Abstract
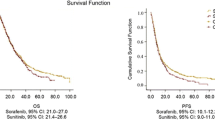
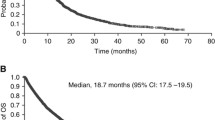
Sorafenib and sunitinib are inhibitors of receptor protein tyrosine kinases (TKIs) and are approved for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). Although the mTOR inhibitor everolimus is effective for the treatment of patients who have failed TKI therapy, it is important to consider all available treatment options before switching therapy mode of action. Herein, we report outcomes in patients with mRCC switched to sorafenib following disease progression on sunitinib treatment. The medical records of 35 patients treated between November 2006 and November 2009 at two large referral centers in Greece were retrospectively analyzed for time-to-progression (TTP), overall survival (OS), and tolerability of sorafenib after sunitinib. Median TTP and OS on sorafenib were 4.9 and 11.5 months, respectively. Among 33 patients evaluable for tumor response, three had a partial response and 17 achieved disease stabilization (objective response rate 8.5%; total clinical benefit rate 57%). Sorafenib was well tolerated, with mostly grade 1/2 adverse events and no treatment-related deaths. Sorafenib was effective and well tolerated in this group of patients. The TTP with sorafenib following sunitinib was comparable to outcomes reported previously, providing further support that TKIs should be used in sequence before switching to an mTOR inhibitor.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, et al. Estimates of the cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2006. Ann Oncol. 2007;18:581–92.
Lam JS, Leppert JT, Belldegrun AS, Figlin RA. Novel approaches in the therapy of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. World J Urol. 2005;23:202–12.
Thompson RH, et al. Renal cell carcinoma in young and old patients—is there a difference? J Urol. 2008;180:1262–6.
Escudier B, et al. for the TARGET Study Group. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:125–34.
Escudier B, et al. for the AVOREN trial investigators. Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a for treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, double-blind phase III trial. Lancet. 2007;370:2103–11.
Motzer RJ, et al. for the RECORD-1 study group. Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Lancet. 2008;372:449–56.
Hudes G, et al. Global ARCC trial: temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2271–81.
Motzer RJ, et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:115–24.
Sternberg CN, et al. A randomized, double-blind phase III study of pazopanib in treatment-naive and cytokine-pretreated patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1061–8.
EU SmPC Nexavar. Available at: http://emc.medicines.org.uk/medicine/18520/SPC/Nexavar+200mg+film-coated+tablets/ (2010). Accessed Aug 2010.
EU SmPC Sutent. Available at: http://emc.medicines.org.uk/medicine/18531/SPC/SUTENT+12.5mg%2c+25mg%2c+37.5mg+and+50mg+Hard+Capsules/ (2010) Accessed Jul 2010.
EU SmPC Torisel. Available at: http://emc.medicines.org.uk/medicine/21260/SPC/TORISEL+25+mg+ml+concentrate+and+diluent+for+solution+for+infusion/ (2010) Accessed Jul 2010.
EU SmPC Avastin. Available at: http://emc.medicines.org.uk/medicine/15748/SPC/Avastin+25mg+ml+concentrate+for+solution+for+infusion/ (2010). Accessed Aug 2010.
US PI Votrient. FDA 2009. Available at: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/022465lbl.pdf (2009). Accessed Jul 2010.
EU SmPC Afinitor. Available at: http://emc.medicines.org.uk/medicine/22281/SPC/Afinitor+Tablets/ (2010) Accessed Jul 2010.
Choueiri TK, et al. Treatment and dosing patterns for angiogenesis inhibitor (AIS) therapies in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). Ann Oncol. 2008;19:viii191. abstract 593P.
Dudek AZ, et al. Sequential therapy with sorafenib and sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2009;115:61–7.
Porta C, et al. Retrospective analysis of the sequential use of sorafenib and sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Eur Urol Suppl. 2009;8:183. abstract 252.
Sablin MP, et al. Sequential sorafenib and sunitinib for renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2009;182:29–34.
Tamaskar I, et al. Antitumor effects of sunitinib or sorafenib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who received prior antiangiogenic therapy. J Urol. 2008;179:81–6.
Richter S, et al. Second-line treatment of progressive metastatic renal cell cancer with temsirolimus following first-line therapy with sunitinib or sorafenib. Onkologie. 2008;31(Suppl. 4):Abstract V684.
Therasse P, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European organization for research and treatment of cancer, National cancer institute of the United States, National cancer institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:205–16.
Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v4.0. Available at: http://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm#ctc_40 (2010) Accessed Sep 2010.
Karaman MW, et al. A quantitative analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26:127–32.
National Comprehensive Cancer network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology kidney cancer v.2.2009. Available at www.nccn.org (2009) Accessed Jun 2009.
Kontovinis LF, et al. Sunitinib treatment for patients with clear-cell metastatic renal cell carcinoma: clinical outcomes and plasma angiogenesis markers. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:82.
Di Lorenzo G, et al. Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with sunitinib-refractory metastatic renal cell cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4469–74.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank 7.4 Limited for their editorial support (supported by Bayer Schering Pharma). The authors are grateful to Bayer Schering Pharma for providing financial support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no relevant conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kontovinis, L., Laschos, K., Karadimou, A. et al. Sequential treatment with sorafenib and sunitinib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: clinical outcomes from a retrospective clinical study. Med Oncol 29, 750–754 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9815-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9815-6