Abstract
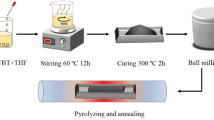
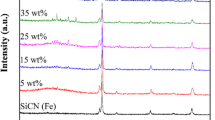
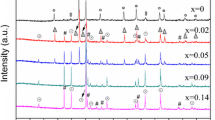
Multiphase polymer-derived ceramics have the advantages of thermal stability and adjustable dielectric properties, which exhibit significant potential for use in high-temperature microwave absorbing materials. Herein, Co-containing polymer-derived SiCN (Co–SiCN) ceramics were successfully synthesized by the physical mixing of zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF)-67 and polysilazane precursors and subsequent pyrolysis. The phase and chemical compositions, microstructures, dielectric properties, electromagnetic wave absorption (EWA) performance, and mechanism of the ceramics were investigated. The results showed that the introduction of ZIF-67 promoted the in situ formation of dielectric loss phases, including SiC nanocrystals, CoSi nanocrystals, and free carbon. The phase composition can be regulated by controlling the pyrolysis temperature to achieve ideal EWA properties. The Co–SiCN ceramic pyrolyzed at 1500 °C demonstrated excellent EWA performance, with a maximum effective absorption band (EABmax) of 3.0 GHz at an ultralow thickness of 1.05 mm and minimum reflection loss (RLmin) of − 46.4 dB at a low frequency of 6 GHz. Compared with other reported SiCN-based ceramics containing magnetic metals, the ceramics prepared in this study stand out because of their low RL and high EAB at low thicknesses. The superior microwave absorption performance of the Co–SiCN ceramics is attributed to the heterointerface polarization, and impedance matching induced by the synergistic effects of their co-existing electromagnetic transparent/absorption phases. This study provides new insights into the development of high-performance SiCN-based microwave absorbers.
Graphical abstract

摘要
多相聚合物衍生陶瓷具有良好热稳定性和介电性能可调的优点,在高温微波吸收材料中显示出巨大的应用潜力。本文通过物理混合法将ZIF-67 纳米颗粒引入聚硅氮烷前驱体中,经过高温热解合成了含钴聚合物衍生的硅碳氮陶瓷(Co–SiCN)。研究了陶瓷化学组成、微观结构、介电性质、电磁波吸收性能及机理。结果表明,ZIF-67 的引入促进了介电损耗相如SiC 纳米晶、CoSi 纳米晶和游离碳的形成。在1500 °C下热解Co–SiCN 陶瓷表现出优异的吸波性能,在1.05 mm 的超低厚度下,最大有效吸收带为3.0 GHz,在6 GHz 低频时,最小反射损耗为−46.4 dB。Co–SiCN 陶瓷优异的微波吸收性能归因于电磁透过/吸收相共存引起的丰富异质界面极化损耗和良好阻抗匹配特性。这项研究为高性能SiCN 基微波吸收材料的开发提供了新的见解。








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao ZH, Zhang LM, Wu HJ. Hydro/organo/ionogels: “controllable” electromagnetic wave absorbers. Adv Mater. 2022;34(43):2205376. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202205376.
Guan XM, Yang ZH, Zhou M, Yang L, Peymanfar R, Aslibeiki B, Ji GB. 2D MXene nanomaterials: synthesis, mechanism, and multifunctional applications in microwave absorption. Small Struct. 2022;3(10):2200102. https://doi.org/10.1002/sstr.202200102.
Chen XT, Zhou M, Zhao Y, Gu WH, Wu Y, Tang SL, Ji GB. Morphology control of eco-friendly chitosan-derived carbon aerogels for efficient microwave absorption at thin thickness and thermal stealth. Green Chem. 2022;24(13):5280. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2gc01604d.
Liang HS, Zhang LM, Wu HJ. Exploration of twin-modified grain boundary engineering in metallic copper predominated electromagnetic wave absorber. Small. 2022;18(38):2203620. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202203620.
Hui SC, Zhang LM, Wu HJ. Cationic doping induced sulfur vacancy formation in polyionic sulfide for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.09.078.
Huang XG, Wei JW, Zhang YK, Qian BB, Jia Q, Liu J, Zhao XJ, Feng SG. Ultralight magnetic and dielectric aerogels achieved by metal-organic framework initiated gelation of graphene oxide for enhanced microwave absorption. Nanomicro Lett. 2022;14(1):107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-022-00851-3.
Chang Q, Liang HS, Shi B, Wu HJ. Microstructure induced dielectric loss in lightweight Fe3O4 foam for electromagnetic wave absorption. Science. 2022;25(3):103925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2022.103925.
Wang J, Schölch V, Görke O, Schuck G, Wang XF, Shao GF, Schorr SS, Bekheet MF, Gurlo A. Metal-containing ceramic nanocomposites synthesized from metal acetates and polysilazane. Open Ceram. 2020;1:100001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceram.2020.100001.
Sun SJ, Liu YB, Ma Z, Jiao J, Jiao CR, Yang JH. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the ZrB2–SiC eutectic phase obtained via induction plasma spheroidization. Ceram Int. 2021;47(20):29120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.07.074.
Zhang YJ, Yin XW, Ye F, Kong L. Effects of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the crystallization behavior of PDCs-SiBCN and their improved dielectric and EM absorbing properties. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2014;34(5):1053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2013.11.044.
Luo CJ, Miao P, Tang YS, Kong J. Excellent electromagnetic wave absorption of MOF/SiBCN nanomaterials at high temperature. Chin J Aeronaut. 2021;34(11):277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2020.06.028.
Feng YR, Guo X, Gong HY, Zhang YJ, Liu Y, Lin X, Mao JJ. Microwave absorption performance of PDCs-SiCN(Fe) ceramics with negative imaginary permeability. Ceram Int. 2018;44(9):10420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.03.058.
Liu Y, Feng YR, Gong HY, Zhang YJ, Lin X, Xie BY, Mao JJ. Microwave absorbing performance of polymer-derived SiCN (Ni) ceramics prepared from different nickel sources. J Alloys Compd. 2018;749:620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.03.346.
Li Q, Yin XW, Duan WY, Cheng LF, Zhang LT. Improved dielectric properties of PDCs-SiCN by in-situ fabricated nano-structured carbons. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2017;37(4):1243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.11.034.
Li Q, Yin XW, Duan WY, Hao BL, Kong L, Liu XM. Dielectric and microwave absorption properties of polymer derived SiCN ceramics annealed in N2 atmosphere. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2014;34(3):589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2013.08.042.
Lu JB, Feng YR, Liu J, Liu CM, Tong YC, Wu SG, Sun HB, Gong HY, Guo X. Improved electromagnetic wave absorbing performance of PDCs-SiCN(Ni) fibers with different nickel content. Ceram Int. 2022;48(16):23578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.05.006.
Feng YR, Guo X, Gong HY, Zhang YJ, Lin X. Enhanced electromagnetic microwave absorption of Fe/C/SiCN composite ceramics targeting in integrated structure and function. Ceram Int. 2021;47(3):3842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.09.244.
Liu MY, Lu JB, Gong HY, Sheng MM, Jing J, Sun S, Wang GT, Miao YL. Enhanced microwave absorbing performance of Ni-containing SiCN ceramics by constructing multiple interfaces and in-situ generating MWCNTs. Ceram Int. 2022;48(22):33871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.07.335.
Xue JM, Ren FY, Dong YP, Wei HJ, Yang F, Cheng LF. Si3N4-BN-SiCN ceramics with unique hetero-interfaces for enhancing microwave absorption properties. Ceram Int. 2021;47(9):12261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.01.075.
Guo X, Xiao FF, Li J, Zhang H, Hu QQ, Li GC, Sun HB. Fe-doped SiCN composite fibers for electromagnetic waves absorption. Ceram Int. 2021;47(1):1184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.08.236.
Jia T, Gu YF, Li FT. Progress and potential of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for gas storage and separation: a review. J Environ Chem Eng. 2022;10(5):108300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108300.
Zhang ZW, Cai ZH, Wang ZY, Peng YL, Xia L, Ma SP, Yin ZZ, Huang Y. A review on metal-organic framework-derived porous carbon-based novel microwave absorption materials. Nanomicro Lett. 2021;13(1):56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-020-00582-3.
Tao JQ, Xu LL, Jin HS, Gu YS, Zhou JT, Yao ZJ, Tao XW, Chen P, Dinghui W, Li Z, Wu HJ. Selective coding dielectric genes based on proton tailoring to improve microwave absorption of MOFs. Adv Powder Mater. 2023;2(1):100091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmate.2022.100091.
Song CK, Liu YS, Ye F, Wang J, Cheng LF. Microstructure and electromagnetic wave absorption property of reduced graphene oxide-SiCnw/SiBCN composite ceramics. Ceram Int. 2020;46(6):7719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.11.275.
Ding CX, Hu DX, He XR, Lai YF, Shao GF. Fabrication and microstructure evolution of monolithic bridged polysilsesquioxane-derived SiC ceramic aerogels. Ceram Int. 2022;48(18):25833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.05.259.
Feng YR, Guo X, Huang K, Elsayed H, Franchin G, Gong HY, Colombo P. Enhanced electromagnetic microwave absorption of SiOC ceramics targeting the integration of structure and function. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2021;41(13):6393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2021.06.007.
Shao GF, Shen XD, Huang XG. Multilevel structural design and heterointerface engineering of a host-guest binary aerogel toward multifunctional broadband microwave absorption. ACS Mater Lett. 2022;4(9):1787. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmaterialslett.2c00634.
Yuan KK, Han DY, Zhao WY, Zhang WW, You GQ, Li ML, Fan BB, Lu HX, Wang HL, Xu HL, Shao G, Zhang R. Structure regulation and microwave absorption property of SiCN ceramic aerogels produced by catalytic pyrolysis. Ceram Int. 2021;47(22):31561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.08.035.
Wang S, Lin X, Ashfaq MZ, Zhang XF, Zhao CC, Sheng MM, Yang RK, Pei YR, Gong HY, Zhang YJ. Microwave absorption properties of SiCN ceramics doped with cobalt nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 2020;31(5):3803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-02912-y.
Wang S, Gong HY, Zhang YJ, Ashfaq MZ. Microwave absorption properties of polymer-derived SiCN(CNTs) composite ceramics. Ceram Int. 2021;47(1):1294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.08.250.
Liu XM, Yu ZJ, Ishikawa R, Chen LQ, Liu XF, Yin XW, Ikuhara Y, Riedel R. Single-source-precursor derived RGO/CNTs-SiCN ceramic nanocomposite with ultra-high electromagnetic shielding effectiveness. Acta Mater. 2017;130:83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2017.03.031.
Liu XM, Yu ZJ, Ishikawa R, Chen LQ, Yin XW, Ikuhara Y, Riedel R. Single-source-precursor synthesis and electromagnetic properties of novel RGO–SiCN ceramic nanocomposites. J Mater Chem C. 2017;5(31):7950. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tc00395a.
Li Q, Yin XW, Zhang LT, Cheng LF. Effects of SiC fibers on microwave absorption and electromagnetic interference shielding properties of SiCf/SiCN composites. Ceram Int. 2016;42(16):19237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.09.089.
Huang XG, Qiao M, Lu XC, Li YF, Ma YB, Kang B, Quan B, Ji GB. Evolution of dielectric loss-dominated electromagnetic patterns in magnetic absorbers for enhanced microwave absorption performances. Nano Res. 2021;14(11):4006. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3327-x.
Wang P, Liu PA, Ye S. Preparation and microwave absorption properties of Ni(Co/Zn/Cu)Fe2O4/SiC@SiO2 composites. Rare Met. 2016;38(1):59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0752-1.
Qin M, Zhang LM, Wu HJ. Dual-template hydrothermal synthesis of multi-channel porous NiCo2O4 hollow spheres as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorber. Appl Surf Sci. 2020;515:146132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146132.
Wu Y, Zhao Y, Zhou M, Tan SJ, Peymanfar R, Aslibeiki B, Ji GB. Ultrabroad microwave absorption ability and infrared stealth property of nano-micro CuS@rGO lightweight aerogels. Nanomicro Lett. 2022;14(1):51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-022-00906-5.
Mu ZG, Wei GK, Zhang H, Gao L, Zhao Y, Tang SL, Ji GB. The dielectric behavior and efficient microwave absorption of doped nanoscale LaMnO3 at elevated temperature. Nano Res. 2022;15(8):7731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4500-6.
Huang XG, Yu GY, Zhang YK, Zhang MJ, Shao GF. Design of cellular structure of graphene aerogels for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem Eng J. 2021;426:131894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131894.
Pan HX, Yin XW, Xue JM, Cheng LF, Zhang LT. In-situ synthesis of hierarchically porous and polycrystalline carbon nanowires with excellent microwave absorption performance. Carbon. 2016;107:36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.05.045.
An J, Zhao CY, He ZJ, Mu X, Guo SH, Xu LH, He J, Zhao DL. Synthesis and microwave absorption property of nanostructured Ketjen black/Fe3O4 core/shell particles. Rare Met. 2022;41(10):3351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02046-6.
Wu XM, Xie F, Yao YL, Sun Y, Hua ZS, Zhao Z, Yang YX. Template-free preparation of porous Co microfibers from spent lithium-ion batteries as a promising microwave absorber. Rare Met. 2022;41(10):3475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02034-w.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 62071239 and 52102361), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20200827), the National Key Laboratory on Electromagnetic Environmental Effects and Electro-optical Engineering (No. JCKYS2022LD2), the Startup Foundation for Introducing Talent of NUIST (No. 2020r025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, TB., Yu, GY., Shao, GF. et al. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties of ZIF-67 modified polymer-derived SiCN ceramics by in situ construction of multiple heterointerfaces. Rare Met. 42, 1635–1644 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02270-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02270-8