Abstract
Background and aims
In patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) who have failed on other nucleos(t)ide analogs (NUCs), the combination of entecavir (ETV) plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), two potent agents with non-overlapping resistance profiles, may provide a single rescue regimen.
Methods
In this single-arm, open-label study, 92 CHB patients with a primary non-response, partial response, or virologic breakthrough on their current NUC were switched to ETV (1 mg) plus TDF (300 mg) and treated for 96 weeks.
Results
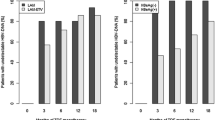
At baseline, 62 % of patients were HBeAg(+) and mean HBV DNA was 4.4 log10IU/mL. Patients had received ≥1 line of prior NUC therapy, with the latest regimen consisting of monotherapy with ETV (53 %), lamivudine (LVD 22 %), TDF (12 %), adefovir (ADV 4 %), or telbivudine (2 %), or combinations of these agents (7 %); 58 % had evidence of single- or multidrug resistance mutations (LVD 52 %, ETV 26 %; ADV 7 %). Response rates for HBV DNA <50 IU/mL were 76 % (70/92) at week 48 (primary endpoint), and 85 % (78/92) at week 96, including 80 % (16/20) in prior LVD failures, 100 % (4/4) in ADV failures, 82 % (9/11) in TDF failures, and 88 % (42/48) in ETV failures. No treatment-emergent resistance to ETV or ADV was observed. ETV/TDF was well tolerated, with no significant renal or additive toxicities observed.
Conclusions
In NUC-experienced patients who have failed prior NUC therapy, ETV/TDF was well tolerated and effective, achieving virologic suppression through 96 weeks in the majority (85 %), irrespective of prior NUC exposure, without occurrence of treatment-emergent resistance to either agent.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
European Association For The Study Of The Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2012;57:167–185
Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B: update 2009. Hepatology 2009;50:661–662
Liaw YF, Kao JH, Piratvisuth T, Chan HLY, Chien RN, Liu CJ, et al. Asian-Pacific consensus statement on the management of chronic hepatitis B: a 2012 update. Hepatol Int 2012;6:531–561
Zoulim F, Locarnini S. Management of treatment failure in chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2012;56(Suppl 1):S112–S122
Zoulim F, Locarnini S. Hepatitis B virus resistance to nucleos(t)ide analogues. Gastroenterology 2009;137:1593–1608
Gaia S, Barbon V, Smedile A, Olivero A, Carenzi S, Lagget M, et al. Lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B: an observational study on adefovir in monotherapy or in combination with lamivudine. J Hepatol 2008;48:540–547
Pellicelli AM, Barbaro G, Francavilla R, Romano M, Barbarini G, Mazzoni E, et al. Adefovir and lamivudine in combination compared with adefovir monotherapy in HBeAg-negative adults with chronic hepatitis B virus infection and clinical or virologic resistance to lamivudine: a retrospective, multicenter, nonrandomized, open-label study. Clin Ther 2008;30:317–323
Ijaz S, Arnold C, Dervisevic S, Mechurova J, Tatman N, Tedder RS, et al. Dynamics of lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus during adefovir monotherapy versus lamivudine plus adefovir combination therapy. J Med Virol 2008;80:1160–1170
Kwon HC, Cheong JY, Cho SW, Choi JM, Hong SP, Kim SO, et al. Emergence of adefovir-resistant mutants after reversion to YMDD wild-type in lamivudine-resistant patients receiving adefovir monotherapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;24:49–54
Tenney DJ, Rose RE, Baldick CJ, Pokornowski KA, Eggers BJ, Fang J, et al. Long-term monitoring shows hepatitis B virus resistance to entecavir in nucleoside-naïve patients is rare through 5 years of therapy. Hepatology 2009;49:1503–1514
Marcellin P, Gane E, Buti M, Afdhal N, Sievert W, Jacobson IM, et al. Regression of cirrhosis during treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for chronic hepatitis B: a 5-year open-label follow-up study. Lancet 2013;381:468–475
Lok AS, Trinh H, Carosi G, Akarca US, Gadano A, Habersetzer F, et al. Efficacy of entecavir with or without tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for nucleos(t)ide-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2012;143(619–628):e1
Petersen J, Ratziu V, Buti M, Janssen HL, Brown A, Lampertico P, et al. Entecavir plus tenofovir combination as rescue therapy in pre-treated chronic hepatitis B patients: an international multicenter cohort study. J Hepatol 2012;56:520–526
Park JY, Kim CW, Bae SH, Hoon S. Entecavir plus tenofovir combination therapy in patients with multi-drug resistant chronic hepatitis B: the 48-week results of a multicenter, prospective study. Hepatology 2014;60:1096A (abstract 1865)
Lee YB, Lee JH, Lee DH, Cho H, Ahn H, Choi WM, et al. Efficacy of entecavir-tenofovir combination therapy for chronic hepatitis B patients with multidrug-resistant strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2014;58:6710–6716
Lim YS, Byun KS, Yoo BC, Kwon SY, Kim YJ, An J, et al. Tenofovir monotherapy versus tenofovir and entecavir combination therapy in patients with entecavir-resistant chronic hepatitis B with multiple drug failure: results of a randomised trial. Gut 2015. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308353
Lutgehetmann M, Schollmeyer J, Volz T, Lohse A, Buggisch P, Sterneck M, et al. Rescue therapy with combination of entecavir and tenofovir in patients with chronic HBV, advanced fibrosis and multiple previous treatment failures is safe and highly efficient. J Hepatol 2009;50(suppl):S335 (poster 922)
Zeuzem S, Gane E, Liaw YF, Lim SG, DiBisceglie A, Buti M, et al. Baseline characteristics and early on-treatment response predict the outcomes of 2 years of telbivudine treatment of chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2009;51:11–20
van Bömmel F, de Man RA, Wedemeyer H, Deterding K, Petersen J, Buggisch P, et al. Long-term efficacy of tenofovir monotherapy for hepatitis B virus-monoinfected patients after failure of nucleoside/nucleotide analogues. Hepatology 2010;51:73–80
Patterson SJ, George J, Strasser SI, Lee AU, Sievert W, Nicoll AJ, et al. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate rescue therapy following failure of both lamivudine and adefovir dipivoxil in chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2011;60:247–254
Berg T, Marcellin P, Zoulim F, Moller B, Trinh H, Chan S, et al. Tenofovir is effective alone or with emtricitabine in adefovir-treated patients with chronic-hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology 2010;139:1207–1217
Berg T, Zoulim F, Moeller B, Trinh H, Marcellin P, Chan S, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of emtricitabine plus tenofovir DF vs. tenofovir DF monotherapy in adefovir-experienced chronic hepatitis B patients. J Hepatol 2014;60:715–722
Kim YJ, Sinn DH, Gwak GY, Choi MS, Koh KC, Paik SW, et al. Tenofovir rescue therapy for chronic hepatitis B patients after multiple treatment failures. World J Gastroenterol 2012;18:6996–7002
Lim YS, Yoo BC, Byun KS, Kwon SY, Kim YJ, An J, et al. Tenofovir monotherapy versus tenofovir and entecavir combination therapy in adefovir-resistant chronic hepatitis B patients with multiple drug failure: results of a randomised trial. Gut 2015. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308435
Keskin O, Ormeci AC, Baran B, Kabaçam G, Tüzün A, Karatayli E, et al. Efficacy of tenofovir in adefovir-experienced patients compared with treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B. Antivir Ther 2014;19:543–550
Lavocat F, Dény P, Pichoud C, Al Hawajri N, Kitrinos K, Borroto-Esoda K, et al. Similar evolution of hepatitis B virus quasispecies in patients with incomplete adefovir response receiving tenofovir/emtricitabine combination or tenofovir monotherapy. J Hepatol 2013;59:684–695
van Bömmel F, Trojan J, Deterding K, Wedemeyer H, Wasmuth HE, Hüppe D, et al. Evolution of adefovir-resistant HBV polymerase gene variants after switching to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate monotherapy. Antivir Ther 2012;17:1049–1058
Lee S, Park JY, Park H, Kim MY, Ahn SH, Kim P, et al. Tenofovir mono-rescue therapy vs. tenofovir plus entecavir combination-rescue therapy in chronic hepatitis B with lamivudine and entecavir resistance: a Korean multi-center study. Hepatology 2014;60:1105A (abstract 1880)
Zoutendijk R, Reijnders JG, Brown A, Zoulim F, Mutimer D, Deterding K, et al. Entecavir treatment for chronic hepatitis B: adaptation is not needed for the majority of naïve patients with a partial virological response. Hepatology 2011;54:443–451
Luo J, Li X, Wu Y, Lin G, Pang Y, Zhang X, et al. Efficacy of entecavir treatment for up to 5 years in nucleos(t)ide-naïve chronic hepatitis B patients in real life. Int J Med Sci 2013;10:427–433
Hosaka T, Suzuki F, Kobayashi M, Seko Y, Kawamura Y, Sezaki H, et al. Long-term entecavir treatment reduces hepatocellular carcinoma incidence in patients with hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2013;58:98–107
Tien C, Xu JJ, Chan LS, Chang M, Lim C, Lee S, et al. Long-term treatment with tenofovir in Asian-American chronic hepatitis B patients is associated with abnormal renal phosphate handling. Dig Dis Sci 2015;60:566–572
Gara N, Zhao X, Collins MT, Chong WH, Kleiner DE, Jake Liang T, et al. Renal tubular dysfunction during long-term adefovir or tenofovir therapy in chronic hepatitis B. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2012;35:1317–1325
Gracey DM, Snelling P, McKenzie P, Strasser SI. Tenofovir-associated Fanconi syndrome in patients with chronic hepatitis B monoinfection. Antivir Ther 2013;18:945–948
Vigano M, Lampertico P, Mangia G, Soffredini R, Facchetti F, Invernizzi F, et al. Incidence and clinical consequences of reduced tubular phosphate reabsorption in naïve chronic hepatitis B patients either untreated or treated with tenofovir for 2 years in a field practice study. Hepatology 2013;58 (suppl):678A (abstract 978)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all principal investigators involved in this study: Gioacchino Angarano, Victoria Arama, Christoph Berg, Xavier Causse, Robert De Knegt, Christoph Eisenbach, Robert Galle, Maciej Jabłkowski, Dominique Larrey, Stefan Luth, Hendrik W Reesink, Eckart Schott, Adrian Streinu-Cercel, Andreas Umgelter, Bart Van Hoek, and Stefan Zeuzem, as well as Aleksandra Kedzierska from Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declaration of funding
The study was sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb. The study was designed and conducted by the sponsor in collaboration with the principal investigators. The sponsor collected the data, monitored study conduct, and performed the statistical analyses. All authors had access to the study data, and have reviewed and approved the final manuscript. Editorial assistance was provided by Isabelle Kaufmann of Articulate Science UK, and was supported by a grant from Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Conflict of interest
Fabien Zoulim has received consulting, lecture fees or research grants from Assembly Bioscience, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Novira, Roche, and Tekmira. Patrick Marcellin has received grants and research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb, and participated as a speaker and in advisory boards for Bristol-Myers Squibb. Jörg Petersen has received research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, and Roche, and has received personal fees from AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, and Roche. Krzysztof Simon has received lecturing fees and has participated in advisory boards for AbbVie, Alfa Wassermann, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Janssen, MSD, and Roche-Poland. Wojciech Wasiak is an employee of inVentiv Health Clinical. Harry L. A. Janssen has received consulting fees and research grants from Anadys, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Innogenetics, Kirin, Merck, Medtronic, Novartis, Roche, and Santaris. Soumaya Bendahmane and Isabelle Klauck are employees of Bristol-Myers Squibb. Jolanta Białkowska-Warzecha, Mircea Mihai Diculescu, Adrian Eugen Goldis, Renate Heyne, and Tomasz Mach have nothing to declare.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients. The study protocol conforms to the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki, as reflected in a priori approval by the institution’s human research committee.
Additional information
Study registration number: NCT01063036.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12072_2016_9737_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Table 1: Baseline HBV variants detected in patients with failure on prior ETV therapy. Supplementary Table 2: Baseline and on-treatment characteristics of the six patients with HBV DNA ≥50 IU/mL at week 96 of ETV/TDF. Supplementary Table 3: Baseline and on-treatment characteristics of the seven patients with primary non-response and/or virologic breakthrough on ETV/TDF (PDF 133 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zoulim, F., Białkowska-Warzecha, J., Diculescu, M.M. et al. Entecavir plus tenofovir combination therapy for chronic hepatitis B in patients with previous nucleos(t)ide treatment failure. Hepatol Int 10, 779–788 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-016-9737-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-016-9737-2