Abstract
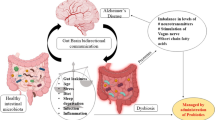
Neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, are major age-related concerns in elderly people. Since no drug fully addresses the progression of neurodegenerative diseases, advance treatment strategies are urgently needed. Several studies have noted the senescence of immune system and the perturbation of gut microbiota in the aged population. In recent years, the role of gut microbiota has been increasingly studied in the manifestation of age-related CNS disorders. In this context, prebiotics, probiotics, and paraprobiotics are reported to improve the behavioural and neurobiological abnormalities in elderly patients. As live microbiota, prescribed in the form of probiotics, shows some adverse effects like sepsis, translocation, and horizontal gene transfer, paraprobiotics could be a possible alternative strategy in designing microbiome-based therapeutics. This review describes the health-beneficial effects of paraprobiotics in age-associated neurodegenerative diseases.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi, S., Wang, S., Nagpal, R., Wang, B., Jain, S., Razazan, A., Mishra, S. P., Zhu, X., Wang, Z., & Kavanagh, K. (2020). A human-origin probiotic cocktail ameliorates aging-related leaky gut and inflammation via modulating the microbiota/taurine/tight junction axis. JCI Insight. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.132055
Akiyama, H., Barger, S., Barnum, S., Bradt, B., Bauer, J., Cole, G. M., Cooper, N. R., Eikelenboom, P., Emmerling, M., & Fiebich, B. L. (2000). Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 21(3), 383–421.
Ananta, E., Volkert, M., & Knorr, D. (2005). Cellular injuries and storage stability of spray-dried Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. International Dairy Journal, 15(4), 399–409.
Arai, S., Iwabuchi, N., Takahashi, S., Xiao, J., Abe, F., & Hachimura, S. (2018). Orally administered heat-killed Lactobacillus paracasei MCC1849 enhances antigen-specific IgA secretion and induces follicular helper T cells in mice. PLoS ONE, 13(6), e0199018.
Arentsen, T., Qian, Y., Gkotzis, S., Femenia, T., Wang, T., Udekwu, K., Forssberg, H., & Diaz Heijtz, R. (2017). The bacterial peptidoglycan-sensing molecule Pglyrp2 modulates brain development and behavior. Molecular Psychiatry, 22(2), 257–266.
Asama, T., Kimura, Y., Kono, T., Tatefuji, T., Hashimoto, K., & Benno, Y. (2016). Effects of heat-killed Lactobacillus kunkeei YB38 on human intestinal environment and bowel movement: A pilot study. Beneficial Microbes, 7(3), 337–344.
Banati, R. B., Daniel, S. E., & Blunt, S. B. (1998). Glial pathology but absence of apoptotic nigral neurons in long-standing Parkinson’s disease. Movement Disorders: Official Journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 13(2), 221–227.
Biagi, E., Nylund, L., Candela, M., Ostan, R., Bucci, L., Pini, E., Nikkïla, J., Monti, D., Satokari, R., & Franceschi, C. (2010). Through ageing, and beyond: Gut microbiota and inflammatory status in seniors and centenarians. PLoS ONE, 5(5), e10667.
Bleau, C., Monges, A., Rashidan, K., Laverdure, J., Lacroix, M., Van Calsteren, M., Millette, M., Savard, R., & Lamontagne, L. (2010). Intermediate chains of exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus rhamnosus RW-9595M increase IL-10 production by macrophages. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 108(2), 666–675.
Bloem, B. R., Okun, M. S., & Klein, C. (2021). Parkinson’s disease. The Lancet, 397(10291), 2284–2303. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00218-X
Boulangé, C. L., Neves, A. L., Chilloux, J., Nicholson, J. K., & Dumas, M.-E. (2016). Impact of the gut microbiota on inflammation, obesity, and metabolic disease. Genome Medicine, 8(1), 1–12.
Bruunsgaard, H., Andersen-Ranberg, K., Jeune, B., Pedersen, A. N., Skinhøj, P., & Pedersen, B. K. (1999). A high plasma concentration of TNF-α is associated with dementia in centenarians. Journals of Gerontology Series a: Biomedical Sciences and Medical Sciences, 54(7), M357–M364.
Brüünsgaard, H., & Pedersen, B. K. (2003). Age-related inflammatory cytokines and disease. Immunology and Allergy Clinics, 23(1), 15–39.
Buford, T. W. (2017). (Dis) Trust your gut: The gut microbiome in age-related inflammation, health, and disease. Microbiome, 5(1), 1–11.
Cai, Z., Yan, L.-J., & Ratka, A. (2013). Telomere shortening and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuromolecular Medicine, 15(1), 25–48.
Canani, R. B., Di Costanzo, M., Leone, L., Pedata, M., Meli, R., & Calignano, A. (2011). Potential beneficial effects of butyrate in intestinal and extraintestinal diseases. World Journal of Gastroenterology: WJG, 17(12), 1519.
Carding, S., Verbeke, K., Vipond, D. T., Corfe, B. M., & Owen, L. J. (2015). Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota in disease. Microbial Ecology in Health and Disease, 26(1), 26191.
Cattaneo, A., Cattane, N., Galluzzi, S., Provasi, S., Lopizzo, N., Festari, C., Ferrari, C., Guerra, U. P., Paghera, B., & Muscio, C. (2017). Association of brain amyloidosis with pro-inflammatory gut bacterial taxa and peripheral inflammation markers in cognitively impaired elderly. Neurobiology of Aging, 49, 60–68.
Cecchini, D. A., Laville, E., Laguerre, S., Robe, P., Leclerc, M., Dore, J., Henrissat, B., Remaud-Siméon, M., Monsan, P., & Potocki-Véronèse, G. (2013). Functional metagenomics reveals novel pathways of prebiotic breakdown by human gut bacteria. PLoS ONE, 8(9), e72766.
Cenit, M. C., Sanz, Y., & Codoñer-Franch, P. (2017). Influence of gut microbiota on neuropsychiatric disorders. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 23(30), 5486.
Chen, R., Xu, Y., Wu, P., Zhou, H., Lasanajak, Y., Fang, Y., Tang, L., Ye, L., Li, X., & Cai, Z. (2019). Transplantation of fecal microbiota rich in short chain fatty acids and butyric acid treat cerebral ischemic stroke by regulating gut microbiota. Pharmacological Research, 148, 104403.
Choi, J. J., Choi, Y. J., Chen, L., Zhang, B., Eum, S. Y., Abreu, M. T., & Toborek, M. (2012). Lipopolysaccharide potentiates polychlorinated biphenyl-induced disruption of the blood–brain barrier via TLR4/IRF-3 signaling. Toxicology, 302(2–3), 212–220.
Chuang, L., Wu, K.-G., Pai, C., Hsieh, P.-S., Tsai, J.-J., Yen, J.-H., & Lin, M.-Y. (2007). Heat-killed cells of lactobacilli skew the immune response toward T helper 1 polarization in mouse splenocytes and dendritic cell-treated T cells. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55(26), 11080–11086.
Chudzik, A., Orzyłowska, A., Rola, R., & Stanisz, G. J. (2021). Probiotics, prebiotics and postbiotics on mitigation of depression symptoms: Modulation of the brain–gut–microbiome axis. Biomolecules, 11(7), 1000.
Cirstea, M. S., Yu, A. C., Golz, E., Sundvick, K., Kliger, D., Radisavljevic, N., Foulger, L. H., Mackenzie, M., Huan, T., & Finlay, B. B. (2020). Microbiota composition and metabolism are associated with gut function in Parkinson’s disease. Movement Disorders, 35(7), 1208–1217.
Ciszek-Lenda, M., Nowak, B., Śróttek, M., Gamian, A., & Marcinkiewicz, J. (2011). Immunoregulatory potential of exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus rhamnosus KL37: Effects on the production of inflammatory mediators by mouse macrophages. International Journal of Experimental Pathology, 92(6), 382–391.
Claesson, M. J., Cusack, S., O’Sullivan, O., Greene-Diniz, R., de Weerd, H., Flannery, E., Marchesi, J. R., Falush, D., Dinan, T., & Fitzgerald, G. (2011). Composition, variability, and temporal stability of the intestinal microbiota of the elderly. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(Suppl 1), 4586–4591.
Claesson, M. J., Jeffery, I. B., Conde, S., Power, S. E., O’connor, E. M., Cusack, S., Harris, H. M. B., Coakley, M., Lakshminarayanan, B., & O’Sullivan, O. (2012). Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly. Nature, 488(7410), 178–184.
Clark, R. I., Salazar, A., Yamada, R., Fitz-Gibbon, S., Morselli, M., Alcaraz, J., Rana, A., Rera, M., Pellegrini, M., & William, W. J. (2015). Distinct shifts in microbiota composition during Drosophila aging impair intestinal function and drive mortality. Cell Reports, 12(10), 1656–1667.
Costantini, A., Viola, N., Berretta, A., Galeazzi, R., Matacchione, G., Sabbatinelli, J., Storci, G., De Matteis, S., Butini, L., & Rippo, M. R. (2018). Age-related M1/M2 phenotype changes in circulating monocytes from healthy/unhealthy individuals. Aging (albany NY), 10(6), 1268.
Cross, M. L., Ganner, A., Teilab, D., & Fray, L. M. (2004). Patterns of cytokine induction by gram-positive and gram-negative probiotic bacteria. FEMS Immunology & Medical Microbiology, 42(2), 173–180.
Davani-Davari, D., Negahdaripour, M., Karimzadeh, I., Seifan, M., Mohkam, M., Masoumi, S. J., Berenjian, A., & Ghasemi, Y. (2019). Prebiotics: Definition, types, sources, mechanisms, and clinical applications. Foods, 8(3), 92.
de Almada, C. N., Almada, C. N., Martinez, R. C. R., & Sant’Ana, A. S. (2016). Paraprobiotics: Evidences on their ability to modify biological responses, inactivation methods and perspectives on their application in foods. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 58, 96–114.
Du, D., Tang, W., Zhou, C., Sun, X., Wei, Z., Zhong, J., & Huang, Z. (2021). Fecal microbiota transplantation is a promising method to restore gut microbiota dysbiosis and relieve neurological deficits after traumatic brain injury. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2021, 1–21.
Fagiolo, U., Cossarizza, A., Scala, E., Fanales-Belasio, E., Ortolani, C., Cozzi, E., Monti, D., Franceschi, C., & Paganelli, R. (1993). Increased cytokine production in mononuclear cells of healthy elderly people. European Journal of Immunology, 23(9), 2375–2378.
FAO/WHO. (2002). FAO/WHO, Guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in Food, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and World Health Organization Group Report, London Ontario, Canada. FAO.
Fernandez, E. M., Valenti, V., Rockel, C., Hermann, C., Pot, B., Boneca, I. G., & Grangette, C. (2011). Anti-inflammatory capacity of selected lactobacilli in experimental colitis is driven by NOD2-mediated recognition of a specific peptidoglycan-derived muropeptide. Gut, 60(8), 1050–1059.
Ferrón, S. R., Marqués-Torrejón, M. Á., Mira, H., Flores, I., Taylor, K., Blasco, M. A., & Farinas, I. (2009). Telomere shortening in neural stem cells disrupts neuronal differentiation and neuritogenesis. Journal of Neuroscience, 29(46), 14394–14407.
Finger, C. E., Moreno-Gonzalez, I., Gutierrez, A., Moruno-Manchon, J. F., & McCullough, L. D. (2022). Age-related immune alterations and cerebrovascular inflammation. Molecular Psychiatry, 27(2), 803–818.
Foster, J. A., & Neufeld, K.-A.M. (2013). Gut–brain axis: How the microbiome influences anxiety and depression. Trends in Neurosciences, 36(5), 305–312.
Franceschi, C., & Campisi, J. (2014). Chronic inflammation (inflammaging) and its potential contribution to age-associated diseases. Journals of Gerontology Series a: Biomedical Sciences and Medical Sciences, 69(Suppl 1), S4–S9.
Fransen, F., van Beek, A. A., Borghuis, T., Aidy, S. E., Hugenholtz, F., & van der Gaast–de Jongh, C., Savelkoul, H. F. J., De Jonge, M. I., Boekschoten, M. V, & Smidt, H. (2017). Aged gut microbiota contributes to systemical inflammaging after transfer to germ-free mice. Frontiers in Immunology, 8, 1385.
Fulop, T., Witkowski, J. M., Olivieri, F., & Larbi, A. (2018). The integration of inflammaging in age-related diseases. Seminars in Immunology, 40, 17–35.
Giau, V. V., Wu, S. Y., Jamerlan, A., An, S. S. A., Kim, S., & Hulme, J. (2018). Gut microbiota and their neuroinflammatory implications in Alzheimer’s disease. Nutrients, 10(11), 1765.
Giunta, B., Fernandez, F., Nikolic, W. V., Obregon, D., Rrapo, E., Town, T., & Tan, J. (2008). Inflammaging as a prodrome to Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 5(1), 1–15.
Grochowska, M., Laskus, T., & Radkowski, M. (2019). Gut microbiota in neurological disorders. Archivum Immunologiae Et Therapiae Experimentalis, 67, 1–9.
Guo, S., Nighot, M., Al-Sadi, R., Alhmoud, T., Nighot, P., & Ma, T. Y. (2015). Lipopolysaccharide regulation of intestinal tight junction permeability is mediated by TLR4 signal transduction pathway activation of FAK and MyD88. The Journal of Immunology, 195(10), 4999–5010.
Hakansson, A., & Molin, G. (2011). Gut microbiota and inflammation. Nutrients, 3(6), 637–682.
Haran, J. P., Bhattarai, S. K., Foley, S. E., Dutta, P., Ward, D. V., Bucci, V., & McCormick, B. A. (2019). Alzheimer’s disease microbiome is associated with dysregulation of the anti-inflammatory P-glycoprotein pathway. Mbio, 10(3), e00632-e719.
He, F., Ouwehand, A. C., Isolauri, E., Hosoda, M., Benno, Y., & Salminen, S. (2001). Differences in composition and mucosal adhesion of bifidobacteria isolated from healthy adults and healthy seniors. Current Microbiology, 43(5), 351–354.
Heiss, C. N., & Olofsson, L. E. (2018). Gut microbiota-dependent modulation of energy metabolism. Journal of Innate Immunity, 10(3), 163–171.
Hill, C., Guarner, F., Reid, G., Gibson, G. R., Merenstein, D. J., Pot, B., Morelli, L., Canani, R. B., Flint, H. J., & Salminen, S. (2014). Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 11(8), 506–514.
Hill-Burns, E. M., Debelius, J. W., Morton, J. T., Wissemann, W. T., Lewis, M. R., Wallen, Z. D., Peddada, S. D., Factor, S. A., Molho, E., & Zabetian, C. P. (2017). Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease medications have distinct signatures of the gut microbiome. Movement Disorders, 32(5), 739–749.
Hirose, Y., Murosaki, S., Yamamoto, Y., Yoshikai, Y., & Tsuru, T. (2006). Daily intake of heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum L-137 augments acquired immunity in healthy adults. The Journal of Nutrition, 136(12), 3069–3073.
Hirose, Y., Yamamoto, Y., Yoshikai, Y., & Murosaki, S. (2013). Oral intake of heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum L-137 decreases the incidence of upper respiratory tract infection in healthy subjects with high levels of psychological stress. Journal of Nutritional Science. https://doi.org/10.1017/jns.2013.35
Holmes, A., Finger, C., Morales-Scheihing, D., Lee, J., & McCullough, L. D. (2020). Gut dysbiosis and age-related neurological diseases; An innovative approach for therapeutic interventions. Translational Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2020.07.012
Holmes, C. (2013). Systemic inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology, 39(1), 51–68.
Holmqvist, S., Chutna, O., Bousset, L., Aldrin-Kirk, P., Li, W., Björklund, T., Wang, Z.-Y., Roybon, L., Melki, R., & Li, J.-Y. (2014). Direct evidence of Parkinson pathology spread from the gastrointestinal tract to the brain in rats. Acta Neuropathologica, 128(6), 805–820.
Hong, Y.-F., young Lee, H., Jung, B. J., Jang, S., Chung, D. K., & Kim, H. (2015). Lipoteichoic acid isolated from Lactobacillus plantarum down-regulates UV-induced MMP-1 expression and up-regulates type I procollagen through the inhibition of reactive oxygen species generation. Molecular Immunology, 67(2), 248–255.
Hooper, L. V., Midtvedt, T., & Gordon, J. I. (2002). How host-microbial interactions shape the nutrient environment of the mammalian intestine. Annual Review of Nutrition, 22(1), 283–307.
Hou, Y., Dan, X., Babbar, M., Wei, Y., Hasselbalch, S. G., Croteau, D. L., & Bohr, V. A. (2019). Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nature Reviews Neurology, 15(10), 565–581.
Howcroft, T. K., Campisi, J., Louis, G. B., Smith, M. T., Wise, B., Wyss-Coray, T., Augustine, A. D., McElhaney, J. E., Kohanski, R., & Sierra, F. (2013). The role of inflammation in age-related disease. Aging (albany NY), 5(1), 84.
Hu, Z., Wang, W., Ling, J., & Jiang, C. (2016). α-Mangostin inhibits α-synuclein-induced microglial neuroinflammation and neurotoxicity. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, 36(5), 811–820.
Jeffery, I. B., Lynch, D. B., & O’toole, P. W. (2016). Composition and temporal stability of the gut microbiota in older persons. The ISME Journal, 10(1), 170–182.
Johnson, M. E., Stringer, A., & Bobrovskaya, L. (2018). Rotenone induces gastrointestinal pathology and microbiota alterations in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology, 65, 174–185.
Kaji, R., Kiyoshima-Shibata, J., Nagaoka, M., Nanno, M., & Shida, K. (2010). Bacterial teichoic acids reverse predominant IL-12 production induced by certain lactobacillus strains into predominant IL-10 production via TLR2-dependent ERK activation in macrophages. The Journal of Immunology, 184(7), 3505–3513.
Kambe, J., Watcharin, S., Makioka-Itaya, Y., Inoue, R., Watanabe, G., Yamaguchi, H., & Nagaoka, K. (2020). Heat-killed Enterococcus fecalis (EC-12) supplement alters the expression of neurotransmitter receptor genes in the prefrontal cortex and alleviates anxiety-like behavior in mice. Neuroscience Letters, 720, 134753.
Kawase, M., He, F., Miyazawa, K., Kubota, A., Yoda, K., & Hiramatsu, M. (2012). Orally administered heat-killed Lactobacillus gasseri TMC0356 can upregulate cell-mediated immunity in senescence-accelerated mice. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 326(2), 125–130.
Kechagia, M., Basoulis, D., Konstantopoulou, S., Dimitriadi, D., Gyftopoulou, K., Skarmoutsou, N., & Fakiri, E. M. (2013). Health benefits of probiotics: A review. International Scholarly Research Notices, 2013, 1–7.
Kelly, L. P., Carvey, P. M., Keshavarzian, A., Shannon, K. M., Shaikh, M., Bakay, R. A. E., & Kordower, J. H. (2014). Progression of intestinal permeability changes and alpha-synuclein expression in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Movement Disorders, 29(8), 999–1009.
Keshavarzian, A., Green, S. J., Engen, P. A., Voigt, R. M., Naqib, A., Forsyth, C. B., Mutlu, E., & Shannon, K. M. (2015). Colonic bacterial composition in Parkinson’s disease. Movement Disorders, 30(10), 1351–1360.
Kho, Z. Y., & Lal, S. K. (2018). The human gut microbiome–a potential controller of wellness and disease. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9, 1835.
Kim, H. G., Lee, S. Y., Kim, N. R., Lee, H. Y., Ko, M. Y., Jung, B. J., Kim, C. M., Lee, J. M., Park, J. H., & Han, S. H. (2011). Lactobacillus plantarum lipoteichoic acid down-regulated Shigella flexneri peptidoglycan-induced inflammation. Molecular Immunology, 48(4), 382–391.
Knott, C., Stern, G., & Wilkin, G. P. (2000). Inflammatory regulators in Parkinson’s disease: INOS, lipocortin-1, and cyclooxygenases-1 and-2. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, 16(6), 724–739.
Konieczna, C., Słodziński, M., & Schmidt, M. T. (2018). Exopolysaccharides produced by Lactobacillus rhamnosus KL 53A and Lactobacillus casei Fyos affect their adhesion to enterocytes. Polish Journal of Microbiology, 67(3), 273.
Korf, J. M., Ganesh, B. P., & McCullough, L. D. (2022). Gut dysbiosis and age-related neurological diseases in females. Neurobiology of Disease, 168, 105695.
Kowalski, K., & Mulak, A. (2019). Brain-gut-microbiota axis in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility, 25(1), 48.
Kumar, H., Lim, H.-W., More, S. V., Kim, B.-W., Koppula, S., Kim, I. S., & Choi, D.-K. (2012). The role of free radicals in the aging brain and Parkinson’s disease: Convergence and parallelism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(8), 10478–10504.
Landaburu, M. F., Daneri, G. A. L., Relloso, S., Zarlenga, L. J., Vinante, M. A., & Mujica, M. T. (2020). Fungemia following Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. boulardii probiotic treatment in an elderly patient. Revista Argentina De Microbiologia, 52(1), 27–30.
Leng, F., & Edison, P. (2021). Neuroinflammation and microglial activation in Alzheimer disease: Where do we go from here? Nature Reviews Neurology, 17(3), 157–172.
Li, W., Wu, X., Hu, X., Wang, T., Liang, S., Duan, Y., Jin, F., & Qin, B. (2017). Structural changes of gut microbiota in Parkinson’s disease and its correlation with clinical features. Science China Life Sciences, 60(11), 1223–1233.
Lim, L. H., Li, H. Y., Huang, C. H., Lee, B. W., Lee, Y. K., & Chua, K. Y. (2009). The effects of heat-killed wild-type Lactobacillus casei Shirota on allergic immune responses in an allergy mouse model. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology, 148(4), 297–304.
Ling, Z., Cheng, Y., Yan, X., Shao, L., Liu, X., Zhou, D., Zhang, L., Yu, K., & Zhao, L. (2020). Alterations of the fecal microbiota in Chinese patients with multiple sclerosis. Frontiers in Immunology, 11, 3284.
Liu, L., & Caselli, R. J. (2018). Age stratification corrects bias in estimated hazard of APOE genotype for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions, 4, 602–608.
Liu, M., Huo, Y. R., Wang, J., Wang, C., Liu, S., Liu, S., Wang, J., & Ji, Y. (2016a). Telomere shortening in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, 46(3), 260–265.
Liu, Z., Jiang, J., Yang, Q., Xiong, Y., Zou, D., Yang, C., Xu, J., & Zhan, H. (2016b). Microrna-682-mediated downregulation of PTEN in intestinal epithelial cells ameliorates intestinal ischemia–reperfusion injury. Cell Death and Disease, 7(4), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.84
Lue, L.-F., Walker, D. G., & Rogers, J. (2001). Modeling microglial activation in Alzheimer’s disease with human postmortem microglial cultures. Neurobiology of Aging, 22(6), 945–956.
Ma, Q., Xing, C., Long, W., Wang, H. Y., Liu, Q., & Wang, R.-F. (2019). Impact of microbiota on central nervous system and neurological diseases: The gut-brain axis. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 16(1), 1–14.
Maehata, H., Arai, S., Iwabuchi, N., & Abe, F. (2021). Immuno-modulation by heat-killed Lacticaseibacillus paracasei MCC1849 and its application to food products. SAGE Publications.
Maekawa, T., Ishijima, A. S., Ida, M., Izumo, T., Ono, Y., Shibata, H., & Abe, S. (2016). Prophylactic effect of lactobacillus pentosus strain s-pt84 on candida infection and gastric inflammation in a murine gastrointestinal candidiasis model [Errata]. Medical Mycology Journal, 57(4), E81–E92.
Man, A. L., Bertelli, E., Rentini, S., Regoli, M., Briars, G., Marini, M., Watson, A. J. M., & Nicoletti, C. (2015). Age-associated modifications of intestinal permeability and innate immunity in human small intestine. Clinical Science, 129(7), 515–527.
Mariat, D., Firmesse, O., Levenez, F., Guimarăes, V. D., Sokol, H., Doré, J., Corthier, G., & Furet, J. (2009). The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio of the human microbiota changes with age. BMC Microbiology, 9(1), 1–6.
Martín, R., & Langella, P. (2019). Emerging health concepts in the probiotics field: Streamlining the definitions. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 1047.
Martínez-Cué, C., & Rueda, N. (2020). Cellular senescence in neurodegenerative diseases. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 14, 16.
Martín-Muñoz, M. F., Fortuni, M., Caminoa, M., Belver, T., Quirce, S., & Caballero, T. (2012). Anaphylactic reaction to probiotics: Cow’s milk and hen’s egg allergens in probiotic compounds. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology, 23(8), 778–784.
Matsuoka, K., & Kanai, T. (2015). The gut microbiota and inflammatory bowel disease. Seminars in Immunopathology, 37(1), 47–55.
Mattson, M. P., & Magnus, T. (2006). Ageing and neuronal vulnerability. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 7(4), 278–294.
Miklossy, J. (2008). Chronic inflammation and amyloidogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease–role of Spirochetes. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 13(4), 381–391.
Misiak, B., Leszek, J., & Kiejna, A. (2012). Metabolic syndrome, mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease—The emerging role of systemic low-grade inflammation and adiposity. Brain Research Bulletin, 89(3–4), 144–149.
Miyazawa, K., He, F., Kawase, M., Kubota, A., Yoda, K., & Hiramatsu, M. (2011). Enhancement of immunoregulatory effects of Lactobacillus gasseri TMC0356 by heat treatment and culture medium. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 53(2), 210–216.
Miyazawa, K., Kawase, M., Kubota, A., Yoda, K., Harata, G., Hosoda, M., & He, F. (2015). Heat-killed Lactobacillus gasseri can enhance immunity in the elderly in a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. Beneficial Microbes, 6(4), 441–449.
Moore, D. J., West, A. B., Dawson, V. L., & Dawson, T. M. (2005). Molecular pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 28, 57–87.
Morais, L. H., Schreiber, H. L., & Mazmanian, S. K. (2021). The gut microbiota–brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 19(4), 241–255.
Murata, M., Kondo, J., Iwabuchi, N., Takahashi, S., Yamauchi, K., Abe, F., & Miura, K. (2018). Effects of paraprobiotic Lactobacillus paracasei MCC1849 supplementation on symptoms of the common cold and mood states in healthy adults. Beneficial Microbes, 9(6), 855–864.
Murosaki, S., Muroyama, K., Yamamoto, Y., & Yoshikai, Y. (2000). Antitumor effect of heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum L-137 through restoration of impaired interleukin-12 production in tumor-bearing mice. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy, 49(3), 157–164.
Murosaki, S., Yamamoto, Y., Ito, K., Inokuchi, T., Kusaka, H., Ikeda, H., & Yoshikai, Y. (1998). Heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum L-137 suppresses naturally fed antigen–specific IgE production by stimulation of IL-12 production in mice. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 102(1), 57–64.
Nagpal, R., Mainali, R., Ahmadi, S., Wang, S., Singh, R., Kavanagh, K., Kitzman, D. W., Kushugulova, A., Marotta, F., & Yadav, H. (2018). Gut microbiome and aging: Physiological and mechanistic insights. Nutrition and Healthy Aging, 4(4), 267–285. https://doi.org/10.3233/NHA-170030
Naidu, K. S. B., Adam, J. K., & Govender, P. (2012). The use of probiotics and safety concerns: A review. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 6(41), 6871–6877.
Nakamura, F., Ishida, Y., Aihara, K., Sawada, D., Ashida, N., Sugawara, T., Aoki, Y., Takehara, I., Takano, K., & Fujiwara, S. (2016). Effect of fragmented Lactobacillus amylovorus CP1563 on lipid metabolism in overweight and mildly obese individuals: A randomized controlled trial. Microbial Ecology in Health and Disease, 27(1), 30312.
Nataraj, B. H., Ali, S. A., Behare, P. V., & Yadav, H. (2020). Postbiotics-parabiotics: The new horizons in microbial biotherapy and functional foods. Microbial Cell Factories, 19(1), 1–22.
Nikolova, V. L., Hall, M. R. B., Hall, L. J., Cleare, A. J., Stone, J. M., & Young, A. H. (2021). Perturbations in gut microbiota composition in psychiatric disorders: A review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry, 78(12), 1343–1354.
Nishida, K., Sawada, D., Kawai, T., Kuwano, Y., Fujiwara, S., & Rokutan, K. (2017a). Para-psychobiotic Lactobacillus gasseri CP 2305 ameliorates stress-related symptoms and sleep quality. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 123(6), 1561–1570.
Nishida, K., Sawada, D., Kuwano, Y., Tanaka, H., Sugawara, T., Aoki, Y., Fujiwara, S., & Rokutan, K. (2017b). Daily administration of paraprobiotic Lactobacillus gasseri CP2305 ameliorates chronic stress-associated symptoms in Japanese medical students. Journal of Functional Foods, 36, 112–121.
Noh, S. Y., Kang, S.-S., Yun, C.-H., & Han, S. H. (2015). Lipoteichoic acid from Lactobacillus plantarum inhibits Pam2CSK4-induced IL-8 production in human intestinal epithelial cells. Molecular Immunology, 64(1), 183–189.
O’Toole, P. W., & Jeffery, I. B. (2015). Gut microbiota and aging. Science, 350(6265), 1214–1215.
Ouwehand, A. C., Bergsma, N., Parhiala, R., Lahtinen, S., Gueimonde, M., Finne-Soveri, H., Strandberg, T., Pitkälä, K., & Salminen, S. (2008). Bifidobacterium microbiota and parameters of immune function in elderly subjects. FEMS Immunology & Medical Microbiology, 53(1), 18–25.
Percy, M. G., & Gründling, A. (2014). Lipoteichoic acid synthesis and function in gram-positive bacteria. Annual Review of Microbiology, 68, 81–100.
Piqué, N., Berlanga, M., & Miñana-Galbis, D. (2019). Health benefits of heat-killed (Tyndallized) probiotics: An overview. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(10), 2534.
Plowden, J., Renshaw-Hoelscher, M., Engleman, C., Katz, J., & Sambhara, S. (2004). Innate immunity in aging: Impact on macrophage function. Aging Cell, 3(4), 161–167.
Rahman, Z., & Dandekar, M. P. (2021). Crosstalk between gut microbiome and immunology in the management of ischemic brain injury. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 353, 577498.
Rera, M., Clark, R. I., & Walker, D. W. (2012). Intestinal barrier dysfunction links metabolic and inflammatory markers of aging to death in Drosophila. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109(52), 21528–21533.
Rinne, J. O. (1987). Muscarinic and dopaminergic receptors in the aging human brain. Brain Research, 404(1–2), 162–168.
Rinne, J. O., Lönnberg, P., & Marjamäki, P. (1990). Age-dependent decline in human brain dopamine D1 and D2 receptors. Brain Research, 508(2), 349–352.
Rolyan, H., Scheffold, A., Heinrich, A., Begus-Nahrmann, Y., Langkopf, B. H., Hölter, S. M., Vogt-Weisenhorn, D. M., Liss, B., Wurst, W., & Lie, D. C. (2011). Telomere shortening reduces Alzheimer’s disease amyloid pathology in mice. Brain, 134(7), 2044–2056.
Ruas-Madiedo, P., & De Los Reyes-Gavilán, C. G. (2005). Invited review: Methods for the screening, isolation, and characterization of exopolysaccharides produced by lactic acid bacteria. Journal of Dairy Science, 88(3), 843–856.
Salminen, S., Collado, M. C., Endo, A., Hill, C., Lebeer, S., Quigley, E. M. M., Sanders, M. E., Shamir, R., Swann, J. R., Szajewska, H., & Vinderola, G. (2021). The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 18(9), 649–667. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-021-00440-6
Sanabria-Castro, A., Alvarado-Echeverría, I., & Monge-Bonilla, C. (2017). Molecular pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: An update. Annals of Neurosciences, 24(1), 46–54.
Scheperjans, F., Aho, V., Pereira, P. A. B., Koskinen, K., Paulin, L., Pekkonen, E., Haapaniemi, E., Kaakkola, S., Eerola-Rautio, J., & Pohja, M. (2015). Gut microbiota are related to Parkinson’s disease and clinical phenotype. Movement Disorders, 30(3), 350–358.
Schmitt, N., Morita, R., Bourdery, L., Bentebibel, S. E., Zurawski, S. M., Banchereau, J., & Ueno, H. (2009). Human dendritic cells induce the differentiation of interleukin-21-producing T follicular helper-like cells through interleukin-12. Immunity, 31(1), 158–169.
Schneewind, O., & Missiakas, D. (2014). Lipoteichoic acids, phosphate-containing polymers in the envelope of gram-positive bacteria. Journal of Bacteriology, 196(6), 1133–1142.
Schrezenmeir, J., & de Vrese, M. (2001). Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics—approaching a definition. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 73(2), 361s–364s.
Seki, E., & Schnabl, B. (2012). Role of innate immunity and the microbiota in liver fibrosis: Crosstalk between the liver and gut. The Journal of Physiology, 590(3), 447–458.
Shamila-Syuhada, A. K., Chuah, L.-O., Wan-Nadiah, W. A., Cheng, L. H., Alkarkhi, A. F. M., Effarizah, M. E., & Rusul, G. (2016). Inactivation of microbiota and selected spoilage and pathogenic bacteria in milk by combinations of ultrasound, hydrogen peroxide, and active lactoperoxidase system. International Dairy Journal, 61, 120–125.
Sharma, N., & Nehru, B. (2015). Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide induced model of Parkinson’s disease: Role of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. Neurochemistry International, 87, 92–105.
Shaw, A. C., Goldstein, D. R., & Montgomery, R. R. (2013). Age-dependent dysregulation of innate immunity. Nature Reviews Immunology, 13(12), 875–887.
Shida, K., Kiyoshima-Shibata, J., Kaji, R., Nagaoka, M., & Nanno, M. (2009). Peptidoglycan from lactobacilli inhibits interleukin-12 production by macrophages induced by Lactobacillus casei through Toll-like receptor 2-dependent and independent mechanisms. Immunology, 128(1), e858–e869.
Sirin, S., & Aslim, B. (2020). Characterization of lactic acid bacteria derived exopolysaccharides for use as a defined neuroprotective agent against amyloid beta1–42-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–18.
Sokol, H., Pigneur, B., Watterlot, L., Lakhdari, O., Bermúdez-Humarán, L. G., Gratadoux, J.-J., Blugeon, S., Bridonneau, C., Furet, J.-P., & Corthier, G. (2008). Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105(43), 16731–16736.
Song, J., Xing, G., Cao, J., Teng, L., Li, C., Meng, Q., Lu, J., Zhou, Y., Liu, Y., & Wang, D. (2016). Investigation of the antidepressant effects of exopolysaccharides obtained from Marasmius androsaceus fermentation in a mouse model. Molecular Medicine Reports, 13(1), 939–946.
Sovran, B., Hugenholtz, F., Elderman, M., Van Beek, A. A., Graversen, K., Huijskes, M., Boekschoten, M. V., Savelkoul, H. F. J., De Vos, P., & Dekker, J. (2019). Age-associated impairment of the mucus barrier function is associated with profound changes in microbiota and immunity. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1–13.
Spychala, M. S., Venna, V. R., Jandzinski, M., Doran, S. J., Durgan, D. J., Ganesh, B. P., Ajami, N. J., Putluri, N., Graf, J., & Bryan, R. M. (2018). Age-related changes in the gut microbiota influence systemic inflammation and stroke outcome. Annals of Neurology, 84(1), 23–36.
Stadlbauer, V., Engertsberger, L., Komarova, I., Feldbacher, N., Leber, B., Pichler, G., Fink, N., Scarpatetti, M., Schippinger, W., & Schmidt, R. (2020). Dysbiosis, gut barrier dysfunction and inflammation in dementia: A pilot study. BMC Geriatrics, 20(1), 1–13.
Sugahara, H., Yao, R., Odamaki, T., & Xiao, J. Z. (2017). Differences between live and heat-killed bifidobacteria in the regulation of immune function and the intestinal environment. Beneficial Microbes, 8(3), 463–472.
Sun, M.-F., & Shen, Y.-Q. (2018). Dysbiosis of gut microbiota and microbial metabolites in Parkinson’s disease. Ageing Research Reviews, 45, 53–61.
Sun, M.-F., Zhu, Y.-L., Zhou, Z.-L., Jia, X.-B., Xu, Y.-D., Yang, Q., Cui, C., & Shen, Y.-Q. (2018). Neuroprotective effects of fecal microbiota transplantation on MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease mice: Gut microbiota, glial reaction and TLR4/TNF-α signaling pathway. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 70, 48–60.
Tang, Y., & Le, W. (2016). Differential roles of M1 and M2 microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Molecular Neurobiology, 53(2), 1181–1194.
Tansey, M. G., & Goldberg, M. S. (2010). Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: Its role in neuronal death and implications for therapeutic intervention. Neurobiology of Disease, 37(3), 510–518.
Taverniti, V., & Guglielmetti, S. (2011). The immunomodulatory properties of probiotic microorganisms beyond their viability (ghost probiotics: Proposal of paraprobiotic concept). Genes & Nutrition, 6(3), 261–274.
Teame, T., Wang, A., Xie, M., Zhang, Z., Yang, Y., Ding, Q., Gao, C., Olsen, R. E., Ran, C., & Zhou, Z. (2020). Paraprobiotics and postbiotics of probiotic Lactobacilli, their positive effects on the host and action mechanisms: A review. Frontiers in Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2020.570344
Terada, A., Bukawa, W., Kan, T., & Mitsuoka, T. (2004). Effects of the consumption of heat-killed Enterococcus faecalis EC-12 preparation on microbiota and metabolic activity of the faeces in healthy adults. Microbial Ecology in Health and Disease, 16(4), 188–194.
Thursby, E., & Juge, N. (2017). Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochemical Journal, 474(11), 1823–1836.
Tsilingiri, K., Barbosa, T., Penna, G., Caprioli, F., Sonzogni, A., Viale, G., & Rescigno, M. (2012). Probiotic and postbiotic activity in health and disease: Comparison on a novel polarised ex-vivo organ culture model. Gut, 61(7), 1007–1015.
Unger, M. M., Spiegel, J., Dillmann, K.-U., Grundmann, D., Philippeit, H., Bürmann, J., Faßbender, K., Schwiertz, A., & Schäfer, K.-H. (2016). Short chain fatty acids and gut microbiota differ between patients with Parkinson’s disease and age-matched controls. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 32, 66–72.
van Beek, A. A., Sovran, B., Hugenholtz, F., Meijer, B., Hoogerland, J. A., Mihailova, V., van der Ploeg, C., Belzer, C., Boekschoten, M. V., & Hoeijmakers, J. H. J. (2016). Supplementation with Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 prevents decline of mucus barrier in colon of accelerated aging Ercc1−/Δ7 mice. Frontiers in Immunology, 7, 408.
Van Hoffen, E., Korthagen, N. M., De Kivit, S., Schouten, B., Bardoel, B., Duivelshof, A., Knol, J., Garssen, J., & Willemsen, L. E. M. (2010). Exposure of intestinal epithelial cells to UV-killed Lactobacillus GG but not Bifidobacterium breve enhances the effector immune response in vitro. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology, 152(2), 159–168.
Vascellari, S., Palmas, V., Melis, M., Pisanu, S., Cusano, R., Uva, P., Perra, D., Madau, V., Sarchioto, M., & Oppo, V. (2020). Gut microbiota and metabolome alterations associated with Parkinson’s disease. Msystems, 5(5), e00561-e620.
Vollmer, W., Blanot, D., & De Pedro, M. A. (2008). Peptidoglycan structure and architecture. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 32(2), 149–167.
Wang, B., Yao, M., Lv, L., Ling, Z., & Li, L. (2017). The human microbiota in health and disease. Engineering, 3(1), 71–82.
Wang, Y., Xie, J., Wang, N., Li, Y., Sun, X., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, H. (2013). Lactobacillus casei Zhang modulate cytokine and Toll-like receptor expression and beneficially regulate poly I: C-induced immune responses in RAW264 7 macrophages. Microbiology and Immunology, 57(1), 54–62.
Warda, A. K., Rea, K., Fitzgerald, P., Hueston, C., Gonzalez-Tortuero, E., Dinan, T. G., & Hill, C. (2019). Heat-killed lactobacilli alter both microbiota composition and behaviour. Behavioural Brain Research, 362, 213–223.
Wegh, C. A. M., Geerlings, S. Y., Knol, J., Roeselers, G., & Belzer, C. (2019). Postbiotics and their potential applications in early life nutrition and beyond. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(19), 4673.
Wei, C.-L., Wang, S., Yen, J.-T., Cheng, Y.-F., Liao, C.-L., Hsu, C.-C., Wu, C.-C., & Tsai, Y.-C. (2019). Antidepressant-like activities of live and heat-killed Lactobacillus paracasei PS23 in chronic corticosterone-treated mice and possible mechanisms. Brain Research, 1711, 202–213.
Witkowski, M., Weeks, T. L., & Hazen, S. L. (2020). Gut microbiota and cardiovascular disease. Circulation Research, 127(4), 553–570.
Woodmansey, E. J. (2007). Intestinal bacteria and ageing. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 102(5), 1178–1186.
Woodmansey, E. J., McMurdo, M. E. T., Macfarlane, G. T., & Macfarlane, S. (2004). Comparison of compositions and metabolic activities of fecal microbiotas in young adults and in antibiotic-treated and non-antibiotic-treated elderly subjects. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70(10), 6113–6122.
Zhang, F., Yue, L., Fang, X., Wang, G., Li, C., Sun, X., Jia, X., Yang, J., Song, J., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Altered gut microbiota in Parkinson’s disease patients/healthy spouses and its association with clinical features. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 81, 84–88.
Zhang, X.-X., Tian, Y., Wang, Z.-T., Ma, Y.-H., Tan, L., & Yu, J.-T. (2021). The epidemiology of Alzheimer’s disease modifiable risk factors and prevention. The Journal of Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease. https://doi.org/10.14283/jpad.2021.15
Zhao, Y., Jaber, V., & Lukiw, W. J. (2017). Secretory products of the human GI tract microbiome and their potential impact on Alzheimer’s disease (AD): Detection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in AD hippocampus. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 7, 318.
Zheng, M., Zhang, R., Tian, X., Zhou, X., Pan, X., & Wong, A. (2017). Assessing the risk of probiotic dietary supplements in the context of antibiotic resistance. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8, 908.
Zhu, Y., Armstrong, J. L., Tchkonia, T., & Kirkland, J. L. (2014). Cellular senescence and the senescent secretory phenotype in age-related chronic diseases. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition & Metabolic Care, 17(4), 324–328.
Zhuang, Z. Q., Shen, L. L., Li, W. W., Fu, X., Zeng, F., Gui, L., Lü, Y., Cai, M., Zhu, C., Tan, Y. L., Zheng, P., Li, H. Y., Zhu, J., Zhou, H. D., Bu, X. L., & Wang, Y. J. (2018). Gut microbiota is altered in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 63(4), 1337–1346. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-180176
Acknowledgements
The authors (ZR and MPD) want to thank the Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers, Government of India for financial support. NIPER
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZR gathered literature and drafted the manuscript; MPD conceptualized, reviewed, and corrected the draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, Z., Dandekar, M.P. Implication of Paraprobiotics in Age-Associated Gut Dysbiosis and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neuromol Med 25, 14–26 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-022-08722-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-022-08722-1