Abstract
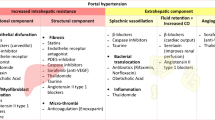
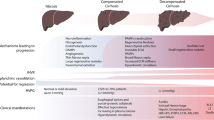
Portal hypertension (PH) is a common complication of chronic liver disease, and it determines most complications leading to death or liver transplantation in patients with liver cirrhosis. PH results from increased resistance to portal blood flow through the cirrhotic liver. This is caused by two mechanisms: (a) distortion of the liver vascular architecture and (b) hepatic microvascular dysfunction. Increment in hepatic resistance is latterly accompanied by splanchnic vasodilation, which further aggravates PH. Hepatic microvascular dysfunction occurs early in the course of chronic liver disease as a consequence of inflammation and oxidative stress and determines loss of the normal phenotype of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSEC). The cross-talk between LSEC and hepatic stellate cells induces activation of the latter, which in turn proliferate, migrate and increase collagen deposition around the sinusoids, contributing to fibrogenesis, architectural disruption and angiogenesis. Therapy for PH aims at correcting these pathophysiological abnormalities: liver injury, fibrogenesis, increased hepatic vascular tone and splanchnic vasodilatation. Continuing liver injury may be counteracted specifically by etiological treatments, while architectural disruption and fibrosis can be ameliorated by a variety of anti-fibrogenic drugs and anti-angiogenic strategies. Sinusoidal endothelial dysfunction is ameliorated by statins and other drugs increasing NO availability. Splanchnic hyperemia can be counteracted by non-selective beta-blockers (NSBBs), vasopressin analogs and somatostatin analogs. Future treatment of portal hypertension will evolve to use etiological treatments together with anti-fibrotic agents and/or drugs improving microvascular function in initial stages of cirrhosis (pre-primary prophylaxis), while NSBBs will be added in advanced stages of the disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsochatzis EA, Bosch J, Burroughs AK. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet 2014;10:6736
Bosch J, Pizcueta P, Feu F, Fernandez M, Garcia-Pagan JC. Pathophysiology of portal hypertension. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 1992;21:1–14
Iwakiri Y, Groszmann RJ. The hyperdynamic circulation of chronic liver diseases: from the patient to the molecule. Hepatology 2006;43:S121–S131
Garcia-Pagan JC, Gracia-Sancho J, Bosch J. Functional aspects on the pathophysiology of portal hypertension in cirrhosis. J Hepatol 2012;57:458–461
Befeler AS, Di Bisceglie AM. Hepatocellular carcinoma: diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology 2002;122:1609–1619
Pinzani M, Rosselli M, Zuckermann M. Liver cirrhosis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2011;25:281–290
Bathal PS, Grossmann HJ. Reduction of the increased portal vascular resistance of the isolated perfused cirrhotic rat liver by vasodilators. J Hepatol 1985;1:325–329
DeLeve LD. Hepatic microvasculature in liver injury. Semin Liver Dis 2007;27:390–400
Pinzani M, Gentilini P. Biology of hepatic stellate cells and their possible relevance in the pathogenesis of portal hypertension in cirrhosis. Semin Liver Dis 1999;19:397–410
Smedsrod B, Le CD, Ikejima K, Jaeschke H, Kawada N, Naito M, et al. Hepatic sinusoidal cells in health and disease: update from the 14th international symposium. Liver Int 2009;29:490–501
Gracia-Sancho J, Lavina B, Rodriguez-Vilarrupla A, Garcia-Caldero H, Bosch J, Garcia-Pagan JC. Enhanced vasoconstrictor prostanoid production by sinusoidal endothelial cells increases portal perfusion pressure in cirrhotic rat livers. J Hepatol 2007;47:220–227
Steib CJ, Gerbes AL, Bystron M, op den Winkel M, Hartl J, Roggel F et al. Kupffer cell activation in normal and fibrotic livers increases portal pressure via thromboxane A(2). J Hepatol 2007; 47:228–238
Pinzani M. Hepatic stellate (Ito) cells—expanding roles for A liver-specific pericyte. J Hepatol 1995;22:700–706
Friedman SL. Liver fibrosis—from bench to bedside. J Hepatol 2003;38 Suppl 1:S38–S53
DeLeve LD, Wang X, Guo Y. Sinusoidal endothelial cells prevent rat stellate cell activation and promote reversion to quiescence. Hepatology 2008;48:920–930
Nieto N. Oxidative-stress and IL-6 mediate the fibrogenic effects of [corrected] Kupffer cells on stellate cells. Hepatology 2006;44:1487–1501
Smedsrod B, De Bleser PJ, Braet F, Lovisetti P, Vanderkerken K, Wisse E, et al. Cell biology of liver endothelial and Kupffer cells. Gut 1994;35:1509–1516
Wisse E. An ultrastructural characterization of the endothelial cell in the rat liver sinusoid under normal and various experimental conditions, as a contribution to the distinction between endothelial and Kupffer cells. J Ultrastruct Res 1972;38:528–562
Smedsrod B, Pertoft H, Gustafson S, Laurent TC. Scavenger functions of the liver endothelial cell. Biochem J 1990;266:313–327
McCuskey RS, Bethea NW, Wong J, McCuskey MK, Abril ER, Wang X, et al. Ethanol binging exacerbates sinusoidal endothelial and parenchymal injury elicited by acetaminophen. J Hepatol 2005;42:371–377
March S, Hui EE, Underhill GH, Khetani S, Bhatia SN. Microenvironmental regulation of the sinusoidal endothelial cell phenotype in vitro. Hepatology 2009;50:920–928
Graupera M, March S, Engel P, Rodes J, Bosch J, Garcia-Pagan JC. Sinusoidal endothelial COX-1-derived prostanoids modulate the hepatic vascular tone of cirrhotic rat livers. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2005;288:G763–G770
Rockey DC, Fouassier L, Chung JJ, Carayon A, Vallee P, Rey C, et al. Cellular localization of endothelin-1 and increased production in liver injury in the rat: potential for autocrine and paracrine effects on stellate cells. Hepatology 1998;27:472–480
Rockey DC, Chung JJ. Reduced nitric oxide production by endothelial cells in cirrhotic rat liver: endothelial dysfunction in portal hypertension. Gastroenterology 1998;114:344–351
Pinzani M, Failli P, Ruocco C, Casini A, Milani S, Baldi E, et al. Fat-storing cells as liver-specific pericytes. Spatial dynamics of agonist-stimulated intracellular calcium transients. J Clin Invest 1992;90:642–646
Marra F, Pinzani M. Role of hepatic stellate cells in the pathogenesis of portal hypertension. Nefrologia 2002; 22 Suppl 5:34–40
Sleyster EC, Knook DL. Relation between localization and function of rat liver Kupffer cells. Lab Invest 1982;47:484–490
Steib CJ, Bilzer M, op den Winkel M, Pfeiler S, Hartmann AC, Hennenberg M, et al. Treatment with the leukotriene inhibitor montelukast for 10 days attenuates portal hypertension in rat liver cirrhosis. Hepatology 2010; 51:2086–2096
Rockey DC, Weisiger RA. Endothelin induced contractility of stellate cells from normal and cirrhotic rat liver: implications for regulation of portal pressure and resistance. Hepatology 1996;24:233–240
Bosch J, Arroyo V, Betriu A, Mas A, Carrilho F, Rivera F, et al. Hepatic hemodynamics and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 1980;78:92–99
Bataller R, Gines P, Nicolas JM, Gorbig MN, Garcia-Ramallo E, Gasull X, et al. Angiotensin II induces contraction and proliferation of human hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology 2000;118:1149–1156
Graupera M, Garcia-Pagan JC, Abraldes JG, Peralta C, Bragulat M, Corominola H, et al. Cyclooxygenase-derived products modulate the increased intrahepatic resistance of cirrhotic rat livers. Hepatology 2003;37:172–181
Gracia-Sancho J, Lavina B, Rodriguez-Vilarupla A, Garcia-Caldero H, Fernandez M, Bosch J, et al. Increased oxidative stress in cirrhotic rat livers: a potential mechanism contributing to reduced nitric oxide bioavailability. Hepatology 2008;47:1248–1256
Yokoyama Y, Xu H, Kresge N, Keller S, Sarmadi AH, Baveja R, et al. Role of thromboxane A2 in early BDL-induced portal hypertension. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2002;284:G453–G460
Rosado E, Rodriguez-Vilarrupla A, Gracia-Sancho J, Tripathi D, Garcia-Caldero H, Bosch J, et al. Terutroban, a TP-receptor antagonist, reduces portal pressure in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 2013;58:1424–1435
Gracia-Sancho J, Russo L, Garcia-Caldero H, Garcia-Pagan JC, Garcia-Cardena G, Bosch J. Endothelial expression of transcription factor Kruppel-like factor 2 and its vasoprotective target genes in the normal and cirrhotic rat liver. Gut 2011;60:517–524
Shah V, Toruner M, Haddad F, Cadelina G, Papapetropoulos A, Choo K, et al. Impaired endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity associated with enhanced caveolin binding in experimental cirrhosis in the rat. Gastroenterology 1999;117:1222–1228
Shah V, Wiest R, Garcia-Cardena G, Cadelina G, Groszmann RJ, Sessa WC. Hsp90 regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase contributes to vascular control in portal hypertension. Am J Physiol 1999;277:G463–G468
Shah V, Cao S, Hendrickson H, Yao J, Katusic ZS. Regulation of hepatic eNOS by caveolin and calmodulin after bile duct ligation in rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2001;280:G1209–G1216
Laleman W, Omasta A, Van de CM, Zeegers M, Vander EI, Van LL, et al. A role for asymmetric dimethylarginine in the pathophysiology of portal hypertension in rats with biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 2005;42:1382–1390
Liu SL, Premont RT, Kontos CD, Zhu SK, Rockey DC. A crucial role for GRK2 in regulation of endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase function in portal hypertension. Nat Med 2005;11:952–958
Matei V, Rodriguez-Vilarrupla A, Deulofeu R, Colomer D, Fernandez M, Bosch J, et al. The eNOS cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin improves endothelial dysfunction in livers of rats with CCl4 cirrhosis. Hepatology 2006;44:44–52
Gracia-Sancho J, Laviña B, Rodriguez-Vilarupla A, Brandes RP, Fernandez M, Bosch J, et al. Evidence against NADPH oxidase modulating hepatic vascular tone in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:959–966
Rosado E, Rodriguez-Vilarrupla A, Gracia-Sancho J, Monclus M, Bosch J, Garcia-Pagan JC. Interaction between NO and COX pathways modulating hepatic endothelial cells from control and cirrhotic rats. J Cell Mol Med 2012;16:2461–2470
Groszmann RJ. Hyperdynamic circulation of liver disease 40 years later: pathophysiology and clinical consequences. Hepatology 1994;20:1359–1363
Wiest R, Shah V, Sessa WC, Groszmann RJ. NO overproduction by eNOS precedes hyperdynamic splanchnic circulation in portal hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol 1999;276:G1043–G1051
Martell M, Coll M, Ezkurdia N, Raurell I, Genesca J. Physiopathology of splanchnic vasodilation in portal hypertension. World J Hepatol 2010;2:208–220
Hennenberg M, Biecker E, Trebicka J, Jochem K, Zhou Q, Schmidt M, et al. Defective RhoA/Rho-kinase signaling contributes to vascular hypocontractility and vasodilation in cirrhotic rats. Gastroenterology 2006;130:838–854
Fernandez M, Mejias M, Angermayr B, Garcia-Pagan JC, Rodes J, Bosch J. Inhibition of VEGF receptor-2 decreases the development of hyperdynamic splanchnic circulation and portal-systemic collateral vessels in portal hypertensive rats. J Hepatol 2005;43:98–103
Fernandez M, Mejias M, Garcia-Pras E, Mendez R, Garcia-Pagan JC, Bosch J. Reversal of portal hypertension and hyperdynamic splanchnic circulation by combined vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor blockade in rats. Hepatology 2007;46:1208–1217
Mejias M, Garcia-Pras E, Tiani C, Miquel R, Bosch J, Fernandez M. Beneficial effects of sorafenib on splanchnic, intrahepatic, and portocollateral circulations in portal hypertensive and cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 2009;49:1245–1256
Trebicka J, Hennenberg M, Odenthal M, Shir K, Klein S, Granzow M, et al. Atorvastatin attenuates hepatic fibrosis in rats after bile duct ligation via decreased turnover of hepatic stellate cells. J Hepatol 2010;53:702–712
Marrone G, Maeso-Díaz R, Garcia-Cardena G, Garcia-Pagan JC, Bosch J, Gracia-Sancho J. KLF2 exerts anti-fibrotic and vasoprotective effects in cirrhotic rat livers: behind the molecular mechanisms of statins. Gut 2014; doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308338
Marrone G, Russo L, Rosado E, Hide D, Garcia-Cardena G, Garcia-Pagan JC, et al. The transcription factor KLF2 mediates hepatic endothelial protection and paracrine endothelial-stellate cell deactivation induced by statins. J Hepatol 2013;58:98–103
Di Pascoli M, Divi M, Rodriguez-Vilarrupla A, Rosado E, Gracia-Sancho J, Vilaseca M, et al. Resveratrol improves intrahepatic endothelial dysfunction and reduces hepatic fibrosis and portal pressure in cirrhotic rats. J Hepatol 2013;58:904–910
Guillaume M, Rodriguez-Vilarrupla A, Gracia-Sancho J, Rosado E, Mancini A, Bosch J, et al. Recombinant human manganese superoxide dismutase reduces liver fibrosis and portal pressure in CCl4-cirrhotic rats. J Hepatol 2013;58:240–246
Hsu SJ, Wang SS, Hsin IF, Lee FY, Huang HC, Huo TI, et al. Green tea polyphenol decreases the severity of portosystemic collaterals and mesenteric angiogenesis in rats with liver cirrhosis. Clin Sci (Lond) 2014;126:633–644
Verbeke L, Farre R, Trebicka J, Komuta M, Roskams T, Klein S, et al. Obeticholic acid, a farnesoid X receptor agonist, improves portal hypertension by two distinct pathways in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 2014;59:2286–2298
Klein S, Van Beuge MM, Granzow M, Beljaars L, Schierwagen R, Kilic S, et al. HSC-specific inhibition of Rho-kinase reduces portal pressure in cirrhotic rats without major systemic effects. J Hepatol 2012;57:1220–1227
Fallowfield JA, Hayden AL, Snowdon VK, Aucott RL, Stutchfield BM, Mole DJ, et al. Relaxin modulates human and rat hepatic myofibroblast function and ameliorates portal hypertension in vivo. Hepatology 2014;59:1492–1504
Matei V, Rodriguez-Vilarrupla A, Deulofeu R, Garcia-Caldero H, Fernandez M, Bosch J, et al. Three-day tetrahydrobiopterin therapy increases in vivo hepatic NOS activity and reduces portal pressure in CCl4 cirrhotic rats. J Hepatol 2008;49:192–197
Mookerjee RP, Mehta G, Balasubramaniyan V, Mohamed F, Davies N, Sharma V, et al. Hepatic dimethylarginine-dimethylaminohydrolase1 is reduced in cirrhosis and is a target for therapy in portal hypertension. J Hepatol 2014;10
Hernandez-Guerra M, Garcia-Pagan JC, Turnes J, Bellot P, Deulofeu R, Abraldes JG, et al. Ascorbic acid improves the intrahepatic endothelial dysfunction of patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Hepatology 2006;43:485–491
Yang YY, Lee TY, Huang YT, Chan CC, Yeh YC, Lee FY, et al. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) determines the improvement of hepatic endothelial dysfunction by vitamin E in cirrhotic rats. Liver Int 2012;32:48–57
De Gottardi A, Berzigotti A, Seijo S, D’Amico M, Thormann W, Abraldes JG, et al. Postprandial effects of dark chocolate on portal hypertension in patients with cirrhosis: results of a phase 2, double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr 2012;96:584–590
Abraldes JG, Rodriguez-Vilarrupla A, Graupera M, Zafra C, Garcia-Caldero H, Garcia-Pagan JC, et al. Simvastatin treatment improves liver sinusoidal endothelial dysfunction in CCl(4) cirrhotic rats. J Hepatol 2007;46:1040–1046
Trebicka J, Hennenberg M, Laleman W, Shelest N, Biecker E, Schepke M, et al. Atorvastatin lowers portal pressure in cirrhotic rats by inhibition of RhoA/Rho-kinase and activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Hepatology 2007;46:242–253
Abraldes JG, Albillos A, Banares R, Turnes J, Gonzalez R, Garcia-Pagan JC, et al. Simvastatin lowers portal pressure in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension: a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2009;136:1651–1658
Abraldes JG, Villanueva C, Aracil C, Turnes J, Hernandez-Guerra M, Genesca J, et al. Addition of simvastatin to standard treatment improves survival after variceal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis. A double-blind randomized trial (NCT01095185). J Hepatol 2014;60:S525
Bosch J, Abraldes JG, Fernandez M, Garcia-Pagan JC. Hepatic endothelial dysfunction and abnormal angiogenesis: new targets in the treatment of portal hypertension. J Hepatol 2010;53:558–567
Mejias M, Coch L, Berzigotti A, Garcia-Pras E, Gallego J, Bosch J, et al. Antiangiogenic and antifibrogenic activity of pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) in bile duct-ligated portal hypertensive rats. Gut 2014. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307138
Yang L, Kwon J, Popov Y, Gajdos GB, Ordog T, Brekken RA, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes fibrosis resolution and repair in mice. Gastroenterology 2014;146:1339–1350
Coch L, Mejias M, Berzigotti A, Garcia-Pras E, Gallego J, Bosch J, et al. Disruption of negative feedback loop between vasohibin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor decreases portal pressure, angiogenesis, and fibrosis in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 2014;60:633–647
D’Amico M, Mejias M, Garcia-Pras E, Abraldes JG, Garcia-Pagan JC, Fernandez M, et al. Effects of the combined administration of propranolol plus sorafenib on portal hypertension in cirrhotic rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2012;302:G1191–1198
Yang YY, Lee KC, Huang YT, Wang YW, Hou MC, Lee FY, et al. Effects of N-acetylcysteine administration in hepatic microcirculation of rats with biliary cirrhosis. J Hepatol 2008;49:25–33
Delgado MG, Gracia-Sancho J, Marrone G, Rodriguez-Vilarupla A, Deulofeu R, Abraldes JG, et al. Leptin receptor blockade reduces intrahepatic vascular resistance and portal pressure in an experimental model of rat liver cirrhosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2013;305:G496–G502
Tripathi D, Erice E, Gracia-Sancho J, Garcia-Caldero H, Sarin SK, Bosch J, et al. Metformin reduces hepatic resistance and portal pressure in CCl4 and BDL cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 2013;58:294A–297A
Laleman W, Van Landeghem L, Van der Elst I, Zeegers M, Fevery J, Nevens F. Nitroflurbiprofen, a nitric oxide-releasing cyclooxygenase inhibitor, improves cirrhotic portal hypertension in rats. Gastroenterology 2007;132:709–719
Luo W, Meng Y, Ji HL, Pan CQ, Huang S, Yu CH, et al. Spironolactone lowers portal hypertension by inhibiting liver fibrosis, ROCK-2 activity and activating NO/PKG pathway in the bile-duct-ligated rat. PLoS ONE 2012;7:e34230
Klein S, Klosel J, Schierwagen R, Korner C, Granzow M, Huss S, et al. Atorvastatin inhibits proliferation and apoptosis, but induces senescence in hepatic myofibroblasts and thereby attenuates hepatic fibrosis in rats. Lab Invest 2012;92:1440–1450
Acknowledgements
Research from Dr. Gracia-Sancho & Prof. Bosch teams is funded by grants from the Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (Ramón y Cajal program & ACI colabora), the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (FIS & CIBEREHD), and the European Union (fondos FEDER).
Compliance with ethical requirements and Conflict of interest
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects. Jordi Gracia-Sancho, Raquel Maeso-Díaz, Anabel Fernández-Iglesias, María Navarro-Zornoza and Jaime Bosch declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gracia-Sancho, J., Maeso-Díaz, R., Fernández-Iglesias, A. et al. New cellular and molecular targets for the treatment of portal hypertension. Hepatol Int 9, 183–191 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-015-9613-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-015-9613-5