Abstract
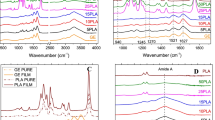
Biopolymeric films have been the focus of research for the past few decades because they offer favorable advantages compared to synthetic polymeric films in the field of biomedical engineering. In this study, collagen (C) was extracted from skin waste using acetic acid and blended with starch (ST)/soy protein (SP) to prepare C/ST/SP hybrid films. The prepared hybrid films were examined for biocompatibility, physical and chemical properties. The results demonstrated that the strength properties of hybrid films increase as the composition of starch increases while elongation increases as the composition of soy protein increases. Thermogravimetric analysis of select hybrid films showed that the thermal stability of the hybrid films improved moderately. The infrared spectroscopy of hybrid films show functional groups associated with C, ST and SP. Scanning electron microscopy reveals that the hybrid films becomes smoother as the starch concentration increases while increasing soy protein concentration lead to roughness in the hybrid films. The equilibrium swelling, in vitro biodegradation and in vitro cytotoxicity studies show good biostability and biocompatibility for the hybrid films. Therefore, it is envisaged that the promising mechanical, thermal, swelling, biostability and biocompatibility properties of the developed hybrid films suggest a beneficial role for the biomedical applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Langer, R., Vacanti, J.: Tissue engineering. Science 260, 920–926 (1993)
Reddi, A.H.: Morphogenesis and tissue engineering of bone and cartilage: inductive signals, stem cells and biomimetic biomaterials. Tissue Eng. 6, 351–359 (2000)
Nerem, R.M., Sambanis, A.: Tissue engineering: from biology to biological substitutes. Tissue Eng. 1, 3–13 (1995)
Lee, C.H., Singla, A., Lee, Y.: Biomedical applications of collagen. Int. J. Pharm. 221, 1–22 (2001)
Sittinger, M., Bujia, J., Rotter, N., Reitzel, D., Minuth, W.W., Burmester, G.R.: Tissue engineering and antologous transplant formation: practical approaches with resorbable biomaterials and new cell culture techniques. Biomaterials 17, 237–242 (1996)
Bergsma, E.J., Brujn, W., Rozema, F.R., Bos, R.M., Boering, G.: Late tissue response to poly(l-lactide) bone plates and screws. Biomaterials 16, 25–31 (1995)
Bergsma, E.J., Rozema, F.R., Bos, R.M., Brujn, W.: Foreign body reactions to resorbable poly(l-lactide) bone plates and screws used for the the fixation of unstable zygomatic fractures. J. Maxillofacial Surg. 51, 666–670 (1993)
Bostmann, O., Hirvensalo, E., Makinen, J., Rokkanen, P.: Foreign body reactions to fracture fixation implants of biodegradable synthetic polymers. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 72B, 592–596 (1990)
Rehm, K.E., Claes, L., Helling, H.J., Hutmacher, D.: Application of a polylactide pin. An open clinical prospective study. In: Leung, K.S., Hung, L.K., Leung, P.C. (eds.) Biodegradable Implants in Fracture Fixation, p. 54. World Scientific, Hong Kong (1994)
Langer, R., Tirrell, D.A.: Designing materials for biology and medicine. Nature 428, 487–492 (2004)
Rosso, F., Marino, G., Giordano, A., Barbarisi, M., Parmeggiani, D., Barbarisi, A.: Smart materials as scaffolds for tissue engineering. J. Cell. Physiol. 203, 465–470 (2005)
Zhang, S.: Fabrication of novel biomaterials through molecular self-assembly. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 1171–1178 (2003)
Furth, M.E., Atala, A., Dyke, M.E.V.: Smart biomaterials design for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Biomaterials 28, 5068–5073 (2007)
Maeda, M., Kadota, K., Kajihara, M., Sano, A., Fujioka, K.: Sustained release of human growth hormone (hGH) from collagen film and evaluation of effect on wound healing in db/db mice. J. Control Release 77, 261–272 (2001)
Gopinath, D., Ahmed, M.R., Gomathi, K., Chitra, K., Sehgal, P.K., Jayakumar, R.: Dermal wound healing processes with curcumin incorporated collagen films. Biomaterials 25, 1911–1917 (2004)
Boyce, S.T., Christanson, D.J., Hsbrough, J.F.: Structure of a collagen-GAG skin substitute optimized for cultured human epidermal keratinocytes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 22, 939–957 (1988)
Lee, K.Y., Kwon, I.C., Kim, Y.H., Jo, W.H., Jeong, S.Y.: Preparation of chitosan self-aggregates as a gene delivery system. J. Control Release 51, 213–220 (1998)
Auger, F.A., Rouabhia, M., Goulet, F., Berthod, F., Moulin, V., Germain, L.: Tissue-engineered human skin substitutes developed from collagen-populated hydrated gels: clinical and fundamental applications. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 36, 801–812 (1998)
Ma, L., Gao, C., Mao, Z., Zhou, J., Shen, J., Hu, X., Han, C.: Collagen/chitosan porous scaffolds with improved biostability for skin tissue engineering. Biomaterials 24, 4833–4841 (2003)
Wang, X.H., Li, D.P., Wang, W.J., Feng, Q.L., Cui, F.Z., Xu, Y.X., Song, X.H., Werf, M.V.D.: Crosslinked collagen/chitosan matrix for artificial livers. Biomaterials 24, 3213–3220 (2003)
Huang, L.L.H., Lee, P.C., Chen, L.W., Hsieh, K.H.: Comparison of epoxides on grafting collagen to polyurethane and their effects on cellular growth. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 39, 630–636 (1998)
Dai, N.T., Williamson, M.R., Khammo, N., Adams, E.F., Coombes, A.G.A.: Composite cell support membranes based on collagen and polycaprolactone for tissue engineering of skin. Biomaterials 25, 4263–4271 (2004)
Toba, T., Nakamura, T., Shimizu, Y., Matsumoto, K., Ohnishi, K., Fukuda, S., Yoshitani, M., Ueda, H., Hori, Y., Endo, K.: Regeneration of canine peroneal nerve with the use of a polyglycolic acid-collagen tube filled with laminin-soaked collagen sponge: a comparative study of collagen sponge and collagen fibers as filling materials for nerve conduits. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B. 58, 622–630 (2001)
Yang, J., Bei, J., Wang, S.: Enhanced cell affinity of poly (d, l-lactide) by combining plasma treatment with collagen anchorage. Biomaterials 23, 2607–2614 (2002)
Nasir, N.F.M., Raha, M.G., Kadri, N.A., Sahidan, S.I., Rampado, M., Azlan, C.A.: The study of morphological structure, phase structure and molecular structure of collagen-PEO 600K blends for tissue engineering application. Am. J. Biochem. Biotech. 2, 175–179 (2006)
Weadock, K.S., Miller, E.J., Bellincampi, L.D., Zawadsky, J.P., Dunn, M.G.: Physical crosslinking of collagen fibers: comparison of ultraviolet irradiation and dehydrothermal treatment. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 29, 1373–1379 (1995)
Levy, R.J., Schoen, F.J., Sherman, F.S., Nichols, J., Hawley, M.A., Lund, S.A.: Calcification of subcutaneously implanted type I collagen sponges. Effects of formaldehyde and glutaraldehyde pretreatments. Am. J. Pathol. 122, 71–82 (1986)
Barbani, N., Giusti, P., Lazzeri, L., Polacco, G., Pizzirani, G.: Bioartificial materials based on collagen: 1. collagen cross-linking with gaseous glutaraldehyde. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 7, 461–469 (1996)
Bradley, W.G., Wilkes, G.L.: Some mechanical property considerations of reconstituted collagen for drug release supports. Biomater. Med. Dev. Artif. Organs 5, 159–175 (1977)
Charulatha, V., Rajaram, A.: Influence of different crosslinking treatments on the physical properties of collagen membranes. Biomaterials 24, 759–767 (2003)
Golomb, G., Schoen, F.J., Smith, M.S., Linden, J., Dixon, M., Levy, R.J.: The role of glutaraldehyde-induced crosslinks in calcification of bovine pericardium used in cardiac valve bioprostheses. Am. J. Pathol. 127, 122–130 (1987)
Luyn, M.J.A.V., Wachem, P.B.V., Damink, L.H.H.O., Dijkstra, P.J., Feijen, J., Nieuwenhuis, P.: Secondary cytotoxicity of cross-linked dermal sheep collagens during repeated exposure to human fibroblasts. Biomaterials 13, 1017–1024 (1992)
Luyn, M.J.A.V., Wachem, P.B.V., Damink, L.H.H.O., Dijkstra, P.J., Feijen, J., Nieuwenhuis, P.: Relations between in vitro cytotoxicity and crosslinked dermal sheep collagen. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 26, 1091–1110 (1992)
Nimni, M.E., Cheung, D., Strates, B., Kodama, M., Skeikh, K.: Chemically modified collagen: a natural biomaterial for tissue replacement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 21, 741–771 (1987)
Hardy, P.M., Nicholls, A.C., Rydon, H.N.: The nature of the crosslinking of proteins by glutaraldehyde. Part 1. Interaction of glutaraldehyde with the amino groups of 6-amino hexanoic acid and of α-N-acetyl-lysine. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans I. 958–962 (1976)
Hardy, P.M., Hughes, G.J., Rydon, H.N.: The nature of the crosslinking of proteins by glutaraldehyde. Part 2. The formation of quaternary pyridinium compounds by the action of glutaraldehyde on proteins and the identification of a 3-(2-piperidyl)-pyridinium derivative, anabilysine, as a crosslinking entity. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans I. 2282–2288 (1979)
Speer, D.P., Chvapil, M., Eskelson, C.D., Ulreich, J.: Biological effects of residual glutaraldehyde-tanned collagen biomaterials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 14, 753–764 (1980)
Lee, L.L.H.H., Cheung, D.T., Nimni, M.E.: Biochemical changes and cytotoxicity associated with the degradation of polymeric glutaraldehyde derived crosslinks. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 24, 1185–1201 (1990)
Damink, L.H.H.O., Dijkstra, P.J., Luyn, M.J.A.V., Wachem, P.B.V., Nieuwenhuis, P., Feijen, J.: Glutaraldehyde as a crosslinking agent for collagen-based biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 6, 460–472 (1995)
Yannas, I.V., Lee, E., Orgill, D.P., Skrabut, E.M., Murphy, G.F.: Synthesis and characterization of a model extracellular matrix that induces partial regeneration of adult mammalian skin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 86, 933–937 (1989)
Marques, A.P., Reis, R.L., Hunt, J.A.: An in vivo study of the host response to starch-based polymers and composites subcutaneously implanted in rats. Macromol. Biosci. 5, 775–785 (2005)
Reis, R.L., Cunha, A.M.: New degradable load-bearing biomaterials composed of reinforced starch based blends. J. Appl. Med. Polym. 4, 1–5 (2000)
Leonor, I.B., Sousa, R.A., Cunha, A.M., Zhong, Z.P., Greenspan, D., Reis, R.L.: Novel starch thermoplastic/Bioglass composites: mechanical properties, degradation behaviour and in vitro bioactivity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 13, 939–945 (2002)
Sousa, R.A., Reis, R.L., Cunha, A.M., Bevis, M.J.: Structure and properties of hydroxylapatite reinforced starch bone–analogue composites. In: Giannini, S., Moroni, A. (eds.) Bioceramics: Proceedings of 13th International Symposium on Ceramics in Medicine, pp. 669–672. Trans Tech Publications, Zurich (2000)
Reis, R.L., Leonor, I.B., Rego, M.T., Cunha, A.M., Fernandes, M.H., Correia, R.N.: Stiff and bioactive composites based on starch, polyethylene and SiO2-CaO.P2O5-MgO glasses and glass-ceramics. In: LeGeros, R.Z., LeGeros, J.P. (eds.) Bioceramics: Proceedings of 11th International Symposium on Ceramics in Medicine, pp. 169–172. World Scientific, New York (1998)
Sousa, R.A., Kalay, G., Reis, R.L., Cunha, A.M., Bevis, M.J.: Injection molding of a starch/EVOH blend aimed as an alternative biomaterial for temporary applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 77, 1303–1315 (2000)
Reis, R.L., Cunha, A.M., Bevis, M.J.: Using nonconventional processing to develop an isotropic and biodegradable composites of starch-based thermoplastics reinforced with bone-like ceramics. Med. Plast. Biomater. 4, 46–50 (1997)
Pereira, C.S., Cunha, A.M., Reis, R.L., Vazquez, B., Roman, J.S.: New starch-based thermoplastic hydrogels for use as bone cements or drug-delivery carriers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 9, 825–833 (1998)
Espigares, I., Elvira, C., Mano, J.F., Vazquez, B., Roman, J.S., Reis, R.L.: New partially degradable and bioactive acrylic bone cements based on starch blends and ceramic fillers. Biomaterials 23, 1883–1895 (2002)
Boesel, L.F., Mano, J.F., Reis, R.L.: Optimization of the formulation and mechanical properties of starch based partially degradable bone cements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 15, 73–83 (2004)
Elvira, C., Mano, J.F., Roman, J.S., Reis, R.L.: Starch based biodegradable hydrogels with potential biomedical applications as drug delivery systems. Biomaterials 23, 1955–1966 (2002)
Malafaya, P.B., Elvira, C., Gallardo, A., Roman, J.S., Reis, R.L.: Porous starch-based drug delivery systems processed by a microwave treatment. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 12, 1227–1241 (2001)
Gomes, M.E., Ribeiro, A.S., Malafaya, P.B., Reis, R.L., Cunha, A.M.: A new approach based on injection moulding to produce biodegradable starch based polymeric scaffolds: morphology, mechanical and degradation behaviour. Biomaterials 22, 883–889 (2001)
Gomes, M.E., Reis, R.L., Cunha, A.M., Blitterswijk, C.A., Bruijn, J.D.D.: Cytocompatibility and response of osteoblastic-like cells to starch based polymers: effects of several additives and processing conditions. Biomaterials 22, 1911–1917 (2001)
Gomes, M.E., Godinho, J.S., Tchalamov, D., Cunha, A.M., Reis, R.L.: Alternative tissue engineering scaffolds based on starch: processing methodologies, morphology, degradation and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 20, 19–26 (2002)
Mo, X., Hu, J., Sun, X.S., Ratto, J.A.: Compression and tensile strength of low-density straw-protein particle board. Ind. Crops Prod. 14, 1–9 (2001)
Were, L., Hettiarachchy, N.S., Coleman, M.: Properties of cysteine-added soy protein-wheat gluten films. J. Food Sci. 64, 514–518 (1999)
Vaz, C.M., Fossen, M., Tuil, R.F.V., Graaf, L.A.D., Reis, R.L., Cunha, A.M.: Casein and soybean protein-based thermoplastics and composites as alternative biodegradable polymers for biomedical applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 65A, 60–70 (2003)
Hua, Y., Cui, S.W., Wang, Q.: Gelling property of soy protein-gum mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 17, 889–894 (2003)
Rhim, J.W., Gennadios, A., Weller, C.L., Cezeirat, C., Hanna, M.A.: Soy protein isolate-dialdehyde starch films. Ind. Crop Prod. 8, 195–203 (1998)
Tonkova, E.V., Nustorova, M., Gushterova, A.: New protein hydrolysates from collagen wastes used as peptone for bacterial growth. Curr. Microbiol. 54, 54–67 (2007)
Li, G.Y., Fukunaga, S., Takenouchi, K., Nakamura, F.: Physiological and cell biological properties in vitro of collagen isolated from calf limed splits. J. Soc. Leather Technol. Chem. 88, 66–71 (2004)
Thanikaivelan, P., Rao, J.R., Nair, B.U., Ramasami, T.: Zero discharge tanning: a shift from chemical to biocatalytic leather processing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 36, 4187–4194 (2002)
Woessner, J.F.: The determination of hydroxyproline in tissue and protein samples containing small proportions of this imino acid. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 93, 440–447 (1961)
Sripriya, R., Kumar, R., Balaji, S., Kumar, M.S., Seghal, P.K.: Characterizations of polyanionic collagen prepared by linking additional carboxylic groups. React. Funct. Polym. 71, 62–69 (2011)
Scheide, J.D.: Process for the extraction of protein from soy flour. U.S. Patent 4,704,289 (1987)
Shantha, K.L., Ravichandran, P., Rao, K.P.: Azo polymeric hydrogels for colon targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials 16, 1313–1318 (1995)
Anumary, A., Thanikaivelan, P., Ashokkumar, M., Kumar, R., Sehgal, P.K., Chandrasekaran, B.: Synthesis and characterization of hybrid biodegradable films from bovine hide collagen and cellulose derivatives for biomedical applications. Soft Mater. (in press)
Shanmugasundaram, N., Ravichandran, P., Reddy, P.N., Ramamurty, N., Pal, S., Rao, K.P.: Collagen-chitosan polymeric scaffolds for the in vitro culture of human epidermoid carcinoma cells. Biomaterials 22, 1943–1951 (2001)
Fang, M., Fowler, P.A., Tomkinson, J., Hill, C.A.S.: The preparation and characterisation of a series of chemically modified potato starches. Carbohyd. Polym. 47, 245–252 (2002)
Schmidt, V., Giacomelli, C., Soldi, V.: Thermal stability of films formed by soy protein isolate-sodium dodecyl sulfate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 87, 25–31 (2005)
Chiellini, E., Cinelli, P., Fernandes, E.G., Kenawy, E.S., Lazzeri, A.: Gelatin-based blends and composites. morphological and thermal mechanical characterization. Biomacromol. 2, 806–811 (2001)
Silva, S.S., Goodfellow, B.J., Benesch, J., Rocha, J., Mano, J.F., Reis, R.L.: Morphology and miscibility of chitosan/soy protein blended membranes. Carbohyd. Polym. 70, 25–31 (2007)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India for their financial support under Young Scientist Award project. The authors also wish to thank Dr. A.B. Mandal, Director, Central Leather Research Institute, India for his constant encouragement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murali, R., Anumary, A., Ashokkumar, M. et al. Hybrid Biodegradable Films from Collagenous Wastes and Natural Polymers for Biomedical Applications. Waste Biomass Valor 2, 323–335 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-011-9072-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-011-9072-8