Abstract
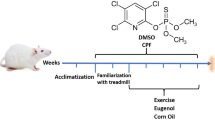
The purpose of this study is to examine the effect of the caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) fortification applied to the rats, which were made to exercise, on the liver elements. The study was conducted on 32 Sprague-Dawley male rats. The experimental animals were divided into 4 groups in equal numbers. Group 1 is the group which was applied 10 μmol/kg/day CAPE as intraperitoneal (IP) for 4 weeks, and they were not made to exercise at the end of the application. Group 2 is the group which was applied 10 μmol/kg/day CAPE as IP for 4 weeks, and they were made to exercise at the end of the 4th week. Group 3 is the general control group. Group 4 is the swimming control group. A 10 mmol/kg CAPE application dissolved in ethyl alcohol of 10 % was applied to the CAPE group. Sodium (Na), zinc (Zn), calcium (Ca), iron (Fe), chrome (Cr), magnesium (Mg), potassium (K), copper (Cu) and cadmium (Cd) levels were identified in the liver samples at the end of the application. The results of the study suggest that exercise and CAPE fortification in rats cause changes in the Na, Zn, Ca, Fe and Cr parameters in liver tissues, and it does not affect Cd, Cu, Mg and K element distribution. It is thought that CAPE fortification would be helpful for preserving those parameters whose levels are known to be changing with exercise.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borrelli F, Maffia P, Pinto L, Ianaro A, Russo A, Capasso F, Ialenti A (2002) Phytochemical compounds involved in the anti-inflammatory effect of propolis extract. Fitoterapia 73:53–63
Castaldo S, Capasso F (2002) Propolis, an old remedy used in modern medicine. Fitoterapia 73:1–6
Sud’ina GF, Mirzoeva OK, Pushkareva MA, Korshunova GA, Sumbatyan NV, Varfolomeev SD (1993) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester as a lipoxygenase inhibitor with antioxidant properties. FEBS Lett 329:21–24
Koksel O, Ozdulger A, Tamer L, Cinel L, Ercil M, Degirmenci U, Unlu S, Kanik A (2006) Effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in rats. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 19:90–95
Speich M, Pineau A, Ballereau F (2001) Minerals, trace elements and related biological variables in athletes and during physical activity. Clin Chim Acta 312:1–11
Tellford RD, Catchpole EA, Deakin V, Hahn AG, Plank AW (1992) The effect of 7 to 8 months of vitamin/mineral supplementation on athletic performance. Int Sports Nutr 2:135–153
Cordova A, Alvarez-Mon M (1996) Serum magnesium and immune parameters after maximal exercise in sportsmen. Magnes Bull 18:66–70
Mumtaz M, Sıddıque A, Mukhtar N, Mehboob T (1999) Status of trace elements level in blood samples of different age population of Karachi. Turk J Med Sci 29:697–700
Maughan R, Shirreffs SM, Bater Jones ADG (2000) Nutrition and the young athlete. Med Spotiva Pol 4:51–58
Sivrikaya A, Akil M, Bicer M, Kilic M, Baltaci AK, Mogulkoc R (2013) The effect of selenium supplementation on elements distribution in liver of rats subject to strenuous swimming. Bratisl Lek Listy 114(1):12–14
Kara E, Akil M, Yalçinkaya O (2012) The effect of aerobic exercise programme on trace element levels of young men. Afr J Microbiol Res 6(1):165–168
Jin LG, Chu JJ, Pang QF, Zhang FZ, Wu G, Zhou LY, Zhang XJ, Xing CG (2015) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester attenuates ionize radiation-induced intestinal injury through modulation of oxidative stress, apoptosis and p38MAPK in rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40(1):156–163
Dawson CA, Horvarth SM (1970) Swimming in small laboratory animals. Med Sci Sports 2:51–78
Sivrikaya A, Bicer M, Akil M, Baltaci AK, Mogulkoc R (2012) Effects of zinc supplementation on the element distribution in kidney tissue of diabetic rats subjected to acute swimming. Biol Trace Elem Res 147:195–199
Bicer M, Akil M, Baltaci AK, Mogulkoc R, Sivrikaya A, Akkus H (2015) Effect of melatonin on element distribution in the liver tissue of diabetic rats subjected to forced exercise. Bratisl Lek Listy 116(2):119–123
Sivrikaya A, Akil M, Bicer M, Kilic M, Baltaci AK, Mogulkoc R. (2013) The effect of selenium supplementation on elements distribution in liver of rats subject to strenuous swimming. Bratisl Lek Listy. 114(1):12–14
Patlar S, Boyali E, Baltaci AK, Mogulkoc R, Gunay M (2011) Elements in sera of elite taekwondo athletes: effects of vitamin E supplementation. Biol Trace Elem Res 139(2):119–25
Patlar S, Boyali E, Baltaci AK, Mogulkoc R (2011) The effect of vitamin A supplementation on various elements in elite taekwondo players. Biol Trace Elem Res 139(3):296–300
Barry DW, Kohrt WM (2007) Acute effects of 2 hours of moderate-intensity cycling on serum parathyroid hormone and calcium. Calcif Tissue Int 80:359–65
Henderson SA, Graham HK, Mollan RAB, Riddoch C, Sheridan B, Johnston H (1989) Calcium Homeostasis and Exercise. International Orthopaedics 13:69–73
Schwartz K, Mertz W (1959) Chromium (III) and the Glucose Tolerance Factor. Arch Bichem Biophys 85:292–5
Bicer M, Akil M, Sivrikaya A, Kara E, Baltaci AK, Mogulkoc R (2011) Effect of zinc supplementation on the distribution of various elements in the serum of diabetic rats subjected to an acute swimming exercise. J Physiol Biochem 67(4):511–7
Baltaci AK, Gokbel H, Mogulkoc R, Okudan N, Ucok K, Halifeoglu I (2010) The effects of exercise and zinc deficiency on some elements in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 134(1):79–83
Baltaci AK, Uzun A, Kilic M, Mogulkoc R (2009) Effects of acute swimming exercise on some elements in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 127(2):148–53
Tomur A, Kanter M, Gurel A, Erboga M (2011) The efficiency of CAPE on retardation of hepatic fibrosis in biliary obstructed rats. J Mol Hist 42:451–458
Gergerlioglu HS, Gokbel H, Okudan N, Gergerlioglu N, Demir EA (2015) Quercetin and caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) attenuate acute exercise-induced oxidative stress. Prog Nutr 17(1):41–49
Erboga M, Kanter M, Aktas C, Bozdemir Donmez Y, Fidanol Erboga Z, Aktas E, Gurel A (2015) Anti-apoptotic and anti-oxidant effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on cadmium-induced testicular toxicity in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res. doi:10.1007/s12011-015-0509-y
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by a grant from the Usak University Scientific Research Council, Usak, Turkey (Project no: 2012/MF007).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akil, M., Coban, F.K. & Yalcinkaya, O. The Effect of Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester (CAPE) Fortification on the Liver Element Distribution that Occurs After Exercise. Biol Trace Elem Res 172, 419–423 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0608-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0608-9