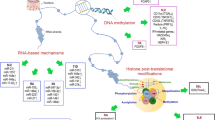
Abstract
Kabuki syndrome (KS) is a rare multi-systemic disorder characterized by a distinct face, postnatal growth deficiency, mild-to-moderate intellectual disability, skeletal and visceral (mainly cardiovascular, renal, and skeletal) malformations, dermatoglyphic abnormalities. Its cause is related to mutations of two genes: KMT2D (histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2D) and KDM6A (lysine-specific demethylase 6A), both functioning as epigenetic modulators through histone modifications in the course of embryogenesis and in several biological processes. Epigenetic regulation is defined as the complex of hereditable modifications to DNA and histone proteins that modulates gene expression in the absence of DNA nucleotide sequence changes. Different human disorders are caused by mutations of genes involved in the epigenetic regulation, and not surprisingly, all these share developmental defects, disturbed growth (in excess or defect), multiple congenital organ malformations, and also hematological and immunological defects. In particular, most KS patients show increased susceptibility to infections and have reduced serum immunoglobulin levels, while some suffer also from autoimmune manifestations, such as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, hemolytic anemia, autoimmune thyroiditis, and vitiligo. Herein we review the immunological aspects of KS and propose a novel model to account for the immune dysfunction observed in this condition.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Niikawa N, Matsuura N, Fukushima Y, Ohsawa T, Kajii T. Kabuki make-up syndrome: a syndrome of mental retardation, unusual facies, large and protruding ears, and postnatal growth deficiency. J Pediatr. 1981;99:565–9.
Kuroki Y, Suzuki Y, Chyo H, Hata A, Matsui I. A new malformation syndrome of long palpebral fissures, large ears, depressed nasal tip, and skeletal anomalies associated with postnatal dwarfism and mental retardation. J Pediatr. 1981;99:570–3.
Niikawa N, Kuroki Y, Kajii T, Matsuura N, lshikiriyarna S, Tonoki H, et al. Kabuki make-up (Niikawa-Kuroki) syndrome: a study of 62 patients. Am J Med Genet. 1988;31:562–9.
Hannibal MC, Buckingham KJ, Ng SB, Ming JE, Beck AE, McMillin MJ, et al. Spectrum of MLL2 (ALR) mutations in 110 cases of Kabuki syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2011;155A:1511–6.
Ng SB, Bigham AW, Buckingham KJ, Hannibal MC, McMillin MJ, Gildersleeve HI, et al. Exome sequencing identifies MLL2 mutations as a cause of Kabuki syndrome. Nat Genet. 2010;42:790–3.
Paulussen AD, Stegmann AP, Blok MJ, Tserpelis D, Posma-Velter C, Detisch Y, et al. MLL2 mutation spectrum in 45 patients with Kabuki syndrome. Hum Mutat. 2011;32:E2018–25.
Lederer D, Grisart B, Digilio MC, Benoit V, Crespin M, Ghariani SC, et al. Deletion of KDM6A, a histone demethylase interacting with MLL2, in three patients with Kabuki syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2012;90:119–24.
Miyake N, Koshimizu E, Okamoto N, Mizuno S, Ogata T, Nagai T, et al. MLL2 and KDM6A mutations in patients with Kabuki syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2013;161A:2234–43.
Hoffman JD, Ciprero KL, Sullivan KE, Kaplan PB, McDonald-McGinn DM, Zackai EH, et al. Immune abnormalities are a frequent manifestation of Kabuki syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2005;135:278–81.
Lin JL, Lee WI, Huang JL, Chen PK, Chan KC, Lo LJ, et al. Immunologic assessment and KMT2D mutation detection in Kabuki syndrome. Clin Genet. 2014. doi:10.1111/cge.12484.
Ming JE, Russell KL, McDonald-McGinn DM, Zackai EH. Autoimmune disorders in Kabuki syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2005;132A:260–2.
Morin RD, Johnson NA, Severson TM, Mungall AJ, An J, Goya R, et al. Somatic mutations altering EZH2 (Tyr641) in follicular and diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of germinal-center origin. Nat Genet. 2010;42:181–5.
Guo C, Chen LH, Huang Y, Chang CC, Wang P, Pirozzi CJ, et al. KMT2D maintains neoplastic cell proliferation and global histone H3 lysine 4 monomethylation. Oncotarget. 2013;4:2144–53.
Li G, Zan H, Xu Z, Casali P. Epigenetics of the antibody response. Trends Immunol. 2013;34:460–70.
Roh TY, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Zhao K. The genomic landscape of histone modifications in human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:15782–7.
Banka S, Veeramachaneni R, Reardon W, Howard E, Bunstone S, Ragge N, et al. How genetically heterogeneous is Kabuki syndrome?: MLL2 testing in 116 patients, review and analyses of mutation and phenotypic spectrum. Eur J Hum Genet. 2012;20:381–8.
Makrythanasis P, van Bon BW, Steehouwer M, Rodríguez-Santiago B, Simpson M, Dias P, et al. MLL2 mutation detection in 86 patients with Kabuki syndrome: a genotype-phenotype study. Clin Genet. 2013;84:539–45.
Micale L, Augello B, Fusco C, Selicorni A, Loviglio MN, Silengo MC, et al. Mutation spectrum of MLL2 in a cohort of Kabuki syndrome patients. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2011;6:38.
Cheon CK, Sohn YB, Ko JM, Lee YJ, Song JS, Moon JW, et al. Identification of KMT2D and KDM6A mutations by exome sequencing in Korean patients with Kabuki syndrome. J Hum Genet. 2014;59:321–5.
Banka S, Lederer D, Benoit V, Jenkins E, Howard E, Bunstone S, et al. Novel KDM6A (UTX) mutations and a clinical and molecular review of the X-linked Kabuki syndrome (KS2). Clin Genet. 2015;87:252–8.
Miyake N, Mizuno S, Okamoto N, Ohashi H, Shiina M, Ogata K, et al. KDM6A point mutations cause Kabuki syndrome. Hum Mutat. 2013;34:108–10.
Priolo M, Micale L, Augello B, Fusco C, Zucchetti F, Prontera P, et al. Absence of deletion and duplication of MLL2 and KDM6A genes in a large cohort of patients with Kabuki syndrome. Mol Genet Metab. 2012;107:627–9.
Dillon SC, Zhang X, Trievel RC, Cheng X. The SET-domain protein superfamily: protein lysine methyltransferases. Genome Biol. 2005;6:227.
Glaser S, Schaft J, Lubitz S, Vintersten K, van der Hoeven F, Tufteland KR, et al. Multiple epigenetic maintenance factors implicated by the loss of Mll2 in mouse development. Development. 2006;133:1423–32.
Banka S, Howard E, Bunstone S, Chandler KE, Kerr B, Lachlan K, et al. MLL2 mosaic mutations and intragenic deletion-duplications in patients with Kabuki syndrome. Clin Genet. 2013;83:467–71.
Bögershausen N, Wollnik B. Unmasking Kabuki syndrome. Clin Genet. 2013;83:201–11.
Micale L, Augello B, Maffeo C, Selicorni A, Zucchetti F, Fusco C, et al. Molecular analysis, pathogenic mechanisms, and readthrough therapy on a large cohort of Kabuki syndrome patients. Hum Mutat. 2014;35:841–50.
Casanova M, Selicorni A, Ferrari A. Cancer predisposition in children with Kabuki syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2011;155A:1504.
Hong S, Cho YW, Yu LR, Yu H, Veenstra TD, Ge K. Identification of JmjC domain-containing UTX and JMJD3 as histone H3 lysine 27 demethylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:18439–44.
Kim JH, Sharma A, Dhar SS, Lee SH, Gu B, Chan CH, et al. UTX and MLL4 coordinately regulate transcriptional programs for cell proliferation and invasiveness in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2014;74:1705–17.
Van Laarhoven PM, Neitzel LR, Quintana AM, Geiger E, Zackai EH, Clouthier DE, et al. Kabuki syndrome genes KMT2D and KDM6A: functional analyses demonstrate critical roles in craniofacial, heart and brain development. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24:4443–53.
Bjornsson HT, Benjamin JS, Zhang L, Weissman J, Gerber EE, Chen YC, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibition rescues structural and functional brain deficits in a mouse model of Kabuki syndrome. Sci Trans Med. 2014;6(256):256ra135.
Ijichi O, Kawakami K, Matsuda Y, Ikarimoto N, Miyata K, Takamatsu H, Tokunaga M. A case of Kabuki make-up syndrome with EBV+ Burkitt’s lymphoma. Acta Paediatr J. 1996;38:66–8.
Kawame H, Hannibal MC, Hudgins L, Pagon RA. Phenotypic spectrum and management issues in Kabuki syndrome. J Pediatr. 1999;134:480–5.
De Dios JA, Javaid AA, Ballesteros E, Metersky ML. An 18-year-old woman with Kabuki syndrome, immunoglobulin deficiency and granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease. Conn Med. 2012;76:15–8.
Frenk NE, Kim CA, Carneiro-Sampaio M, Orii NM, de MoraesVasconcelos D. Basic evaluation of the immunocompetence of Brazilian patients with Kabuki syndrome. Pediatria (São Paulo). 2009;31:170–7.
Genevieve D, Amiel J, Viot G, Le Merrer M, Sanlaville D, Urtizberea A, et al. Atypical findings in Kabuki syndrome: report of 8 patients in a series of 20 and review of the literature. Am J Med Genet. 2004;129A:64–8.
Hostoffer RW, Bay CA, Wagner K, Venglarcik J 3rd, Sahara H, Omair E, et al. Kabuki make-up syndrome associated with an acquired hypogammaglobulinemia and anti-IgA antibodies. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1996;35:273–6.
Shah M, Bogucki B, Mavers M, deMello DE, Knutsen A. Cardiac conduction abnormalities and congenital immunodeficiency in a child with Kabuki syndrome: case report. BMC Med Gen. 2005;6:28.
Chrzanowska KH, Krajewska-Walasek M, Kuś J, Michałkiewicz J, Maziarka D, Wolski JK, et al. Kabuki (Niikawa-Kuroki) syndrome associated with immunodeficiency. Clin Genet. 1998;53:308–12.
Watanabe T, Miyakawa M, Satoh M, Abe T, Oda Y. Kabuki make-up syndrome associated with chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Acta Paediatr Jpn. 1994;36:727–9.
McGaughran J, Aftimos S, Jefferies C, Winship I. Clinical phenotypes of nine cases of Kabuki syndrome from New Zealand. Clin Dysmorphol. 2001;10:257–62.
Armstrong L, Abd El Moneim A, Aleck K, Aughton DJ, Baumann C, Braddock SR, et al. Further delineation of Kabuki syndrome in 48 well-defined new individuals. Am J Med Genet A. 2005;132A:265–72.
Shotelersuk V, Punyashthiti R, Srivuthana S, Wacharasindhu S. Kabuki syndrome: report of six Thai children and further phenotypic and genetic delineation. Am J Med Genet. 2002;110:384–90.
Trimarchi G, Guarnaccia F, Mazzola E, Pitta R, Merla G, Zelante L, et al. Tre casi di sindrome Kabuki positivi per la mutazione del gene mll2. Riv Ital Genet Immunol Pediatr. 2012;anno IV(n.1):32.
Gidwani P, Segal E, Shanske A, Driscoll C. Chorea associated with antiphospholipid antibodies in a patient with Kabuki syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2007;143A:1338–41.
Giordano P, Lassandro G, Sangerardi M, Faienza MF, Valente F, Martire B. Autoimmune haematological disorders in two Italian children with Kabuki syndrome. Ital J Pediatr. 2014;40:10.
Shalev SA, Clarke LA, Koehn D, Langlois S, Zackai EH, Hall JG, et al. Long-term follow-up of three individuals with Kabuki syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2004;125A:191–200.
Torii Y, Yagasaki H, Tanaka H, Mizuno S, Nishio N, Muramatsu H, et al. Successful treatment with rituximab of refractory idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in a patient with Kabuki syndrome. Int J Hematol. 2009;90:174–6.
Nako Y, Maruyama K, Sakaguchi M, Kuroki M, Terao K, Kuribayashi T, et al. Two cases of autoimmune hemolytic anemia: a case associated with Kabuki make-up syndrome and a case with IgD as an anti-erythrocyte autoantibody. J Jpn Pediatr Soc. 1984;99:565–9.
Artigas M, Alcazar R, Bel J, Fernandez P, Javier G, Ortega E, et al. Kabuki syndrome and common variable immunodeficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 1997;61(suppl):A91.
Ewart-Toland A, Enns GM, Cox VA, Mohan GC, Rosenthal P, Golabi M. Severe congenital anomalies requiring transplantation in children with Kabuki syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1998;80:362–7.
Ho J, Fox D, Innes AM, McLeod R, Butzner D, Johnson N, et al. Kabuki syndrome and Crohn disease in a child with familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2010;23:975–9.
Andersen MS, Menazzi S, Brun P, Cocah C, Merla G, Solari A. Clinical diagnosis of Kabuki syndrome: phenotype and associated abnormalities in two new cases. Arch Argent Pediatr. 2014;112:26–32.
Michot C, Corsini C, Sanlaville D, Baumann C, Toutain A, Philip N, et al. Finger creases lend a hand in Kabuki syndrome. Eur J Med Genet. 2013;56:556–60.
Nishizaki N, Fujinaga S, Hirano D, Murakami H, Kamei K, Ohtomo Y, et al. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis type 3 associated with Kabuki syndrome. Clin Nephrol. 2014;81:369–73.
Oto J, Mano A, Nakataki E, Yamaguchi H, Inui D, Imanaka H, et al. An adult patient with Kabuki syndrome presenting with Henoch-Schönlein purpura complicated with pulmonary hemorrhage. J Anesth. 2008;22:460–3.
Zannolli R, Buoni S, Macucci F, Scarinci R, Viviano M, Orsi A, et al. Kabuki syndrome with trichrome vitiligo, ectodermal defect and hypogammaglobulinemia A and G. Brain Dev. 2007;29:373–6.
Schrander-Stumpel C, Theunissen P, Hulsmans R, Fryns JP. Kabuki make-up (Niikawa-Kuroki) syndrome in a girl presenting with vitiligo vulgaris, cleft palate, somatic and psychomotor retardation and facial dysmorphism. Genet Couns. 1993;4:71–2.
Fujishiro M, Ogihara T, Tsukuda K, Shojima N, Fukushima Y, Kimura S, et al. A case showing an association between type 1 diabetes mellitus and Kabuki syndrome. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2003;60:25–31.
Lai KV, Nussbaum E, Do P, Chen J, Randhawa IS, Chin T. Congenital lung anomalies in Kabuki syndrome. J Pediatr Cong Disord. 2014;1:1–5.
Venkatesh S, Workman JL. Histone exchange, chromatin structure and the regulation of transcription. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015;16:178–89.
Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 2007;128:693–705.
Kirmizis A, Bartley SM, Kuzmichev A, Margueron R, Reinberg D, Green R, et al. Silencing of human polycomb target genes is associated with methylation of histone H3 Lys 27. Genes Dev. 2004;18:1592–605.
Goldberg AD, Allis CD, Bernstein E. Epigenetics: landscape takes shape. Cell. 2007;128:635–8.
Eissenberg JC, Shilatifard A. Histone H3 Lysine 4 (H3K4) methylation in development and differentiation. Dev Biol. 2010;339:240–9.
Wei G, Wei L, Zhu J, Zang C, Hu-Li J, Yao Z, et al. Global mapping of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 reveals specificity and plasticity in lineage fate determination of differentiating CD4+ T cells. Immunity. 2009;30:155–67.
Ansel KM, Djuretic I, Tanasa B, Rao A. Regulation of Th2 differentiation and IL4 locus accessibility. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:607–56.
Murphy KM. Reiner SL the lineage decisions of helper T cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:933–44.
Szabo SJ, Sullivan BM, Peng SL, Glimcher LH. Molecular mechanisms regulating Th1 immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:713–58.
Weaver CT, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Harrington LE. IL-17 family cytokines and the expanding diversity of effector T cell lineages. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:821–52.
Zhu J, Paul WE. CD4 T cells: fates, functions, and faults. Blood. 2008;112:1557–69.
Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T, Ono M. Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell. 2008;133:775–87.
Gambineri E, Perroni L, Passerini L, Bianchi L, Doglioni C, Meschi F, et al. Clinical and molecular profile of a new series of patients with immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome: inconsistent correlation between forkhead box protein 3 expression and disease severity. J Allergy Clin Immun. 2008;122:1105–12.
Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Schones DE, Wang Z, et al. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell. 2007;129:823–37.
Roh TY, Cuddapah S, Zhao K. Active chromatin domains are defined by acetylation islands revealed by genome-wide mapping. Genes Dev. 2005;19:542–52.
Wang Z, Zang C, Rosenfeld JA, Schones DE, Barski A, Cuddapah S, et al. Combinatorial patterns of histone acetylations and methylations in the human genome. Nat Genet. 2008;40:897–903.
Schones DE, Cui K, Cuddapah S, Roh TY, Barski A, Wang Z, et al. Dynamic regulation of nucleosome positioning in the human genome. Cell. 2008;132:887–98.
Shaknovich R, Cerchietti L, Tsikitas L, Kormaksson M, De S, Figueroa ME, et al. DNA methyltransferase 1 and DNA methylation patterning contribute to germinal center B-cell differentiation. Blood. 2011;118:3559–69.
Liu Z, Mai A, Sun J. Lysine acetylation regulates Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in B cell activation. J Immunol. 2010;184:244–54.
Schmidlin H, Diehl SA, Blom B. New insights into the regulation of human B-cell differentiation. Trends Immunol. 2009;30:277–85.
Decker T, di Magliano MP, McManus S, Sun Q, Bonifer C, Tagoh H, Busslinger M. Stepwise activation of enhancer and promoter regions of the B cell commitment gene Pax5 in early lymphopoiesis. Immunity. 2009;30:508–20.
Ramachandrareddy H, Bouska A, Shen Y, Ji M, Rizzino A, Chan WC, McKeithan TW. BCL6 promoter interacts with far upstream sequences with greatly enhanced activating histone modifications in germinal center B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:11930–5.
Jeevan-Raj BP, Robert I, Heyer V, Page A, Wang JH, Cammas F, et al. Epigenetic tethering of AID to the donor switch region during immunoglobulin class switch recombination. J Exp Med. 2011;208:1649–60.
Shapiro-Shelef M, Calame K. Regulation of plasma-cell development. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:230–42.
McHeyzer-Williams M, Okitsu S, Wang N, McHeyzer-Williams L. Molecular programming of B cell memory. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12:24–34.
Portela A, Esteller M. Epigenetic modifications and human disease. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28:1057–68.
Corneo B, Moshous D, Gungor T, Wulffraat N, Philippet P, Le Deist F, et al. Identical mutations in RAG1 or RAG2 genes leading to defective V(D)J recombinase activity can cause either T-B-severe combined immune deficiency or Omenn syndrome. Blood. 2001;97:2772–6.
Durandy A, Kracker S. Immunoglobulin class-switch recombination deficiencies. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14:218.
Daniel JA, Santos MA, Wang Z, Zang C, Schwab KR, Jankovic M, et al. PTIP promotes chromatin changes critical for immunoglobulin class switch recombination. Science. 2010;329:917–23.
Xu Z, Zan H, Pone EJ, Mai T, Casali P. Immunoglobulin class-switch DNA recombination: induction, targeting and beyond. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12:517–31.
Stanlie A, Aida M, Muramatsu M, Honjo T, Begum NA. Histone3 lysine4 trimethylation regulated by the facilitates chromatin transcription complex is critical for DNA cleavage in class switch recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:22190–5.
Kuang FL, Luo Z, Scharff MD. H3 trimethyl K9 and H3 acetyl K9 chromatin modifications are associated with class switch recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:5288–93.
Pei H, Wu X, Liu T, Yu K, Jelinek DF, Lou Z. The histone methyltransferase MMSET regulates class switch recombination. J Immunol. 2013;190:756–63.
Lee S, Lee DK, Dou Y, Lee J, Lee B, Kwak E, et al. Coactivator as a target gene specificity determinant for histone H3 lysine 4 methyltransferases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:15392–7.
Ansari KI, Mandal SS. Mixed lineage leukemia: roles in gene expression, hormone signaling and mRNA processing. FEBS J. 2010;277:1790–804.
Ansari KI, Hussain I, Shrestha B, Kasiri S, Mandal SS. HOXC6 is transcriptionally regulated via coordination of MLL histone methylase and estrogen receptor in an estrogen environment. J Mol Biol. 2011;411:334–49.
Guo Y, Brown C, Ortiz C, Noelle RJ. Leukocyte homing, fate, and function are controlled by retinoic acid. Physiol Rev. 2015;95:125–48.
Kovats S. Estrogen receptors regulate innate immune cells and signaling pathways. Cell Immunol. 2015;294:63–9.
Ochs H. Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID): new genetic insight and unanswered questions. Clin Exp Immunol. 2014;178:5–6.
Acknowledgments
Thanks are due to Prof. L.D. Notarangelo for his critical reading of the manuscript and to Dr. A. Pilotta for sharing clinical data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Stefano Stagi and Anna Virginia Gulino equally contributed to the preparation of this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stagi, S., Gulino, A.V., Lapi, E. et al. Epigenetic control of the immune system: a lesson from Kabuki syndrome. Immunol Res 64, 345–359 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-015-8707-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-015-8707-4