Abstract
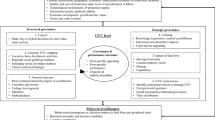
Industry 4.0 (I4.0) is a relatively new and still emerging concept. Due to its novelty, companies find it extremely difficult to adopt I4.0 and reap the full benefit of the digital transformation of the fourth industrial revolution. Even though challenges to I4.0 adoption are well explored, the extant literature has hardly investigated the numerous human-based behavioural factors that are fundamental for I4.0 adoption. Human experience, engagement, and dedication to I4.0 adoption are crucial due to the complex nature of human behaviour and can significantly affect the success of I4.0 adoption. To address the gap, this paper aims to unveil the indispensable behavioural factors for I4.0 adoption and portray a hierarchical relationship among these factors. An extensive literature review is conducted to identify behaviour critical for I4.0 adoption to operationalise this research. Then, a decision support framework based on the Delphi technique and a revised rough DEMATEL method is used to map the relationships among the behavioural factors. The results reveal that the most critical behavioural factor to I4.0 adoption is “communication,” which is followed by “I4.0 training” and “resistance to I4.0 initiatives”. This study substantiates the research on I4.0 adoption and assists in I4.0 adoption. I4.0 adoption is also essential for a country’s competitiveness; therefore, the paper will support relevant policy formulation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abatecola G, Cristofaro M, Giannetti F, Kask J (2022) How can biases affect entrepreneurial decision making? Toward a behavioral approach to unicorns. Int Entrep Manag J 18(2):693–711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-021-00772-4
Acuña-Carvajal F, Pinto-Tarazona L, López-Ospina H, Barros-Castro R, Quezada L, Palacio K (2019) An integrated method to plan, structure and validate a business strategy using fuzzy DEMATEL and the balanced scorecard. Expert Syst Appl 122:351–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2019.01.030
Ahmed S, Taqi HMM, Farabi YI, Sarker M, Ali SM, Sankaranarayanan B (2021) Evaluation of Flexible Strategies to Manage the COVID-19 Pandemic in the Education Sector. Glob J Flex Syst Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-021-00267-9
Akkas MA, Chakma A, Hossain MI (2015) Employee-Management Cooperation: The Key to Employee Productivity. J US-China Public Adm, 12(2). https://doi.org/10.17265/1548-6591/2015.02.001
Alhasan A, Audah L, Ibrahim I, Al-Sharaa A, Al-Ogaili AS, Mohammed JM (2020) A case-study to examine doctors’ intentions to use IoT healthcare devices in Iraq during COVID-19 pandemic. Int J Pervasive Comput Commun. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPCC-10-2020-0175
Alkhafaji A, Nelson RA (2013) Strategic Management: Formulation, Implementation, and Control in a Dynamic Environment. Routledge-Taylor and Francis, United Kingdom
Aoun A, Ilinca A, Ghandour M, Ibrahim H (2021) A review of Industry 4 0 characteristics and challenges, with potential improvements using Blockchain technology. Comput Ind Eng 162:107746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2021.107746
Bag S, Yadav G, Dhamija P, Kataria KK (2021) Key resources for industry 4.0 adoption and its effect on sustainable production and circular economy: An empirical study. J Clean Prod 281:125233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125233
Belinski R, Peixe AMM, Frederico GF, Garza-Reyes JA (2020) Organizational learning and Industry 4.0: findings from a systematic literature review and research agenda. Benchmarking 27(8):2435–2457. https://doi.org/10.1108/BIJ-04-2020-0158
Bittencourt VL, Alves AC, Leão CP (2021) Industry 4.0 triggered by Lean Thinking: insights from a systematic literature review. Int J Prod Res 59(5):1496–1510. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2020.1832274
Cárcel-Carrasco J, Gómez-Gómez C (2021) Qualitative Analysis of the Perception of Company Managers in Knowledge Management in the Maintenance Activity in the Era of Industry 4.0. Processes 9(1):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9010121
Carvalho N, Chaim O, Cazarini E, Gerolamo M (2018) Manufacturing in the fourth industrial revolution: A positive prospect in Sustainable Manufacturing. Procedia Manuf 21:671–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2018.02.170. (Elsevier B.V)
Castelo-Branco I, Cruz-Jesus F, Oliveira T (2019) Assessing Industry 4.0 readiness in manufacturing: Evidence for the European Union. Comput Ind 107:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2019.01.007
Cezarino LO, Liboni LB, Oliveira Stefanelli N, Oliveira BG, Stocco LC (2019) Diving into emerging economies bottleneck: Industry 4.0 and implications for circular economy. Manag Decis. https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-10-2018-1084
Chauhan C, Singh A, Luthra S (2021) Barriers to industry 4.0 adoption and its performance implications: An empirical investigation of emerging economy. J Clean Prod 285:124809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124809
Chen Z, Lu M, Ming X, Zhang X, Zhou T (2020) Explore and evaluate innovative value propositions for smart product service system: A novel graphics-based rough-fuzzy DEMATEL method. J Clean Prod 243:118672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118672
Chowdhury TM, Murzi H (2020) The evolution of teamwork in engineering workplace from first industry revolution to industry 4.0: A literature review. ASEE Annual Conference and Exposition, Conference Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.18260/1-2--35318
Cimini C, Boffelli A, Lagorio A, Kalchschmidt M, Pinto R (2021) How do industry 4.0 technologies influence organisational change? An empirical analysis of Italian SMEs. J Manuf Technol Manag 32(3):695–721. https://doi.org/10.1108/JMTM-04-2019-0135
Cirillo V, Rinaldini M, Staccioli J, Virgillito ME (2021) Technology vs. workers: the case of Italy’s Industry 4.0 factories. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 56:166–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strueco.2020.09.007
Dana L-P, Salamzadeh A, Hadizadeh M, Heydari G, Shamsoddin S (2022) Urban entrepreneurship and sustainable businesses in smart cities: Exploring the role of digital technologies. Sustain Technol Entrep 1(2):100016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stae.2022.100016
de Sousa Jabbour ABL, Jabbour CJC, Foropon C, Filho MG (2018) When titans meet – Can industry 4.0 revolutionise the environmentally-sustainable manufacturing wave? The role of critical success factors. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 132:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2018.01.017
Ding Z, Jiang X, Liu Z, Long R, Xu Z, Cao Q (2018) Factors affecting low-carbon consumption behavior of urban residents: A comprehensive review. Resour Conserv Recycl 132:3–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.01.013
Giroux M, Kim J, Lee JC, Park J (2022) Artificial Intelligence and Declined Guilt: Retailing Morality Comparison Between Human and AI. J Bus Ethics 1:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10551-022-05056-7/FIGURES/1
Hasson F, Keeney S (2011) Enhancing rigour in the Delphi technique research. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 78(9):1695–1704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2011.04.005
Horváth D, Szabó RZ (2019) Driving forces and barriers of Industry 4.0: Do multinational and small and medium-sized companies have equal opportunities? Technol Forecast Soc Chang 146:119–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2019.05.021
Hwang B-G, Ngo J, Teo JZK (2022) Challenges and Strategies for the Adoption of Smart Technologies in the Construction Industry: The Case of Singapore. J Manag Eng 38(1):5479. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)ME.1943-5479.0000986
Javaid M, Haleem A, Singh RP, Suman R, Gonzalez ES (2022) Understanding the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies in improving environmental sustainability. Sustainable Operations and Computers 3:203–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susoc.2022.01.008
Jermsittiparsert K (2020) Leadership and Industry 4.0 As A Tool to Enhance Organization Performance: Direct and Indirect Role of Job Satisfaction, Competitive Advantage and Business Sustainability. In Agile Business Leadership Methods for Industry 4.0 (pp. 233–257). Emerald Publishing Limited. https://doi.org/10.1108/978-1-80043-380-920201014
Kadir BA, Broberg O, da Conceição CS (2019) Current research and future perspectives on human factors and ergonomics in Industry 4.0. Comput Ind Eng 137:106004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2019.106004
Kamble SS, Gunasekaran A, Sharma R (2018) Analysis of the driving and dependence power of barriers to adopt industry 4.0 in Indian manufacturing industry. Comput Ind 101:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2018.06.004
Klar S, Leeper TJ (2019) Identities and Intersectionality: A Case for Purposive Sampling in <scp>Survey‐Experimental</scp> Research. In Experimental Methods in Survey Research (pp. 419–433). Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119083771.ch21
Kouhizadeh M, Saberi S, Sarkis J (2021) Blockchain technology and the sustainable supply chain: Theoretically exploring adoption barriers. Int J Prod Econ 231:107831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107831
Kovacs O (2018) The dark corners of industry 4.0 – Grounding economic governance 2.0. Technol Soc 55:140–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2018.07.009
Kumar A, Moktadir MA, Khan SAR, Garza-Reyes JA, Tyagi M, Kazançoğlu Y (2020a) Behavioral factors on the adoption of sustainable supply chain practices. Resour Conserv Recycl 158:104818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.104818
Kumar R, Singh RK, Dwivedi YK (2020b) Application of industry 4.0 technologies in SMEs for ethical and sustainable operations: Analysis of challenges. J Clean Prod 275:124063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124063
Kumar S, Suhaib M, Asjad M (2020c) Narrowing the barriers to Industry 4.0 practices through PCA-Fuzzy AHP-K means. J Adv Manag Res 18(2):200–226. https://doi.org/10.1108/JAMR-06-2020-0098
Lee MT, Suh I (2022) Understanding the effects of Environment, Social, and Governance conduct on financial performance: Arguments for a process and integrated modelling approach. Sustain Technol Entrep 1(1):100004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stae.2022.100004
Li W, Bhutto TA, Xuhui W, Maitlo Q, Zafar AU, Ahmed Bhutto N (2020) Unlocking employees’ green creativity: The effects of green transformational leadership, green intrinsic, and extrinsic motivation. J Clean Prod 255:120229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120229
Lin B, Wu W, Song M (2019) Industry 4.0: driving factors and impacts on firm’s performance: an empirical study on China’s manufacturing industry. Ann Oper Res 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-019-03433-6
Liu Z, Ming X (2019) A framework with revised rough-DEMATEL to capture and evaluate requirements for smart industrial product-service system of systems. Int J Prod Res 57(22):7104–7122. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2019.1577566
Moktadir MA, Ali SM, Kusi-Sarpong S, Shaikh MAA (2018) Assessing challenges for implementing Industry 4.0: Implications for process safety and environmental protection. Process Saf Environ Prot 117:730–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.04.020
Muduli K, Barve A (2013) Modelling the behavioural factors of green supply chain management implementation in mining industries in Indian scenario. Asian J Manag Sci Appl 1(1):26. https://doi.org/10.1504/ajmsa.2013.056007
Muduli KK, Luthra S, Kumar Mangla S, Jabbour CJC, Aich S, de Guimarães JCF (2020) Environmental management and the “soft side” of organisations: Discovering the most relevant behavioural factors in green supply chains. Bus Strateg Environ 29(4):1647–1665. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2459
Muduli K, Kusi-Sarpong S, Yadav DK, Gupta H, Jabbour CJC (2021) An original assessment of the influence of soft dimensions on implementation of sustainability practices: implications for the thermal energy sector in fast growing economies. Oper Manag Res 14(3):337–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12063-021-00215-x
Neumann WP, Winkelhaus S, Grosse EH, Glock CH (2021) Industry 4.0 and the human factor – A systems framework and analysis methodology for successful development. Int J Prod Econ 233:107992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107992
Oliva FL, Teberga PMF, Testi LIO, Kotabe M, Del Giudice M, Kelle P, Cunha MP (2021) Risks and critical success factors in the internationalization of born global startups of industry 4.0: A social, environmental, economic, and institutional analysis. Technol Forecast Social Chang 121346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121346
Oztemel E, Gursev S (2020) Literature review of Industry 4.0 and related technologies. J Intell Manuf 31:127–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-018-1433-8. (Springer)
Patyal VS, Sarma PRS, Modgil S, Nag T, Dennehy D (2022) Mapping the links between Industry 4.0, circular economy and sustainability: a systematic literature review. J Enterp Inf Manag 35(1):1–35. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEIM-05-2021-0197
Psarommatis F, Sousa J, Mendonça JP, Kiritsis D (2022) Zero-defect manufacturing the approach for higher manufacturing sustainability in the era of industry 4.0: a position paper. Int J Prod Res 60(1):73–91. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2021.1987551
Raj A, Dwivedi G, Sharma A, de LopesSousa, Jabbour AB, Rajak S (2020) Barriers to the adoption of industry 4.0 technologies in the manufacturing sector: An inter-country comparative perspective. Int J Prod Econ 224:107546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2019.107546
Satoglu SI, Ustundag A, Cevikcan E, Durmusoglu MB (2018) Managing The Digital. Transformation. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-57870-5
Shahzad M, Qu Y, Javed SA, Zafar AU, Rehman SU (2020) Relation of environment sustainability to CSR and green innovation: A case of Pakistani manufacturing industry. J Clean Prod 253:119938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119938
Sharma M, Kamble S, Mani V, Sehrawat R, Belhadi A, Sharma V (2020) Industry 4.0 adoption for sustainability in multi-tier manufacturing supply chain in emerging economies. J Clean Prod 125013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125013
Shayganmehr M, Kumar A, Garza-Reyes JA, Moktadir MA (2020) Industry 4.0 enablers for a cleaner production and circular economy within the context of business ethics: A study in a developing country. J Clean Prod 125280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125280
Sony M (2018) Industry 4.0 and lean management: a proposed integration model and research propositions. Prod Manuf Res 6(1):416–432. https://doi.org/10.1080/21693277.2018.1540949
Sony M, Naik S (2020) Industry 4.0 integration with socio-technical systems theory: A systematic review and proposed theoretical model. Technol Soc 61(3):101248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101248
Sony M, Antony J, Mc Dermott O, Garza-Reyes JA (2021) An empirical examination of benefits, challenges, and critical success factors of industry 4.0 in manufacturing and service sector. Technol Soc 67:101754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101754
Stentoft J, Adsbøll Wickstrøm K, Philipsen K, Haug A (2020) Drivers and barriers for Industry 4.0 readiness and practice: empirical evidence from small and medium-sized manufacturers. Prod Plan Control. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2020.1768318
Strear M, Forbes L, Henninger J (2018) Procedures, pitfalls, and product: Delphi methodology in counseling research. Couns Outcome Res Eval 9(1):55–66. https://doi.org/10.1080/21501378.2017.1403847
Tohidi H, Jabbari MM (2012) Organizational culture and leadership. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 31:856–860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.12.156
Torbacki W, Kijewska K (2019) Identifying key performance indicators to be used in logistics 4.0 and industry 4.0 for the needs of sustainable municipal logistics by means of the DEMATEL method. Transp Res Procedia 39:534–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2019.06.055. (Elsevier B.V)
Tortorella GL, Mac CawleyVergara A, Garza-Reyes JA, Sawhney R (2020) Organizational learning paths based upon industry 4.0 adoption: An empirical study with Brazilian manufacturers. Int J Prod Econ 219:284–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2019.06.023
Tulasi D, Sigit R, Pradana DW, Ellitan L (2019) The Role of Leadership in Industrial Revolution 4.0. Int J Trend Res Dev 6(5):97–100
Wankhede VA, Vinodh S (2021) Analysis of Industry 4.0 challenges using best worst method: A case study. Comput Ind Eng 159(6):107487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2021.107487
Yadav G, Luthra S, Jakhar SK, Mangla SK, Rai DP (2020) A framework to overcome sustainable supply chain challenges through solution measures of industry 4.0 and circular economy: An automotive case. J Clean Prod 254:120112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120112
Yilmaz A, Dora M, Hezarkhani B, Kumar M (2021) Lean and industry 4.0: Mapping determinants and barriers from a social, environmental, and operational perspective. Technol Forecast Social Chang 121320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121320
Yüksel H (2020) An empirical evaluation of industry 4.0 applications of companies in Turkey: The case of a developing country. Technol Soc 63:101364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101364
Zhai LY, Khoo LP, Zhong ZW (2009) Design concept evaluation in product development using rough sets and grey relation analysis. Expert Syst Appl 36(3 PART 2):7072–7079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.08.068
Zhang W, Deng Y (2019) Combining conflicting evidence using the DEMATEL method. Soft Comput 23(17):8207–8216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3455-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article is solely submitted to Operations Management Resource.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Table 7
Table 8
Table 9
Table 10
Table 11
Table 12
Table 13
Questionnaire:
Delphi Stage 1
Greetings.
Industry 4.0 (I4.0) is a relatively new and still emerging concept. Due to its novelty, companies find it extremely difficult to adopt I4.0 and reap the full benefit of the digital transformation of the fourth industrial revolution. Even though challenges to I4.0 adoption are well explored, the extant literature has hardly investigated the numerous human-based behavioural factors that are fundamental for I4.0 adoption. In this study, behavioural factors for adopting Industry 4.0 initiatives are done. Possible BFs have been identified from the current literature. Please, rate the following factors on a scale of 1 to 5, where 5 means the most important and 1 means the least important.
Delphi Stage 2
Dear respondent,
Greetings.
We are trying to find some behavioural factors for adopting industry 4.0. The relevance of the behavioural factors was analysed in terms of cognitive, psychological, and human factors aspects. Please consider cognitive and human psychology to refine the list of behavioural factors and provide your valuable feedback. You can rate the following factors on a scale of 1 to 5, where 5 means the most important and 1 means the least important.
Delphi Stage 3
Dear respondent,
Greetings!
We are trying to finalise some behavioural factors for adopting industry 4.0. Industry 4.0 (I4.0) is a relatively new and still emerging concept. Due to its novelty, companies find it extremely difficult to adopt I4.0 and reap the full benefit of the digital transformation of the fourth industrial revolution. Even though challenges to I4.0 adoption are well explored, the extant literature has hardly investigated the numerous human-based behavioural factors that are fundamental for I4.0 adoption. Human experience, engagement, and dedication to I4.0 adoption are crucial due to the complex nature of human behaviour and can significantly affect the success of I4.0 adoption. To address the gap, we aim to unveil the indispensable behavioural factors for I4.0 adoption and portray a hierarchical relationship among these factors. The relevance of the behavioural factors was analysed in terms of cognitive, psychological, and human factors aspects. Please consider cognitive and human psychology to refine the list of behavioural characteristics and provide your valuable feedback. You can rate the following factors on a scale of 1 to 5, where 5 means the most important and 1 means the least important.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Taqi, H.M.M., Nur, S.M.S.A., Salman, S. et al. Behavioural factors for Industry 4.0 adoption: implications for knowledge-based supply chains. Oper Manag Res 16, 1122–1139 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12063-022-00338-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12063-022-00338-9