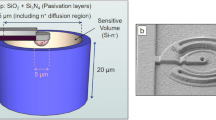
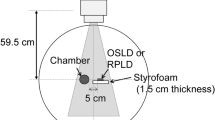
Abstract
A family of prototype 2D monolithic silicon-diode array detectors (MP512, Duo, Octa) has been proposed by the Centre for Medical Radiation Physics, University of Wollongong (Australia) for relative dosimetry in small megavoltage photon beams. These detectors, which differ in the topology of their 512 sensitive volumes, were originally fabricated on bulk p-type substrates. More recently, they have also been fabricated on epitaxial p-type substrates. In the literature, their performance has been individually characterized for quality assurance (QA) applications. The present study directly assessed and compared that of a MP512-bulk and that of a MP512-epitaxial in terms of radiation hardness, long-term stability, response linearity with dose, dose per pulse and angular dependence. Their measurements of output factors, off-axis ratios and percentage depth doses in square radiation fields collimated by the jaws and produced by 6 MV and 10 MV flattened photon beams were then benchmarked against those by commercially available detectors. The present investigation was aimed at establishing, from a medical physicist’s perspective, how the bulk and epitaxial fabrication technologies would affect the implementation of the MP512s into a QA protocol. Based on results, the MP512-epitaxial would offer superior radiation hardness, long-term stability and achievable uniformity and reproducibility of the response across the 2D active area.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosenfeld AB (2007) Electronic dosimetry in radiation therapy. Radiat Meas 41:S134–S153
Rosenfeld AB (2011) Advanced semiconductor dosimetry in radiation therapy. In: Rozenfeld A (eds) Concepts and trends in medical radiation dosimetry, vol. 1345. American Institute of Physics, Melville, NY, pp. 48–74
Fuduli I, Newall MK, Espinoza A, Porumb CS, Carolan MG, Lerch MLF, Metcalfe P, Rosenfeld AB, Petasecca M (2014) Multichannel data acquisition system comparison for quality assurance in external beam radiation therapy. Radiat Meas 71:338–341
Charles PH, Crowe SB, Kairn T, Knight RT, Hill B, Kenny J, Langton CM, Trapp JV (2013) Monte Carlo-based diode design for correction-less small field dosimetry. Phys Med Biol 58(13):4501–4512
Utitsarn K, Alrowaili ZA, Stansook N, Lerch MLF, Petasecca M, Carolan MG, Rosenfeld AB (2017) Optimisation of output factor measurements using the Magic Plate 512 silicon dosimeter array in small megavoltage photon fields. J Phys Conf Ser 777:012022
Andreo P (2018) The physics of small megavoltage photon beam dosimetry. Radiother Oncol 126(2):205–213
Czochralski J (1918) Ein neues Verfahren zur Messung der Kristallisationsgeschwindigkeit der Metalle. Zeitschrift für Phys Chemie 92U(1):219–221
Rikner G, Grusell E (1987) General specifications for semiconductors for use in radiation dosimetry. Phys Med Biol 32(9):1109–1117
Sze SM, Ng KK (2007) Physics of semiconductor devices, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Bruzzi M, Bucciolini M, Casati M, Menichelli D, Talamonti C, Piemonte C, Svensson BG (2007) Epitaxial silicon devices for dosimetry applications. Appl Phys Lett 90(17):17–19
Bruzzi M (2016) Novel silicon devices for radiation therapy monitoring. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A 809:105–112
Aldosari AH, Petasecca M, Espinoza A, Newall MK, Fuduli I, Porumb CS, AlShaikh S, Alrowaili ZA, Weaver MR, Metcalfe P, Carolan MG, Lerch MLF, Perevertaylo V, Rosenfeld AB (2014) A two dimensional silicon detectors array for quality assurance in stereotactic radiotherapy: MagicPlate-512. Med Phys 41(9):091707
Petasecca M, Newall MK, Booth JT, Duncan M, Aldosari AH, Fuduli I, Espinoza A, Porumb CS, Guatelli S, Metcalfe P, Colvill E, Cammarano D, Carolan MG, Oborn BM, Lerch MLF, Perevertaylo V, Keall PJ, Rosenfeld AB (2015) MagicPlate-512: a 2D silicon detector array for quality assurance of stereotactic motion adaptive radiotherapy. Med Phys 42(6):2992–3004
Duncan M, Newall MK, Caillet V, Booth JT, Keall PJ, Lerch MLF, Perevertaylo V, Rosenfeld AB, Petasecca M (2018) Real-time high spatial resolution dose verification in stereotactic motion adaptive arc radiotherapy. J Appl Clin Med Phys 19(4):173–184
Al Shukaili K, Petasecca M, Newall MK, Espinoza A, Perevertaylo V, Corde S, Lerch MLF, Rosenfeld AB (2017) A 2D silicon detector array for quality assurance in small field dosimetry: DUO. Med Phys 44(2):628–636
Al Shukaili K, Corde S, Petasecca M, Perevertaylo V, Lerch MLF, Jackson M, Rosenfeld AB (2018) Characterization of ELEKTA SRS cone collimator using high spatial resolution monolithic silicon detector array. J Appl Clin Med Phys 19(4):114–124
Biasi G, Petasecca M, Guatelli S, Hardcastle N, Carolan M, Perevertaylo V, Kron T, Rosenfeld AB (2018) A novel high-resolution 2D silicon array detector for small field dosimetry with FFF photon beams. Phys Medica 45:117–126
Biasi G, Petasecca M, Guatelli S, Martin EA, Grogan G, Hug B, Lane J, Perevertaylo V, Kron T, Rosenfeld AB (2018) CyberKnife® fixed cone and Iris™ defined small radiation fields: assessment with a high-resolution solid-state detector array. J Appl Clin Med Phys 19(5):547–557
Kwan IS, Rosenfeld AB, Qi ZY, Wilkinson D, Lerch MLF, Cutajar DL, Safavi-Naeini M, Butson MJ, Bucci J, Chin Y, Perevertaylo V (2008) Skin dosimetry with new MOSFET detectors. Radiat Meas 43(2–6):929–932
Metcalfe P, Quinn A, Loo K, Lerch MLF, Petasecca M, Wong JHD, Hardcastle N, Carolan MG, McNamara J, Cutajar DL, Fuduli I, Espinoza A, Porumb CS, Rosenfeld AB (2013) Review of four novel dosimeters developed for use in radiotherapy. J Phys Conf Ser 444:012008
Saini AS, Zhu TC (2004) Dose rate and SDD dependence of commercially available diode detectors. Med Phys 31(4):914–924
Huet C, Moignier C, Fontaine J, Clairand I (2014) Characterization of the gafchromic EBT3 films for dose distribution measurements in stereotactic radiotherapy. Radiat Meas 71:364–368
Yuasa Y, Kawamura S, Shiinoki T, Uehara T, Koike M, Kanzaki R, Hanazawa H, Takahashi S, Shibuya K (2016) Evaluation of the incident directional dependence of radiochromic film by use of Monte Carlo simulation and measurement. Radiol Phys Technol 9(2):227–232
Stansook N, Utitsarn K, Petasecca M, Newall MK, Duncan M, Nitschke K, Carolan MG, Metcalfe P, Lerch MLF, Perevertaylo V, Tomé WA, Rosenfeld AB (2017) Technical note: angular dependence of a 2D monolithic silicon diode array for small field dosimetry. Med Phys 44(8):4313–4321
Gerbi BJ, Khan FM (1990) Measurement of dose in the buildup region using fixed-separation plane-parallel ionization chambers. Med Phys 17(1):17–26
Mellenberg DE (1990) Determination of build-up region over-response corrections for a Markus-type chamber. Med Phys 17(6):1041–1044
Biasi G, Davis J, Petasecca M, Guatelli S, Perevertaylo V, Kron T, Rosenfeld AB (2018) On monolithic silicon array detectors for small-field photon beam dosimetry. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 65(9):2640–2649
Jursinic PA (2013) Dependence of diode sensitivity on the pulse rate of delivered radiation. Med Phys 40(2):021720
Shi J, Simon WE, Zhu TC (2003) Modeling the instantaneous dose rate dependence of radiation diode detectors. Med Phys 30(9):2509–2519
Budgell G, Brown K, Cashmore J, Duane S, Frame J, Hardy M, Paynter D, Thomas R (2016) IPEM topical report 1: guidance on implementing flattening filter free (FFF) radiotherapy. Phys Med Biol 61(23):8360–8394
Rikner G, Grusell E (1983) Effects of radiation damage on p-type silicon detectors. Phys Med Biol 28(11):1261–1267
Biasi G, Hardcastle N, Petasecca M, Guatelli S, Perevertaylo V, Kron T, Rosenfeld AB (2019) On the instantaneous dose rate and angular dependence of monolithic silicon array detectors. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 66(1):519–527
Grusell E, Rikner G (1993) Linearity with dose rate of low resistivity p-type silicon semiconductor detectors. Phys Med Biol 38(6):785
Jursinic PA, Sharma R, Reuter J (2010) MapCHECK used for rotational IMRT measurements: step-and-shoot, Tomotherapy, RapidArc. Med Phys 37(6):2837–2846
Aldosari AH, Espinoza A, Robinson D, Fuduli I, Porumb CS, AlShaikh S, Carolan MG, Lerch MLF, Perevertaylo V, Rosenfeld AB, Petasecca M (2013) Characterization of an innovative p-type epitaxial diode for dosimetry in modern external beam radiotherapy. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 60(6):4705–4712
Acknowledgements
Nauljun Stansook was supported by a faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital (Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand). We would like to acknowledge the Gross Foundation (Melbourne, Australia) for financial support. The authors are also grateful to Dr. Justin Davies at the GATRI facility (ANSTO, Lucas Heights, Australia).
Funding
This study was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia with the Project Grant No. APP1030159.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Research involving human and animal participants
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stansook, N., Biasi, G., Utitsarn, K. et al. 2D monolithic silicon-diode array detectors in megavoltage photon beams: does the fabrication technology matter? A medical physicist’s perspective. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 42, 443–451 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-019-00736-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-019-00736-7