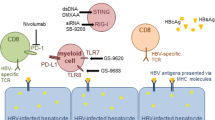
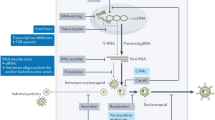
Abstract
Chronic hepatitis B infection remains a major global health problem despite the existence of an effective vaccine. The current treatment options are either nucleos(t)ide analog therapy, which inhibits viral replication, or peginterferon-α, which has mainly immunomodulatory effects. However, treatment-induced HBeAg seroconversion with suppressed viral replication is mostly not sustainable, and loss of HBsAg is a rarely achieved endpoint. In addition, the hepatitis B virus persists in hepatocytes even after HBsAg clearance as covalently closed circular DNA is not eliminated from the hepatocytes. Because the course of chronic hepatitis B is determined by an ongoing interaction between the virus and the host immune system, immunomodulation may be the most logical approach in attempting to accomplish control or even cure of chronic hepatitis B. In the last years, methods for measuring the degree of immune control have been a major area of interest, with an important role for monitoring of HBsAg levels. In addition, new immunomodulatory agents are being developed and tested, providing promising options for future treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADV:
-
Adefovirdipivoxil
- ALT:
-
Alanine transaminase
- cccDNA:
-
Covalently closed circular DNA
- CHB:
-
Chronic hepatitis B
- DCs:
-
Dendritic cells
- ENH:
-
HBeAg-negative hepatitis
- ETV:
-
Entecavir
- HBsAg:
-
Hepatitis B surface antigen
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HBV:
-
Hepatitis B virus
- IA phase:
-
Immune-active phase
- IC:
-
Inactive carrier
- IT phase:
-
Immune-tolerant phase
- IFNα:
-
Interferon-α
- IFNαR:
-
IFNα-receptor
- LTbR:
-
Lymphotoxin-beta receptor
- NA:
-
Nucleos(t)ide analog
- PEG-IFNα:
-
Peginterferon-α
- NKcell:
-
Natural killer cell
- PD:
-
Programmed death
- PEG-IFNλ:
-
Peginterferon-λ
- RNAi:
-
RNA interference
- TDF:
-
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate
- TLR-7:
-
Toll-like receptor 7
- ZFNs:
-
Zinc-finger nucleases
- ZFPs:
-
Zinc-finger proteins
References
World Health Organization. Hepatitis B. World Health Organization Fact Sheet 204 (Updated July 2013) 2013
Yapali S, Lok AS. Does suppression of HBV replication by antiviral therapy confer the same benefit as host immune control of HBV? Gut; 2014
Rijckborst V, ter Borg MJ, Cakaloglu Y, Ferenci P, Tabak F, Akdogan M, et al. A randomized trial of peginterferon alpha-2a with or without ribavirin for HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105(8):1762–1769
van Zonneveld M, Honkoop P, Hansen BE, Niesters HG, Darwish Murad S, de Man RA, et al. Long-term follow-up of alpha-interferon treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2004;39(3):804–810
Buster EH, Flink HJ, Cakaloglu Y, Simon K, Trojan J, Tabak F, et al. Sustained HBeAg and HBsAg loss after long-term follow-up of HBeAg-positive patients treated with peginterferon alpha-2b. Gastroenterology. 2008;135(2):459–467
Chan HL, Leung NW, Hui AY, Wong VW, Liew CT, Chim AM, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of combination therapy for chronic hepatitis B: comparing pegylated interferon-alpha2b and lamivudine with lamivudine alone. Ann Intern Med. 2005;142(4):240–250
Lau GK, Piratvisuth T, Luo KX, Marcellin P, Thongsawat S, Cooksley G, et al. Peginterferon Alfa-2a, lamivudine, and the combination for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(26):2682–2695
Song BC, Suh DJ, Lee HC, Chung YH, Lee YS. Hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion after lamivudine therapy is not durable in patients with chronic hepatitis B in Korea. Hepatology. 2000;32(4 Pt 1):803–806
Reijnders JG, Perquin MJ, Zhang N, Hansen BE, Janssen HL. Nucleos(t)ide analogues only induce temporary hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in most patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 2010;139(2):491–498
Wong VW, Wong GL, Tsang SW, Hui AY, Chim AM, Yiu KK, et al. Long-term follow-up of lamivudine treatment in patients with severe acute exacerbation of hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg)-positive chronic hepatitis B. Antivir Ther. 2008;13(4):571–579
Dhedin N, Douvin C, Kuentz M, SaintMarc MF, Reman O, Rieux C, et al. Reverse seroconversion of hepatitis B after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: a retrospective study of 37 patients with pretransplant anti-HBs and anti-HBc. Transplantation. 1998;66(5):616–619
Knoll A, Boehm S, Hahn J, Holler E, Jilg W. Reactivation of resolved hepatitis B virus infection after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2004;33(9):925–929
Mason AL, Xu L, Guo L, Kuhns M, Perrillo RP. Molecular basis for persistent hepatitis B virus infection in the liver after clearance of serum hepatitis B surface antigen. Hepatology. 1998;27(6):1736–1742
Sung JJ, Wong ML, Bowden S, Liew CT, Hui AY, Wong VW, et al. Intrahepatic hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA can be a predictor of sustained response to therapy. Gastroenterology. 2005;128(7):1890–1897
Li W, Zhao J, Zou Z, Liu Y, Li B, Sun Y, et al. Analysis of hepatitis B virus intrahepatic covalently closed circular DNA and serum viral markers in treatment-naive patients with acute and chronic HBV infection. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(2):e89046
Chan HL, Wong VW, Tse AM, Tse CH, Chim AM, Chan HY, et al. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen quantitation can reflect hepatitis B virus in the liver and predict treatment response. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;5(12):1462–1468
Wang M, Qiu N, Lu S, Xiu D, Yu J, Wang XT, et al. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen is correlated with intrahepatic total HBV DNA and cccDNA in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B but not in patients with HBV related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Med Virol. 2013;85(2):219–227
Thompson A, Nguyen T, Gane E, Abbott W, Lau G, Desmond P, et al. 380 Serum HBSAG concentration: relationship to intrahepatic and serum markers of HBV replication. J Hepatol. 2009;50:S144–S145
Chan HL, Wong VW, Wong GL, Tse CH, Chan HY, Sung JJ. A longitudinal study on the natural history of serum hepatitis B surface antigen changes in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2010;52(4):1232–1241
Wursthorn K, Lutgehetmann M, Dandri M, Volz T, Buggisch P, Zollner B, et al. Peginterferon alpha-2b plus adefovir induce strong cccDNA decline and HBsAg reduction in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2006;44(3):675–684
Werle-Lapostolle B, Bowden S, Locarnini S, Wursthorn K, Petersen J, Lau G, et al. Persistence of cccDNA during the natural history of chronic hepatitis B and decline during adefovir dipivoxil therapy. Gastroenterology. 2004;126(7):1750–1758
Laras A, Koskinas J, Dimou E, Kostamena A, Hadziyannis SJ. Intrahepatic levels and replicative activity of covalently closed circular hepatitis B virus DNA in chronically infected patients. Hepatology. 2006;44(3):694–702
Rijckborst V, Hansen BE, Cakaloglu Y, Ferenci P, Tabak F, Akdogan M, et al. Early on-treatment prediction of response to peginterferon alfa-2a for HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B using HBsAg and HBV DNA levels. Hepatology. 2010;52(2):454–461
Brunetto MR, Moriconi F, Bonino F, Lau GK, Farci P, Yurdaydin C, et al. Hepatitis B virus surface antigen levels: a guide to sustained response to peginterferon alfa-2a in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2009;49(4):1141–1150
Sonneveld MJ, Rijckborst V, Boucher CA, Hansen BE, Janssen HL. Prediction of sustained response to peginterferon alfa-2b for hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B using on-treatment hepatitis B surface antigen decline. Hepatology. 2010;52(4):1251–1257
Sonneveld MJ, Hansen BE, Piratvisuth T, Jia JD, Zeuzem S, Gane E, et al. Response-guided peginterferon therapy in hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B using serum hepatitis B surface antigen levels. Hepatology. 2013;58(3):872–880
Rijckborst V, Hansen BE, Ferenci P, Brunetto MR, Tabak F, Cakaloglu Y, et al. Validation of a stopping rule at week 12 using HBsAg and HBV DNA for HBeAg-negative patients treated with peginterferon alfa-2a. J Hepatol. 2012;56(5):1006–1011
Hou J, Ma H, Sun J, Xie Q, Xie Y, Sun Y, et al. Response-guided peginterferon alfa-2a (pegifn alfa-2a) therapy in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis b (CHB). J Hepatol. 2014;60(1):S432–S433
Reijnders JG, Rijckborst V, Sonneveld MJ, Scherbeijn SM, Boucher CA, Hansen BE, et al. Kinetics of hepatitis B surface antigen differ between treatment with peginterferon and entecavir. J Hepatol. 2011;54(3):449–454
Wursthorn K, Jung M, Riva A, Goodman ZD, Lopez P, Bao W, et al. Kinetics of hepatitis B surface antigen decline during 3 years of telbivudine treatment in hepatitis B e antigen-positive patients. Hepatology. 2010;52(5):1611–1620
Zoutendijk R, Hansen BE, Van Vuuren AJ, Boucher CA, Janssen HL. Prediction of HBSAG loss using HBSAG decline after long-term virological response to nucleos (T) IDE analogue therapy for chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. In Zoutendijk R, Hansen BE, Van Vuuren AJ, Janssen HL, editors. Gastroenterology and Hepatology. Rotterdam, Netherlands: Erasmus MC; 2010; 52, 509A
Sonneveld MJ, Wong VWS, Piratvisuth T, Jia JD, Zeuzem S, Gane E, et al. Estimating the probability of response to PEG-interferon therapy in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B: the EPIC-B study. J Hepatol. 2014;60(1):S423–S424
Manesis EK, Hadziyannis ES, Angelopoulou OP, Hadziyannis SJ. Prediction of treatment-related HBsAg loss in HBeAG-negative chronic hepatitis B: a clue from serum HBsAg levels. Antivir Ther. 2007;12(1):73–82
Cai W, Xie Q, An B, Wang H, Zhou X, Zhao G, et al. On-treatment serum HBsAg level is predictive of sustained off-treatment virologic response to telbivudine in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients. J Clin Virol. 2010;48(1):22–26
Chan HL, Wong GL, Chim AM, Chan HY, Chu SH, Wong VW. Prediction of off-treatment response to lamivudine by serum hepatitis B surface antigen quantification in hepatitis B e antigen-negative patients. Antivir Ther. 2011;16(8):1249–1257
Janssen HL, van Zonneveld M, Senturk H, Zeuzem S, Akarca US, Cakaloglu Y, et al. Pegylated interferon alfa-2b alone or in combination with lamivudine for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2005;365(9454):123–129
Marcellin P, Lau GK, Bonino F, Farci P, Hadziyannis S, Jin R, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a alone, lamivudine alone, and the two in combination in patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(12):1206–1217
Christen V, Duong F, Bernsmeier C, Sun D, Nassal M, Heim MH. Inhibition of alpha interferon signaling by hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 2007;81(1):159–165
Tjwa ET, van Oord GW, Hegmans JP, Janssen HL, Woltman AM. Viral load reduction improves activation and function of natural killer cells in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 2011;54(2):209–218
Op den Brouw ML, Binda RS, van Roosmalen MH, Protzer U, Janssen HL, van der Molen RG, et al. Hepatitis B virus surface antigen impairs myeloid dendritic cell function: a possible immune escape mechanism of hepatitis B virus. Immunology. 2009;126(2):280–289
Boni C, Laccabue D, Lampertico P, Giuberti T, Vigano M, Schivazappa S, et al. Restored function of HBV-specific T cells after long-term effective therapy with nucleos(t)ide analogues. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(4):963–973
Brouwer WP, Xie Q, Sonneveld MJ, Zhang NP, Zhang Q, Tabak F, et al. Adding peginterferon to entecavir increases response rates in HBEAG-positive chronic hepatitis B patients: week 96 results of a global multicenter randomised trial (ares study). J Hepatol. 2014;60(1):S2
Tan AT, Hoang LT, Chin D, Rasmussen E, Lopatin U, Hart S, et al. Reduction of HBV replication prolongs the early immunological response to IFNα therapy. J Hepatol. 2014;60(1):54–61
Chan HL, Ahn SH, Chang TT, Peng CY, Wong D, Coffin CS, et al. Peginterferon lambda for the treatment of chronic hepatitis b (CHB): a phase 2b comparison with peginterferon alfa in patients with HBeAg-positive disease. J Hepatol. 2014;60(1):S48
Lanford RE, Guerra B, Chavez D, Giavedoni L, Hodara VL, Brasky KM, et al. GS-9620, an oral agonist of Toll-like receptor-7, induces prolonged suppression of hepatitis B virus in chronically infected chimpanzees. Gastroenterology. 2013; 144(7):1508–1517, 17 e1–e10
Gane EJ, Sicard E, Gordon SC, Gruener D, Roberts SK, Kim S, et al. Safety and pharmacodynamics of oral TLR-7 agonist GS-9620 in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2013;58(4):661A–662A
Tzeng HT, Tsai HF, Liao HJ, Lin YJ, Chen L, Chen PJ, et al. PD-1 blockage reverses immune dysfunction and hepatitis B viral persistence in a mouse animal model. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(6):e39179
Bachy E, Coiffier B. Anti-PD1 antibody: a new approach to treatment of lymphomas. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(1):7–8
Khodabakhshi B, Moradi A, Semnani S, Amiriani T, Roshandel G. Vaccine therapy in hepatitis B carriers: a randomized double blind clinical trial. HIp Int. 2013;7:S226
Brillanti S, Laterza L, Cecinato P, Bazzoli F. Loss and seroconversion of hepatitis B surface antigen after vaccine therapy in chronic hepatitis B patients treated with nucleoside/nucleotide analogues. Hip Int. 2013;7:S169–S170
Jiang W, Chen R, Kong X, Long F, Shi Y. Immunization with adenovirus LIGHT-engineered dendritic cells induces potent T cell responses and therapeutic immunity in HBV transgenic mice. Vaccine. 2014;32(35):4565–4570
Lucifora J, Xia Y, Reisinger F, Zhang K, Stadler D, Cheng X, et al. Specific and nonhepatotoxic degradation of nuclear hepatitis B virus cccDNA. Science. 2014;343(6176):1221–1228
Piratvisuth T, Marcellin P. Further analysis is required to identify an early stopping rule for peginterferon therapy that is valid for all hepatitis B e antigen-positive patients. Hepatology. 2011; 53(3):1054–1055; author reply 5.
Lau GKK, Marcellin P, Brunetto M, Piratvisuth T, Kapprell HP, Messinger D, et al. On-treatment monitoring of HBsAg levels to predict response to peginterferon alfa-2A in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Journal of Hepatology. In Lau GKK, liesjethomas@elementscommunications.com. Hong Kong, Hong Kong: Department of Medicine, Queen Mary Hospital, University of Hong Kong; 2009; 50; S333
Gane E, Jia J, Han K, Tanwandee T, Chuang WL, Marcellin P, et al. 69 Neptune study: on-treatment hbsag level analysis confirms prediction of response observed in phase 3 study of peginterferon alfa-2a in hbeag-positive patients. Journal of Hepatology. 2011; 54, Suppl 1(0):S31
Chan HL, Wong VW, Chim AM, Chan HY, Wong GL, Sung JJ. Serum HBsAg quantification to predict response to peginterferon therapy of e antigen positive chronic hepatitis B. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;32(11–12):1323–1331
Rijckborst V, Hansen BE, Ferenci P, Brunetto MR, Tabak F, Cakaloglu Y, et al. Early on-treatment HBsAG and HBV DNA levels identify HBeAG-negative patients not responding to 48 or 96 weeks of peginterferon alfa- 2a therapy. Hepatology. In Rijckborst V, Hansen BE, editors. Gastroenterology and Hepatology. Rotterdam, Netherlands: Erasmus MC University Medical Center; 2010; 52; 557A-8A
Moucari R, Mackiewicz V, Lada O, Ripault MP, Castelnau C, Martinot-Peignoux M, et al. Early serum HBsAg drop: a strong predictor of sustained virological response to pegylated interferon alfa-2a in HBeAg-negative patients. Hepatology. 2009;49(4):1151–1157
Marcellin P, Piratvisuth T, Brunetto M, Bonino F, Farci P, Yurdaydin C, et al. On-treatment decline in serum HBsAg levels predicts sustained immune control 1 year post-treatment and subsequent HBsAg clearance in HBeAg-negative hepatitis B virus-infected patients treated with peginterferon alfa-2a [40 kD] (PEGASYS). Hep Intl. 2010;4(1):151
Marcellin P, Bonino F, Yurdaydin C, Hadziyannis S, Moucari R, Kapprell HP, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen levels: association with 5-year response to peginterferon alfa-2a in hepatitis B e-antigen-negative patients. Hepatol Int. 2013;7(1):88–97
Janssen HL, Sonneveld MJ, Brunetto MR. Quantification of serum hepatitis B surface antigen: is it useful for the management of chronic hepatitis B? Gut. 2012;61(5):641–645
Acknowledgments
Prof.Dr. H.L.A. Janssen received grants from and is a consultant for Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Novartis, Roche, Merck and Innogenetics.
Compliance with ethical requirements and Conflict of interest
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects. Margo J. H. van Campenhout and Harry L. A. Janssen declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Campenhout, M.J.H., Janssen, H.L.A. How to achieve immune control in chronic hepatitis B?. Hepatol Int 9, 9–16 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-014-9571-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-014-9571-3