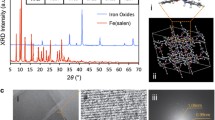
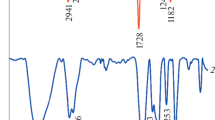
Abstract
Recently, increasing attention has been paid to magneto-conjugated polymer core–shell nanoparticles (NPs) as theranostic platforms. However, the utilization of surfactants and extra oxidizing agents with potential toxicity in synthesis, the lack of general methods for the controlled synthesis of various kinds of magnetic NP (MNP)@conjugated polymer NPs, and the difficulty of obtaining balanced magneto-optical properties have greatly limited the applications of magneto-conjugated polymers in theranostics. We developed an in situ surface polymerization method free of extra surfactants and oxidizing agents to synthesize MNP@polypyrrole (PPy) NPs with balanced, prominent magneto-optical properties. MNP@PPy NPs with an adjustable size, different shapes, and a controlled shell thickness were obtained using this method. The method was extended to synthesize other MNP-conjugated polymer core–shell NPs, such as MNP@polyaniline and MNP@poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(4-styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS). We discuss the formation mechanism of the proposed method according to our experimental results. Finally, using the optical and magnetic properties of the obtained MNP@PEDOT:PSS NPs, in vivo multimodal imaging-guided hyperthermia was induced in mice, achieving an excellent tumor-ablation therapeutic effect. Our work is beneficial for extending the application of MNP-conjugated polymer core–shell NPs in the biomedical field.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel, R. L.; Miller, K. D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 5–29.
Chen, X. Y.; Gambhlr, S. S.; Cheon, J. Theranostic nanomedicine. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 841.
Deveza, L.; Choi, J.; Yang, F. Therapeutic angiogenesis for treating cardiovascular diseases. Theranostics 2012, 2, 801–814.
Muthu, M. S.; Leong, D. T.; Mei, L.; Feng, S. S. Nanotheranostics—Application and further development of nanomedicine strategies for advanced theranostics. Theranostics 2014, 4, 660–677.
Song, X. R.; Wang, X. Y.; Yu, S. X.; Cao, J. B.; Li, S. H.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; Yang, H. H.; Chen, X. Y. Co9Se8 nanoplates as a new theranostic platform for photoacoustic/magnetic resonance dual-modal-imaging-guided chemo-photothermal combination therapy. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3285–3291.
Li, J. W.; Arnal, B.; Wei, C. W.; Shang, J.; Nguyen, T.-M.; O’Donnell, M.; Gao, X. H. Magneto-optical nanoparticles for cyclic magnetomotive photoacoustic imaging. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 1964–1976.
Yu, J.; Yang, C.; Li, J. D. S.; Ding, Y. C.; Zhang, L.; Yousaf, M. Z.; Lin, J.; Pang, R.; Wei, L. B.; Xu, L. L. et al. Multifunctional Fe5C2 nanoparticles: A targeted theranostic platform for magnetic resonance imaging and photoacoustic tomography-guided photothermal therapy. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4114–4120.
Yu, J.; Ju, Y. M.; Zhao, L. Y.; Chu, X.; Yang, W. L.; Tian, Y. L.; Sheng, F. G.; Lin, J.; Liu, F.; Dong, Y. H. et al. Multistimuli-regulated photochemothermal cancer therapy remotely controlled via Fe5C2 nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 159–169.
Anselmo, A. C.; Mitragotri, S. A review of clinical translation of inorganic nanoparticles. AAPS J. 2015, 17, 1041–1054.
Tassa, C.; Shaw, S. Y.; Weissleder, R. Dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles: A versatile platform for targeted molecular imaging, molecular diagnostics, and therapy. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 842–852.
Wu, H. X.; Liu, G.; Zhuang, Y. M.; Wu, D. M.; Zhang, H. Q.; Yang, H.; Hu, H.; Yang, S. P. The behavior after intravenous injection in mice of multiwalled carbon nanotube/Fe3O4 hybrid MRI contrast agents. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4867–4876.
Kwon, O. S.; Park, S. J.; Jang, J. A high-performance VEGF aptamer functionalized polypyrrole nanotube biosensor. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4740–4747.
Runge, M. B.; Dadsetan, M.; Baltrusaitis, J.; Knight, A. M.; Ruesink, T.; Lazcano, E. A.; Lu, L. C.; Windebank, A. J.; Yaszemski, M. J. The development of electrically conductive polycaprolactone fumarate-polypyrrole composite materials for nerve regeneration. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5916–5926.
Fonner, J. M.; Forciniti, L.; Nguyen, H.; Byrne, J. D.; Kou, Y.-F.; Syeda-Nawaz, J.; Schmidt, C. E. Biocompatibility implications of polypyrrole synthesis techniques. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 3, 034124.
Ramanaviciene, A.; Kausaite, A.; Tautkus, S.; Ramanavicius, A. Biocompatibility of polypyrrole particles: An in-vivo study in mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 311–315.
Zha, Z. B.; Yue, X. L.; Ren, Q. S.; Dai, Z. F. Uniform polypyrrole nanoparticles with high photothermal conversion efficiency for photothermal ablation of cancer cells. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 777–782.
Yang, K.; Xu, H.; Cheng, L.; Sun, C. Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z. In vitro and in vivo near-infrared photothermal therapy of cancer using polypyrrole organic nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5586–5592.
Cheng, L.; Yang, K.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Z. Organic stealth nanoparticles for highly effective in vivo near-infrared photothermal therapy of cancer. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5605–5613.
Bardhan, R.; Chen, W. X.; Perez-Torres, C.; Bartels, M.; Huschka, R. M.; Zhao, L. L.; Morosan, E.; Pautler, R. G.; Joshi, A.; Halas, N. J. Nanoshells with targeted simultaneous enhancement of magnetic and optical imaging and photothermal therapeutic response. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 3901–3909.
Wang, J.; Zhu, G. Z.; You, M. X.; Song, E. Q.; Shukoor, M. I.; Zhang, K. J.; Altman, M. B.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, C. Z. et al. Assembly of aptamer switch probes and photosensitizer on gold nanorods for targeted photothermal and photodynamic cancer therapy. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5070–5077.
Song, X. J.; Gong, H.; Yin, S. N.; Cheng, L.; Wang, C.; Li, Z. W.; Li, Y. G.; Wang, X. Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, Z. Ultra-small iron oxide doped polypyrrole nanoparticles for in vivo multimodal imaging guided photothermal therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 1194–1201.
Tian, Q. W.; Wang, Q.; Yao, K. X.; Teng, B. Y.; Zhang, J. Z.; Yang, S. P.; Han, Y. Multifunctional polypyrrole@Fe3O4 nanoparticles for dual-modal imaging and in vivo photothermal cancer therapy. Small 2014, 10, 1063–1068.
Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Liang, C.; Liu, Y. M.; Li, Z. W.; Yang, G. B.; Cheng, L.; Li, Y. G.; Liu, Z. Iron oxide@polypyrrole nanoparticles as a multifunctional drug carrier for remotely controlled cancer therapy with synergistic antitumor effect. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6782–6795.
Gong, H.; Cheng, L.; Xiang, J.; Xu, H.; Feng, L. Z.; Shi, X. Z.; Liu, Z. Near-infrared absorbing polymeric nanoparticles as a versatile drug carrier for cancer combination therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 6059–6067.
Xiao, Q.; Tan, X. K.; Ji, L. L.; Xue, J. Preparation and characterization of polyaniline/nano-Fe3O4 composites via a novel pickering emulsion route. Synth. Met. 2007, 157, 784–791.
Minehan, D. S.; Marx, K. A.; Tripathy, S. K. Kinetics of DNA binding to electrically conducting polypyrrole films. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 777–783.
Zhang, H.; Zhong, X.; Xu, J. J.; Chen, H.-Y. Fe3O4/ polypyrrole/Au nanocomposites with core/shell/shell structure: Synthesis, characterization, and their electrochemical properties. Langmuir 2008, 24, 13748–13752.
Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Li, T.; Lin, M.; Lin, X.; Zhang, H.; Sun, H.; Yang, B. Composite photothermal platform of polypyrrole-enveloped Fe3O4 nanoparticle self-assembled superstructures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 14552–14561.
Zhang, Z. M.; Li, Q.; Yu, L. M.; Cui, Z. J.; Zhang, L. J.; Bowmaker, G. A. Highly conductive polypyrrole/Fe2O3 nanospheres with good magnetic properties obtained through an improved chemical one-step method. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4610–4615.
Gai, L. G.; Han, X. Y.; Hou, Y. H.; Chen, J.; Jiang, H. H.; Chen, X. C. Surfactant-free synthesis of Fe3O4@PANI and Fe3O4@PPy microspheres as adsorbents for isolation of pcr-ready DNA. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 1820–1826.
Jiang, W.; Kim, B. Y. S.; Rutka, J. T.; Chan, W. C. W. Nanoparticle-mediated cellular response is size-dependent. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 145–150.
Stigliano, C.; Key, J.; Ramirez, M.; Aryal, S.; Decuzzi, P. Radiolabeled polymeric nanoconstructs loaded with docetaxel and curcumin for cancer combinatorial therapy and nuclear imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3371–3379.
Xuan, S. H.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. X. J.; Yu, J. C.; Leung, K. C. F. Facile synthesis of size-controllable monodispersed ferrite nanospheres. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 5086–5094.
Gao, Q.; Zhang, J. L.; Hong, G.-Y.; Ni, J. Z. Solvothermal synthesis of the magnetite micro-nano particles (Fe3O4) with different morphologies. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2011, 32, 552–559.
Levin, C. S.; Hofmann, C.; Ali, T. A.; Kelly, A. T.; Morosan, E.; Nordlander, P.; Whitmire, K. H.; Halas, N. J. Magnetic-plasmonic core–shell nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1379–1388.
Di Corato, R.; Béalle, G.; Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Espinosa, A.; Clément, O.; Silva, A. K. A.; Ménager, C.; Wilhelm, C. Combining magnetic hyperthermia and photodynamic therapy for tumor ablation with photoresponsive magnetic liposomes. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 2904–2916.
Wang, Y. Q.; Zou, B. F.; Gao, T.; Wu, X. P.; Lou, S. Y.; Zhou, S. M. Synthesis of orange-like Fe3O4/PPy composite microspheres and their excellent Cr(VI) ion removal properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 9034–9040.
Alves, K. G. B.; Andrade, C. A. S.; Campello, S. L.; de Souza, R. E.; de Melo, C. P. Magnetite/polypyrrole hybrid nanocomposites as a promising magnetic resonance imaging contrast material. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 3170–3176.
Kim, S.; Oh, W. K.; Jeong, Y. S.; Hong, J. Y.; Cho, B. R.; Hahn, J. S.; Jang, J. Cytotoxicity of, and innate immune response to, size-controlled polypyrrole nanoparticles in mammalian cells. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2342–2350.
Walter, A.; Billotey, C.; Garofalo, A.; Ulhaq-Bouillet, C.; Lefè vre, C.; Taleb, J.; Laurent, S.; Vander Elst, L.; Muller, R. N.; Lartigue, L. et al. Mastering the shape and composition of dendronized iron oxide nanoparticles to tailor magnetic resonance imaging and hyperthermia. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 5252–5264.
Xu, J. K.; Shi, G. Q.; Xu, Z. J.; Chen, F. G.; Hong, X. Y. Low potential electrochemical polymerization of 3-chlorothiophene in mixed electrolytes of boron trifluoride diethyl etherate and trifluoroacetic acid. J. Electroanalyt. Chem. 2001, 514, 16–25.
Kvarnström, C.; Neugebauer, H.; Blomquist, S.; Ahonen, H. J.; Kankare, J.; Ivaska, A. In situ spectroelectrochemical characterization of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene). Electrochim. Acta 1999, 44, 2739–2750.
Liu, Y.; Song, Z. J.; Zhang, Q. H.; Zhou, Z. X.; Tang, Y. J.; Wang, L. J.; Zhu, J. J.; Luo, W.; Jiang, W. Preparation of bulk AgNWs/PEDOT:PSS composites: A new model towards high-performance bulk organic thermoelectric materials. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 45106–45112.
Sun, Z. C.; Geng, Y. H.; Li, J.; Jing, X. B.; Wang, F. S. Chemical polymerization of aniline with hydrogen peroxide as oxidant. Synth. Met. 1997, 84, 99–100.
Rohrer, M.; Bauer, H.; Mintorovitch, J.; Requardt, M.; Weinmann, H. J. Comparison of magnetic properties of MRI contrast media solutions at different magnetic field strengths. Invest. Radiol. 2005, 40, 715–724.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the professional technical support for the MRI analysis by Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Tsinghua University. We thank Tsinghua University Initiative Scientific Research Program (No. 20131089199), National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFB0700800), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81172182 and 81671829) for support of funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2016_1330_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
General synthesis of high-performing magneto-conjugated polymer core–shell nanoparticles for multifunctional theranostics
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, H., Zhao, L., Shang, W. et al. General synthesis of high-performing magneto-conjugated polymer core–shell nanoparticles for multifunctional theranostics. Nano Res. 10, 704–717 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1330-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1330-4