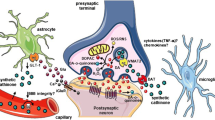
Abstract
Morphinans are a class of compounds containing the basic structure of morphine. It is well-known that morphinans possess diverse pharmacological effects on the central nervous system. This review will demonstrate novel neuroprotective effects of several morphinans such as, dextromethorphan, its analogs and naloxone on the models of multiple neurodegenerative disease by modulating glial activation associated with the production of a host of proinflammatory and neurotoxic factors, although dextromethorphan possesses neuropsycotoxic potentials. The neuroprotective effects and the therapeutic potential for the treatment of excitotoxic and inflammatory neurodegenerative diseases, and underlying mechanism of morphinans are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aram, J. A., Martin, D., Tomczyk, M., Zeman, S., Millar, J., Pohler, G., and Lodge, D., Neocortical epileptogenesis in vitro: studies with N-methyl-D-aspartate, phencyclidine, sigma and dextromethorphan receptor ligands. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 248, 320–328 (1989).
Bem, J. L. and Peck, R., Dextromethorphan. An overview of safety issues. Drug Saf., 7, 190–199 (1992).
Bokesch, P. M., Marchand, J. E., Connelly, C. S., Wurm, W. H., and Kream, R. M., Dextromethorphan inhibits ischemiainduced c-fos expression and delayed neuronal death in hippocampal neurons. Anesthesiology, 81, 470–477 (1994).
Britton, P., Lu, X. C., Laskosky, M. S., and Tortella, F. C., Dextromethorphan protects against cerebral injury following transient, but not permanent, focal ischemia in rats. Life Sci., 60, 1729–1740 (1997).
Carliss, R. D., Radovsky, A., Chengelis, C. P., O’neill, T. P., and Shuey, D. L., Oral administration of dextromethorphan does not produce neuronal vacuolation in the rat brain. Neurotoxicology, 28, 813–818 (2007).
Chang, R. C., Rota, C., Glover, R. E., Mason, R. P., and Hong, J. S., A novel effect of an opioid receptor antagonist, naloxone, on the production of reactive oxygen species by microglia: a study by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Brain Res., 854, 224–229 (2000).
Chapman, A. G. and Meldrum, B. S., Non-competitive Nmethyl-D-aspartate antagonists protect against soundinduced seizures in DBA/2 mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 166, 201–211 (1989).
Chatterjie, N., Alexander, G. J., Sechzer, J. A., and Lieberman, K. W., Prevention of cocaine-induced hyperactivity by a naloxone isomer with no opiate antagonist activity. Neurochem. Res., 21, 691–693 (1996).
Chen, C. J., Liao, S. L., Chen, W. Y., Hong, J. S., and Kuo, J. S., Cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat brain: effects of naloxone. Neuroreport, 12, 1245–1249 (2001).
Chen, C. S., Gates, G. R., and Reynoldson, J. A., Effect of morphine and naloxone on priming-induced audiogenic seizures in BALB/c mice. Br. J. Pharmacol., 58, 517–520 (1976).
Chien, G. L. and Van Winkle, D. M., Naloxone blockade of myocardial ischemic preconditioning is stereoselective. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol., 28, 1895–1900 (1996).
Choi, D. W., Dextrorphan and dextromethorphan attenuate glutamate neurotoxicity. Brain Res., 403, 333–336 (1987).
Chung, H., Park, M., Hahn, E., Choi, H., and Lim, M., Recent trends of drug abuse and drug-associated deaths in Korea. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 1025, 458–464 (2004).
Cole, A. E., Eccles, C. U., Aryanpur, J. J., and Fisher, R. S., Selective depression of N-methyl-D-aspartate-mediated responses by dextrorphan in the hippocampal slice in rat. Neuropharmacology, 28, 249–254 (1989).
Cranston, J. W. and Yoast, R., Abuse of dextromethorphan. Arch. Fam. Med., 8, 99–100 (1999).
Craviso, G. L. and Musacchio, J. M., High-affinity dextromethorphan binding sites in guinea pig brain. II. Competition experiments. Mol. Pharmacol., 23, 629–640 (1983).
Desai, S., Aldea, D., Daneels, E., Soliman, M., Braksmajer, A. S., and Kopes-Kerr, C. P., Chronic addiction to dextromethorphan cough syrup: a case report. J. Am. Board Fam. Med., 19, 320–323 (2006).
Donato, R., Intracellular and extracellular roles of S100 proteins. Microsc. Res. Tech., 60, 540–551 (2003).
Dziki, M., Honack, D., and Loscher, W., Kindled rats are more sensitive than non-kindled rats to the behavioural effects of combined treatment with MK-801 and valproate. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 222, 273–278 (1992).
Echevarria, E., Robles, L., and Tortella, F. C., Differential profiles of putative dextromrthorphan sigma ligands in experimental seizure models. FASEB J., 4, A331 (1990).
Feeser, H. R., Kadis, J. L., and Prince, D. A., Dextromethorphan, a common antitussive, reduces kindled amygdala seizures in the rat. Neurosci. Lett., 86, 340–345 (1988).
Ferkany, J. W., Borosky, S. A., Clissold, D. B., and Pontecorvo, M. J., Dextromethorphan inhibits NMDA-induced convulsions. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 151, 151–154 (1988).
Franklin, P. H. and Murray, T. F., Identification and initial characterization of high-affinity [3H]dextrorphan binding sites in rat brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 189, 89–93 (1990).
Gao, H. M., Jiang, J., Wilson, B., Zhang, W., Hong, J. S., and Liu, B., Microglial activation-mediated delayed and progressive degeneration of rat nigral dopaminergic neurons: relevance to Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem., 81, 1285–1297 (2002).
Gao, H. M., Liu, B., Zhang, W., and Hong, J. S., Critical role of microglial NADPH oxidase-derived free radicals in the in vitro MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. FASEB J., 17, 1954–1956 (2003).
George, C. P., Goldberg, M. P., Choi, D. W., and Steinberg, G. K., Dextromethorphan reduces neocortical ischemic neuronal damage in vivo. Brain Res., 440, 375–379 (1988).
Glick, S. D., Maisonneuve, I. M., Dickinson, H. A., and Kitchen, B. A., Comparative effects of dextromethorphan and dextrorphan on morphine, methamphetamine, and nicotine self-administration in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 422, 87–90 (2001).
Hashimoto, K., Tomitaka, S.-I., Narita, N., Minabe, Y., Iyo, M., and Fukui, S., Induction of heat shock protein HSP-70 in rat retrosplenial cortex following administration of dextromethorphan. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 1, 235–239 (1996).
Herling, S., Solomon, R. E., and Woods, J. H., Discriminative stimulus effects of dextrorphan in pigeons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 227, 723–731 (1983).
Holtzman, S. G., Phencyclidine-like discriminative effects of opioids in the rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 214, 614–619 (1980).
Holtzman, S. G., Discriminative stimulus effects of dextromethorphan in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 116, 249–254 (1994).
Iijima, I., Minamikawa, J., Jacobson, A. E., Brossi, A., and Rice, K. C., Studies in the (+)-morphinan series. 5. Synthesis and biological properties of (+)-naloxone. J. Med. Chem., 21, 398–400 (1978).
Jhoo, W. K., Shin, E. J., Lee, Y. H., Cheon, M. A., Oh, K. W., Kang, S. Y., Lee, C., Yi, B. C., and Kim, H. C., Dual effects of dextromethorphan on cocaine-induced conditioned place preference in mice. Neurosci. Lett., 288, 76–80 (2000).
Khurgel, M., Switzer, R. C., 3rd, Teskey, G. C., Spiller, A. E., Racine, R. J., and Ivy, G. O., Activation of astrocytes during epileptogenesis in the absence of neuronal degeneration. Neurobiol. Dis., 2, 23–35 (1995).
Kim, H. C. and Jhoo, W. K., Alterations in motor activity induced by high dose oral administration of dextromethorphan throughout two consecutive generations in mice. Arch. Pharm. Res., 18, 146–152 (1995).
Kim, H. C., Jhoo, W. K., Kwan, M. S., and Hong, J. S., Effects of chronic dextromethorphan administration on the cellular immune responses in mice. Arch. Pharm. Res., 18, 267–270 (1995).
Kim, H. C., Pennypacker, K. R., Bing, G., Bronstein, D., Mcmillian, M. K., and Hong, J. S., The effects of dextromethorphan on kainic acid-induced seizures in the rat. Neurotoxicology, 17, 375–385 (1996).
Kim, H. C., Park, B. K., Hong, S. Y., and Jhoo, W. K., Dextromethorphan alters the reinforcing effect of cocaine in the rat. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol., 19, 627–631 (1997a).
Kim, H. C., Suh, H. W., Bronstein, D., Bing, G., Wilson, B., and Hong, J. S., Dextromethorphan blocks opioid peptide gene expression in the rat hippocampus induced by kainic acid. Neuropeptides, 31, 105–112 (1997b).
Kim, H. C., Bing, G., Jhoo, W. K., Ko, K. H., Kim, W. K., Lee, D. C., Shin, E. J., and Hong, J. S., Dextromethorphan modulates the AP-1 DNA-binding activity induced by kainic acid. Brain Res., 824, 125–132 (1999).
Kim, H. C., Bing, G., Shin, E. J., Jhoo, H. S., Cheon, M. A., Lee, S. H., Choi, K. H., Kim, J. I., and Jhoo, W. K., Dextromethorphan affects cocaine-mediated behavioral pattern in parallel with a long-lasting Fos-related antigen-immunoreactivity. Life Sci., 69, 615–624 (2001a).
Kim, H. C., Ko, K. H., Kim, W. K., Shin, E. J., Kang, K. S., Shin, C. Y., and Jhoo, W. K., Effects of dextromethorphan on the seizures induced by kainate and the calcium channel agonist BAY k-8644: comparison with the effects of dextrorphan. Behav. Brain Res., 120, 169–175 (2001b).
Kim, H. C., Nabeshima, T., Jhoo, W. K., Ko, K. H., Kim, W. K., Shin, E. J., Cho, M., and Lee, P. H., Anticonvulsant effects of new morphinan derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 11, 1651–1654 (2001c).
Kim, H. C., Bing, G., Jhoo, W. K., Kim, W. K., Shin, E. J., Im, D. H., Kang, K. S., and Ko, K. H., Metabolism to dextrorphan is not essential for dextromethorphan’s anticonvulsant activity against kainate in mice. Life Sci., 72, 769–783 (2003a).
Kim, H. C., Shin, C. Y., Seo, D. O., Jhoo, J. H., Jhoo, W. K., Kim, W. K., Shin, E. J., Lee, Y. H., Lee, P. H., and Ko, K. H., New morphinan derivatives with negligible psychotropic effects attenuate convulsions induced by maximal electroshock in mice. Life Sci., 72, 1883–1895 (2003b).
Klette, K. L., Decoster, M. A., Moreton, J. E., and Tortella, F. C., Role of calcium in sigma-mediated neuroprotection in rat primary cortical neurons. Brain Res., 704, 31–41 (1995).
Knapp, P. E., Maderspach, K., and Hauser, K. F., Endogenous opioid system in developing normal and jimpy oligodendrocytes: mu and kappa opioid receptors mediate differential mitogenic and growth responses. Glia, 22, 189–201 (1998).
Knapp, R. J., Malatynska, E., Collins, N., Fang, L., Wang, J. Y., Hruby, V. J., Roeske, W. R., and Yamamura, H. I., Molecular biology and pharmacology of cloned opioid receptors. FASEB J., 9, 516–525 (1995).
Le Gal La Salle, G., Calvino, B., and Ben-Ari, Y., Morphine enhances amygdaloid seizures and increases inter-ictal spike frequency in kindled rats. Neurosci. Lett., 6, 255–260 (1977).
Leander, J. D., Evaluation of dextromethorphan and carbetapentane as anticonvulsants and N-methyl-D-aspartic acid antagonists in mice. Epilepsy Res., 4, 28–33 (1989).
Liu, B., Du, L., and Hong, J. S., Naloxone protects rat dopaminergic neurons against inflammatory damage through inhibition of microglia activation and superoxide generation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 293, 607–617 (2000a).
Liu, B., Jiang, J. W., Wilson, B. C., Du, L., Yang, S. N., Wang, J. Y., Wu, G. C., Cao, X. D., and Hong, J. S., Systemic infusion of naloxone reduces degeneration of rat substantia nigral dopaminergic neurons induced by intranigral injection of lipopolysaccharide. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 295, 125–132 (2000b).
Liu, Y., Qin, L., Wilson, B. C., An, L., Hong, J. S., and Liu, B., Inhibition by naloxone stereoisomers of beta-amyloid peptide (1–42)-induced superoxide production in microglia and degeneration of cortical and mesencephalic neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 302, 1212–1219 (2002).
Loscher, W. and Honack, D., Responses to NMDA receptor antagonists altered by epileptogenesis. Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 12, 52 (1991).
Luhmann, H. J. and Scheid, M., Dextromethorphan attenuates hypoxia-induced neuronal dysfunction in rat neocortical slices. Neurosci. Lett., 178, 171–174 (1994).
Mendelsohn, L. G., Kerchner, G. A., Kalra, V., Zimmerman, D. M., and Leander, J. D., Phencyclidine receptors in rat brain cortex. Biochem. Pharmacol., 33, 3529–3535 (1984).
Monyer, H. and Choi, D. W., Morphinans attenuate cortical neuronal injury induced by glucose deprivation in vitro. Brain Res., 446, 144–148 (1988).
Murray, T. F. and Leid, M. E., Interaction of dextrorotatory opioids with phencyclidine recognition sites in rat brain membranes. Life Sci., 34, 1899–1911 (1984).
Netzer, R., Pflimlin, P., and Trube, G., Dextromethorphan blocks N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced currents and voltageoperated inward currents in cultured cortical neurons. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 238, 209–216 (1993).
Newman, A. H., Bevan, K., Bowery, N., and Tortella, F. C., Synthesis and evaluation of 3-substituted 17-methylmor phinan analogs as potential anticonvulsant agents. J. Med. Chem., 35, 4135–4142 (1992).
Olney, J. W., Labruyere, J., and Price, M. T., Pathological changes induced in cerebrocortical neurons by phencyclidine and related drugs. Science, 244, 1360–1362 (1989).
Oprica, M., Eriksson, C., and Schultzberg, M., Inflammatory mechanisms associated with brain damage induced by kainic acid with special reference to the interleukin-1 system. J. Cell. Mol. Med., 7, 127–140 (2003).
Pulvirenti, L., Balducci, C., and Koob, G. F., Dextromethorphan reduces intravenous cocaine self-administration in the rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 321, 279–283 (1997).
Qin, L., Block, M. L., Liu, Y., Bienstock, R. J., Pei, Z., Zhang, W., Wu, X., Wilson, B., Burka, T., and Hong, J. S., Microglial NADPH oxidase is a novel target for femtomolar neuroprotection against oxidative stress. FASEB J., 19, 550–557 (2005).
Quirion, R., Bowen, W. D., Itzhak, Y., Junien, J. L., Musacchio, J. M., Rothman, R. B., Su, T. P., Tam, S. W., and Taylor, D. P., A proposal for the classification of sigma binding sites. Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 13, 85–86 (1992).
Ravizza, T., Rizzi, M., Perego, C., Richichi, C., Veliskova, J., Moshe, S. L., De Simoni, M. G., and Vezzani, A., Inflammatory response and glia activation in developing rat hippocampus after status epilepticus. Epilepsia, 46Suppl 5, 113–117 (2005).
Rizzi, M., Perego, C., Aliprandi, M., Richichi, C., Ravizza, T., Colella, D., Veliskova, J., Moshe, S. L., De Simoni, M. G., and Vezzani, A., Glia activation and cytokine increase in rat hippocampus by kainic acid-induced status epilepticus during postnatal development. Neurobiol. Dis., 14, 494–503 (2003).
Rogawski, M. A. and Porter, R. J., Antiepileptic drugs: pharmacological mechanisms and clinical efficacy with consideration of promising developmental stage compounds. Pharmacol. Rev., 42, 223–286 (1990).
Roy, S. and Loh, H. H., Effects of opioids on the immune system. Neurochem. Res., 21, 1375–1386 (1996).
Satoh, M. and Minami, M., Molecular pharmacology of the opioid receptors. Pharmacol. Ther., 68, 343–364 (1995).
Sharp, F. R., Butaman, M., Aardalen, K., Nickolenko, J., Nakki, R., Massa, S. M., Swanson, R. A., and Sagar, S. M., Neuronal injury produced by NMDA antagonists can be detected using heat shock proteins and can be blocked with antipsychotics. Psychopharmacol. Bull., 30, 555–560 (1994).
Shin, E. J., Nabeshima, T., Lee, P. H., Kim, W. K., Ko, K. H., Jhoo, J. H., Jhoo, W. K., Cha, J. Y., and Kim, H. C., Dimemorfan prevents seizures induced by the L-type calcium channel activator BAY k-8644 in mice. Behav. Brain Res., 151, 267–276 (2004).
Shin, E. J., Nah, S. Y., Kim, W. K., Ko, K. H., Jhoo, W. K., Lim, Y. K., Cha, J. Y., Chen, C. F., and Kim, H. C., The dextromethorphan analog dimemorfan attenuates kainateinduced seizures via sigma1 receptor activation: comparison with the effects of dextromethorphan. Br. J. Pharmacol., 144, 908–918 (2005).
Shin, E. J., Nah, S. Y., Chae, J. S., Bing, G., Shin, S. W., Yen, T. P., Baek, I. H., Kim, W. K., Maurice, T., Nabeshima, T., and Kim, H. C., Dextromethorphan attenuates trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity via sigma1 receptor activation in rats. Neurochem. Int., 50, 791–799 (2007).
Shin, E. J., Lee, P. H., Kim, H. J., Nabeshima, T., and Kim, H. C., Neuropsychotoxicity of abused drugs: potential of dextromethorphan and novel neuroprotective analogs of dextromethorphan with improved safety profiles in terms of abuse and neuroprotective effects. J. Pharmacol. Sci., 106, 22–27 (2008).
Snyder, E. W., Shearer, D. E., Beck, E. C., and Dustmann, R. E., Naloxone-induced electrographic seizures in the primate. Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 67, 211–214 (1980).
Somera-Molina, K. C., Robin, B., Somera, C. A., Anderson, C., Stine, C., Koh, S., Behanna, H. A., Van Eldik, L. J., Watterson, D. M., and Wainwright, M. S., Glial activation links early-life seizures and long-term neurologic dysfunction: evidence using a small molecule inhibitor of proinflammatory cytokine upregulation. Epilepsia, 48, 1785–1800 (2007).
Steinberg, G. K., Lo, E. H., Kunis, D. M., Grant, G. A., Poljak, A., and Delapaz, R., Dextromethorphan alters cerebral blood flow and protects against cerebral injury following focal ischemia. Neurosci. Lett., 133, 225–228 (1991).
Steinmiller, C. L., Maisonneuve, I. M., and Glick, S. D., Effects of dextromethorphan on dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens: Interactions with morphine. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 74, 803–810 (2003).
Takazawa, A., Anderson, P., and Abraham, W. C., Effects of dextromethorphan, a nonopioid antitussive, on development and expression of amygdaloid kindled seizures. Epilepsia, 31, 496–502 (1990).
Tortella, F. C. and Musacchio, J. M., Dextromethorphan and carbetapentane: centrally acting non-opioid antitussive agents with novel anticonvulsant properties. Brain Res., 383, 314–318 (1986).
Tortella, F. C., Martin, D. A., Allot, C. P., Steel, J. A., Blackburn, T. P., Loveday, B. E., and Russell, N. J., Dextromethorphan attenuates post-ischemic hypoperfusion following incomplete global ischemia in the anesthetized rat. Brain Res., 482, 179–183 (1989a).
Tortella, F. C., Pellicano, M., and Bowery, N. G., Dextromethorphan and neuromodulation: old drug coughs up new activities. Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 10, 501–507 (1989b).
Tortella, F. C., Robles, L., Witkin, J. M., and Newman, A. H., Novel anticonvulsant analogs of dextromethorphan: Improved efficacy, potency, duration and side-effect profile. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 268, 727–733 (1994).
Tortella, F. C., Britton, P., Williams, A., Lu, X. C., and Newman, A. H., Neuroprotection (focal ischemia) and neurotoxicity (electroencephalographic) studies in rats with AHN649, a 3-amino analog of dextromethorphan and low-affinity N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 291, 399–408 (1999).
Trube, G. and Netzer, R., Dextromethorphan: cellular effects reducing neuronal hyperactivity. Epilepsia, 35Suppl 5, S62–S67 (1994).
Turski, L., Ikonomidou, C., Cavalheiro, E. A., Kleinrok, Z., Czuczwar, S. J., and Turski, W. A., Effects of morphine and naloxone on pilocarpine-induced convulsions in rats. Neuropeptides, 5, 315–318 (1985).
Vaglini, F., Pardini, C., Bonuccelli, U., Maggio, R., and Corsini, G. U., Dextromethorphan prevents the diethyldithiocarbamate enhancement of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine toxicity in mice. Brain Res., 973, 298–302 (2003).
Vezzani, A. and Granata, T., Brain inflammation in epilepsy: experimental and clinical evidence. Epilepsia, 46, 1724–1743 (2005)
Viviani, B., Bartesaghi, S., Gardoni, F., Vezzani, A., Behrens, M. M., Bartfai, T., Binaglia, M., Corsini, E., Di Luca, M., Galli, C. L., and Marinovich, M., Interleukin-1beta enhances NMDA receptor-mediated intracellular calcium increase through activation of the Src family of kinases. J. Neurosci., 23, 8692–8700 (2003).
Wainwright, M. S., Craft, J. M., Griffin, W. S., Marks, A., Pineda, J., Padgett, K. R., and Van Eldik, L. J., Increased susceptibility of S100B transgenic mice to perinatal hypoxia-ischemia. Ann. Neurol., 56, 61–67 (2004).
Wolfe, T. R. and Caravati, E. M., Massive dextromethorphan ingestion and abuse. Am. J. Emerg. Med., 13, 174–176 (1995).
Wu, D., Otton, S. V., Kalow, W., and Sellers, E. M., Effects of route of administration on dextromethorphan pharmacokinetics and behavioral response in the rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 274, 1431–1437 (1995).
Yang, P. P., Huang, E. Y., Yeh, G. C., and Tao, P. L., Coadministration of dextromethorphan with methamphetamine attenuates methamphetamine-induced rewarding and behavioral sensitization. J. Biomed. Sci., 13, 695–702 (2006).
Zapata, A., Gasior, M., Geter-Douglass, B., Tortella, F. C., Newman, A. H., and Witkin, J. M., Attenuation of the stimulant and convulsant effects of cocaine by 17-substituted-3-hydroxy and 3-alkoxy derivatives of dextromethorphan. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 74, 313–323 (2003).
Zhang, W., Wang, T., Qin, L., Gao, H. M., Wilson, B., Ali, S. F., Hong, J. S., and Liu, B., Neuroprotective effect of dextromethorphan in the MPTP Parkinson’s disease model: role of NADPH oxidase. FASEB J., 18, 589–591 (2004).
Zhang, W., Qin, L., Wang, T., Wei, S. J., Gao, H. M., Liu, J., Wilson, B., Liu, B., Kim, H. C., and Hong, J. S., 3-hydroxymorphinan is neurotrophic to dopaminergic neurons and is also neuroprotective against LPS-induced neurotoxicity. FASEB J., 19, 395–397 (2005).
Zhang, W., Shin, E. J., Wang, T., Lee, P. H., Pang, H., Wie, M. B., Kim, W. K., Kim, S. J., Huang, W. H., Wang, Y., Hong, J. S., and Kim, H. C., 3-Hydroxymorphinan, a metabolite of dextromethorphan, protects nigrostriatal pathway against MPTP-elicited damage both in vivo and in vitro. FASEB J., 20, 2496–2511 (2006).
Zhou, G. Z. and Musacchio, J. M., Computer-assisted modeling of multiple dextromethorphan and sigma binding sites in guinea pig brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 206, 261–269 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, EJ., Hong, JS. & Kim, HC. Neuropsychopharmacological understanding for therapeutic application of morphinans. Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 1575–1587 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-1009-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-1009-4