Abstract
Background and Objectives
Desloratadine, the major active metabolite of loratadine, is a non-sedating long-acting antihistamine that is widely used in the treatment of allergic rhinitis and chronic idiopathic urticaria. This study aimed to investigate the prevalence of desloratadine slow-metabolizer (DSM) phenotype and the effects of food on the pharmacokinetics of desloratadine and its active metabolite 3-OH-desloratadine in healthy Chinese volunteers.
Methods
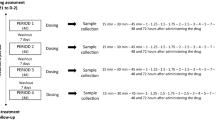
A total of 46 healthy Chinese male volunteers were included in this investigation. All subjects received a single dose of a 5-mg desloratadine tablet under fasting or fed conditions and the plasma concentrations of desloratadine and 3-OH-desloratadine were measured by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. The pharmacokinetic profiles were analyzed using a non-compartmental method in the Phoenix WinNonlin program. The individuals with a 3-OH-desloratadine-to-desloratadine exposure ratio lower than 10 % or a desloratadine half-life (t 1/2) of ≥50 h were supposed to be DSM.
Results
There was only one DSM among the 46 volunteers, with a prevalence of 2.2 %. Moreover, administration in a fed state resulted in 34.07 and 32.06 % decreases in maximum plasma concentration and area under the concentration-time curve from time zero to infinity for desloratadine and 47.26 and 48.46 % for 3-OH-desloratadine compared with those values under fasting conditions.
Conclusions
Taken together, these results indicated that the incidence of the DSM phenotype in the Chinese population was low and that food intake could significantly decrease the absorption rate and extent of desloratadine.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Canonica GW, Tarantini F, Compalati E, Penagos M. Efficacy of desloratadine in the treatment of allergic rhinitis: a meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, controlled trials. Allergy. 2007;62:359–66.
Augustin M, Ehrle S. Safety and efficacy of desloratadine in chronic idiopathic urticaria in clinical practice: an observational study of 9246 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol. 2009;23:292–99.
Geha RS, Meltzer EO. Desloratadine: a new, nonsedating, oral antihistamine. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;107:751–62.
Agrawal DK. Pharmacology and clinical efficacy of desloratadine as an anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory drug. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2001;10:547–60.
Gupta S, Banfield C, Kantesaria B, Marino M, Clement R, Affrime M, Batra V. Pharmacokinetic and safety profile of desloratadine and fexofenadine when coadministered with azithromycin: a randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Clin Ther. 2001;23:451–66.
Xu HR, Li XN, Chen WL, Chu NN. Simultaneous determination of desloratadine and its active metabolite 3-hydroxydesloratadine in human plasma by LC/MS/MS and its application to pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2007;45:659–66.
Ponnuru VS, Challa BR, Nadendla R. Quantification of desloaratadine in human plasma by LC-ESI-MS/MS and application to a pharmacokinetic study. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012;2:180–87.
Yang L, Clement RP, Kantesaria B, Reyderman L, Beaudry F, Grandmaison C, Di Donato L, Masse R, Rudewicz PJ. Validation of a sensitive and automated 96-well solid-phase extraction liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of desloratadine and 3-hydroxydesloratadine in human plasma. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2003;792:229–40.
Ramanathan R, Reyderman L, Su AD, Alvarez N, Chowdhury SK, Alton KB, Wirth MA, Clement RP, Statkevich P, Patrick JE. Disposition of desloratadine in healthy volunteers. Xenobiotica. 2007;37:770–87.
Gupta S, Banfield C, Affrime M, Marbury T, Padhi D, Glue P. Oral bioavailability of desloratadine is unaffected by food. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002;41:7–12.
Affrime M, Banfield C, Gupta S, Cohen A, Boutros T, Thonoor M, Cayen M. Effect of race and sex on single and multiple dose pharmacokinetics of desloratadine. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002;41:21–88.
Hakooz N, Salem II. Prevalence of desloratadine poor metabolizer phenotype in healthy Jordanian males. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2012;33:15–21.
Bruce P, Kenneth K, Samir G, Khalilieh S, Kantesaria B, Manitpisitkul P, Lorber R, Wang Z, Lutsky B. Adult and paediatric poor metabolisers of desloratadine: an assessment of pharmacokinetics and safety. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2006;5:211–23.
Blum RA, Frick G, Kovacs SJ, Meeves S, Georges G, Kraft W. Clinical implications of the desloratadine slow metabolizer (DSM) phenotype based on pharmacokinetic (PK) principles. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113:S200.
Surampudi P, Page ST, Swerdloff RS, Nya-Ngatchou JJ, Liu PY, Amory JK, Leung A, Hull L, Blithe DL, Woo J, Bremner WJ, Wang C. A first in human study of the pharmacokinetics, safety and food effects of orally administered DMAU: a prototype oral male hormonal contraceptive. Andrology. 2004;2:579–87.
Lee J, Zhang W, Moy S, Kowalski D, Kowalski D, Kerbusch V, van Gelderen M, Sawamoto T, Grunenberg N, Keirns J. Effects of food intake on the pharmacokinetic properties of mirabegron oral controlled-absorption system: a single-dose, randomized, crossover study in healthy adults. Clin Ther. 2013;35:333–41.
Bello CL, Sherman L, Zhou J, Verkh L, Smeraglia J, Mount J, Klamerus KJ. Effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of sunitinib malate (SU11248), a multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor: results from a phase I study in healthy subjects. Anti Cancer Drug. 2006;17:353–58.
Salmun LM, Lorber R. 24-hour efficacy of once-daily desloratadine therapy in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis. BMC Fam Pract. 2002;3:14.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the subjects who were involved in this study, the investigators, and research staff. The authors further appreciate the collaboration and help from Dr. Yi He, Blood Center of Chengdu (Chengdu, China).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest directly relevant to the content of this study.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Zhang, K., Li, T. et al. Prevalence of Desloratadine Slow-metabolizer Phenotype and Food-dependent Pharmacokinetics of Desloratadine in Healthy Chinese Volunteers. Clin Drug Investig 35, 807–813 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-015-0343-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-015-0343-1