simplex virus infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55:4728–34.
Boivin N, Menasria R, Piret J, Rivest S, Boivin G. The combination of valacyclovir with an anti-TNF alpha antibody increases survival rate compared to antiviral therapy alone in a murine model of herpes simplex virus encephalitis. Antivir Res. 2013.
Canivet C, Menasria R, Rheaume C, Piret J, Boivin G. Valacyclovir combined with artesunate or rapamycin improves the outcome of herpes simplex virus encephalitis in mice compared to antiviral therapy alone. Antivir Res. 2015;123:105–13.
Utley TF, Ogden JA, Gibb A, McGrath N, Anderson NE. The long-term neuropsychological outcome of herpes simplex encephalitis in a series of unselected survivors. Neuropsychiatry Neuropsychol Behav Neurol. 1997;10:180–9.
Whitley RJ, Lakeman F. Herpes simplex virus infections of the central nervous system: therapeutic and diagnostic considerations. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;20:414–20.
Erdem H, Cag Y, Ozturk-Engin D, et al. Results of a multinational study suggest the need for rapid diagnosis and early antiviral treatment at the onset of herpetic meningoencephalitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:3084–9.
Poissy J, Wolff M, Dewilde A, et al. Factors associated with delay to acyclovir administration in 184 patients with herpes simplex virus encephalitis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2009;15:560–4.
Raschilas F, Wolff M, Delatour F, et al. Outcome of and prognostic factors for herpes simplex encephalitis in adult patients: results of a multicenter study. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;35:254–60.
Bell DJ, Suckling R, Rothburn MM, et al. Management of suspected herpes simplex virus encephalitis in adults in a U.K. teaching hospital. Clin Med. 2009;9:231–5.
McGrath N, Anderson NE, Croxson MC, Powell KF. Herpes simplex encephalitis treated with acyclovir: diagnosis and long term outcome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997;63:321–6.
Benson PC, Swadron SP. Empiric acyclovir is infrequently initiated in the emergency department to patients ultimately diagnosed with encephalitis. Ann Emerg Med. 2006;47:100–5.
Whitley RJ, Soong SJ, Dolin R, Galasso GJ, Ch’ien LT, Alford CA. Adenine arabinoside therapy of biopsy-proved herpes simplex encephalitis. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases collaborative antiviral study. N Engl J Med. 1977;297:289–94.
Gordon B, Selnes OA, Hart Jr J, Hanley DF, Whitley RJ. Long-term cognitive sequelae of acyclovir-treated herpes simplex encephalitis. Arch Neurol. 1990;47:646–7.
Whitley RJ. Herpes simplex encephalitis: adolescents and adults. Antivir Res. 2006;71:141–8.
Grydeland H, Walhovd KB, Westlye LT, et al. Amnesia following herpes simplex encephalitis: diffusion-tensor imaging uncovers reduced integrity of normal-appearing white matter. Radiology. 2010;257:774–81.
Skelly MJ, Burger AA, Adekola O. Herpes simplex virus-1 encephalitis: a review of current disease management with three case reports. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2013;23:13–8.
Skoldenberg B, Aurelius E, Hjalmarsson A, et al. Incidence and pathogenesis of clinical relapse after herpes simplex encephalitis in adults. J Neurol. 2006;253:163–70.
VanLandingham KE, Marsteller HB, Ross GW, Hayden FG. Relapse of herpes simplex encephalitis after conventional acyclovir therapy. JAMA. 1988;259:1051–3.
Rigamonti A, Lauria G, Mantero V, Salmaggi A. A case of late herpes simplex encephalitis relapse. J Clin Virol. 2013;58:269–70.
Bamford A, Crowe BH, Hacohen Y, et al. Pediatric herpes simplex virus encephalitis complicated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antibody encephalitis. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2015;4:e17–21.
Desena A, Graves D, Warnack W, Greenberg BM. Herpes simplex encephalitis as a potential cause of anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antibody encephalitis: report of 2 cases. JAMA Neurol. 2014;71:344–6.
Hacohen Y, Deiva K, Pettingill P, et al. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antibodies in post-herpes simplex virus encephalitis neurological relapse. Mov Disord. 2014;29:90–6.
Morris NA, Kaplan TB, Linnoila J, Cho T. HSV encephalitis-induced anti-NMDAR encephalitis in a 67-year-old woman: report of a case and review of the literature. J Neurovirol. 2016;22:33–7.
Sutcu M, Akturk H, Somer A, et al. Role of autoantibodies to N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor in relapsing herpes simplex encephalitis: a retrospective, one-center experience. J Child Neurol. 2016;31:345–50.
Hoftberger R, Armangue T, Leypoldt F, Graus F, Dalmau J. Clinical neuropathology practice guide 4–2013: post-herpes simplex encephalitis: N-methyl-daspartate receptor antibodies are part of the problem. Clin Neuropathol. 2013;32:251–4.
Pruss H, Finke C, Holtje M, et al. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antibodies in herpes simplex encephalitis. Ann Neurol. 2012;72:902–11.
Westman G, Studahl M, Ahlm C, et al. N-Methyl-D-Aspartate receptor autoimmunity affects cognitive performance in herpes simplex encephalitis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016.
Armangue T, Leypoldt F, Malaga I, et al. Herpes simplex virus encephalitis is a trigger of brain autoimmunity. Ann Neurol. 2014;75:317–23.
Mohammad SS, Sinclair K, Pillai S, et al. Herpes simplex encephalitis relapse with chorea is associated with autoantibodies to N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor or dopamine-2 receptor. Mov Disord. 2014;29:117–22.
•• Armangue T, Moris G, Cantarin-Extremera V, et al. Autoimmune post-herpes simplex encephalitis of adults and teenagers. Neurology. 2015;85:1736–43. Describes NMDAR autoimmune encephalitis as a complication of HSE.
Granerod J, Ambrose HE, Davies NW, et al. Causes of encephalitis and differences in their clinical presentations in England: a multicentre, population-based prospective study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2010;10:835–44.
Kennedy PG, Adams JH, Graham DI, Clements GB. A clinico-pathological study of herpes simplex encephalitis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1988;14:395–415.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Dr. Gnann declares serving as a DSMB member with GlaxoSmithKline & BioCryst and clinical adjudication member with Merck.
Dr. Whitley declares grants from NIH and serving as a board member of Gilead Sciences..
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the author.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Central Nervous System Infections
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gnann, J.W., Whitley, R.J. Herpes Simplex Encephalitis: an Update. Curr Infect Dis Rep 19, 13 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11908-017-0568-7
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11908-017-0568-7