Abstract
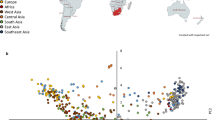
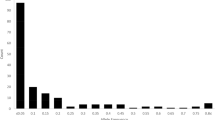
The radish is both an agronomically important root vegetable crop and a wild species of genus Raphanus in the Brassicaceae family. To date, at least four independent draft genome assemblies, marker development studies, and an analysis of radish evolution have been performed; however, there is no core collection of germplasm representing the genetic diversity in radish with minimum genetic redundancy. We report the assembly of a radish core collection consisting of 125 accessions. These accessions were selected by using 25 sequence-tagged site insertion/deletion markers to genotype 70 alleles in 886 accessions obtained from three germplasm banks in Korea, Japan, and Germany. An unweighted pair-group method with arithmetic mean (UPGMA) analysis of the genotyping data classified the accessions into 125 groups based on a Jaccard’s similarity coefficient of 0.72. One representative accession from each group was selected for a core collection that included 125 accessions, corresponding to 14.1% of the whole collection and including all 70 alleles. Principal coordinates analysis demonstrated that the genetic distribution within the core collection was similar to that of the whole collection, and 94% of the total variance within the whole collection could be explained using the analysis of molecular variance from the core collection. The UPGMA and STRUCTURE software analyses identified three major groups of accessions within the core collection, which were the Asian cultivated radish, the European cultivated radish, and the wild radish. The radish core collection developed in this study will be an important plant resource in future research and radish breeding.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown AHD (1989) The case for core collections. In: Brown AHD, Frankel OH, Marshall DR, Williams JT (eds) The use of plant genetic resources. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 136–156
Coimbra RR, Miranda GV, Cruz CD, Silva DJH, Vilela RA (2009) Development of a Brazilian maize core collection. Genet Mol Biol 32:538–545
Earl DA, von Holdt BM (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4:359–361
Ellstrand NC, Marshall DL (1985) The impact of domestication on distribution of allozyme variation within and among cultivars of radish, Raphanus sativus L. Theor Appl Genet 69:393–398
FAO (2011) Second global plan of action for plant genetic resources for food and agriculture. http://www.fao.org/docrep/015/i2624e/i2624e00.pdf. Accessed 11 Sept 2017
Frankel OH (1984) Genetic perspectives of germplasm conservation. In: Arber W, Llimensee K, Peacock WJ, Starlinger P (eds) Genetic manipulation: impact on man and society. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 161–170
Frankel OH, Brown AHD (1984) Plant genetic resources today: a critical appraisal. In: Holden JHW, Williams JT (eds) Crop genetic resources: conservation & evaluation. George Alien and Unwin, London, pp 249–257
Hamon S, Hodgkin T, Dussert S, Anthony F, Noirot M (1994) Core collection: theoretical and applied aspects. In: Evaluation and exploitation of genetic resources pre-breeding: proceedings of the genetic resources section. Eucarpia, France, pp 73–82
Jeong YM, Kim N, Ahn BO, Oh M, Chung WH, Chung H, Jeong S, Lim KB, Hwang YJ et al (2016) Elucidating the triplicated ancestral genome structure of radish based on chromosome-level comparison with the Brassica genomes. Theor Appl Genet 129:1357–1372
Jie Z, Yi W, Xinzhong Z, Tianzhong L, Kun W, Xuefeng X, Zhenhai H (2010) Sampling strategy to develop a primary core collection of apple cultivars based on fruit traits. Afr J Biotechnol 9:123–127
Kim N, Jeong YM, Jeong S, Kim GB, Baek S, Kwon YE, Cho A, Choi SB, Kim J et al (2016) Identification of candidate domestication regions in the radish genome based on high-depth resequencing analysis of 17 genotypes. Theor Appl Genet 129:1797–1814
Kitashiba H, Li F, Hirakawa H, Kawanabe T, Zou Z, Hasegawa Y, Tonosaki K, Shirasawa S, Fukushima A et al (2014) Draft sequences of the radish (Raphanus sativus L.) genome. DNA Res 21:481–490
Kong Q, Li X, Xiang C, Wang H, Song J, Zhi H (2011) Genetic diversity of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) Germplasm resources revealed by AFLP and RAPD markers. Plant Mol Biol Rep 29:217–223
Kwak J, Kim S, Seong K, Yoo M, Park K, Lim Y, Park J (2017) Relationship between major components and physicochemical properties of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) combinations for developing new cultivars targeting Chinese market. Korean J Hortic Sci Technol 35:577–587
Lee ON, Park HY (2017) Assessment of genetic diversity of cultivated radishes (Raphanus sativus) by agronomic traits and SSR markers. Sci Hortic 223:19–30
Li F, Hasegawa Y, Saito M, Shirasawa S, Fukushima A, Ito T, Fujii H, Kishitani S, Kitashiba H et al (2011) Extensive chromosome homoeology among Brassiceae species were revealed by comparative genetic mapping with high-density EST-based SNP markers in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). DNA Res 18:401–411
Liu LW, Zhao LP, Gong YQ, Wang MX, Chen LM, Yang JL, Wang Y, Yu FM, Wang LZ (2008) DNA fingerprinting and genetic diversity analysis of late-bolting radish cultivars with RAPD, ISSR and SRAP markers. Sci Hortic 116:240–247
Lü N, Yamane K, Ohnishi O (2008) Genetic diversity of cultivated and wild radish and phylogenetic relationships among Raphanus and Brassica species revealed by the analysis of trnK/matK sequence. Breed Sci 58:15–22
Martínez IB, de la Cruz MV, Nelson MR, Bertin P (2017) Establishment of a core collection of traditional Cuban Theobroma cacao plants for conservation and utilization purposes. Plant Mol Biol Rep 35:47–60
Mitsui Y, Shimomura M, Komatsu K, Namiki N, Shibata-Hatta M, Imai M, Katayose Y, Mukai Y, Kanamori H et al (2015) The radish genome and comprehensive gene expression profile of tuberous root formation and development. Sci Rep 5:10835
Moghe GD, Hufnagel DE, Tang H, Xiao Y, Dworkin I, Town CD, Conner JK, Shiu SH (2014) Consequences of whole-genome triplication as revealed by comparative genomic analyses of the wild radish Raphanus raphanistrum and three other Brassicaceae species. Plant Cell 26:1925–1937
Mun JH, Chung H, Chung WH, Oh M, Jeong YM, Kim N, Ahn BO, Park BS, Park S et al (2015) Construction of a reference genetic map of Raphanus sativus based on genotyping by whole-genome resequencing. Theor Appl Genet 128:259–272
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4326
Oliveira E, Ferreira C, Santos V, Oliveira G (2014) Development of a cassava core collection based on single nucleotide polymorphism markers. Genet Mol Res 13:6472–6485
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2012) GenAlEx 6.5: genetic analysis in excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics 28:2537–9253
Perseguini JMKC, Silva GMB, Rosa JRBF, Gazaffi R, Marçal JF, Carbonell SAM, Chiorato AF, Zucchi MI, Garcia AAF et al (2015) Developing a common bean core collection suitable for association mapping studies. Genet Mol Biol 38:67–78
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Sadowski J, Kole C (2011) Genetics, genomics and breeding of vegetable brassicas, 1st edn. CRC Press, New York
Shirasawa K, Oyama M, Hirakawa H, Sato S, Tabata S, Fujioka T, Kimizuka-Takagi C, Sasamoto S, Watanabe A et al (2011) An EST-SSR linkage map of Raphanus sativus and comparative genomics of the Brassicaceae. DNA Res 18:221–232
Upadhyaya H, Gowda C, Reddy K, Singh S (2009) Augmenting the pearl millet core collection for enhancing germplasm utilization in crop improvement. Crop Sci 49:573–580
van Hintum TJL (1999) The general methodology for creating a core collection. In: Johnson RC, Hodgkin T (eds) Core collections for today and tomorrow. International Plant Genetic Resources Institute, Italy, pp 10–17
van Hintum TJL, Brown AHD, Spillane C, Hodgkin T (2000) Core collections of plant genetic resources. International Plant Genetic Resources Institute, Rome, Italy
Wang S, Wang X, He Q, Liu X, Xu W, Li L, Gao J, Wang F (2012) Transcriptome analysis of the roots at early and late seedling stages using illumina paired-end sequencing and development of EST-SSR markers in radish. Plant Cell Rep 31:1437–1447
Wang Y, Pan Y, Liu Z, Zhu X, Zhai L, Xu L, Yu R, Gong Y, Liu L (2013) De novo transcriptome sequencing of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) and analysis of major genes involved in glucosinolate metabolism. BMC Genom 14:836
Wang J, Guan Y, Wang Y, Zhu L, Wang Q, Hu Q, Hu J (2014) A strategy for finding the optimal scale of plant core collection based on Monte Carlo simulation. Sci World J 2014:503473
Wang Q, Zhang L, Zheng P (2015) Genetic diversity and evolutionary relationship analyses within and among Raphanus species using EST-SSR markers. Mol Breed 35:62
Warwick SI, Francis A (2005) The biology of Canadian weeds. 132. Raphanus raphanistrum L. Can J Plant Sci 85:709–733
Xiaohui Z, Zhen Y, Shiyung M, Yang Q, Xinhua Y, Xiaohua C, Feng C, Zhangyan W, Yuyan S et al (2015) A de novo genome of a Chineses radish cultivar. Hortic Plant J 1:155–164
Xie Y, Ye S, Wang Y, Xu L, Zhu X, Yang J, Feng H, Yu R, Karanja B et al (2015) Transcriptome-based gene profiling provides novel insights into the characteristics of radish root response to Cr stress with next-generation sequencing. Front Plant Sci 6:202
Yamagishi H (2004) Assessment of cytoplasmic polymorphisms by PCR-RFLP of the mitochondrial orfB region in wild and cultivated radishes (Raphanus). Plant Breed 123:141–144
Yamagishi H, Terachi T (2003) Multiple origins of cultivated radishes as evidenced by a comparison of the structural variations in mitochondrial DNA of Raphanus. Genome 46:89–94
Yamane K, Lü N, Ohnishi O (2005) Chloroplast DNA variations of cultivated radish and its wild relatives. Plant Sci 168:627–634
Yamane K, Lü N, Ohnishi O (2009) Multiple origins and high genetic diversity of cultivated radish inferred from polymorphism in chloroplast simple sequence repeats. Breed Sci 59:55–65
Yao QI, Ping FAN, Zou SX (2008) Constructing a core collection for Maize (Zea mays L.) landrace from Wuling mountain region in China. Agric Sci China 7:1423–1432
Yu R, Xu L, Zhang W, Wang Y, Luo X, Wang R, Zhu X, Xie Y, Karanja B et al (2016) De novo taproot transcriptome sequencing and analysis of major genes involved in sucrose metabolism in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Front Plant Sci 7:585
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Next-Generation Biogreen21 program [Grant Number PJ013194 to HJY], the Research Fund, 2018 of The Catholic University of Korea [to HJY] and the National Research Foundation of Korea [Grant Number NRF-2017R1D1A1B06029741 to JHM]. We would like to thank the Genebank Information Center, the RDA in the Republic of Korea, the NARO in Japan, and the IPK in Germany for providing seeds for the radish accessions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YJ., Mun, JH., Jeong, YM. et al. Assembly of a radish core collection for evaluation and preservation of genetic diversity. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 59, 711–721 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-018-0079-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-018-0079-y