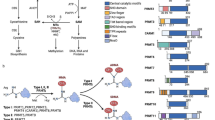
Abstract
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is a dynamic reversible methylation modification of the adenosine N6 position and is the most common chemical epigenetic modification among mRNA post-transcriptional modifications, including methylation, demethylation, and recognition. Post-transcriptional modification involves multiple protein molecules, including METTL3, METTL14, WTAP, KIAA1429, ALKBH5, YTHDF1/2/3, and YTHDC1/2. m6A-related proteins are expressed in almost all cells. However, the abnormal expression of m6A-related proteins may occur in the nervous system, thereby affecting neuritogenesis, brain volume, learning and memory, memory formation and consolidation, etc., and is implicated in the development of diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, depression, epilepsy, and brain tumors. This review focuses on the functions of m6A in the development of central nervous system diseases, thus contributing to a deeper understanding of disease pathogenesis and providing potential clinical therapeutic targets for neurological diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang Y, Chen K, Song B, Ma J, Wu X, Xu Q, Wei Z, Su J, Liu G, Rong R, Lu Z, de Magalhaes JP, Rigden DJ, Meng J (2021) m6A-Atlas: a comprehensive knowledgebase for unraveling the N6-methyladenosine (m6A) epitranscriptome. Nucleic Acids Res 49(D1):D134–D143. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa692
Wu Z, Shi Y, Lu M, Song M, Yu Z, Wang J, Wang S, Ren J, Yang YG, Liu GH, Zhang W, Ci W, Qu J (2020) METTL3 counteracts premature aging via m6A-dependent stabilization of MIS12 mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res 48(19):11083–11096. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa816
Zhang Z, Wang Q, Zhang M, Zhang W, Zhao L, Yang C, Wang B, Jiang K, Ye Y, Shen Z, Wang S (2021) Comprehensive analysis of the transcriptome-wide m6A methylome in colorectal cancer by MeRIP sequencing. Epigenetics 16(4):425–435. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592294.2020.1805684
Rasheed M, Liang J, Wang C, Deng Y, Chen Z. Epigenetic regulation of neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094956
Livneh I, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Amariglio N, Rechavi G, Dominissini D (2019) The m6A epitranscriptome: transcriptome plasticity in brain development and function. Nat Rev Neurosci 21(1):36–51. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-019-0244-z
Engel M, Eggert C, Kaplick PM, Eder M, Roh S, Tietze L, Namendorf C, Arloth J, Weber P, Rex-Haffner M, Geula S, Jakovcevski M, Hanna JH, Leshkowitz D, Uhr M, Wotjak CT, Schmidt MV, Deussing JM, Binder EB, Chen A. The role of m(6)A/m-RNA methylation in stress response regulation. Neuron. 2018;99(2):389–403 e389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.07.009
Bale TL (2015) Epigenetic and transgenerational reprogramming of brain development. Nat Rev Neurosci 16(6):332–344. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3818
Huang AZ, Delaidelli A, Sorensen PH (2020) RNA modifications in brain tumorigenesis. Acta Neuropathol Commun 8(1):64. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-020-00941-6
Shafik AM, Zhang F, Guo Z, Dai Q, Pajdzik K, Li Y, Kang Y, Yao B, Wu H, He C, Allen EG, Duan R, Jin P (2021) N6-methyladenosine dynamics in neurodevelopment and aging, and its potential role in Alzheimer’s disease. Genome Biol 22(1):17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-020-02249-z
Armstrong MJ, Jin Y, Allen EG, Jin P (2019) Diverse and dynamic DNA modifications in brain and diseases. Hum Mol Genet 28(R2):R241–R253. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddz179
Shi H, Zhang X, Weng YL, Lu Z, Liu Y, Lu Z, Li J, Hao P, Zhang Y, Zhang F, Wu Y, Delgado JY, Su Y, Patel MJ, Cao X, Shen B, Huang X, Ming GL, Zhuang X, Song H, He C, Zhou T (2018) m(6)A facilitates hippocampus-dependent learning and memory through YTHDF1. Nature 563(7730):249–253. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0666-1
Du T, Li G, Yang J, Ma K (2020) RNA demethylase Alkbh5 is widely expressed in neurons and decreased during brain development. Brain Res Bull 163:150–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.07.018
Shi JB, Wang DY, Xia Q, Gao X. The effects of m (6)A modification in central nervous system function and disease. Yi Chuan. 2020;42(12):1156–1167. https://doi.org/10.16288/j.yczz.20-233
Leonetti AM, Chu MY, Ramnaraign FO, Holm S, Walters BJ. An emerging role of m6A in memory: a case for translational priming. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207447
Mathoux J, Henshall DC, Brennan GP (2021) Regulatory mechanisms of the RNA modification mA and significance in brain function in health and disease. Front Cell Neurosci 15:671932. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.671932
Mathoux J, Henshall DC, Brennan GP (2021) Regulatory mechanisms of the RNA modification m(6)A and significance in brain function in health and disease. Front Cell Neurosci 15:671932. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.671932
Weng YL, Wang X, An R, Cassin J, Vissers C, Liu Y, Liu Y, Xu T, Wang X, Wong SZH, Joseph J, Dore LC, Dong Q, Zheng W, Jin P, Wu H, Shen B, Zhuang X, He C, Liu K, Song H, Ming GL. Epitranscriptomic m(6)A regulation of axon regeneration in the adult mammalian nervous system. Neuron. 2018;97(2):313–325 e316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.12.036
Yang Y, Feng Y, Hu Y, Liu J, Shi H, Zhao R (2021) Exposure to constant light impairs cognition with FTO inhibition and m(6)A-dependent TrkappaB repression in mouse hippocampus. Environ Pollut 283:117037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117037
Westmark CJ, Maloney B, Alisch RS, Sokol DK, Lahiri DK (2020) FMRP regulates the nuclear export of Adam9 and Psen1 mRNAs: secondary analysis of an N(6)-methyladenosine dataset. Sci Rep 10(1):10781. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66394-y
Huang X, Lv D, Yang X, Li M, Zhang H (2020) m6A RNA methylation regulators could contribute to the occurrence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Cell Mol Med 24(21):12706–12715. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15848
Yu J, Chen M, Huang H, Zhu J, Song H, Zhu J, Park J, Ji SJ (2018) Dynamic m6A modification regulates local translation of mRNA in axons. Nucleic Acids Res 46(3):1412–1423. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1182
Bufill E, Ribosa-Nogue R, Blesa R. The therapeutic potential of epigenetic modifications in Alzheimer’s disease [M]// Huang X. Alzheimer’s Disease: Drug Discovery. Brisbane (AU): 2020.
Xue A, Huang Y, Li M, Wei Q, Bu Q (2021) Comprehensive analysis of differential m6A RNA methylomes in the hippocampus of cocaine-conditioned mice. Mol Neurobiol 58(8):3759–3768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02363-4
Huang H, Camats-Perna J, Medeiros R, Anggono V, Widagdo J. Altered expression of the m6A methyltransferase METTL3 in Alzheimer’s disease. eneuro. 2020;7(5). https://doi.org/10.1523/eneuro.0125-20.2020
Chen XY, Zhang J, Zhu JS (2019) The role of m(6)A RNA methylation in human cancer. Mol Cancer 18(1):103. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1033-z
Li M, Zhao X, Wang W, Shi H, Pan Q, Lu Z, Perez SP, Suganthan R, He C, Bjoras M, Klungland A (2018) Ythdf2-mediated m(6)A mRNA clearance modulates neural development in mice. Genome Biol 19(1):69. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-018-1436-y
Choi H, Baek S, Cho B, Kim S, Kim J, Chang Y, Shin J, Kim J (2020) Epitranscriptomic N(6)-methyladenosine modification is required for direct lineage reprogramming into neurons. ACS Chem Biol 15(8):2087–2097. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.0c00265
Ryu J, Hwang NS, Park HH, Park TH (2020) Protein-based direct reprogramming of fibroblasts to neuronal cells using 30Kc19 protein and transcription factor Ascl1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 121:105717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2020.105717
Qiu X, He H, Huang Y, Wang J, Xiao Y (2020) Genome-wide identification of m(6)A-associated single-nucleotide polymorphisms in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 737:135315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135315
Han M, Liu Z, Xu Y, Liu X, Wang D, Li F, Wang Y, Bi J (2020) Abnormality of m6A mRNA methylation is involved in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurosci 14:98. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00098
Pan T, Wu F, Li L, Wu S, Zhou F, Zhang P, Sun C, Xia L. The role m6A RNA methylation is CNS development and glioma pathogenesis. Molecular Brain. 2021;14(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-021-00831-5
Marino BLB, de Souza LR, Sousa KPA, Ferreira JV, Padilha EC, da Silva C, Taft CA, Hage-Melim LIS (2020) Parkinson’s disease: a review from pathophysiology to treatment. Mini Rev Med Chem 20(9):754–767. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557519666191104110908
Sun L, Zhang J, Chen W, Chen Y, Zhang X, Yang M, Xiao M, Ma F, Yao Y, Ye M, Zhang Z, Chen K, Chen F, Ren Y, Ni S, Zhang X, Yan Z, Sun ZR, Zhou HM, Yang H, Xie S, Haque ME, Huang K, Yang Y (2020) Attenuation of epigenetic regulator SMARCA4 and ERK-ETS signaling suppresses aging-related dopaminergic degeneration. Aging Cell 19(9):e13210. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13210
Henderson AR, Wang Q, Meechoovet B, Siniard AL, Naymik M, De Both M, Huentelman MJ, Caselli RJ, Driver-Dunckley E, Dunckley T (2021) DNA Methylation and expression profiles of whole blood in Parkinson’s disease. Front Genet 12:640266. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.640266
Mohd Murshid N, Aminullah Lubis F, Makpol S (2020) Epigenetic Changes and its intervention in age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00979-z
Chen X, Yu C, Guo M, Zheng X, Ali S, Huang H, Zhang L, Wang S, Huang Y, Qie S, Wang J (2019) Down-regulation of m6A mRNA methylation is involved in dopaminergic neuronal death. ACS Chem Neurosci 10(5):2355–2363. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00657
Koranda JL, Dore L, Shi H, Patel MJ, Vaasjo LO, Rao MN, Chen K, Lu Z, Yi Y, Chi W, He C, Zhuang X. Mettl14 is essential for epitranscriptomic regulation of striatal function and learning. Neuron. 2018;99(2):283–292 e285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.06.007
Zhang Y, Geng X, Li Q, Xu J, Tan Y, Xiao M, Song J, Liu F, Fang C, Wang H (2020) m6A modification in RNA: biogenesis, functions and roles in gliomas. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 39(1):192. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-020-01706-8
Wei W, Huo B, Shi X (2019) miR-600 inhibits lung cancer via downregulating the expression of METTL3. Cancer Manag Res 11:1177–1187. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S181058
Selberg S, Yu LY, Bondarenko O, Kankuri E, Seli N, Kovaleva V, Herodes K, Saarma M, Karelson M. Small-molecule inhibitors of the RNA M6A demethylases FTO potently support the survival of dopamine neurons. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094537
Qin L, Min S, Shu L, Pan H, Zhong J, Guo J, Sun Q, Yan X, Chen C, Tang B, Xu Q. Genetic analysis of N6-methyladenosine modification genes in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2020;93:143 e149–143 e113. "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2020.03.018
Hess ME, Hess S, Meyer KD, Verhagen LA, Koch L, Bronneke HS, Dietrich MO, Jordan SD, Saletore Y, Elemento O, Belgardt BF, Franz T, Horvath TL, Ruther U, Jaffrey SR, Kloppenburg P, Bruning JC (2013) The fat mass and obesity associated gene (Fto) regulates activity of the dopaminergic midbrain circuitry. Nat Neurosci 16(8):1042–1048. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3449
Bai L, Tang Q, Zou Z, Meng P, Tu B, Xia Y, Cheng S, Zhang L, Yang K, Mu S, Wang X, Qin X, Lv B, Cao X, Qin Q, Jiang X, Chen C (2018) m6A demethylase FTO regulates dopaminergic neurotransmission deficits caused by arsenite. Toxicol Sci 165(2):431–446. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfy172
Yang P, Perlmutter JS, Benzinger TLS, Morris JC, Xu J. Dopamine D3 receptor: a neglected participant in Parkinson disease pathogenesis and treatment? Ageing Res Rev. 2020;57:100994. , https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2019.100994
Bono F, Mutti V, Fiorentini C, Missale C. Dopamine D3 Receptor heteromerization: implications for neuroplasticity and neuroprotection. Biomolecules. 2020;10(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10071016
Fan SF, Chao PL, Lin AM (2010) Arsenite induces oxidative injury in rat brain: synergistic effect of iron. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1199:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05170.x
Ma C, Chang M, Lv H, Zhang ZW, Zhang W, He X, Wu G, Zhao S, Zhang Y, Wang D, Teng X, Liu C, Li Q, Klungland A, Niu Y, Song S, Tong WM (2018) RNA m(6)A methylation participates in regulation of postnatal development of the mouse cerebellum. Genome Biol 19(1):68. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-018-1435-z
Kurt S, Tomatir AG, Tokgun PE, Oncel C (2020) Altered expression of long non-coding RNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 57(12):5352–5361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-020-02106-x
Balmik AA, Chinnathambi S. Methylation as a key regulator of Tau aggregation and neuronal health in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Commun Signal. 2021;19(1):51. , https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-021-00732-z
Wang F, Chen D, Wu P, Klein C, Jin C (2019) Formaldehyde, epigenetics, and Alzheimer’s disease. Chem Res Toxicol 32(5):820–830. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.9b00090
Chokkalla AK, Mehta SL, Vemuganti R (2020) Epitranscriptomic regulation by m(6)A RNA methylation in brain development and diseases. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 40(12):2331–2349. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X20960033
Wang Y, Li Y, Yue M, Wang J, Kumar S, Wechsler-Reya RJ, Zhang Z, Ogawa Y, Kellis M, Duester G, Zhao JC (2018) N(6)-methyladenosine RNA modification regulates embryonic neural stem cell self-renewal through histone modifications. Nat Neurosci 21(2):195–206. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0057-1
Pereira JD, Sansom SN, Smith J, Dobenecker MW, Tarakhovsky A, Livesey FJ (2010) Ezh2, the histone methyltransferase of PRC2, regulates the balance between self-renewal and differentiation in the cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(36):15957–15962. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1002530107
Talebian S, Daghagh H, Yousefi B, Ozkul Y, Ilkhani K, Seif F, Alivand MR (2020) The role of epigenetics and non-coding RNAs in autophagy: a new perspective for thorough understanding. Mech Ageing Dev 190:111309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2020.111309
Chen J, Zhang YC, Huang C, Shen H, Sun B, Cheng X, Zhang YJ, Yang YG, Shu Q, Yang Y, Li X (2019) m(6)A regulates neurogenesis and neuronal development by modulating histone methyltransferase Ezh2. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 17(2):154–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2018.12.007
Cao Y, Zhuang Y, Chen J, Xu W, Shou Y, Huang X, Shu Q, Li X (2020) Dynamic effects of Fto in regulating the proliferation and differentiation of adult neural stem cells of mice. Hum Mol Genet 29(5):727–735. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddz274
Reitz C, Tosto G, Mayeux R, Luchsinger JA, Group N-LNFS, Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging I. genetic variants in the fat and obesity associated (FTO) gene and risk of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50354. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0050354
Li L, Zang L, Zhang F, Chen J, Shen H, Shu L, Liang F, Feng C, Chen D, Tao H, Xu T, Li Z, Kang Y, Wu H, Tang L, Zhang P, Jin P, Shu Q, Li X (2017) Fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) protein regulates adult neurogenesis. Hum Mol Genet 26(13):2398–2411. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddx128
Gao H, Cheng X, Chen J, Ji C, Guo H, Qu W, Dong X, Chen Y, Ma L, Shu Q, Li X (2020) Fto-modulated lipid niche regulates adult neurogenesis through modulating adenosine metabolism. Hum Mol Genet 29(16):2775–2787. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddaa171
Wang CX, Cui GS, Liu X, Xu K, Wang M, Zhang XX, Jiang LY, Li A, Yang Y, Lai WY, Sun BF, Jiang GB, Wang HL, Tong WM, Li W, Wang XJ, Yang YG, Zhou Q (2018) METTL3-mediated m6A modification is required for cerebellar development. PLoS Biol 16(6):e2004880. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2004880
Li H, Ren Y, Mao K, Hua F, Yang Y, Wei N, Yue C, Li D, Zhang H (2018) FTO is involved in Alzheimer’s disease by targeting TSC1-mTOR-Tau signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 498(1):234–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.201
Urbina-Varela R, Soto-Espinoza MI, Vargas R, Quinones L, Del Campo A. Influence of BDNF genetic polymorphisms in the pathophysiology of aging-related diseases. Aging Dis. 2020;11(6):1513–1526. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2020.0310
Olszewski PK, Fredriksson R, Olszewska AM, Stephansson O, Alsio J, Radomska KJ, Levine AS, Schioth HB (2009) Hypothalamic FTO is associated with the regulation of energy intake not feeding reward. BMC Neurosci 10:129. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-10-129
Vujovic P, Stamenkovic S, Jasnic N, Lakic I, Djurasevic SF, Cvijic G, Djordjevic J (2013) Fasting induced cytoplasmic Fto expression in some neurons of rat hypothalamus. PLoS ONE 8(5):e63694. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063694
Poritsanos NJ, Lew PS, Fischer J, Mobbs CV, Nagy JI, Wong D, Ruther U, Mizuno TM (2011) Impaired hypothalamic Fto expression in response to fasting and glucose in obese mice. Nutr Diabetes 1:e19. https://doi.org/10.1038/nutd.2011.15
Wang X, Huang N, Yang M, Wei D, Tai H, Han X, Gong H, Zhou J, Qin J, Wei X, Chen H, Fang T, Xiao H (2017) FTO is required for myogenesis by positively regulating mTOR-PGC-1alpha pathway-mediated mitochondria biogenesis. Cell Death Dis 8(3):e2702. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.122
Wu R, Jiang D, Wang Y, Wang X (2016) N (6)-Methyladenosine (m(6)A) methylation in mRNA with a dynamic and reversible epigenetic modification. Mol Biotechnol 58(7):450–459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-016-9947-9
Dermentzaki G, Lotti F (2020) New insights on the role of N (6)-methyladenosine RNA methylation in the physiology and pathology of the nervous system. Front Mol Biosci 7:555372. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2020.555372
Zhang L, Cheng Y, Xue Z, Li J, Wu N, Yan J, Wang J, Wang C, Chen W, Zhou T, Qiu Z, Jiang H (2021) Sevoflurane impairs m6A-mediated mRNA translation and leads to fine motor and cognitive deficits. Cell Biol Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09601-4
Friocourt F, Kozulin P, Belle M, Suarez R, Di-Poi N, Richards LJ, Giacobini P, Chedotal A (2019) Shared and differential features of Robo3 expression pattern in amniotes. J Comp Neurol 527(12):2009–2029. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.24648
Friocourt F, Chedotal A (2017) The Robo3 receptor, a key player in the development, evolution, and function of commissural systems. Dev Neurobiol 77(7):876–890. https://doi.org/10.1002/dneu.22478
Zhuang M, Li X, Zhu J, Zhang J, Niu F, Liang F, Chen M, Li D, Han P, Ji SJ. The m6A reader YTHDF1 regulates axon guidance through translational control of Robo3.1 expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(9):4765–4777. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz157
Hauser SL, Cree BAC. Treatment of multiple sclerosis: a review. Am J Med. 2020;133(12):1380–1390 e1382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.05.049
Filippi M, Preziosa P, Langdon D, Lassmann H, Paul F, Rovira A, Schoonheim MM, Solari A, Stankoff B, Rocca MA (2020) Identifying progression in multiple sclerosis: new perspectives. Ann Neurol 88(3):438–452. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25808
Ye F, Wang T, Wu X, Liang J, Li J, Sheng W (2021) N6-methyladenosine RNA modification in cerebrospinal fluid as a novel potential diagnostic biomarker for progressive multiple sclerosis. J Transl Med 19(1):316. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-021-02981-5
Kofahi RM, Kofahi HM, Sabaheen S, Qawasmeh MA, Momani A, Yassin A, Alhayk K, El-Salem K. Prevalence of seropositivity of selected herpesviruses in patients with multiple sclerosis in the North of Jordan. BMC Neurology. 2020;20(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-020-01977-w
Xu H, Dzhashiashvili Y, Shah A, Kunjamma RB, Weng YL, Elbaz B, Fei Q, Jones JS, Li YI, Zhuang X, Ming GL, He C, Popko B. m(6)A mRNA methylation is essential for oligodendrocyte maturation and CNS myelination. Neuron. 2020;105(2):293–309 e295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.12.013
Zhang J, Chen M-J, Zhao G-X, Li H-F, Wu L, Xu Y-F, Liao Y, Yuan Z, Wu Z-Y (2020) Common genetic variants in PRRC2A are associated with both neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder and multiple sclerosis in Han Chinese population. J Neurol 268(2):506–515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-020-10184-z
Wu R, Li A, Sun B, Sun J-G, Zhang J, Zhang T, Chen Y, Xiao Y, Gao Y, Zhang Q, Ma J, Yang X, Liao Y, Lai W-Y, Qi X, Wang S, Shu Y, Wang H-L, Wang F, Yang Y-G, Yuan Z (2018) A novel m6A reader Prrc2a controls oligodendroglial specification and myelination. Cell Res 29(1):23–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-018-0113-8
Park SJ, Choi JW (2020) Brain energy metabolism and multiple sclerosis: progress and prospects. Arch Pharm Res 43(10):1017–1030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-020-01278-3
Mo XB, Lei SF, Qian QY, Guo YF, Zhang YH, Zhang H (2019) Integrative analysis revealed potential causal genetic and epigenetic factors for multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 266(11):2699–2709. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09476-w
Moyon S, Casaccia P (2017) DNA methylation in oligodendroglial cells during developmental myelination and in disease. Neurogenesis (Austin) 4(1):e1270381. https://doi.org/10.1080/23262133.2016.1270381
Arosio B, Guerini FR, Voshaar RCO, Aprahamian I (2021) Blood brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and major depression: do we have a translational perspective? Front Behav Neurosci 15:626906. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2021.626906
Barbon A, Magri C. RNA Editing and modifications in mood disorders. Genes (Basel). 2020;11(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11080872
Shen J, Yang L, Wei W. Role of Fto on CaMKII/CREB signaling pathway of hippocampus in depressive-like behaviors induced by chronic restraint stress mice. Behavioural Brain Research. 2021;406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113227
Yao Y, Wen Y, Du T, Sun N, Deng H, Ryan J, Rao S (2016) Meta-analysis indicates that SNP rs9939609 within FTO is not associated with major depressive disorder (MDD) in Asian population. J Affect Disord 193:27–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2015.12.048
Rivera M, Cohen-Woods S, Kapur K, Breen G, Ng MY, Butler AW, Craddock N, Gill M, Korszun A, Maier W, Mors O, Owen MJ, Preisig M, Bergmann S, Tozzi F, Rice J, Rietschel M, Rucker J, Schosser A, Aitchison KJ, Uher R, Craig IW, Lewis CM, Farmer AE, McGuffin P (2012) Depressive disorder moderates the effect of the FTO gene on body mass index. Mol Psychiatry 17(6):604–611. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2011.45
Farmer A, Korszun A, Owen MJ, Craddock N, Jones L, Jones I, Gray J, Williamson RJ, McGuffin P (2018) Medical disorders in people with recurrent depression. Br J Psychiatry 192(5):351–355. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.107.038380
Benedict C, Axelsson T, Soderberg S, Larsson A, Ingelsson E, Lind L, Schioth HB (2014) Fat mass and obesity-associated gene (FTO) is linked to higher plasma levels of the hunger hormone ghrelin and lower serum levels of the satiety hormone leptin in older adults. Diabetes 63(11):3955–3959. https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-0470
McTaggart JS, Lee S, Iberl M, Church C, Cox RD, Ashcroft FM (2011) FTO is expressed in neurones throughout the brain and its expression is unaltered by fasting. PLoS ONE 6(11):e27968. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0027968
Tung YC, Ayuso E, Shan X, Bosch F, O’Rahilly S, Coll AP, Yeo GS (2010) Hypothalamic-specific manipulation of Fto, the ortholog of the human obesity gene FTO, affects food intake in rats. PLoS ONE 5(1):e8771. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0008771
Sideratou T, Atkinson F, Campbell GJ, Petocz P, Bell-Anderson KS, Brand-Miller J. Glycaemic index of maternal dietary carbohydrate differentially alters Fto and Lep expression in offspring in C57BL/6 mice. Nutrients. 2018;10(10). " https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101342
Chmurzynska A, Mlodzik MA (2017) Genetics of fat intake in the determination of body mass. Nutr Res Rev 30(1):106–117. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954422417000014
Olszewski PK, Radomska KJ, Ghimire K, Klockars A, Ingman C, Olszewska AM, Fredriksson R, Levine AS, Schioth HB (2011) Fto immunoreactivity is widespread in the rodent brain and abundant in feeding-related sites, but the number of Fto-positive cells is not affected by changes in energy balance. Physiol Behav 103(2):248–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.01.022
de Araujo TM, Velloso LA (2020) Hypothalamic IRX3: a new player in the development of obesity. Trends Endocrinol Metab 31(5):368–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2020.01.002
Cheung MK, Gulati P, O’Rahilly S, Yeo GS (2013) FTO expression is regulated by availability of essential amino acids. Int J Obes (Lond) 37(5):744–747. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2012.77
Du T, Rao S, Wu L, Ye N, Liu Z, Hu H, Xiu J, Shen Y, Xu Q (2015) An association study of the m6A genes with major depressive disorder in Chinese Han population. J Affect Disord 183:279–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2015.05.025
Huang R, Zhang Y, Bai Y, Han B, Ju M, Chen B, Yang L, Wang Y, Zhang H, Zhang H, Xie C, Zhang Z, Yao H (2020) N(6)-Methyladenosine modification of fatty acid amide hydrolase messenger RNA in circular RNA STAG1-regulated astrocyte dysfunction and depressive-like behaviors. Biol Psychiatry 88(5):392–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.02.018
Wang X, Wu R, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Bi Z, Yao Y, Liu Q, Shi H, Wang F, Wang Y. m(6)A mRNA methylation controls autophagy and adipogenesis by targeting Atg5 and Atg7. Autophagy. 2020;16(7):1221–1235. "https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2019.1659617
Cai M, Liu Q, Jiang Q, Wu R, Wang X, Wang Y (2018) Loss of m6A on FAM134B promotes adipogenesis in porcine adipocytes through m6A-YTHDF2-dependent way. IUBMB Life 71(5):580–586. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1974
Noh K, Park JC, Han JS, Lee SJ (2020) From Bound cells comes a sound mind: the role of neuronal growth regulator 1 in psychiatric disorders. Exp Neurobiol 29(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.5607/en.2020.29.1.1
Treutlein J, Strohmaier J, Frank J, Witt SH, Rietschel L, Forstner AJ, Lang M, Degenhardt F, Dukal H, Herms S, Streit F, Hoffmann P, Cichon S, Nöthen MM, Rietschel M (2017) Association between neuropeptide Y receptor Y2 promoter variant rs6857715 and major depressive disorder. Psychiatr Genet 27(1):34–37. https://doi.org/10.1097/ypg.0000000000000149
Sasayama D, Hori H, Teraishi T, Hattori K, Ota M, Tatsumi M, Higuchi T, Amano N, Kunugi H (2012) Possible impact of ADRB3 Trp64Arg polymorphism on BMI in patients with schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 38(2):341–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2012.05.007
Guerri G, Castori M, D'Agruma L, Petracca A, Kurti D, Bertelli M. Genetic analysis of genes associated with epilepsy. Acta Biomed. 2020;91(13-S):e2020005. https://doi.org/10.23750/abm.v91i13-S.10596
Vu LC, Piccenna L, Kwan P, O’Brien TJ (2018) New-onset epilepsy in the elderly. Br J Clin Pharmacol 84(10):2208–2217. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.13653
Golub V, Reddy DS (2021) Cannabidiol Therapy for refractory epilepsy and seizure disorders. Adv Exp Med Biol 1264:93–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-57369-0_7
Auzmendi J, Puchulu MB, Rodriguez JCG, Balaszczuk AM, Lazarowski A, Merelli A (2020) EPO and EPO-receptor system as potential actionable mechanism for the protection of brain and heart in refractory epilepsy and SUDEP. Curr Pharm Des 26(12):1356–1364. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612826666200219095548
Dias RB, Rodrigues TM, Rombo DM, Ribeiro FF, Rodrigues J, McGarvey J, Orcinha C, Henley JM, Sebastiao AM (2018) Erythropoietin induces homeostatic plasticity at hippocampal synapses. Cereb Cortex 28(8):2795–2809. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhx159
Konishi R, Kanemoto K. Psychosis rarely occurs in patients with late-onset focal epilepsy. Epilepsy & Behavior. 2020;111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2020.107295
Merelli A, Repetto M, Lazarowski A, Auzmendi J (2021) Hypoxia, oxidative stress, and inflammation: three faces of neurodegenerative diseases. J Alzheimers Dis 82(s1):S109–S126. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-201074
Zaman T, Helbig KL, Clatot J, Thompson CH, Kang SK, Stouffs K, Jansen AE, Verstraete L, Jacquinet A, Parrini E, Guerrini R, Fujiwara Y, Miyatake S, Ben-Zeev B, Bassan H, Reish O, Marom D, Hauser N, Vu TA, Ackermann S, Spencer CE, Lippa N, Srinivasan S, Charzewska A, Hoffman-Zacharska D, Fitzpatrick D, Harrison V, Vasudevan P, Joss S, Pilz DT, Fawcett KA, Helbig I, Matsumoto N, Kearney JA, Fry AE, Goldberg EM (2020) SCN3A-related neurodevelopmental disorder: a spectrum of epilepsy and brain malformation. Ann Neurol 88(2):348–362. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25809
Li HJ, Wan RP, Tang LJ, Liu SJ, Zhao QH, Gao MM, Yi YH, Liao WP, Sun XF, Long YS (2015) Alteration of Scn3a expression is mediated via CpG methylation and MBD2 in mouse hippocampus during postnatal development and seizure condition. Biochim Biophys Acta 1849(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.11.004
Tan NN, Tang HL, Lin GW, Chen YH, Lu P, Li HJ, Gao MM, Zhao QH, Yi YH, Liao WP, Long YS (2017) Epigenetic downregulation of Scn3a expression by valproate: a possible role in its anticonvulsant activity. Mol Neurobiol 54(4):2831–2842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9871-9
Zheng G, Cox T, Tribbey L, Wang GZ, Iacoban P, Booher ME, Gabriel GJ, Zhou L, Bae N, Rowles J, He C, Olsen MJ (2014) Synthesis of a FTO inhibitor with anticonvulsant activity. ACS Chem Neurosci 5(8):658–665. https://doi.org/10.1021/cn500042t
Xiao L, Li X, Mu Z, Zhou J, Zhou P, Xie C, Jiang S (2020) FTO inhibition enhances the antitumor effect of temozolomide by targeting MYC-miR-155/23a cluster-MXI1 feedback circuit in glioma. Cancer Res 80(18):3945–3958. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-0132
Xu S, Tang L, Li X, Fan F, Liu Z (2020) Immunotherapy for glioma: current management and future application. Cancer Lett 476:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.02.002
Fang R, Chen X, Zhang S, Shi H, Ye Y, Shi H, Zou Z, Li P, Guo Q, Ma L, He C, Huang S (2021) EGFR/SRC/ERK-stabilized YTHDF2 promotes cholesterol dysregulation and invasive growth of glioblastoma. Nat Commun 12(1):177. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20379-7
Cheng J, Xu L, Deng L, Xue L, Meng Q, Wei F, Wang J (2020) RNA N(6)-methyladenosine modification is required for miR-98/MYCN axis-mediated inhibition of neuroblastoma progression. Sci Rep 10(1):13624. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64682-1
Ma Z, Ji J (2020) N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modification in cancer stem cells. Stem Cells. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.3279
Cui Q, Shi H, Ye P, Li L, Qu Q, Sun G, Sun G, Lu Z, Huang Y, Yang CG, Riggs AD, He C, Shi Y (2017) m(6)A RNA methylation regulates the self-renewal and tumorigenesis of glioblastoma stem cells. Cell Rep 18(11):2622–2634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.02.059
Xu S, Tang L, Dai G, Luo C, Liu Z (2020) Expression of m6A regulators correlated with immune microenvironment predicts therapeutic efficacy and prognosis in gliomas. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:594112. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.594112
Chai RC, Wu F, Wang QX, Zhang S, Zhang KN, Liu YQ, Zhao Z, Jiang T, Wang YZ, Kang CS. mA RNA methylation regulators contribute to malignant progression and have clinical prognostic impact in gliomas. Aging. 2019;11(4):1204–1225. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101829
Chang YZ, Chai RC, Pang B, Chang X, An SY, Zhang KN, Jiang T, Wang YZ (2021) METTL3 enhances the stability of MALAT1 with the assistance of HuR via m6A modification and activates NF-kappaB to promote the malignant progression of IDH-wildtype glioma. Cancer Lett 511:36–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2021.04.020
Dong Z, Cui H. The emerging roles of RNA modifications in glioblastoma. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12030736
Visvanathan A, Patil V, Arora A, Hegde AS, Arivazhagan A, Santosh V, Somasundaram K (2018) Essential role of METTL3-mediated m(6)A modification in glioma stem-like cells maintenance and radioresistance. Oncogene 37(4):522–533. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.351
Visvanathan A, Patil V, Abdulla S, Hoheisel JD, Somasundaram K. N(6)-methyladenosine landscape of glioma stem-like cells: METTL3 is essential for the expression of actively transcribed genes and sustenance of the oncogenic signaling. Genes (Basel). 2019;10(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020141
Wang J, Sha Y, Sun T. m6A modifications play crucial roles in glial cell development and brain tumorigenesis. Frontiers in Oncology. 2021;11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.611660
Zhang S, Zhao BS, Zhou A, Lin K, Zheng S, Lu Z, Chen Y, Sulman EP, Xie K, Bögler O, Majumder S, He C, Huang S (2017) m 6 A demethylase ALKBH5 maintains tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells by sustaining FOXM1 expression and cell proliferation program. Cancer Cell 31(4):591-606.e596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2017.02.013
Kowalski-Chauvel A, Lacore MG, Arnauduc F, Delmas C, Toulas C, Cohen-Jonathan-Moyal E, Seva C. The m6A RNA demethylase ALKBH5 promotes radioresistance and invasion capability of glioma stem cells. Cancers (Basel). 2020;13(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13010040
Chai RC, Chang YZ, Chang X, Pang B, An SY, Zhang KN, Chang YH, Jiang T, Wang YZ (2021) YTHDF2 facilitates UBXN1 mRNA decay by recognizing METTL3-mediated m(6)A modification to activate NF-kappaB and promote the malignant progression of glioma. J Hematol Oncol 14(1):109. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-021-01124-z
Karpel-Massler G, Nguyen TTT, Shang E, Siegelin MD (2019) Novel IDH1-targeted glioma therapies. CNS Drugs 33(12):1155–1166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-019-00684-6
Han S, Liu Y, Cai SJ, Qian M, Ding J, Larion M, Gilbert MR, Yang C (2020) IDH mutation in glioma: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Br J Cancer 122(11):1580–1589. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-020-0814-x
Wesseling P, Capper D (2018) WHO 2016 classification of gliomas. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 44(2):139–150. https://doi.org/10.1111/nan.12432
Galardi S, Michienzi A, Ciafrè SA. Insights into the regulatory role of m6A epitranscriptome in glioblastoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020;21(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082816
Li F, Yi Y, Miao Y, Long W, Long T, Chen S, Cheng W, Zou C, Zheng Y, Wu X, Ding J, Zhu K, Chen D, Xu Q, Wang J, Liu Q, Zhi F, Ren J, Cao Q, Zhao W (2019) N6-methyladenosine modulates nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in human glioblastoma. Can Res 79(22):5785–5798. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-18-2868
Su R, Dong L, Li C, Nachtergaele S, Wunderlich M, Qing Y, Deng X, Wang Y, Weng X, Hu C, Yu M, Skibbe J, Dai Q, Zou D, Wu T, Yu K, Weng H, Huang H, Ferchen K, Qin X, Zhang B, Qi J, Sasaki AT, Plas DR, Bradner JE, Wei M, Marcucci G, Jiang X, Mulloy JC, Jin J, He C, Chen J. R-2HG exhibits anti-tumor activity by targeting FTO/m(6)A/MYC/CEBPA signaling. Cell. 2018;172(1–2):90–105 e123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.031
Zhao WJ, Ou GY, Lin WW (2021) Integrative analysis of neuregulin family members-related tumor microenvironment for predicting the prognosis in gliomas. Front Immunol 12:682415. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.682415
Du J, Ji H, Ma S, Jin J, Mi S, Hou K, Dong J, Wang F, Zhang C, Li Y, Hu S (2021) m6A regulator-mediated methylation modification patterns and characteristics of immunity and stemness in low-grade glioma. Brief Bioinform. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbab013
Radoul M, Lewin L, Cohen B, Oren R, Popov S, Davidov G, Vandsburger MH, Harmelin A, Bitton R, Greneche JM, Neeman M, Zarivach R (2016) Genetic manipulation of iron biomineralization enhances MR relaxivity in a ferritin-M6A chimeric complex. Sci Rep 6:26550. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26550
Tang J, Zheng C, Zheng F, Li Y, Wang YL, Aschner M, Guo Z, Yu G, Wu S, Li H. Global N6-methyladenosine profiling of cobalt-exposed cortex and human neuroblastoma H4 cells presents epitranscriptomics alterations in neurodegenerative disease-associated genes. Environmental pollution (Barking, Essex : 1987). 2020;266:115326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115326
Wen L, Sun W, Xia D, Wang Y, Li J, Yang S (2020) The m6A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes LPS-induced microglia inflammation through TRAF6/NF-κB pathway. NeuroReport. https://doi.org/10.1097/wnr.0000000000001550
Zhao Y, Shi Y, Shen H, Xie W (2020) mA-binding proteins: the emerging crucial performers in epigenetics. J Hematol Oncol 13(1):35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00872-8
Kesika P, Suganthy N, Sivamaruthi BS, Chaiyasut C (2021) Role of gut-brain axis, gut microbial composition, and probiotic intervention in Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci 264:118627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118627
Wu J, Zhao Y, Wang X, Kong L, Johnston LJ, Lu L, Ma X. Dietary nutrients shape gut microbes and intestinal mucosa via epigenetic modifications. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition. 2020:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1828813
Xiao P, Liu YK, Han W, Hu Y, Zhang BY, Liu WL (2021) Exosomal delivery of FTO confers gefitinib resistance to recipient cells through ABCC10 regulation in an m6A-dependent manner. Molecular cancer research : MCR 19(4):726–738. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.Mcr-20-0541
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to all those helped me during the writing of this manuscript. We apologize to all researchers whose relevant contributions were not cited due to space limitations.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81903030); Outstanding Young Aid Program for Education Department of Hunan Province (Grant No.20B511); the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (No. 2021JJ40481); University-level research projects of South China University (NO.190XQD019); Graduate Student Scientific Research Innovation Project of University of South China (NO.S202110555298).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lielian Zuo proposed and revised the manuscript. Nan Zhang and Chunhong Ding co-writed this manuscript and contributed equally to this work. All authors reviewed the manuscript and all approved of the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, N., Ding, C., Zuo, Y. et al. N6-methyladenosine and Neurological Diseases. Mol Neurobiol 59, 1925–1937 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-02739-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-02739-0