Abstract
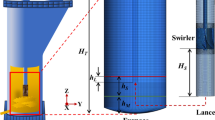
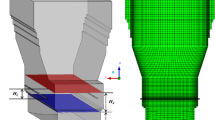
To understand complex behavior in the smelting furnace of Mitsubishi continuous process for copper refining, comprehensive 3-D numerical simulation and field experiment were performed. The numerical simulation results showed that strong and complex velocity fields of gas, matte and slag were generated in the furnace and large amounts of matte and slag were splashed into the gas area. Temperature measurements at the lance during field operation revealed that wide range of temperature variation appeared depending on the injection condition of concentrates. Numerical simulation results provided good agreements with experiments results and showed that the chemical reaction induces temperature increase during gas injection period. On the other hand, lance temperature is decreasing because of cold concentrates during gas and particles injection period. From the FFT analysis results, the fluctuations of matte and slag volume fraction near the lance induce temperature fluctuations of the lance. Through these experimental and simulation results, it was revealed that the lances in the smelting furnace were exposed to severe conditions such as high temperature, repeated large temperature change and cyclic change of large temperature gradient across the thickness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Shibasaki and M. Hayashi, JOM 43, 20 (1991).
R. Sridhar, J. M. Tofuri, and S. Simeonov, JOM 49, 48 (1997).
M. Goto, E. Oshima, and M. Hayashi, JOM 50, 60 (1998).
Z. Asaki, T. Taniguchi, and M. Hayashi, JOM 53, 25 (2001).
W. G. Davenport MK, M. King, M. Schlesinger, A. K. Biswas, Extractive Metall. of Copper, 4 th ed., pp.57–72, Elsevier Science Ltd. (2002).
E. Kimura, ISIJ Int. 23, 522 (1983).
S.-S. Park, N. Dyussekenov, and H.-Y. Sohn, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 41B, 51 (2010).
J.-S. Chang and H.-Y. Sohn, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 43B, 787 (2012).
Y.-B. Hahn and H.-Y. Sohn, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 21B, 945 (1990).
M. Nagamori, W. J. Errington, P. J. Mackey, and D. Poggi, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 25B, 839 (1994).
J. Vaarno, J. Jarvi, T. Ahokainen, T. Laurila, and P. Taskinen, Proc. Third International Conference on CFD in the Minerals and Process Industries, p.147, CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia (2003).
X.-F. Li and T. Xiao, Proc. Third International Conference on CFD in the Minerals and Process Industries, p.147, CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia (2003).
Ansys Fluent Theory Guide 14.0, pp.54-58, ANSYS Inc. (2011).
H.-J. Lee and K.-W. Yi, Met. Mater. Int. 21, 511 (2015).
M. Alam, J. Naser, G. Brooks, and A. Fontana, ISIJ Int. 52, 1026 (2012).
D. Kang and R. K. Strand, Energ. Buildings, 62, 196 (2013).
B. R. Conard, R. Sridhar, and J. S. Warner, K. J. Chem. Thermodynamics 12, 817 (1980).
FACTSAGE 6.4 Thermochemistry Software, Thermfact/ CRCT and GTT-Tech. (accessed December 6, 2014).
Steel Casting Handbook, Supplement 9, High Alloy Data Sheets, Heat Series, p.5, Steel Founders' Society of America (2004).
K.-I. Horai and G. Simmons, Earth Planet. Sc. Lett. 6, 59 (1969).
J.-Y. Lee, Y.-T. Kim, and K.-W. Yi, Met. Mater. Int. 21, 295 (2015).
M. Wakamatsu, H. Nei, and K. Hashiguchi, J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 32, 752 (1995).
L.-W. Hu and M. S. Kazimi, Int. J. Heat Fluid Fl. 27, 54 (2006).
G.-Y. Kim, K.-S. Kim, J.-C. Park, S.-K. Kim, Y.-O. Yoon, and K.-A. Lee, Korean J. Met. Mater. 52, 283 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, Jh., Park, Ss., Han, Xf. et al. Numerical analysis on fluid flow and heat transfer in the smelting furnace of mitsubishi process for Cu refining. Met. Mater. Int. 22, 118–128 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-015-5092-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-015-5092-4