Abstract
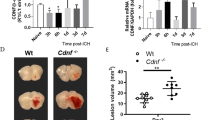
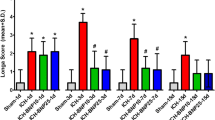
Both experimental studies and surgical clinical trials suggest that hematoma clearance is a therapeutic target in intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). We have investigated effects of CD47, a “don’t eat me” signal expressed on erythrocytes, on hematoma resolution after ICH in young mice. This study expands those findings by examining the effects on a CD47 blocking antibody in aged rats. First, male Fischer 344 rats (18 months old) received an intracaudate injection of 50 μL autologous whole blood or saline. Hematoma features of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and neurological deficits were evaluated within 3 days. Second, rats had an intracaudate co-injection of 50 μL autologous blood with either CD47 blocking antibody or IgG. MRI was used to quantify hematoma/iron volume, hemolysis, brain swelling, and atrophy at different time points, behavioral tests to assess neurological deficits, and immunohistochemistry to assess brain injury and neuroinflammation. The CD47 blocking antibody significantly promoted hematoma clearance, attenuated brain swelling, hemolysis, and neuronal loss and increased the number of phagocytic macrophages in and around hematoma 3 days after ICH. Moreover, CD47 blockade reduced neuronal loss, brain atrophy, and neurobehavioral deficits at day 28. These results indicate that a CD47 blocking antibody can accelerate hematoma clearance and alleviate short- and long-term brain injury after ICH in aged rats and that it might be a therapeutic strategy for ICH.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broderick JP, Brott TG, Duldner JE, Tomsick T, Huster G. Volume of intracerebral hemorrhage. A powerful and easy-to-use predictor of 30-day mortality. Stroke. 1993;24:987–93.
Zhao X, Sun G, Ting SM, Song S, Zhang J, Edwards NJ, et al. Cleaning up after ich: the role of nrf2 in modulating microglia function and hematoma clearance. J Neurochem. 2015;133:144–52.
Wilkinson DA, Keep RF, Hua Y, Xi G. Hematoma clearance as a therapeutic target in intracerebral hemorrhage: from macro to micro. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018;38:741–5.
Hanley DF, Thompson RE, Rosenblum M, Yenokyan G, Lane K, McBee N, et al. Efficacy and safety of minimally invasive surgery with thrombolysis in intracerebral haemorrhage evacuation (mistie iii): a randomised, controlled, open-label, blinded endpoint phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019;393:1021–32.
Zhao X, Sun G, Zhang J, Strong R, Song W, Gonzales N, et al. Hematoma resolution as a target for intracerebral hemorrhage treatment: role for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in microglia/macrophages. Ann Neurol. 2007;61:352–62.
Wang G, Li T, Duan SN, Dong L, Sun XG, Xue F. Ppar-gamma promotes hematoma clearance through haptoglobin-hemoglobin-cd163 in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Behav Neurol. 2018;2018:7646104.
Oldenborg PA, Zheleznyak A, Fang YF, Lagenaur CF, Gresham HD, Lindberg FP. Role of cd47 as a marker of self on red blood cells. Science. 2000;288:2051–4.
Cao S, Zheng M, Hua Y, Chen G, Keep RF, Xi G. Hematoma changes during clot resolution after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 2016;47:1626–31.
Ni W, Mao S, Xi G, Keep RF, Hua Y. Role of erythrocyte cd47 in intracerebral hematoma clearance. Stroke. 2016;47:505–11.
Jing C, Bian L, Wang M, Keep RF, Xi G, Hua Y. Enhancement of hematoma clearance with cd47 blocking antibody in experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 2019;50:1539–47.
Lam D, Lively S, Schlichter LC. Responses of rat and mouse primary microglia to pro- and anti-inflammatory stimuli: molecular profiles, k(+) channels and migration. J Neuroinflammation. 2017;14:166.
Wei J, Wu F, Sun X, Zeng X, Liang JY, Zheng HQ, et al. Differences in microglia activation between rats-derived cell and mice-derived cell after stimulating by soluble antigen of iv larva from angiostrongylus cantonensis in vitro. Parasitol Res. 2013;112:207–14.
Magnani M, Rossi L, Stocchi V, Cucchiarini L, Piacentini G, Fornaini G. Effect of age on some properties of mice erythrocytes. Mech Ageing Dev. 1988;42:37–47.
Shperling T, Danon D. Age population distribution of erythrocytes in young and old healthy donors. Exp Gerontol. 1990;25:413–22.
Takahashi R, Totsuka S, Ishigami A, Kobayashi Y, Nagata K. Attenuated phagocytosis of secondary necrotic neutrophils by macrophages in aged and smp30 knockout mice. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2016;16:135–42.
von Bernhardi R, Tichauer J, Eugenin-von BL. Proliferating culture of aged microglia for the study of neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurosci Methods. 2011;202:65–9.
Zhao H, Garton T, Keep RF, Hua Y, Xi G. Microglia/macrophage polarization after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res. 2015;6:407–9.
Dang G, Yang Y, Wu G, Hua Y, Keep RF, Xi G. Early erythrolysis in the hematoma after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res. 2017;8:174–82.
Liu H, Hua Y, Keep RF, Xi G. Brain ceruloplasmin expression after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage and protection against iron-induced brain injury. Transl Stroke Res. 2019;10:112–9.
Wu J, Hua Y, Keep RF, Nakamura T, Hoff JT, Xi G. Iron and iron-handling proteins in the brain after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 2003;34:2964–9.
Hua Y, Schallert T, Keep RF, Wu J, Hoff JT, Xi G. Behavioral tests after intracerebral hemorrhage in the rat. Stroke. 2002;33:2478–84.
Xi G, Keep RF, Hoff JT. Mechanisms of brain injury after intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:53–63.
Pfefferbaum A, Adalsteinsson E, Sullivan EV. In vivo structural imaging of the rat brain with a 3-t clinical human scanner. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2004;20:779–85.
Allen JS, Damasio H, Grabowski TJ. Normal neuroanatomical variation in the human brain: an mri-volumetric study. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2002;118:341–58.
Liu R, Li H, Hua Y, Keep RF, Xiao J, Xi G, et al. Early hemolysis within human intracerebral hematomas: an mri study. Transl Stroke Res. 2019;10:52–6.
Hatakeyama T, Okauchi M, Hua Y, Keep RF, Xi G. Deferoxamine reduces neuronal death and hematoma lysis after intracerebral hemorrhage in aged rats. Transl Stroke Res. 2013;4:546–53.
Gong Y, Xi G, Wan S, Gu Y, Keep RF, Hua Y. Effects of aging on complement activation and neutrophil infiltration after intracerebral hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2008;105:67–70.
Wasserman JK, Yang H, Schlichter LC. Glial responses, neuron death and lesion resolution after intracerebral hemorrhage in young vs. Aged rats. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;28:1316–28.
Lee JC, Cho GS, Choi BO, Kim HC, Kim WK. Aging exacerbates intracerebral hemorrhage-induced brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2009;26:1567–76.
Gong Y, Hua Y, Keep RF, Hoff JT, Xi G. Intracerebral hemorrhage: effects of aging on brain edema and neurological deficits. Stroke. 2004;35:2571–5.
Khandelwal S, van Rooijen N, Saxena RK. Reduced expression of cd47 during murine red blood cell (rbc) senescence and its role in rbc clearance from the circulation. Transfusion. 2007;47:1725–32.
von Bernhardi R, Tichauer JE, Eugenin J. Aging-dependent changes of microglial cells and their relevance for neurodegenerative disorders. J Neurochem. 2010;112:1099–114.
Lan X, Han X, Li Q, Li Q, Gao Y, Cheng T, et al. Pinocembrin protects hemorrhagic brain primarily by inhibiting toll-like receptor 4 and reducing m1 phenotype microglia. Brain Behav Immun. 2017;61:326–39.
Zhou H, Zhang H, Yan Z, Xu R. Transplantation of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells promotes neurological recovery in an intracerebral hemorrhage rat model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;475:202–8.
Ke K, Rui Y, Li L, Zheng H, Xu W, Tan X, et al. Upregulation of ehd2 after intracerebral hemorrhage in adult rats. J Mol Neurosci. 2014;54:171–80.
Chistiakov DA, Killingsworth MC, Myasoedova VA, Orekhov AN, Bobryshev YV. Cd68/macrosialin: not just a histochemical marker. Lab Investig. 2017;97:4–13.
Funding
YH, RFK, and GX were supported by grants NS-090925, NS-096917, NS-106746, and NS-112394 from the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The protocols for the animal use were approved by the University of Michigan Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical Approval
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, C., Keep, R.F., Xi, G. et al. CD47 Blocking Antibody Accelerates Hematoma Clearance After Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Aged Rats. Transl. Stroke Res. 11, 541–551 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-019-00745-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-019-00745-4