Abstract
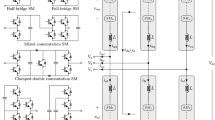
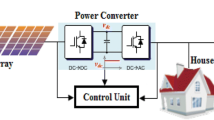
The performance analysis of a grid-connected reduced switch multilevel inverter (MLI) with an auxiliary diode bridge for solar photovoltaic (SPV) systems is presented in this paper. A high-gain interleaved boost converter (HG-IBC) is introduced to boost the output of SPV to the necessary level. Due to the intermittent nature of the SPV's output, a hybrid fuzzy logic perturb and observe-based maximum power point tracking is incorporated to excerpt the maximum possible power from the SPV. A detailed comparative analysis of various existing boost converters with the proposed HG-IBC is provided, with particular emphasis on the number of components and boost factor. The suggested MPPT is also compared with the conventional MPPT methods, and the results are analysed in terms of rise time and percentage oscillations. A sine PWM with a dual reference modulation scheme is used to control the switches of MLI. A phase-locked loop technology is used to ensure that the inverter's output current is in sync with the voltage of the grid. The Simulink platform is used to simulate the complete model. The simulation of SPV with HG-IBC and HFL-PO MPPT shows superior performance with respect to rise time and percentage oscillations at the output with a voltage gain of five. The suggested MLI requires a minimal number of switches, and hence the overall losses are minimized. The THD of MLI is 3.08%, which is within the limits of IEEE regulations. Overall, the simulation results indicate that the model performs better and is more efficient.





























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jia, T., Dai, Y., Wang, R.: Refining energy sources in winemaking industry by using solar energy as alternatives for fossil fuels: a review and perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 88, 278–296 (2018)
Munawwar, S., Ghedira, H.: A review of renewable energy and solar industry growth in the GCC region. Energy Procedia 57, 3191–3202 (2014)
Sanneh, E.S.: Renewable and sustainable energy. In: Systems Thinking for Sustainable Development, pp. 13–23. Springer, Cham (2018)
Al-Shahri, O.A., Ismail, F.B., Hannan, M.A., Lipu, M.H., Al-Shetwi, A.Q., Begum, R.A., Al-Muhsen, N.F. and Soujeri, E., Solar photovoltaic energy optimization methods, challenges and issues: a comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod., 284, 125465 (2021)
Mumtaz, F., Yahaya, N.Z., Meraj, S.T., Singh, B., Kannan, R., Ibrahim, O.: Review on non-isolated DC–DC converters and their control techniques for renewable energy applications. Ain Shams Eng. J. (2021)
Schmitz, L., Martins, D.C., Coelho, R.F.: Comprehensive conception of high step-up DC–DC converters with coupled inductor and voltage multipliers techniques. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 67(6), 2140–2151 (2020)
Raghavendra, K.V.G., Zeb, K., Muthusamy, A., Krishna, T.N.V., Kumar, S.V.S., Kim, D.-H., Kim, M.-S., Cho, H.-G., Kim, H.-J.: A comprehensive review of DC–DC converter topologies and modulation strategies with recent advances in solar photovoltaic systems. Electronics 9(1) (2020).
Kiran Kumar, B.M., Indira, M.S., Nagaraja Rao, S.: Performance analysis of multiple gain boost converter with hybrid maximum power point tracker for solar PV connected to grid. Clean. Energy 5(4), 655–672 (2021)
Alagu, M., Ponnusamy, P., Pandarinathan, S., Ali, J.S.M.: Performance improvement of solar PV power conversion system through low duty cycle DC–DC converter. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 49(2), 267–282 (2021)
Nathan, K., Ghosh, S., Siwakoti, Y., Long, T.: A new DC–DC converter for photovoltaic systems: coupled-inductors combined Cuk-SEPIC converter. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 34(1), 191–201 (2018)
Hanzaei, S.H., Gorji, S.A., Ektesabi, M.: A scheme-based review of MPPT techniques with respect to input variables including solar irradiance and PV arrays’ temperature. IEEE Access 8, 182229–182239 (2020)
Liu, Z., Du, J., Yu, B.: Design method of double-boost DC/DC converter with high voltage gain for electric vehicles. World Electr. Veh. J. 11(4), 64 (2020)
Jotham Jeremy, L., Ooi, C.A., Teh, J.: Non-isolated conventional DC–DC converter comparison for a photovoltaic system: a review. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 12(1), 013502 (2020)
Yadav, I., Maurya, S.K., Gupta, G.K.: A literature review on industrially accepted MPPT techniques for solar PV system. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 10(2), 2088–8708 (2020)
Chaibi, Y., Allouhi, A., Salhi, M., El-jouni, A.: Annual performance analysis of different maximum power point tracking techniques used in photovoltaic systems. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 4(1), 1–10 (2019)
Bollipo, R.B., Mikkili, S., Bonthagorla, P.K.: Critical review on PV MPPT techniques: classical, intelligent and optimisation. IET Renew. Power Gener. 14(9), 1433–1452 (2020)
Al-Majidi, S.D., Abbod, M.F., Al-Raweshidy, H.S.: A novel maximum power point tracking technique based on fuzzy logic for photovoltaic systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 43(31), 14158–14171 (2018)
Janardhan, K., Mittal, A., Ojha, A.: Performance investigation of stand-alone solar photovoltaic system with single phase micro multilevel inverter. Energy Rep. 6, 2044–2055 (2020)
Bhattacharyya, S., Samanta, S., Mishra, S.: Steady output and fast tracking MPPT (SOFT-MPPT) for P&O and InC algorithms. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 12(1), 293–302 (2020)
Basha, C.H.H., Rani, C.: Performance analysis of MPPT Techniques for dynamic irradiation condition of Solar PV. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 22(8), 2577–2598 (2020)
Li, X., Wen, H., Yihua, Hu., Jiang, L.: A novel beta parameter based fuzzy-logic controller for photovoltaic MPPT application. Renew Energy 130, 416–427 (2019)
Yanarates, C., Wang, Y., Zhou, Z.: Unity proportional gain resonant and gain scheduled proportional (PR-P) controller-based variable perturbation size real-time adaptive perturb and observe (P&O) MPPT algorithm for PV systems. IEEE Access 9, 138468–138482 (2021)
Vijeh, M., Rezanejad, M., Samadaei, E., Bertilsson, K.: A general review of multilevel inverters based on main submodules: structural point of view. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 34(10), 9479–9502 (2019)
Sunddararaj, S.P., Srinivasarangan Rangarajan, S., An extensive review of multilevel inverters based on their multifaceted structural configuration, triggering methods and applications. Electronics, 9(3), 433 (2020)
Salem, A., Van Khang, H., Robbersmyr, K.G., Norambuena, M., Rodriguez, J.: Voltage source multilevel inverters with reduced device count: topological review and novel comparative factors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 36(3), 2720–2747 (2020)
Siddique, M.D., Mekhilef, S., Shah, N.M., Sarwar, A., Memon, M.A.: A new single‐phase cascaded multilevel inverter topology with reduced number of switches and voltage stress. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 30(2), e12191 (2020)
Hassan, A., Yang, X., Chen, W., Houran, M.A.: A state of the art of the multilevel inverters with reduced count components. Electronics 9(11), 1924 (2020)
Latifi Majareh, S.H., Sedaghati, F., Hosseinpour, M., Mousavi‐Aghdam, S.R.: Design, analysis and implementation of a generalised topology for multilevel inverters with reduced circuit devices. IET Power Electron. 12(14), 3724–3731 (2019)
Ali, J.S.M., Krishnaswamy, V.: An assessment of recent multilevel inverter topologies with reduced power electronics components for renewable applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 82, 3379–3399 (2018)
Ponraj, R.P., Sigamani, T., Subramanian, V.: A developed H-bridge cascaded multilevel inverter with reduced switch count. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 16(3), 1445–1455 (2021)
Ponraj, R.P., Sigamani, T.: A novel design and performance improvement of symmetric multilevel inverter with reduced switches using genetic algorithm. Soft Comput. 25(6), 4597–4607 (2021)
Chen, W., Hotchkiss, E., Bazzi, A.: Reconfiguration of NPC multilevel inverters to mitigate short circuit faults using back-to-back switches. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 3(1), 46–55 (2018)
Saeedian, M., Hosseini, S.M., Adabi, J.: A five-level step-up module for multilevel inverters: topology, modulation strategy, and implementation. IEEE J. Emerg. Selected Top. Power Electron. 6(4), 2215–2226 (2018)
Hosseinzadeh, M.A., Sarebanzadeh, M., Babaei, E., Rivera, M., Wheeler, P.: A switched-DC source sub-module multilevel inverter topology for renewable energy source applications. IEEE Access 9: 135964–135982 (2021)
Omer, P., Kumar, J., Surjan, B.S.: A review on reduced switch count multilevel inverter topologies. IEEE Access 8: 22281–22302 (2020)
Bana, P.R., Panda, K.P., Naayagi, R.T., Siano, P., Panda, G.: Recently developed reduced switch multilevel inverter for renewable energy integration and drives application: topologies, comprehensive analysis and comparative evaluation. IEEE Access 7, 54888–54909 (2019)
Kotla, R.W., Yarlagadda, S.R.: Mathematical modelling of SPV array by considering the parasitic effects. SN Appl. Sci. 2(1), 1–10 (2020)
Kiran, K.B., Indira, M.S., Nagaraja, R.: Mathematical modeling and evaluation of performance characteristics of a hybrid solar PV and wind energy system. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 25(4), 685–697 (2021)
Reddy, D.S.: Review on power electronic boost converters. Aust. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 18(3), 127–137 (2021)
Elsayad, N., Moradisizkoohi, H., Mohammed, O.: A new three-level flying-capacitor boost converter with an integrated LC2D output network for fuel-cell vehicles: analysis and design. Inventions 3(3), 61 (2018)
Zhang, G., Iu, H.H.C., Zhang, B., Li, Z., Fernando, T., Chen, S.Z., Zhang, Y.: An impedance network boost converter with a high-voltage gain. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 32(9), 6661–6665 (2017)
Kumar, B.K., Indira, M.S., Rao, S.N.: Performance evaluation of solar PV using multiple level voltage gain boost converter with CLC cell. In: Innovations in Electrical and Electronic Engineering (pp. 237–251). Springer, Singapore (2021)
Alamin, A., Abracon, L.L.C.: DC–DC converters & the importance of DCR-optimized inductors
Singh, B.P., Goyal, S.K., Siddiqui, S.A.: Analysis and classification of maximum power point tracking (MPPT) techniques: a review. Intelligent Computing Techniques for Smart Energy Systems, pp. 999–1008 (2020)
Yap, K.Y., Sarimuthu, C.R., Lim, J.M.Y.: Artificial intelligence based MPPT techniques for solar power system: a review. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy (2020)
Robles Algarín, C., Taborda Giraldo, J., Rodriguez Alvarez, O.: Fuzzy logic based MPPT controller for a PV system. Energies, 10(12), 2036 (2017)
Pawar, R., Gawande, S.P., Kadwane, S.G., Waghmare, M.A., Nagpure, R.N.: Five-level diode clamped multilevel inverter (DCMLI) based electric spring for smart grid applications. Energy Procedia 117, 862–869 (2017)
Khadse, S., Mendole, R., Pandey, A.: A 5-level single phase flying capacitor multilevel inverter. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol 4(2), 348–352 (2017)
Miceli, R., Schettino, G., Viola, F.: A novel computational approach for harmonic mitigation in PV systems with single-phase five-level CHBMI. Energies 11(8), 2100 (2018)
Acquaviva, A., Rodionov, A., Kersten, A., Thiringer, T., Liu, Y.: Analytical conduction loss calculation of a mosfet three-phase inverter accounting for the reverse conduction and the blanking time. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68(8), 6682–6691 (2020)
Ahmed, M.H., Wang, M., Hassan, M.A.S., Ullah, I.: Power loss model and efficiency analysis of three-phase inverter based on SiC MOSFETs for PV applications." IEEE Access 7, 75768–75781 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, B.M.K., Rao, S.N. & Indira, M.S. Analysis of grid-connected reduced switch MLI with high-gain interleaved boost converter and hybrid MPPT for solar PV. Int J Energy Environ Eng 13, 1287–1307 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40095-022-00479-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40095-022-00479-4