Abstract
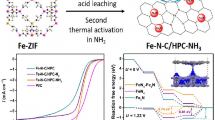
Fe-N-C materials with atomically dispersed Fe—N4 sites could tolerate the poisoning of phosphate, and is regarded as the most promising alternative to costly Pt-based catalysts for the oxygen reduction in high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (HT-PEMFCs). However, they still face the critical issue of insufficient activity in phosphoric acid. Herein, we demonstrate a P-doping strategy to increase the activity of Fe-N-C catalyst via a feasible one-pot method. X-ray absorption spectroscopy and electron microscopy with atomic resolution indicated that the P atom is bonded with the N in Fe—N4 site through C atoms. The as prepared Fe-NCP catalyst shows a half-wave potential of 0.75 V (vs. reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE), 0.1 M H3PO4), which is 60 and 40 mV higher than that of Fe-NC and commercial Pt/C catalysts, respectively. More importantly, the Fe-NCP catalyst could deliver a peak power density of 357 mW·cm−2 in a high temperature fuel cell (160 °C), exceeding the non-noble-metal catalysts ever reported. The enhancement of activity is attributed to the increasing charge density and poisoning tolerance of Fe—N4 caused by neighboring P. This work not only promotes the practical application of Fe-N-C materials in HT-PEMFCs, but also provides a feasible P-doping method for regulating the structure of single atom site.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, S. Y.; Jiang, S. P. Prospects of fuel cell technologies. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 163–166.
Wang, Y.; Chen, K. S.; Mishler, J.; Cho, S. C.; Adroher, X. C. A review of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells: Technology, applications, and needs on fundamental research. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 981–1007.
Zhang, H. W.; Shen, P. K. Advances in the high performance polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2382–2394.
Wu, J. F.; Yuan, X. Z.; Martin, J. J.; Wang, H. J.; Zhang, J. J.; Shen, J.; Wu, S. H.; Merida, W. A review of PEM fuel cell durability: Degradation mechanisms and mitigation strategies. J. Power Sources 2008, 184, 104–119.
Gokhale, R.; Asset, T.; Qian, G. Q.; Serov, A.; Artyushkova, K.; Benicewicz, B. C.; Atanassov, P. Implementing PGM-free electrocatalysts in high-temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2018, 93, 91–94.
Rosli, R. E.; Sulong, A. B.; Daud, W. R. W.; Zulkifley, M. A.; Husaini, T.; Rosli, M. I.; Majlan, E. H.; Haque, M. A. A review of high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell (HT-PEMFC) system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 9293–9314.
Li, G. Q.; Kujawski, W.; Rynkowska, E. Advancements in proton exchange membranes for high-performance high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells (HT-PEMFC). Rev. Chem. Eng. 2022, 38, 327–346.
Jaouen, F.; Jones, D.; Coutard, N.; Artero, V.; Strasser, P.; Kucernak, A. Toward platinum group metal-free catalysts for hydrogen/air proton-exchange membrane fuel cells. Johnson Matthey Technol. Rev. 2018, 62, 231–255.
He, Q. G.; Shyam, B.; Nishijima, M.; Ramaker, D.; Mukerjee, S. Mitigating phosphate anion poisoning of cathodic Pt/C catalysts in phosphoric acid fuel cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 4877–4887.
Kaserer, S.; Caldwell, K. M.; Ramaker, D. E.; Roth, C. Analyzing the influence of H3PO4 as catalyst poison in high temperature PEM fuel cells using in-operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 6210–6217.
Li, Q.; Wu, G.; Cullen, D. A.; More, K. L.; Mack, N. H.; Chung, H. T.; Zelenay, P. Phosphate-tolerant oxygen reduction catalysts. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 3193–3200.
Li, Y. P.; Jiang, L. H.; Wang, S. L.; Sun, G. Q. Influence of phosphoric anions on oxygen reduction reaction activity of platinum, and strategies to inhibit phosphoric anion adsorption. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 1134–1141.
He, Q. G.; Yang, X. F.; Chen, W.; Mukerjee, S.; Koel, B.; Chen, S. W. Influence of phosphate anion adsorption on the kinetics of oxygen electroreduction on low index Pt (hkl) single crystals. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 12544–12555.
Kamat, A.; Herrmann, M.; Ternes, D.; Klein, O.; Krewer, U.; Scholl, S. Experimental investigations into phosphoric acid adsorption on platinum catalysts in a high temperature PEM fuel cell. Fuel Cells 2011, 11, 511–517.
Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L. J.; Fan, C. H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, B. S.; Cui, X. J.; Wang, J. Q.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, S. H. et al. Axial ligand promoted phosphate tolerance of an atomically dispersed Fe catalyst towards the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 16722–16729.
Bai, L.; Duan, Z. Y.; Wen, X. D.; Guan, J. Q. Bifunctional atomic iron-based catalyst for oxygen electrode reactions. J. Catal. 2019, 378, 353–362.
Bai, L.; Hou, C. M.; Wen, X. D.; Guan, J. Q. Catalysis of oxygen reduction reaction on atomically dispersed copper- and nitrogen-codoped graphene. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 4755–4762.
Haider, R.; Wen, Y. C.; Ma, Z. F.; Wilkinson, D. P.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, X. X.; Song, S. Q.; Zhang, J. J. High temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells: Progress in advanced materials and key technologies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 1138–1187.
Zhang, Q. Q.; Guan, J. Q. Single-atom catalysts for electrocatalytic applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000768.
Cheng, Y.; He, S.; Lu, S. F.; Veder, J. P.; Johannessen, B.; Thomsen, L.; Saunders, M.; Becker, T.; De Marco, R.; Li, Q. F. et al. Iron single atoms on graphene as nonprecious metal catalysts for high-temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1802066.
Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J. Y.; Wu, X.; Tang, C. J.; Yang, S. Z.; Su, P. P.; Thomsen, L.; Zhao, F. P.; Lu, S. F.; Liu, J. et al. A template-free method to synthesis high density iron single atoms anchored on carbon nanotubes for high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105534.
Cheng, Y.; Wang, M. E.; Lu, S.; Tang, C.; Wu, X.; Veder, J. P.; Johannessen, B.; Thomsen, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S. Z. et al. First demonstration of phosphate enhanced atomically dispersed bimetallic FeCu catalysts as Pt-free cathodes for high temperature phosphoric acid doped polybenzimidazole fuel cells. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2021, 284, 119717.
Müller-Hülstede, J.; Zierdt, T.; Schmies, H.; Schonvogel, D.; Meyer, Q.; Zhao, C.; Wagner, P.; Wark, M. Implementation of different Fe-N-C catalysts in high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells-effect of catalyst and catalyst layer on performance. J. Power Sources 2022, 537, 231529.
Xu, Y. S.; Zhu, L. P.; Cui, X. X.; Zhao, M. Y.; Li, Y. L.; Chen, L. L.; Jiang, W. C.; Jiang, T.; Yang, S. G.; Wang, Y. Graphitizing N-doped mesoporous carbon nanospheres via facile single atom iron growth for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 752–758.
Xiao, G. F.; Lu, R. H.; Liu, J. F.; Liao, X. B.; Wang, Z. Y.; Zhao, Y. Coordination environments tune the activity of oxygen catalysis on single atom catalysts: A computational study. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 3073–3081.
Li, R.; Wei, Z. D.; Gou, X. L. Nitrogen and phosphorus dual-doped graphene/carbon nanosheets as bifunctional electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction and evolution. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 4133–4142.
Li, W.; Wang, D. D.; Liu, T. Y.; Tao, L.; Zhang, Y. G.; Huang, Y. C.; Du, S. Q.; Dong, C. L.; Kong, Z. J.; Li, Y. F. et al. Doping-modulated strain enhancing the phosphate tolerance on PtFe alloys for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2109244.
Wang, J.; Huang, Z. Q.; Liu, W.; Chang, C. R.; Tang, H. L.; Li, Z. J.; Chen, W. X.; Jia, C. J.; Yao, T.; Wei, S. Q. et al. Design of N-coordinated dual-metal sites: A stable and active Pt-free catalyst for acidic oxygen reduction reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17281–17284.
Fei, H. L.; Dong, J. C.; Arellano-Jiménez, M. J.; Ye, G. L.; Dong Kim, N.; Samuel, E. L. G.; Peng, Z. W.; Zhu, Z.; Qin, F.; Bao, J. M. et al. Atomic cobalt on nitrogen-doped graphene for hydrogen generation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8668.
Jiao, L.; Zhou, Y. X.; Jiang, H. L. Metal-organic framework-based CoP/reduced graphene oxide: High-performance bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 1690–1695.
Qian, Z. J.; Hu, Z. W.; Zhang, Z. P.; Li, Z. L.; Dou, M. L.; Wang, F. Out-of-plane FeII-N4 moiety modified Fe-N co-doped porous carbons as high-performance electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 4017–4023.
Zhang, F.; Zhang, D. Q.; Liu, W. Q.; Li, X. J.; Chen, Q. J. Fluorine enhanced pyridinic-N configuration as an ultra-active site for oxygen reduction reaction in both alkaline and acidic electrolytes. Carbon 2022, 187, 67–77.
Huo, J. J.; Lu, L.; Shen, Z. Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J. J.; Liu, Q. B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, M. H.; Wang, G. X. A rational synthesis of single-atom iron-nitrogen electrocatalysts for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 16271–16282.
Xu, H. X.; Cheng, D. J.; Cao, D. P.; Zeng, X. C. A universal principle for a rational design of single-atom electrocatalysts. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 339–348.
Wang, Y.; Zheng, X. B.; Wang, D. S. Design concept for electrocatalysts. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 1730–1752.
Chen, Y. J.; Gao, R.; Ji, S. F.; Li, H. J.; Tang, K.; Jiang, P.; Hu, H. B.; Zhang, Z. D.; Hao, H. G.; Qu, Q. Y. et al. Atomic-level modulation of electronic density at cobalt single-atom sites derived from metal-organic frameworks: Enhanced oxygen reduction performance. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3212–3221.
Cui, T. T.; Wang, Y. P.; Ye, T.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z. Q.; Li, J.; Lei, Y. P.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Engineering dual single-atom sites on 2D ultrathin N-doped carbon nanosheets attaining ultra-low-temperature zinc-air battery. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202115219.
Han, A.; Wang, X. J.; Tang, K.; Zhang, Z. D.; Ye, C. L.; Kong, K. J.; Hu, H. B.; Zheng, L. R.; Jiang, P.; Zhao, C. X. et al. An adjacent atomic platinum site enables single-atom iron with high oxygen reduction reaction performance. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 19262–19271.
Li, W. H.; Yang, J. R.; Wang, D. S. Long-range interaction on diatomic catalysts boosting electrocatalysis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., in press, https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202213318.
Hou, H. F.; Mao, J. J.; Han, Y. H.; Wu, F.; Zhang, M. N.; Wang, D. S.; Mao, L. Q.; Li, Y. D. Single-atom electrocatalysis: A new approach to in vivo electrochemical biosensing. Sci. China Chem. 2019, 62, 1720–1724.
Tian, S. B.; Hu, M.; Xu, Q.; Gong, W. B.; Chen, W. X.; Yang, J. R.; Zhu, Y. Q.; Chen, C.; He, J.; Liu, Q. et al. Single-atom Fe with Fe1N3 structure showing superior performances for both hydrogenation and transfer hydrogenation of nitrobenzene. Sci. China Mater. 2020, 64, 642–650.
Zhang, G. X.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xiong, X. Y.; Sun, K.; Chen, R. D.; Chen, W. X.; Kuang, Y.; Zheng, L. R.; Tang, H. L. et al. A general route via formamide condensation to prepare atomically dispersed metal-nitrogen-carbon electrocatalysts for energy technologies. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1317–1325.
Zheng, N. C.; Lian, Y. K.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, R. L.; He, X.; Hu, R. T.; Hu, Z. F. An effective Fenton reaction by using waste ferric iron and red phosphorus. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 135265.
Wang, Y. X.; Xu, N. N.; He, R. N.; Peng, L. W.; Cai, D. Q.; Qiao, J. L. Large-scale defect-engineering tailored tri-doped graphene as a metal-free bifunctional catalyst for superior electrocatalytic oxygen reaction in rechargeable Zn-air battery. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2021, 285, 119811.
Sun, X. H.; Tuo, Y. X.; Ye, C. L.; Chen, C.; Lu, Q.; Li, G. N.; Jiang, P.; Chen, S. H.; Zhu, P.; Ma, M. et al. Phosphorus induced electron localization of single iron sites for boosted CO2 electroreduction reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 23614–23618.
Hu, Y.; Jensen, J. O.; Pan, C.; Cleemann, L. N.; Shypunov, I.; Li, Q. F. Immunity of the Fe-N-C catalysts to electrolyte adsorption: Phosphate but not perchloric anions. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2018, 234, 357–364.
Holst-Olesen, K.; Reda, M.; Hansen, H. A.; Vegge, T.; Arenz, M. Enhanced oxygen reduction activity by selective anion adsorption on non-precious-metal catalysts. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 7104–7112.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFA0702002), the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. Z210016), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21935001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2022_5314_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Phosphorus induced activity-enhancement of Fe-N-C catalysts for high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, X., Li, Y., Sun, H. et al. Phosphorus induced activity-enhancement of Fe-N-C catalysts for high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Nano Res. 16, 6531–6536 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5314-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5314-2