Abstract
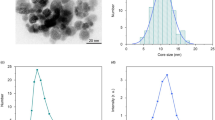
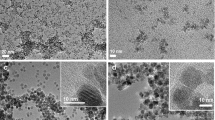
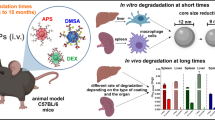
In this study, we followed the biodegradation of ultra-small superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles injected intravenously at clinical doses in mice. An advanced fitting procedure for magnetic susceptibility curves and low-temperature hysteresis loops was used to fully characterize the magnetic size distribution as well as the magnetic anisotropy energy of the injected P904 nanoparticles (Guerbet Laboratory). Additional magnetometry measurements and transmission electronic microscopy observations were systematically performed to examine dehydrated samples from the spleen and liver of healthy C57B16 mice after nanoparticle injection, with sacrifice of the mice for up to 14 months. At 3 months after injection, the magnetic properties of the spleen and liver were dramatically different. While the liver showed no magnetic signals other than those also present in the reference species, the spleen showed an increased magnetic signal attributed to ferritin. This surplus of ferritin remained constant up to 14 months after injection.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yen, S. K.; Padmanabhan, P.; Selvan, S. T. Multifunctional iron oxide nanoparticles for diagnostics, therapy and macromolecule delivery. Theranostics 2013, 3, 986–1003.
Wu, L. C.; Cao, Y. F.; Liao, C.; Huang, J. H.; Gao, F. Diagnostic performance of USPIO-enhanced MRI for lymphnode metastases in different body regions: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 80, 582–589.
Harnan, S. E.; Cooper, K. L.; Meng, Y.; Ward, S. E.; Fitzgerald, P.; Papaioannou, D.; Ingram, C.; Lorenz, E.; Wilkinson, I. D.; Wyld, L. Magnetic resonance for assessment of axillary lymph node status in early breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 37, 928–936.
Aime, S.; Caravan, P. Biodistribution of gadolinium-based contrast agents, including gadolinium deposition. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 30, 1259–1267.
Corot, C.; Robert, P.; Idée, J.-M.; Port, M. Recent advances in iron oxide nanocrystal technology for medical imaging. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1471–1504.
López-Castro, J. D.; Maraloiu, A. V.; Delgado, J. J.; Calvino, J. J.; Blanchin, M.-G.; Gálvez, N.; Dominguez-Vera, J. M. From synthetic to natural nanoparticles: Monitoring the biodegradation of SPIO (P904) into ferritin by electron microscopy. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4597–4599.
Lévy, M.; Lagarde, F.; Maraloiu, V.-A.; Blanchin, M.-G.; Gendron, F.; Wilhelm, C.; Gazeau, F. Degradability of superparamagnetic nanoparticles in a model of intracellular environment: Follow-up of magnetic, structural and chemical properties. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 395103.
Levy, M.; Luciani, N.; Alloyeau, D.; Elgrabli, D.; Deveaux, V.; Pechoux, C.; Chat, S.; Wang, G.; Vats, N.; Gendron, F. et al. Long term in vivo biotransformation of iron oxide nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3988–3999.
Levy, M.; Wilhelm, C.; Luciani, N.; Deveaux, V.; Gendron, F.; Luciani, A.; Devaud, M.; Gazeau, F. Nanomagnetism reveals the intracellular clustering of iron oxide nanoparticles in the organism. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4402–4410.
Lévy, M.; Wilhelm, C.; Devaud, M.; Levitz, P.; Gazeau, F. How cellular processing of superparamagnetic nanoparticles affects their magnetic behavior and NMR relaxivity. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2012, 7, 373–383.
Lartigue, L.; Alloyeau, D.; Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Javed, Y.; Guardia, P.; Riedinger, A.; Péchoux, C.; Pellegrino, T.; Wilhelm, C.; Gazeau, F. Biodegradation of iron oxide nanocubes: High-resolution in situ monitoring. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3939–3952.
Pauling, L.; Coryell, C. D. The magnetic properties and structure of hemoglobin, oxyhemoglobin and carbonmonoxyhemoglobin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1936, 22, 210–216.
Bell, S. H.; Weir, M. P.; Dickson, D. P.; Gibson, J. F.; Sharp, G. A.; Peters, T. J. Mössbauer spectroscopic studies of human haemosiderin and ferritin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1984, 787, 227–236.
Tamion, A.; Hillenkamp, M.; Tournus, F.; Bonet, E.; Dupuis, V. Accurate determination of the magnetic anisotropy in cluster-assembled nanostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 062503.
Tamion, A.; Bonet, E.; Tournus, F.; Raufast, C.; Hillion, A.; Gaier, O.; Dupuis, V. Efficient hysteresis loop simulations of nanoparticle assemblies beyond the uniaxial anisotropy. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 85, 134430.
Sigovan, M.; Boussel, L.; Sulaiman, A.; Sappey-Marinier, D.; Alsaid, H.; Desbleds-Mansard, C.; Ibarrola, D.; Gamondès, D.; Corot, C.; Lancelot, E. et al. Rapid-clearance iron nanoparticles for inflammation imaging of atherosclerotic plaque: Initial experience in animal model. Radiology 2009, 252, 401–409.
Wilhelm, C.; Gazeau, F.; Bacri, J.-C. Magnetophoresis and ferromagnetic resonance of magnetically labeled cells. Eur. Biophys. J. 2002, 31, 118–125.
Jamet, M.; Wernsdorfer, W.; Thirion, C.; Mailly, D.; Dupuis, V.; Mélinon, P.; Pérez, A. Magnetic anisotropy of a single cobalt nanocluster. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 4676–4679.
Oyarzún, S.; Tamion, A.; Tournus, F.; Dupuis, V.; Hillenkamp, M. Size effects in the magnetic anisotropy of embedded cobalt nanoparticles: From shape to surface. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14749.
Thiaville, A. Coherent rotation of magnetization in three dimensions: A geometrical approach. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 12221–12232.
Gutiérrez, L.; Lázaro, F. J.; Abadía, A. R.; Romero, M. S.; Quintana, C.; Morales, M. P.; Patiño, C.; Arranz, R. Bioinorganic transformations of liver iron deposits observed by tissue magnetic characterisation in a rat model. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2006, 100, 1790–1799.
Lévy, M.; Gazeau, F.; Bacri, J.-C.; Wilhelm, C.; Devaud, M. Modeling magnetic nanoparticle dipole–dipole interactions inside living cells. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 075480.
Henkel, O. Remanenzverhalten und Wechselwirkungen in hartmagnetischen Teilchenkollektiven. Phys. Stat. Sol. B 1964, 7, 919–929.
Gamarra, L. F.; Pontuschka, W. M.; Amaro, E., Jr.; Costa-Filho, A. J.; Brito, G. E. S.; Vieira, E. D.; Carneiro, S. M.; Escriba, D. M.; Falleiros, A. M. F.; Salvador, V. L. Kinetics of elimination and distribution in blood and liver of biocompatible ferrofluids based on Fe3O4 nanoparticles: An EPR and XRF study. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 519–525.
Luciani, N.; Wilhelm, C.; Gazeau, F. The role of cell-released microvesicles in the intercellular transfer of magnetic nanoparticles in the monocyte/macrophage system. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7061–7069.
Allen, P. D.; St Pierre, T. G.; Chua-anusorn, W.; Ström, V.; Rao, K. V. Low-frequency low-field magnetic susceptibility of ferritin and hemosiderin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1500, 186–196.
Brem, F.; Stamm, G.; Hirt, A. M. Modeling the magnetic behavior of horse spleen ferritin with a two-phase core structure. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 123906.
Mohie-Eldin, M.-E.; Frankel, R. B.; Gunther, L. A comparison of the magnetic properties of polysaccharide iron complex (PIC) and ferritin. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1994, 135, 65–81.
Tejada, J.; Zhang, X. X. On magnetic relaxation in antiferromagnetic horse-spleen ferritin proteins. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 1994, 6, 263–266.
Kilcoyne, S. H.; Cywinski, R. Ferritin: A model superparamagnet. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1995, 140–144, 1466–1467.
Makhlouf, S. A.; Parker, F. T.; Berkowitz, A. E. Magnetic hysteresis anomalies in ferritin. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 55, R14717–R14720.
Maraloiu, V. A.; Blanchin, M.-G. Multiscale Study of Magnetic Nanovectors; Scholars’ Press: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2013.
Wood, J. C. Guidelines for quantifying iron overload. In Hematology/the Education Program of the American Society of Hematology American Society of Hematology Education Program; The Society: Washington, DC, 2014; pp 210–215.
Storey, P.; Lim, R. P.; Chandarana, H.; Rosenkrantz, A. B.; Kim, D.; Stoffel, D. R.; Lee, V. S. MRI assessment of hepatic iron clearance rates after USPIO administration in healthy adults. Invest. Radiol. 2012, 47, 717–724.
Hunter, J. E. Variable effects of iron status on the concentration of ferritin in rat plasma, liver, and spleen. J. Nutr. 1978, 108, 497–505.
Richter, G. W. The iron-loaded cell—The cytopathology of iron storage. A review. Am. J. Pathol. 1978, 91, 362–404.
Gustafson, H. H.; Holt-Casper, D.; Grainger, D. W.; Ghandehari, H. Nanoparticle uptake: The phagocyte problem. Nano Today 2015, 10, 487–510.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tamion, A., Hillenkamp, M., Hillion, A. et al. Ferritin surplus in mouse spleen 14 months after intravenous injection of iron oxide nanoparticles at clinical dose. Nano Res. 9, 2398–2410 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1126-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1126-6