Abstract
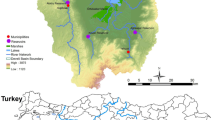
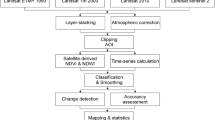
Land cover dynamics were analyzed temporally and spatially in the Al-Hubail wetland (Al-Ahsa, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia) to determine the evolution of the environmental status of this biologically and ecologically interesting area in Saudi Arabia. Using remote sensing data, land cover changes were estimated for 36 years (1985–2021). For this analysis, three images from 1985 (Landsat 5 MSS), 2003 (Landsat 7 ETM +), and 2021 (Sentinel-2) were used to classify and detect changes. A machine learning algorithm was used, and the images were classified into four main land cover classes: Water bodies, hydromorphic areas, vegetation, and open ground. Change detection was performed for the year pairs 1985 to 2003 and 2003 to 2021. The results of this classification showed a significant increase in the area of hydromorphic areas and vegetation. The results were checked with a confusion matrix indicating an overall accuracy between 89.3 and 92.8%. The qualitative trend data show that the Al-Hubail wetland has changed significantly during the study period. Thus, a significant expansion of the wetland was observed in conjunction with an increase in agricultural drainage toward the wetland. This analysis shows the strong anthropogenic pressure on the area and highlights the need to strengthen the existing laws to preserve local biodiversity in the long term. It suggests that more efforts should be made to manage the water resources of the region effectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Moneim, A. (2014). Histopathological and ultrastructural perturbations in tilapia liver as potential indicators of pollution in Lake AlAsfar, Saudi Arabia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 4387–4439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2185-9
Al-Dakheel, Y. Y., Hussein, A. H. A., El-Mahmoudi, A. S., & Massoud, M. A. (2009). Soil, water chemistry and sedimentological studies of Al Asfar evaporation lake and its Inland sabkha, Al-Hassa area, Saudi Arabia. Asian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2, 1–21. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajes.2009.1.21
Alfarhan, A. H. (1999). A phytogeographical analysis of the floristic elements in Saudi Arabia. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 2, 702–711. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjbs.1999.702.711
Al-Hussaini, Y. A. (2005). The use of multi-temporal landsat TM imagery to detect land cover/use changes in AlHassa, Saudi Arabia. Scientific Journal of King Faisal University (basic and Applied Sciences), 6(1), 1426.
Almadini, A. M., & Hassaballa, A. A. (2019). Depicting changes in land surface cover at AlHassa oasis of Saudi Arabia using remote sensing and GIS techniques. PLoS ONE, 14(11), e0221115. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0221115
Almutairi, A., & Warner, T. A. (2010). Change detection accuracy and image properties: A study using simulated data. Remote Sensing, 2, 1508–1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs2061508
Al-Obaid, S., Samraoui, B., Thomas, J., El-Serehy, H. A., Alfarhan, A. H., Schneider, W., & O’Connell, M. (2017). An overview of wetlands of Saudi Arabia: Values, threats, and perspectives. Ambio, 46, 98–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-016-0807-4
Al-Sheikh, H., & Fathi, A. A. (2010). Ecological studies on Al-Asfar lake. Al-Hassa, Saudi Arabia, with special references to the sediment. Research Journal of Environmental Sciences, 4, 13–22. https://doi.org/10.3923/rjes.2010.13.22
Al-Taher, A. A. (1999). Al-Hassa: Geographical studies (pp. 1–385). King Saud University.
Alwashe, M. A., & Bokhari, A. Y. (1993). Monitoring vegetation changes in Al Madinah, Saudi Arabia, using thematic mapper data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 14, 191–197. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431169308904331
Ashraf, M. Y., Al-Fredan, M. A., & Fathi, A. A. (2020). Floristic composition of lake Al-Asfar, Alahsa, Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Botany, 5, 116–125.
Asselen, S. V., Verburg, P. H., Vermaat, J. E., & Janse, J. H. (2013). Drivers of wetland conversion: A global meta-analysis. PLoS ONE, 8(11), e81292. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0081292
Borak, J. S., Lambin, E. F., & Strahler, A. H. (2000). The use of temporal metrics for land-cover change detection at coarse spatial scales. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 21(6–7), 1415–1432. https://doi.org/10.1080/014311600210245
Chen, J., Gong, P., He, C., Pu, R., & Shi, P. (2003). Land-use/land-cover change detection using improved change-vector analysis. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 69(4), 369–379.
Chen, Y., & Cao, Z. (2013). An improved MRF-based change detection approach for multitemporal remote sensing imagery. Signal Processing, 93(1), 163–175.
Chouari, W. (2021a). Contributions of multispectral images to the study of land cover in wet depressions of eastern Tunisia. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Sciences, 24, 443–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2020.11.003
Chouari, W. (2021b). Wetland land cover change detection using multitemporal Landsat data: A case study of the Al-Asfar wetland, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 14, 523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06815-y
Close, O., Petit, S., Beaumont, B., & Hallot, E. (2021). Evaluating the potentiality of sentinel-2 for change detection analysis associated to LULUCF inWallonia. Belgium. Land, 10(1), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10010055
Coppin, P., Jonckheere, I., Nackaerts, K., Muys, B., & Lambin, E. (2004). Review article digital change detection methods in ecosystem monitoring: A review. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 25, 1565–1596. https://doi.org/10.1080/0143116031000101675
Corgne, S. (2004). Modélisation prédictive de l’occupation des sols en contexte agricole intensif : Application à la couverture hivernale des sols en Bretagne, « Predictive modeling of land use in an intensive agricultural context: Application to winter soil cover in Brittany ». Ph.D. Thesis, University of Rennes 2- Haute-Bretagne, France, 230 p
Deng, J. S., Wang, K., Deng, Y. H., & Qi, G. J. (2008). PCA-based land-use change detection and analysis using multitemporal and multisensor satellite data. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 29, 4823–4838. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160801950162
Dubos-Paillard, E., Guermond, Y., & Langlois, P. (2004). Analyse de l’évolution urbaine par automate cellulaire, le modèle Spacelle analysis of urban evolution by cellular automata, the Spacelle model. L’espace Géographique, 32, 357–378.
Eid, A. N. M., Olatubara, C. O., Ewemoje, T. A., Farouk, H., & El-Hennawy, M. T. (2020). Coastal wetland vegetation features and digital change detection mapping based on remotely sensed imagery: El-Burullus Lake. Egypt. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 8(1), 66–79.
El-Hattab, M. M. (2015). Change detection and restoration alternatives for the Egyptian lake Maryut Egypt. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 18(1), 9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2014.12.001
El-Hattab, M. M. (2016). Applying post classification change detection technique to monitor an Egyptian coastal zone (Abu Qir Bay). The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 19(1), 23–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2016.02.002
Fahmy, G. H., & Fathi, A. A. (2011). Limnological studies on the Wetland lake, Al-Asfar, with special references to heavy metal accumulation by fish. American Journal of Environmental Sciences, 7(6), 515–524. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajessp.515-524
Fathi, A. A., Al-Fredan, M. A., & Youssef, A. M. (2009). Water quality and phytoplankton communities in Lake Al-Asfar, AL-Hassa, Saudi Arabia. Research Journal of Environmental Sciences, 3, 504–513. https://doi.org/10.3923/rjes.2009.504.513
Fontinovo, G., Allegrini, A., Atturo, C., & Salvatori, R. (2012). Speedy methodology for geometric correction of MIVIS data. European Journal of Remote Sensing, 45(1), 19–25. https://doi.org/10.5721/EuJRS20124502
Foody, G. M. (2002). Status of land cover classification accuracy assessment. Remote Sensing of Environment, 80(1), 185–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(01)00295-4
Gardner, R., Finlayson, M. (2018). Global Wetland outlook: State of the World’s Wetlands and their services to people; Ramsar Convention: Gland, Switzerland.
Girard, M. C., Girard, C. M. (2010). Traitement des données de télédétection-2e éd. : Environnement et ressources naturelles. Dunod, Paris. 576 p.
Gong, M. G., Su, L. Z., Jia, M., & Chen, W. S. (2014). Fuzzy clustering with a modified MRF energy function for change detection in synthetic aperture radar images. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 22(1), 98–109. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2013.2249072
Gu, W., Lv, Z., & Hao, M. (2017). Change detection method for remote sensing images based on an improved Markov random field. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 76(17), 17719–17734.
Hao, M., Shi, W., Deng, K., & Zhang, H. (2014). A contrast-sensitive Potts model custom-designed for change detection. European Journal of Remote Sensing, 47(1), 643–654. https://doi.org/10.5721/EuJRS20144736
He, P., Shi, W., Miao, Z., Zhang, H., & Cai, L. (2015). Advanced Markov random field model based on local uncertainty for unsupervised change detection. Remote Sensing Letters, 6(9), 667–676. https://doi.org/10.1080/2150704X.2015.1054045
Hussain, M., Chen, D., Cheng, A., Wei, H., & Stanley, D. (2013). Change detection from remotely sensed images: From pixel-based to object-based approaches. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 80, 91–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2013.03.006
Kato, Z. (1994). Modelisations Markovian multiresolutions in vision by computer: Application to the segmentation of image SPOT. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nice, France.
Langlois, P. (2001). Le modèle SpaCell. Base de données du Groupe Modèles du GDR Libergéo, 111–125
Lu, D., Mausel, P., Brondízio, E., & Moran, E. (2004). Change detection techniques. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 25, 2365–2401. https://doi.org/10.1080/0143116031000139863
Macleod, R. D., & Congalton, R. G. (1998). Quantitative comparison of change-detection algorithms for monitoring eelgrass from remotely sensed data. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 64, 207–216.
Maimaitijiang, M., Ghulam, A., Sandoval, J. O., & Maimaitiyiming, M. (2015). Drivers of land cover and land use changes in St. Louismetropolitan area over the past 40 years characterized by remote sensing and census population data. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 35, 161–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2014.08.020
Mccauley, L., Anteau, M., Post van der Burg, M., & Wiltermuth, M. (2015). Land use and wetland drainage affect water levels and dynamics of remaining wetlands. Ecosphere., 6, 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1890/ES14-00494.1
Nemmour, H., & Chibani, Y. (2006). Multiple support vector machines for land cover change detection: An application for mapping urban extensions. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 61(2), 125–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-011-0060-z
Nguyen, T. H. (2015). Optimal ground control points for geometric correction using genetic algorithm with global accuracy. European Journal of Remote Sensing, 48(1), 101–120. https://doi.org/10.5721/EuJRS20154807
Ojaghi, S., Ahmadi, F. F., Ebadi, H., & Bainchetti, R. (2017). Wetland cover change detection using multi-temporal remotely sensed data a case study: Ghara Gheshlagh wetland in the southern part of the Urmia Lake. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 10, 470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3239-y
Patel, N., & Kaushal, B. (2010). Improvement of user’s accuracy through classification of principal component images and stacked temporal images. Geo-Spatial Information Science, 13(4), 243–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11806-010-0380-0
Petropoulos, G. P., Kalivas, D. P., Griffiths, H. M., & Dimou, P. P. (2015). Remote sensing and GIS analysis for mapping spatio-temporal changes of erosion and deposition of two Mediterranean river deltas: The case of the Axios and Aliakmonas rivers, Greece. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 35, 217–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2014.08.004
Pieczynski, W. (2003). Modèles de Markov en traitements d’images. Traitement Du Signal, 20(3), 255–278.
Rapinel, S., Hubert-Moy, L., & Clément, B. (2015). Combined use of LiDAR data and multispectral earth observation imagery for wetland habitat mapping. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 37, 56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2014.09.002
Rokni, K., Ahmad, A., Solaimani, K., & Hazini, S. (2015). A new approach for surface water change detection: Integration of pixel level image fusion and image classification techniques. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 34, 226–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2014.08.014
Salih, A. (2018). Classification and mapping of land cover types and attributes in Al-Ahsaa Oasis, Eastern Region, Saudi Arabia Using Landsat-7 Data. Journal of Remote Sensing & GIS, 7, 228. https://doi.org/10.4172/2469-4134.1000228
Singh, A. (1989). Digital change detection techniques using remotely-sensed data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 10(6), 989–1000. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431168908903939
Solberg, A., Taxt, T., & Jain, A. K. (1996). A Markov random field model for classification of multisource satellite imagery. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 34(1), 100–113.
Tolpekin, V. A., & Stein, A. (2009). Quantification of the effects of land-cover-class spectral separability on the accuracy of Markov-random-field-based superresolution mapping. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 47(9), 3283–3297. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2009.2019126
UNITED STATES GEOLOGICAL SURVEY (2022). Landsat Satellite Missions. Available at: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/
Wang, J., Yong Gea, Y., Heuvelinkc, G., Zhoua, C., & Brusd, D. (2012). Effect of the sampling design of ground control points on the geometric. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 18, 91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2012.01.001
Wu, C., Du, B., Cui, X., & Zhang, L. (2017). A post-classification change detection method based on iterative slow feature analysis and Bayesian soft fusion. Remote Sensing of Environment, 199, 241–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2017.07.009
Xu, T., Weng, B., Yan, D., Wang, K., Li, X., Bi, W., Li, M., Cheng, X., & Liu, Y. (2019). Wetlands of International Importance: Status, threats, and future protection. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16, 1818. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101818
Youssef, A. M., Al-Fredan, M. A., Adel, A., & Fathi, A. A. (2009). Floristic composition of Lake Al-Asfar, Alahsa, Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Botany, 5, 116–125. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijb.2009.116.125
Zheng, Ch., Pan, X., Chen, X., Yang, X., Xin, X., & Su, L. (2019). An object-based markov random field model with anisotropic penalty for semantic segmentation of high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. Remote Sensing, 11(23), 2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232878
Zheng, C., & Yao, H. (2019). Segmentation for remote-sensing imagery using the object-based Gaussian-Markov random field model with region coefficients. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 40, 4441–4472. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2018.1563841
Acknowledgments
The following statement must be included in the article: This work was supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research, Vice Presidency for Graduate Studies and Scientific Research, King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia [Grant No. 831].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The author declares that he has no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Chouari, W. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Land Cover Changes in Al-Hubail Wetland (Kingdom of Saudi Arabia). J Indian Soc Remote Sens 51, 585–599 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-022-01653-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-022-01653-1