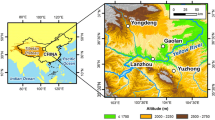
Abstract
Until now, most studies of the isotopic composition of precipitation in the Extensive Hexi Region have described individual sites. A systematic study considering the regional atmospheric circulation, the complex topography, and the re-evaporation process is lacking. This paper compares and summarizes previous studies in the Extensive Hexi Region, to provide a regional picture of the characteristics of isotopic composition of precipitation and moisture sources. δ 18O and δD values exhibit significant seasonal variability, with higher values in summer and lower values in winter due to the seasonality of temperature and moisture sources. The temperature effect is more pronounced in the Extensive Hexi Region than in northwest China. The altitude effects are also evident with a gradient of −0.23 ‰/100 m for δ 18O and −1.67 ‰/100 m for δD. But, the d-excess increases gradually with altitude, and the higher d-excess values occur at mountain sampling sites which are attributed to the difference of the secondary evaporation between mountains and plain. Finally, the moisture source in the study area was investigated, and the results show relatively complex patterns: the westerly and polar air masses dominate in winter; however, there are inconsistent results in summer. Whether or not the westerly air mass is the dominant supply of moisture in summer is yet to be determined. Additionally, in the course of reviewing and integrating, some new research questions are identified for future work.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araguás-Araguás L, Froehlich K, Rozanski K (1998) Stable isotope composition of precipitation over Southeast Asia. J Geophys Res 103(D22):28721–28742
Araguás-Araguás L, Froehlich K, Rozanski K (2000) Deuterium and oxygen-18 isotope composition of precipitation and atmospheric moisture. Hydrol Processes 14:1341–1355
Chen S, Dong A, Han T (2007) Differences in summer precipitation between the East and West of the Qilian Mountains and its contributing factors. J Nanjing Inst Meteorol 30:715–719 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Cheng L, Qu Y (1992) Water and land resources and their rational development and utilization in Hexi Region. Science Press, Beijing, pp 36–46 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Clark I, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrology. Lewis, Boca Raton, 328
Craig H (1961) Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 133:1702–1703
Cui J, An S, Wang Z, Fang CM, Liu YH, Yang HB, Zhen X, Liu SR (2009) Using deuterium excess to determine the sources of high-altitude precipitation: implications in hydrological relations between sub-alpine forests and alpine meadows. J Hydrol 373:24–33
Dansgaard W (1964) Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus B 16:436–468
Dogramaci S, Skrzypek G, Dodson W, Grierson PF (2012) Stable isotope and hydrochemical evolution of groundwater in the semi-arid Hamersley Basin of subtropical northwest Australia. J Hydrol 475:281–293
Dutton A, Wilkinson BH, Welker JM, Bowen GJ, Lohmann KC (2005) Spatial distribution and seasonal variation in 18O/16O of modern precipitation and river water across the conterminous USA. Hydrol Processes 19:4121–4146
Froehlich K, Kralik M, Papesch W, Rank D, Scheifinger H, Stichler W (2008) Deuterium excess in precipitation of Alpine regions—moisture recycling. Isot Environ Healt Stud 44:61–70
Gat J (1980) The isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen in precipitation. In Handbook of environmental isotope geochemistry, 1:21–47
Gat J, Bowser C, Kendall C (1994) The contribution of evaporation from the Great Lakes to the continental atmosphere: estimate based on stable isotope data. Geophys Res Lett 21:557–560
Guo LC, Bai HZ, Yue H (2007) The distribution characteristics and development potential of water vapor resources over Qilian Mountain areas. Resour Sci 29:68–73 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Hamed Y, Dassi L, Ahmadi R, Dhia BH (2008) Geochemical and isotopic study of the multilayer aquifer system in the Moulares-Redayef basin, southern Tunisia. Hydrol Sci J 53(5):1241–1250
He JQ (2011) The spatial and temporal variation of stable isotopes in precipitation and river water in Hexi inland river basins. Ph.D. thesis. State Key Laboratory of Cryospheric Sciences, Cold and Arid Regions Environmental and Engineering Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS)
Henderson A, Holmes J, Zhang JW (2003) A carbon- and oxygen-isotope record of recent environmental change from Qinghai Lake, NE Tibetan Plateau. Chin Sci Bull 48(14):1463–1468
Holdsworth G, Fogarasi S, Krouse HR (1991) Variation of the stable isotopes of water with altitude in the Saint Elias Mountains of Canada. J Geophys Res 96:7483–7494
Holmes J, Zhang JW, Chen FH (2007) Paleoclimatic implications of an 850 year oxygen isotope record form the northern Tibetan plateau. Geophys Res Lett 34, L23403
Hou DJ (2011) The application of stable isotopes and geochemical methods on the hydrological processes in Laohugou Basin. Msc. thesis. State Key Laboratory of Cryospheric Sciences, Cold and Arid Regions Environmental and Engineering Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS)
Hren MT, Bookhagen BB, Blisniuk PM, Blisniuk MP, Booth AL, Chamberiain CP (2009) δ18O and δD of stream waters across the Himalaya and Tibetan Plateau: implications for moisture sources and paleoelevation reconstructions. Earth Planet Sci Lett 288:20–32
Jeelani G, Kumar U, Kumar B (2013) Variation of δ18O and δD in precipitation and stream waters across the Kashmir Himalaya (India) to distinguish and estimate the seasonal sources of stream flow. J Hydrol 481:157–165
Jonsson CE, Leng MJ, Rosqvist CR, Seibert J, Arrowsmith C (2009) Stable oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in sub-Arctic lake waters from northern Sweden. J Hydrol 376(1–2):143–151
Li YL, Yang JC, Tan LH, Duan FJ (1999) Impact of tectonics on alluvial landforms in the Hexi Corridor, Northwest China. Geomorphology 28:299–308
Liu JR, Song XF, Yuan GF, Sun XM, Liu X, Wang SQ (2008a) Characteristics of δ18O in precipitation over Northwest China and its water vapor sources. J Geogr Sci 63(1):12–22
Liu XH, Shao XM, Liang EY, Chen T, Qin DH, An WL, Xu GB, Sun WZ, Wang Y (2009) Climatic significance of tree-ring δ18O in the Qilian Mountains, northwestern China and its relationship to atmospheric circulation patterns. Chem Geol 268:147–154
Liu ZF, Tian LD, Chai XR, Yao TD (2008b) A model-based determination of spatial variation of precipitation δ18O over China. Chem Geol 249(1–2):203–212
Liu ZF, Tian LD, Yao TD, Yu WS (2008c) Seasonal deuterium excess in Nagqu precipitation: influence of moisture transport and recycling in the middle of Tibetan Plateau. Environ Geol 55:1501–1506
Ma JZ, Zhang P, Zhu GF, Wang YQ, Edmunds WM, Ding ZY, He JH (2012) The composition and distribution of chemicals and isotopes in precipitation in the Shiyang River system, northwestern China. J Hydrol 436–437:92–101
Naoki K, Akira S, Sophal C, Tsuboyama Y, Nobuhiro T, Keth N, Tamai, K (2007) Stable isotope studies of rainfall and stream water in forest watersheds in Kampong Thom, Cambodia. Forest Environments in the Mekong River Basin. Part I, 125-134, DOI: 10.1007/978-4-431-46503-4-11
Peng TR, Liu KK, Wang CH, Chuang KH (2011) A water isotope approach to assessing moisture recycling in the island-based precipitation of Taiwan: a case study in the western Pacific. Water Resour Res 47, W08507
Rozanski K, Araguás-Araguás L, Gonfiantini R (1992) Relation between long-term trends of oxygen-18 isotope composition of precipitation and climate. Science 258(5084):981–985
Thompson LG, Mosley-Thompson E, Davis ME, Bolzan JF, Dai J, Yao TD, Gundestrup N, Wu X, Klein L, Xie ZC (1989) Holocene-late Pleistocene climatic ice core records from Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Science 246:474–477
Tian LD, Masson-Delmotte V, Stievenard T, Yao TD, Jouzel J (2001) Tibetan Plateau summer monsoon northward extent revealed by measurements of water stable isotopes. J Geophys Res 106(D22):28081–28088
Tian LD, Yao TD, MacClune K, White JW, Schilla A, Vaughn B, Vachon R, Ichiyanag K (2007) Stable isotopic variations in west China: a consideration of moisture sources. J Geophys Res 112:3–5
Tian LD, Yao TD, Schuster P (2003) Oxygen-18 concentrations in recent precipitation and ice cores on the Tibetan Plateau. J Geophys Res 108(D9):4293–4302
Tian LD, Yao TD, White JW, Yu WS, Wang NL (2005) Westerly moisture transport to the middle of Himalayas revealed from the high deuterium excess. Chinese Sci Bull 50(10):1026–1030
Trenberth K (1999) Atmospheric moisture recycling: role of advection and local evaporation. J Clim 12:1368–1381
Van der Ent RJ, Savenije HH, Schaefli B, Steele-Dunne SC (2010) Origin and fate of atmospheric moisture over continents. Water Resour Res 46, W09525
Wang BJ, Huang YX, Wang JS, Tao JH (2006) The seasonal distribution and Tim e-Varying of the cloud and vapor flux in Qilian Mountain areas. Adv Earth Sci 21(9):948–955 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Wang NA, Zhang JM, Cheng HY, Guo JY, Zhao Q (2003) The age of formation of the mirabilite and sand wedges in the Hexi Corridor and their paleoclimatic interpretation. Chinese Sci Bull 48(14):1439–1445
Wang NL, Zhang SB, He JQ, Pu JC, Wu XB, Jiang X (2009) Tracing the major source area of the mountainous runoff generation of the Heihe River in northwest China using stable isotope technique. Chinese Sci Bull 54:2751–2757
Wang NL, Zhang SB, Pu JC, He JQ, Jiang X, Wu XB (2008) Seasonal variation of δ18O in river water in the upper reaches of Heihe River Basin and its influence factors. J Glacial Geocry 30(6):914–920 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Wang ZT (1981) Glacier inventory of China: I: Qilian Mountains [R]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou Institute of Glaciology and Cryopedology, CAS 1–249 (In Chinese)
Wu JK, Ding YJ, Ye BS, Yang Q, Zhang X, Wang J (2010) Spatio-temporal variation of stable isotopes in precipitation in the Heihe River Basin, Northwestern China. Environ Earth Sci 61:1123–1134
Yamanaka T, Tsujimura M, Oyunbaatar D, Davaa G (2007) Isotopic variation of precipitation over eastern Mongolia and its implication for the atmospheric water cycle. J Hydrol 333:21–34
Yao TD, Zhou H, Yang XX (2009) Indian monsoon influences altitude effect of δ18O in precipitation/river water on the Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Sci Bull 54:2724–2731
Zhang JW, Holmes JA, Chen FH, Qiang MR, Zhou AF, Chen S (2009) An 850-year ostracod-shell trace-element record from Sugan Lake, Northern Tibetan Plateau, China: implications for interpreting the shell chemistry in high-Mg/Ca waters. Quatern Int 194:119–133
Zhang MY, Wang SJ, Wu FC, Yuan XH, Zhang Y (2007a) Chemical compositions of wet precipitation and anthropogenic influences at a developing urban site in Southeastern China. Atmos Res 84(4):311–322
Zhang Q, Zhang J, Song GW, Di XH (2007b) Research on atmospheric water-vapor distribution over Qilian Mountains. Acta Meteor Sini 65(4):633–643 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang XP, Shi YF, Yao TD (1995) Characteristics of δ18O in precipitation over Northeast Tibet plateau. Sci China Ser B 25(5):540–547
Zhang XP, Yao TD (1998) Distributional features of δ18O in precipitation in China. J Geogr Sci 53(4):356-364 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang YH, Wu YQ (2007a) Characteristics of the δ18O in precipitation in the upper and middle reaches of Heihe River. J Glacial Geocry 29(3):440–445 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang YH, Wu YQ (2007b) Variation of δ18O in water in Heihe river basin. Adv Water Sci 18(6):864–870 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang YH, Wu YQ (2009) Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in precipitation in Heihe River Basin, China. J Glacial Geocry 31(1):35–39 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao LJ, Yin L, Xiao HL, Cheng GD, Zhou MX, Yang YG, LiZ ZJ (2011) Isotopic evidence for the moisture origin and composition of surface runoff in the headwaters of the Heihe River basin. Chinese Sci Bull 56(4–5):406–415
Zhou WF, Xiao HB, Sun AP, Zhang GQ, Xiao RX (2012) The relation between orographic cloud and vertical wind in Qilian. J Mt Sci 30(6):641–647 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Key Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KZZD-EW-04-05), the National Key Technology R & D Program (No. 2012BAC08B05), the Cooperation-Innovation team project of Chinese Academy of Sciences, and partly funded by the Australian Research Council (ARC) (No. ARCLP100100546). The authors thank the reviewers and associate editor for their constructive comments during the review process.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Feng, Q., Wei, Y. et al. An overview of precipitation isotopes over the Extensive Hexi Region in NW China. Arab J Geosci 8, 4365–4378 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1521-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1521-9