Abstract
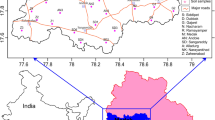
Exposure to toxic metals has been increased during recent decades, especially in megacities where various anthropogenic sources discharge loads of pollution to overcrowded urban districts. Soil as a simultaneous sink and source of metallic pollution is considered as an optimum media for monitoring such pollution. In this study, 41 surface soil samples were collected from a district in south of Tehran megacity. Despite determination of bulk metal concentrations (Ni, Cu, Cr, Zn, Co, Cd, Pb Mn, Fe, Ca and Na), a single-step extraction scheme was used for determination of anthropogenic portions. Enrichment factor and geo-accumulation (Igeo)/pollution (Ipoll) indices were calculated to estimate the enrichment class and degree of contamination, respectively. Except for Cd and Pb, other toxic metals showed no or negligible exceedance of reference values. Descending order of anthropogenic contribution from bulk metal concentrations was detected to be as: Cd > Pb > Mn > Cr > Zn > Co > Cu > Ni. Cadmium and lead were detected by all three indices to be in extreme and moderate/significant classes. Relatively high concentrations of Na were attributed to intense salt spraying for streets deicing during winter time when sampling occurred, while Ca concentrations were justified by geogenic source mainly dominance of limestones (dolomites). A prompt decision should be made to avoid further exposure of metals of concern to citizens in this overcrowded district of Tehran megacity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloway BJ (1995) Heavy metals in soils, 2nd edn. Blackie Academic & Professional, London
Barbieri M (2016) The importance of enrichment factor (EF) and geoaccumulation index (Igeo) to evaluate the soil contamination. J Geol Geophys 5:237. https://doi.org/10.4172/2381-8719.1000237
Cardelli R, Vanni G, Marchini F, Saviozzi A (2017) Characterization and origin of organic and inorganic pollution in urban soils in Pisa (Tuscany, Italy). Environ Monit Assess 189(11):554. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6264-0
Dehghani S, Moore F, Keshavarzi B, Beverley AH (2017) Health risk implications of potentially toxic metals in street dust and surface soil of Tehran, Iran. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 136:92–103
Dias-Ferreira C, Pato RL, Varejão JB, Tavares AO, Ferreira AJ (2016) Heavy metal and PCB spatial distribution pattern in sediments within an urban catchment—contribution of historical pollution sources. J soils sediments 16(11):2594–2605
Horváth A, Szűcs P, Bidló A (2015) Soil condition and pollution in urban soils: evaluation of the soil quality in a Hungarian town. J Soils Sediments 15(8):1825–1835
Hosseini Alhashemi AS, Karbassi AR, Hassanzadeh Kiabi B, Monavari SM, Nabavi SMB (2011) Accumulation and bioaccessibility of trace elements in wetland sediments. Afr J Biotechnol 10(9):1625–1636
Hu Y, Liu X, Bai J, Shih K, Zeng EY, Cheng H (2013) Assessing heavy metal pollution in the surface soils of a region that had undergone three decades of intense industrialization and urbanization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(9):6150–6159
Jami Al-Ahmadi M, Porkhabbaz AR, Sangak Sani BO (2018) Pollution of heavy metals in some farms of Torbat-E Jam, Khorasan Razavi province, Iran. Pollution 4(2):227–237
Karbassi AR, Nabi-Bidhendi GR, Bayati I (2005) Environmental geochemistry of heavy metals in a sediment core off Bushehr, Persian Gulf. Iran J Environ Health Sci Eng 2(4):255–260
Karbassi AR, Monavari SM, Nabi Bidhendi GR, Nouri J, Nematpour K (2008) Metal pollution assessment of sediment and water in the Shur River. Environ Monit Assess 147:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0102-8
Karbassi S, Nasrabadi T, Shahriari T (2016) Metallic pollution of soil in the vicinity of National Iranian Lead and Zinc (NILZ) Company. Environ Earth Sci 75:1433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6244-7
Liu D, Li Y, Ma J, Li C, Chen X (2016) Heavy metal pollution in urban soil from 1994 to 2012 in Kaifeng city, China. Water Air Soil Pollut 227(5):154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2788-0
Muller G (1979) Schwermetalle in den sediments des Rheins. Veranderungen Seit 1971. Umschau 79:778–783
Nasrabadi T, Nabi Bidhendi GR, Karbassi AR, Hoveidi H, Nasrabadi I, Pezeshk H (2009) Influence of Sungun copper mine on groundwater quality, NW Iran. Environ Geol 58:693–700
Nasrabadi T, Nabi Bidhendi GR, Karbassi AR, Mehrdadi N (2010) Evaluating the efficiency of sediment metal pollution indices in interpreting the pollution of Haraz River sediments, southern Caspian Sea basin. Environ Monit Assess 171(1–4):395–410
Nazzal Y, Rosen MA, Al-Rawabdeh AM (2013) Assessment of metal pollution in urban road dusts from selected highways of the Greater Toronto Area in Canada. Environ Monit Assess 185(2):1847–1858
Pan L, Wang Y, Ma J, Hu Y, Su B, Fang G, Wang L, Xiang B (2018) A review of heavy metal pollution levels and health risk assessment of urban soils in Chinese cities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(2):1055–1069
Pekey H (2006) Heavy metal pollution assessment in sediments of the Izmir Bay, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 123:219–231
Qiao X, Schmidt AH, Tang Y, Xu Y, Zhang C (2014) Demonstrating urban pollution using toxic metals of road dust and roadside soil in Chengdu, southwestern China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 28(4):911–919
Qing X, Yutong Z, Shenggao L (2015) Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 120:377–385
Sakan S, Devic G, Relic D, Andelkovic I, Sakan N, Dordevic D (2015) Evaluation of sediment contamination with heavy metals: the importance of determining appropriate background content and suitable element for normalization. Environ Geochem Health 37:97–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-014-9633-4
Shakya PR, Shrestha P, Tamrakar CS, Bhattarai PK (2006) Studies and determination of heavy metals in waste tyres and their impacts on the environment. Pak J Anal Environ Chem 7(2):70–76
Sobhan Ardakani S (2018) Assessment of Pb and Ni contamination in the topsoil of ring roads’ green spaces in the city of Hamadan. Pollution 4(1):43–51
Tepanosyan G, Sahakyan L, Belyaeva O, Maghakyan N, Saghatelyan A (2017) Human health risk assessment and riskiest heavy metal origin identification in urban soils of Yerevan, Armenia. Chemosphere 184:1230–1240
Tume P, González E, King RW, Monsalve V, Roca N, Bech J (2018) Spatial distribution of potentially harmful elements in urban soils, city of Talcahuano, Chile. J Geochem Explor 184(Part B):333–344
Turekian KK, Wedepohl KH (1961) Distribution of the elements in some major units of Earth’s crust. Bull Geol Soc Am 72:175–192
United Nations, D.o.E.a.S.A., Population Division (2014) World urbanization prospects. The 2014 Revision, Highlights (ST/ESA/SER.A/352), New York, p 32
Yu LI, Li HG, Liu FC (2017) Pollution in the urban soils of Lianyungang, China, evaluated using a pollution index, mobility of heavy metals, and enzymatic activities. Environ Monit Assess 189(1):34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5740-2
Zhu X, Yang F, Wei C, Liang T (2016) Bioaccessibility of heavy metals in soils cannot be predicted by a single model in two adjacent areas. Environ Geochem Health 38:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9711-2
Acknowledgements
Authors want to appreciate the kind support of authorities of district sixteen, Tehran municipality, for supplying the required regional data and for coordinating the determination of sampling stations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eghbal, N., Nasrabadi, T., Karbassi, A. et al. Investigating the pattern of soil metallic pollution in urban areas (case study: a district in Tehran city). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 6717–6726 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2076-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2076-1