Abstract
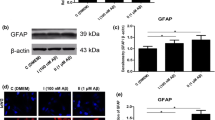
Our earlier studies showed that insulin receptor (IR) dysfunction along with neuroinflammation and amyloidogenesis played a major role in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced toxicity in astrocytes. N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist-memantine shows beneficial effects in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathology. However, the protective molecular and cellular mechanism of memantine in astrocytes is not properly understood. Therefore, the present study was undertaken to investigate the effect of memantine on insulin receptors, neurotrophic factors, neuroinflammation, and amyloidogenesis in STZ-treated astrocytes. STZ (100 μM) treatment for 24 h in astrocytes resulted significant decrease in brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), and insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) expression in astrocytes. Treatment with memantine (1–10 μM) improved STZ-induced neurotrophic factor decline (BDNF, GDNF) along with IR dysfunction as evidenced by a significant increase in IR protein expression, phosphorylation of IRS-1, Akt, and GSK-3 α/β in astrocytes. Further, memantine attenuated STZ-induced amyloid precursor protein (APP), β-site APP-cleaving enzyme-1 and amyloid-β1–42 expression and restored IDE expression in astrocytes. In addition, memantine also displays protective effects against STZ-induced astrocyte activation showed by reduction of inflammatory markers, nuclear factor kappa-B translocation, glial fibrillary acidic protein, cyclooxygenase-2, tumor necrosis factor-α level, and oxidative-nitrostative stress. The results suggest that besides the NMDA receptor antagonisic activity, effect on astroglial IR and neurotrophic factor may also be an important factor in the beneficial effect of memantine in AD pathology.

Novel neuroprotective mechanisms of memenatine in streptozotocin-induced toxicity in astrocytes










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maragakis NJ, Rothstein JD (2006) Mechanisms of disease: astrocytes in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2(12):679–689
Halassa MM, Haydon PG (2010) Integrated brain circuits: astrocytic networks modulate neuronal activity and behavior. Annu Rev Physiol 72:335–355
Henneberger C, Papouin T, Oliet SH, Rusakov DA (2010) Long-term potentiation depends on release of D-serine from astrocytes. Nature 463(7278):232–236
Perea G, Navarrete M, Araque A (2009) Tripartite synapses: astrocytes process and control synaptic information. Trends Neurosci 32(8):421–431
Desagher S, Glowinski J, Premont J (1996) Astrocytes protect neurons from hydrogen peroxide toxicity. J Neurosci 16(8):2553–2562
Chen LW, Yung KL, Chan YS (2005) Reactive astrocytes as potential manipulation targets in novel cell replacement therapy of Parkinson’s disease. Curr Drug Targets 6(7):821–833
Chen PS, Peng GS, Li G, Yang S, Wu X, Wang CC, Wilson B, Lu RB et al (2006) Valproate protects dopaminergic neurons in midbrain neuron/glia cultures by stimulating the release of neurotrophic factors from astrocytes. Mol Psychiatry 11(12):1116–1125
Yeh CW, Yeh SH, Shie FS, Lai WS, Liu HK, Tzeng TT, Tsay HJ, Shiao YJ (2015) Impaired cognition and cerebral glucose regulation are associated with astrocyte activation in the parenchyma of metabolically stressed APPswe/PS1dE9 mice. Neurobiol Aging.
Sofroniew MV, Vinters HV (2010) Astrocytes: biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol 119(1):7–35
Rajasekar N, Dwivedi S, Tota SK, Kamat PK, Hanif K, Nath C, Shukla R (2013) Neuroprotective effect of curcumin on okadaic acid induced memory impairment in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 715(1-3):381–394
Agrawal R, Tyagi E, Shukla R, Nath C (2011) Insulin receptor signaling in rat hippocampus: a study in STZ (ICV) induced memory deficit model. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 21(3):261–273
Steen E, Terry BM, Rivera EJ, Cannon JL, Neely TR, Tavares R, Xu XJ, Wands JR et al (2005) Impaired insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression and signaling mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease--is this type 3 diabetes? J Alzheimers Dis 7(1):63–80
Simpson JE, Ince PG, Shaw PJ, Heath PR, Raman R, Garwood CJ, Gelsthorpe C, Baxter L et al (2011) Microarray analysis of the astrocyte transcriptome in the aging brain: relationship to Alzheimer’s pathology and APOE genotype. Neurobiol Aging 32(10):1795–1807
Cantley LC (2002) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 296(5573):1655–1657
Wang X, Zheng W, Xie JW, Wang T, Wang SL, Teng WP, Wang ZY (2010) Insulin deficiency exacerbates cerebral amyloidosis and behavioral deficits in an Alzheimer transgenic mouse model. Mol Neurodegener 5:46
Barilar JO, Knezovic A, Grunblatt E, Riederer P, Salkovic-Petrisic M (2015) Nine-month follow-up of the insulin receptor signalling cascade in the brain of streptozotocin rat model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 122(4):565–576
Yang LB, Lindholm K, Yan R, Citron M, Xia W, Yang XL, Beach T, Sue L et al (2003) Elevated beta-secretase expression and enzymatic activity detected in sporadic Alzheimer disease. Nat Med 9(1):3–4
Frisardi V, Solfrizzi V, Imbimbo PB, Capurso C, D’Introno A, Colacicco AM, Vendemiale G, Seripa D et al (2010) Towards disease-modifying treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: drugs targeting beta-amyloid. Curr Alzheimer Res 7(1):40–55
Alley GM, Bailey JA, Chen D, Ray B, Puli LK, Tanila H, Banerjee PK, Lahiri DK (2010) Memantine lowers amyloid-beta peptide levels in neuronal cultures and in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. J Neurosci Res 88(1):143–154
Biswas A, Kurkute P, Saleem S, Jana B, Mohapatra S, Mondal P, Adak A, Ghosh S et al (2015) Novel Hexapeptide Interacts with Tubulin and Microtubules, Inhibits Abeta Fibrillation, and Shows Significant Neuroprotection. ACS Chem Neurosci 6(8):1309–1316
Wang Y, Li M, Tang J, Song M, Xu X, Xiong J, Li J, Bai Y (2011) Glucocorticoids facilitate astrocytic amyloid-beta peptide deposition by increasing the expression of APP and BACE1 and decreasing the expression of amyloid-beta-degrading proteases. Endocrinology 152(7):2704–2715
Rajasekar N, Dwivedi S, Nath C, Hanif K, Shukla R (2014) Protection of streptozotocin induced insulin receptor dysfunction, neuroinflammation and amyloidogenesis in astrocytes by insulin. Neuropharmacology 86:337–352
Akiyama H, Mori H, Saido T, Kondo H, Ikeda K, McGeer PL (1999) Occurrence of the diffuse amyloid beta-protein (Abeta) deposits with numerous Abeta-containing glial cells in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Glia 25(4):324–331
Rodriguez JJ, Olabarria M, Chvatal A, Verkhratsky A (2009) Astroglia in dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Differ 16(3):378–385
Saido TC (1998) Alzheimer’s disease as proteolytic disorders: anabolism and catabolism of beta-amyloid. Neurobiol Aging 19(1 Suppl):S69–S75
Farris W, Mansourian S, Chang Y, Lindsley L, Eckman EA, Frosch MP, Eckman CB, Tanzi RE et al (2003) Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid beta-protein, and the beta-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(7):4162–4167
Heni M, Hennige AM, Peter A, Siegel-Axel D, Ordelheide AM, Krebs N, Machicao F, Fritsche A et al (2011) Insulin promotes glycogen storage and cell proliferation in primary human astrocytes. PLoS ONE 6(6):e21594
Reisberg B, Doody R, Stoffler A, Schmitt F, Ferris S, Mobius HJ (2003) Memantine in moderate-to-severe Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 348(14):1333–1341
Wu HM, Tzeng NS, Qian L, Wei SJ, Hu X, Chen SH, Rawls SM, Flood P et al (2009) Novel neuroprotective mechanisms of memantine: increase in neurotrophic factor release from astroglia and anti-inflammation by preventing microglial activation. Neuropsychopharmacology 34(10):2344–2357
Kamat PK, Rai S, Swarnkar S, Shukla R, Ali S, Najmi AK, Nath C (2013) Okadaic acid-induced Tau phosphorylation in rat brain: role of NMDA receptor. Neuroscience 238:97–113
Rai S, Kamat PK, Nath C, Shukla R (2013) A study on neuroinflammation and NMDA receptor function in STZ (ICV) induced memory impaired rats. J Neuroimmunol 254(1-2):1–9
Lipton SA (2007) Pathologically-activated therapeutics for neuroprotection: mechanism of NMDA receptor block by memantine and S-nitrosylation. Curr Drug Targets 8(5):621–632
Zhao X, Marszalec W, Toth PT, Huang J, Yeh JZ, Narahashi T (2006) In vitro galantamine-memantine co-application: mechanism of beneficial action. Neuropharmacology 51(7-8):1181–1191
Arif M, Chikuma T, Ahmed MM, Nakazato M, Smith MA, Kato T (2009) Effects of memantine on soluble Alphabeta(25-35)-induced changes in peptidergic and glial cells in Alzheimer’s disease model rat brain regions. Neuroscience 164(3):1199–1209
Niranjan R, Rajasekar N, Nath C, Shukla R (2012) The effect of guggulipid and nimesulide on MPTP-induced mediators of neuroinflammation in rat astrocytoma cells, C6. Chem Biol Interact 200(2-3):73–83
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Tiwari RL, Singh V, Singh A, Barthwal MK (2011) IL-1R-associated kinase-1 mediates protein kinase Cdelta-induced IL-1beta production in monocytes. J Immunol 187(5):2632–2645
Niranjan R, Nagarajan R, Hanif K, Nath C, Shukla R (2014) LPS induces mediators of neuroinflammation, cell proliferation, and GFAP expression in human astrocytoma cells U373MG: the anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative effect of guggulipid. Neurol Sci 35(3):409–414
Chadwick W, Mitchell N, Caroll J, Zhou Y, Park SS, Wang L, Becker KG, Zhang Y et al (2011) Amitriptyline-mediated cognitive enhancement in aged 3xTg Alzheimer’s disease mice is associated with neurogenesis and neurotrophic activity. PLoS ONE 6(6):e21660
Revilla S, Ursulet S, Alvarez-Lopez MJ, Castro-Freire M, Perpina U, Garcia-Mesa Y, Bortolozzi A, Gimenez-Llort L et al (2014) Lenti-GDNF gene therapy protects against Alzheimer’s disease-like neuropathology in 3xTg-AD mice and MC65 cells. CNS Neurosci Ther 20(11):961–972
Phillips HS, Hains JM, Armanini M, Laramee GR, Johnson SA, Winslow JW (1991) BDNF mRNA is decreased in the hippocampus of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 7(5):695–702
Konishi Y, Yang LB, He P, Lindholm K, Lu B, Li R, Shen Y (2014) Deficiency of GDNF Receptor GFRalpha1 in Alzheimer’s Neurons Results in Neuronal Death. J Neurosci 34(39):13127–13138
Sim YJ (2014) Treadmill exercise alleviates impairment of spatial learning ability through enhancing cell proliferation in the streptozotocin-induced Alzheimer’s disease rats. J Exerc Rehabil 10(2):81–88
Marvanova M, Lakso M, Pirhonen J, Nawa H, Wong G, Castren E (2001) The neuroprotective agent memantine induces brain-derived neurotrophic factor and trkB receptor expression in rat brain. Mol Cell Neurosci 18(3):247–258
Caumont AS, Octave JN, Hermans E (2006) Amantadine and memantine induce the expression of the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in C6 glioma cells. Neurosci Lett 394(3):196–201
Chu JM, Lee DK, Wong DP, Wong RN, Yung KK, Cheng CH, Yue KK (2014) Ginsenosides attenuate methylglyoxal-induced impairment of insulin signaling and subsequent apoptosis in primary astrocytes. Neuropharmacology 85:215–223
Ang LC, Bhaumick B, Munoz DG, Sass J, Juurlink BH (1992) Effects of astrocytes, insulin and insulin-like growth factor I on the survival of motoneurons in vitro. J Neurol Sci 109(2):168–172
Craft S (2006) Insulin resistance syndrome and Alzheimer disease: pathophysiologic mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 20(4):298–301
Tsuchida A, Nakagawa T, Itakura Y, Ichihara J, Ogawa W, Kasuga M, Taiji M, Noguchi H (2001) The effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on insulin signal transduction in the liver of diabetic mice. Diabetologia 44(5):555–566
Yamada M, Ohnishi H, Sano S, Nakatani A, Ikeuchi T, Hatanaka H (1997) Insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1 and IRS-2 are tyrosine-phosphorylated and associated with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor in cultured cerebral cortical neurons. J Biol Chem 272(48):30334–30339
Agrawal R, Mishra B, Tyagi E, Nath C, Shukla R (2010) Effect of curcumin on brain insulin receptors and memory functions in STZ (ICV) induced dementia model of rat. Pharmacol Res 61(3):247–252. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2009.12.008
Agrawal R, Tyagi E, Shukla R, Nath C (2009) A study of brain insulin receptors, AChE activity and oxidative stress in rat model of ICV STZ induced dementia. Neuropharmacology 56(4):779–787
Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich M, Hemmings BA (1995) Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature 378(6559):785–789
Ponce-Lopez T, Liy-Salmeron G, Hong E, Meneses A (2011) Lithium, phenserine, memantine and pioglitazone reverse memory deficit and restore phospho-GSK3beta decreased in hippocampus in intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced memory deficit model. Brain Res 1426:73–85
De Sarno P, Bijur GN, Zmijewska AA, Li X, Jope RS (2006) In vivo regulation of GSK3 phosphorylation by cholinergic and NMDA receptors. Neurobiol Aging 27(3):413–422
Blalock EM, Geddes JW, Chen KC, Porter NM, Markesbery WR, Landfield PW (2004) Incipient Alzheimer’s disease: microarray correlation analyses reveal major transcriptional and tumor suppressor responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(7):2173–2178
Phiel CJ, Wilson CA, Lee VM, Klein PS (2003) GSK-3alpha regulates production of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-beta peptides. Nature 423(6938):435–439
Ly PT, Wu Y, Zou H, Wang R, Zhou W, Kinoshita A, Zhang M, Yang Y et al (2013) Inhibition of GSK3beta-mediated BACE1 expression reduces Alzheimer-associated phenotypes. J Clin Invest 123(1):224–235
Zhao J, O’Connor T, Vassar R (2011) The contribution of activated astrocytes to Abeta production: implications for Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. J Neuroinflammation 8:150
Leuba G, Wernli G, Vernay A, Kraftsik R, Mohajeri MH, Saini KD (2005) Neuronal and nonneuronal quantitative BACE immunocytochemical expression in the entorhinohippocampal and frontal regions in Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 19(4):171–183
Pizzi M, Boroni F, Bianchetti A, Moraitis C, Sarnico I, Benarese M, Goffi F, Valerio A et al (2002) Expression of functional NR1/NR2B-type NMDA receptors in neuronally differentiated SK-N-SH human cell line. Eur J Neurosci 16(12):2342–2350
Okamoto S, Sherman K, Lipton SA (1999) Absence of binding activity of neuron-restrictive silencer factor is necessary, but not sufficient for transcription of NMDA receptor subunit type 1 in neuronal cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 74(1-2):44–54
Lipton SA (2004) Failures and successes of NMDA receptor antagonists: molecular basis for the use of open-channel blockers like memantine in the treatment of acute and chronic neurologic insults. NeuroRx 1(1):101–110
Hostetler KY, Richman DD (1982) Studies on the mechanism of phospholipid storage induced by amantadine and chloroquine in Madin Darby canine kidney cells. Biochem Pharmacol 31(23):3795–3799
Honegger UE, Quack G, Wiesmann UN (1993) Evidence for lysosomotropism of memantine in cultured human cells: cellular kinetics and effects of memantine on phospholipid content and composition, membrane fluidity and beta-adrenergic transmission. Pharmacol Toxicol 73(4):202–208
Caccamo A, Oddo S, Sugarman MC, Akbari Y, LaFerla FM (2005) Age- and region-dependent alterations in Abeta-degrading enzymes: implications for Abeta-induced disorders. Neurobiol Aging 26(5):645–654
Miller BC, Eckman EA, Sambamurti K, Dobbs N, Chow KM, Eckman CB, Hersh LB, Thiele DL (2003) Amyloid-beta peptide levels in brain are inversely correlated with insulysin activity levels in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(10):6221–6226
Mulder SD, Veerhuis R, Blankenstein MA, Nielsen HM (2012) The effect of amyloid associated proteins on the expression of genes involved in amyloid-beta clearance by adult human astrocytes. Exp Neurol 233(1):373–379
Shingo AS, Kanabayashi T, Murase T, Kito S (2012) Cognitive decline in STZ-3V rats is largely due to dysfunctional insulin signalling through the dentate gyrus. Behav Brain Res 229(2):378–383
Leissring MA, Farris W, Chang AY, Walsh DM, Wu X, Sun X, Frosch MP, Selkoe DJ (2003) Enhanced proteolysis of beta-amyloid in APP transgenic mice prevents plaque formation, secondary pathology, and premature death. Neuron 40(6):1087–1093
Shingo AS, Kanabayashi T, Kito S, Murase T (2013) Intracerebroventricular administration of an insulin analogue recovers STZ-induced cognitive decline in rats. Behav Brain Res 241:105–111
Bedse G, Di Domenico F, Serviddio G, Cassano T (2015) Aberrant insulin signaling in Alzheimer’s disease: current knowledge. Front Neurosci 9:204
Nimmerjahn A, Kirchhoff F, Helmchen F (2005) Resting microglial cells are highly dynamic surveillants of brain parenchyma in vivo. Science 308(5726):1314–1318
Rossi DJ, Brady JD, Mohr C (2007) Astrocyte metabolism and signaling during brain ischemia. Nat Neurosci 10(11):1377–1386
Swarnkar S, Singh S, Goswami P, Mathur R, Patro IK, Nath C (2012) Astrocyte activation: a key step in rotenone induced cytotoxicity and DNA damage. Neurochem Res 37(10):2178–2189
Niranjan R, Nath C, Shukla R (2011) Guggulipid and nimesulide differentially regulated inflammatory genes mRNA expressions via inhibition of NF-kB and CHOP activation in LPS-stimulated rat astrocytoma cells, C6. Cell Mol Neurobiol 31(5):755–764
Kashon ML, Ross GW, O’Callaghan JP, Miller DB, Petrovitch H, Burchfiel CM, Sharp DS, Markesbery WR et al (2004) Associations of cortical astrogliosis with cognitive performance and dementia status. J Alzheimers Dis 6(6):595–604, discussion 673-581
Acknowledgments
Financial support from DBT (BT/PR4012/MED/30/672/201 Dated 28/03/2012) and SRF to Rajasekar N from CSIR, New Delhi, India, are gratefully acknowledged. Authors are also thankful to Dr. A.K. Balapure and their team for providing rat astrocytoma cell line (C6).
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict of interest among any of the contributing authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is in accordance with CSIR-CDRI communication no: 9141
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajasekar, N., Nath, C., Hanif, K. et al. Inhibitory Effect of Memantine on Streptozotocin-Induced Insulin Receptor Dysfunction, Neuroinflammation, Amyloidogenesis, and Neurotrophic Factor Decline in Astrocytes. Mol Neurobiol 53, 6730–6744 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9576-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9576-5