Abstract
With the global adoption of smart mobile devices equipped with localization capabilities and broad popularity of microblogging facilities like Twitter, the need for personal privacy has never been greater. This is especially so with computational and data processing infrastructures such as clouds that support big data analysis. Differential privacy of geospatially tagged data such as tweets can potentially ensure that degrees of location privacy can be preserved while allowing the information (tweet contents) to be used for research and analysis, e.g., sentiment analysis. In this paper, we evaluate differential location pattern-mining approaches considering both privacy and precision of geo-located tweets clustered according to Geo-Locations of Interest (GLI). We consider both the privacy protection strength and the accuracy of results, measuring the Euclidean distance between centroids of real GLIs and obfuscated ones, i.e., those incorporating privacy-preserving noise. We record the performance and sensitivity of the approach. We show how privacy and location precision are trade-offs, i.e., the higher the degree of privacy protection, the fewer the GLIs will be identified. We also quantify these trade-offs and their associated sensitivity levels. We illustrate the work through a big data case study on use of Twitter data for traffic-related data protection.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abul O, Bonchi F, Nanni M (2008) Never walk alone: uncertainty for anonymity in moving objects databases. In: Data engineering, 2008. ICDE 2008. IEEE 24th international conference on, pp 376–385. doi:10.1109/icde.2008.4497446
Ali I, Kantarcioglu M, Ghinita G, Bertino E (2010) Private record matching using differential privacy. In: Manolescu I, Spaccapietra S, Teubner J, Kitsuregawa M, Leger A, Naumann F, Ailamaki A, Ozcan F (eds) Proceedings of the 13th international conference on extending database technology (EDBT ‘10). ACM, New York, pp 123–134. doi:10.1145/1739041.1739059
Andrés ME, Bordenabe NE, Chatzikokolakis K, Palamidessi C (2013) Geo-indistinguishability: differential privacy for location-based systems. In: Proceedings of the 2013 ACM SIGSAC conference on computer & communications security (CCS ‘13). ACM, New York, pp 901–914. doi:10.1145/2508859.2516735
Arik F, Schuster A (2010) Data mining with differential privacy. In: Proceedings of the 16th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining (KDD ‘10). ACM, New York, pp 493–502. doi:10.1145/1835804.1835868
Ashwin M, Kifer D, Abowd JM, Gehrke J, Vilhuber L (2008) Privacy: theory meets practice on the map. In: Alonso G, Blakeley JA, Chen ALP (eds) Proceedings of the 24th international conference on data engineering, ICDE 2008, April 7–12, 2008, Cancún, México, pp. 277–286. IEEE
Changqing Z, Frankowski D, Ludford P, Shekhar S, Terveen L (2004) Discovering personal gazetteers: an interactive clustering approach. In: Proceedings of the 12th annual ACM international workshop on Geographic information systems (GIS ‘04). ACM, New York, pp 266–273. doi:10.1145/1032222.1032261
Chow C-Y, Mokbel MF, Aref WG (2009) Casper*: query processing for location services without compromising privacy. ACM Trans Database Syst. Article 24 (December 2009). doi:10.1145/1620585.1620591
Cormode G, Procopiuc C, Srivastava D, Shen E, Yu T (2012) Differentially private spatial decompositions. In: Data engineering (ICDE), 2012 IEEE 28th international conference on, 20–31. doi:10.1109/icde.2012.16
de Berg M, Cheong O, van Kreveld M, Overmars M (2008) Computational geometry: algorithms and applications. Springer, Berlin
Dewri Rinku (2012) Location privacy and attacker knowledge: Who are we fighting against? Lect Notes Inst Comput Sci Soc Inform Telecommun Eng. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-31909-9_6
Dwork C (2006) Differential privacy. In: Automata, languages and programming, ser. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer, Berlin, vol 4052, pp 1–12. doi:10.1007/11787006_1
Dwork C, McSherry F, Nissim K, Smith A (2006) Calibrating noise to sensitivity in private data analysis. In: Proceeding of the 3rd conference on theory of cryptography, NY, pp 265–284. doi:10.1007/11681878_14
Hasan S, Zhan X, Ukkusuri SV (2013) Understanding urban human activity and mobility patterns using large-scale location-based data from online social media. In: Proceedings of the 2nd ACM SIGKDD international workshop on urban computing (UrbComp ‘13). ACM, New York, Article 6. doi:10.1145/2505821.2505823
Ho S-S, Ruan S (2011) Differential privacy for location pattern mining. In: Proceedings of the 4th ACM SIGSPATIAL international workshop on security and privacy in GIS and LBS (SPRINGL ‘11). ACM, New York, pp 17–24. doi:10.1145/2071880.2071884
Ho S-S, Ruan S (2013) Preserving privacy for interesting location pattern mining from trajectory data. Trans Data Priv 6(1):87–106
Hu H, Xu J, On ST, Du J, Ng JK-Y (2010) Privacy-aware location data publishing. ACM Trans Database Syst. Article 18 (July 2010). doi:10.1145/1806907.1806910
Jiang K, Shao D, Bressan S, Kister T, Tan K-L (2013) Publishing trajectories with differential privacy guarantees. In: Szalay A, Budavari T, Balazinska M, Meliou A, Sacan A (eds) Proceedings of the 25th international conference on scientific and statistical database management (SSDBM). ACM, New York, Article 12. doi:10.1145/2484838.2484846
Kido H, Yanagisawa Y, Satoh T (2005) Protection of location privacy using dummies for location-based services. In: Data engineering workshops, 2005. 21st international conference on (ICDEW’05), IEEE, pp 1248–1248. doi:10.1109/icde.2005.269
McSherry F (2009) Privacy integrated queries: an extensible platform for privacy-preserving data analysis. In: SIGMOD, 2009. doi:10.1145/1559845.1559850
Ninghui L, Li T, Venkatasubramanian S (2007) t-Closeness: privacy beyond k-anonymity and l-diversity. ICDE 7:106–115
Nissim K, Raskhodnikova S, Smith A (2007) Smooth sensitivity and sampling in private data analysis. In: Proceedings of the thirty-ninth annual ACM symposium on theory of computing (STOC ‘07). ACM, New York, pp 75–84. doi:10.1145/1250790.1250803
Primault V, Mokhtar SB, Lauradoux C, Brunie L (2014) Differentially private location privacy in practice. Dans mobile security technologies conference, San Jose, pp 1–10
Sadeh Norman, Hong J, Cranor L, Fette I, Kelley P, Prabaker M, Rao J (2009) Understanding and capturing people’s privacy policies in a mobile social networking application. Pers Ubiquitous Comput 13(6):401–412. doi:10.1007/s00779-008-0214-3
Su Z, Yang Q, Zhang H, Xu X, Hu Y (2001) Correlation-based document clustering using web logs. In: Proceedings of the 34th Annual Hawaii international conference on system sciences (HICSS-34), 2001, vol 5, pp 5022–5028. doi:10.1109/hicss.2001.926536
Sweeney L (2002) k-anonymity: a model for protecting privacy. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl-Based Syst 10(05):557–570. doi:10.1142/s0218488502001648
Terrovitis M, Mamoulis N (2008) Privacy preservation in the publication of trajectories. In: Mobile data management, 2008. MDM’08. 9th international conference on, pp 65–72. doi:10.1109/mdm.2008.29
Xiao Y, Xiong L, Yuan C (2010) Differentially private data release through multidimensional partitioning. In: Proceedings of the secure data management, 7th VLDB workshop, Singapore, Sep. 2010, pp 150–168. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-15546-8_11
Xiao X, Wang G, Gehrke J (2011) Differential privacy via wavelet transforms. Knowl Data Eng IEEE Trans 23(8):1200–1214. doi:10.1109/icde.2010.5447831
Xue M, Kalnis P, Pung HK (2009) Location diversity: enhanced privacy protection in location based services. In: Location and context awareness. Springer, Berlin, pp 70–87. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-01721-6_5
Yu Z, Zhang L, Ma Z, Xie X, Ma W-Y (2011) Recommending friends and locations based on individual location history. ACM Trans Web, Article 5 (February 2011). doi:10.1145/1921591.1921596
Acknowledgements
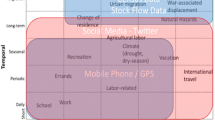
We would like to thank the NeCTAR Research cloud for the (free) use of the cloud resources and the Melbourne eResearch Group for support on Twitter access, use and analysis. Figure 1 was produced as part of the Australian Urban Research Infrastructure Network (AURIN—www.aurin.org.au) project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Sinnott, R.O. Supporting geospatial privacy-preserving data mining of social media. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 6, 109 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-016-0417-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-016-0417-y