Abstract
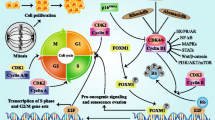
Palbociclib (Ibrance®) is an oral, reversible, selective, small-molecule inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) 4 and CDK6 developed by Pfizer for the treatment of cancer. CDKs are important modulators of cell cycle entry and progression in response to growth signals, and inhibition of these kinases with palbociclib could enhance the activity of other anticancer drugs in tolerable regimens. Palbociclib, in combination with letrozole, was recently approved in the US for the first-line treatment of advanced breast cancer. Phase III development is underway worldwide investigating its use as first-line treatment in advanced breast cancer, as well as treatment of recurrent or advanced breast cancer and high-risk, early-stage breast cancer. A phase II trial is underway in the USA for non-small cell lung cancer under a US National Cancer Institute-funded research collaboration, and several phase I and II investigations are being conducted for various other solid tumour types and haematological malignancies. This article summarizes the milestones in the development of palbociclib leading to this first approval for use in postmenopausal women with estrogen-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER) 2-negative advanced breast cancer as initial endocrine-based therapy for their metastatic disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cadoo KA, Gucalp A, Traina TA. Palbociclib: an evidence-based review of its potential in the treatment of breast cancer. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2014;6:123–33.
Sutherland RL, Musgrove EA. CDK inhibitors as potential breast cancer therapeutics: new evidence for enhanced efficacy in ER+ disease. Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(6):112.
Dickson MA. Molecular pathways: CDK4 inhibitors for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(13):3379–83.
Pfizer Inc. IBRANCE® (palbociclib): US prescribing information. 2015. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov. Accessed 12 Feb 2015.
Choi YJ, Anders L. Signaling through cyclin D-dependent kinases. Oncogene. 2014;33(15):1890–903.
Pfizer. Pfizer receives US FDA accelerated approval of IBRANCE® (palbociclib) [media release]. http://www.pfizer.com. Accessed3 Feb 2015.
Pfizer. Pfizer reports third-quarter 2014 results [media release]. http://press.pfizer.com. Accessed 28 Oct 2014.
Pfizer. Pfizer announces submission of palbociclib new drug application to the FDA [media release]. http://www.pfizer.com. Accessed 18 Aug 2014.
Pfizer. Pfizer reports second-quarter 2014 results [media release]. http://press.pfizer.com. Accessed 29 Jul 2014.
Amgen. Amgen’s third quarter 2013 revenues increased 10 percent to $4.7 billion and adjusted earnings per share (EPS) increased 16 percent to $1.94 [media release]. http://www.amgen.com. Accessed 22 Oct 2013.
Pfizer. Pfizer and GSK to initiate study of novel combination therapy in patients with melanoma [media release]. http://www.pfizer.com. Accessed 21 Nov 2013.
Finn RS, Dering J, Conklin D, et al. PD 0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitor, preferentially inhibits proliferation of luminal estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(5):R77.
Fry DW, Harvey PJ, Keller PR, et al. Specific inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 by PD 0332991 and associated antitumor activity in human tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004;3(11):1427–38.
Lee NV, Yuan J, Eisele K, et al. Mechanistic exploration of combined CDK4/6 and ER inhibition in ER-positive breast cancer [abstract no. LB-136]. 105th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research, AACR. 2014;74(19 Suppl 1).
Zoellner AK, Dietzfelbinger R, Hutter G, et al. The CDK 4/CDK 6 Inhibitor PD0332991 significantly reduces cell growth via a G1 phase arrest in Mantle Cell Lymphoma cell lines and additively increases effects of Ibrutinib [abstract no. V667]. Onkologie. 2013;36(Suppl 7):198.
Zoellner AK, Nestorova V, Hutter G, et al. The CDK4/CDK6 Inhibitor PD0332991 significantly reduces cell growth in GCB and ABC DLBCL cell lines and additively increases effects of GS-1101 [abstract no. V666]. Onkologie. 2013;36(Suppl 7):198.
Logan JE, Mostofizadeh N, Desai AJ, et al. PD-0332991, a potent and selective inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6, demonstrates inhibition of proliferation in renal cell carcinoma at nanomolar concentrations and molecular markers predict for sensitivity. Anticancer Res. 2013;33(8):2997–3004.
Comstock CE, Augello MA, Goodwin JF, et al. Targeting cell cycle and hormone receptor pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 2013;32(48):5481–91.
Barton KL, Misuraca K, Cordero F, et al. PD-0332991, a CDK4/6 inhibitor, significantly prolongs survival in a genetically engineered mouse model of brainstem glioma. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e77639.
Baughn LB, Di Liberto M, Wu K, et al. A novel orally active small molecule potently induces G1 arrest in primary myeloma cells and prevents tumor growth by specific inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6. Cancer Res. 2006;66(15):7661–7.
Konecny GE, Winterhoff B, Kolarova T, et al. Expression of p16 and retinoblastoma determines response to CDK4/6 inhibition in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(6):1591–602.
Von Euw EM, Conklin D, Rong HM, et al. Identification of markers of sensitivity and resistance to palbociclib (PD0332991) in melanoma [abstract no. 1321]. Cancer Res. 2014;74(19 Suppl 1).
Flaherty KT, Lorusso PM, DeMichele A, et al. Phase I, dose-escalation trial of the oral cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor PD 0332991, administered using a 21-day schedule in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(2):568–76.
Schwartz GK, LoRusso PM, Dickson MA, et al. Phase I study of PD 0332991, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, administered in 3-week cycles (Schedule 2/1). Br J Cancer. 2011;104(12):1862–8.
O’Dwyer PJ, LoRusso P, DeMichele A, et al. A phase I dose escalation trial of a daily oral CDK 4/6 inhibitor PD-0332991 [abstract no. 3550]. 2007;25(18S).
Ruiz-Garcia A, Plotka A, Pawlak S, et al. Effect of food on the bioavailability of palbociclib 125 mg capsules in healthy volunteers [abstract no. 463P]. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(suppl 4):iv154.
Sun W, Wang DD. A population pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis of palbociclib (PD-0332991) in patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors [abstract no. 462P]. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(Suppl 4):iv154.
Hoffman JT, Plotka A, O’Gorman M, et al. A phase 1 randomized, open-label, 2-sequence, 2-period crossover study of the effect of multiple doses of palbociclib (PD-0332991) on midazolam pharmacokinetics in healthy women of non-childbearing potential [abstract no. Abstract CT419]. Cancer Res. 2014;74(19 Suppl).
Finn RS, Crown JP, Lang I, et al. The cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in combination with letrozole versus letrozole alone as first-line treatment of oestrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer (PALOMA-1/TRIO-18): a randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(1):25–35.
DeMichele A, Clark AS, Tan KS, et al. CDK 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib (PD0332991) in Rb+ advanced breast cancer: phase II activity, safety, and predictive biomarker assessment. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-14-2258.
Gopalan PK, Pinder MC, Chiappori A, et al. A phase II clinical trial of the CDK 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib (PD 0332991) in previously treated, advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with inactivated CDKN2A [abstract no. 8077]. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(15 Suppl 1).
Vaughn DJ, Hwang W, Lal P, et al. Phase 2 trial of the cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in patients with retinoblastoma protein-expressing germ cell tumors. Cancer. 2014. doi:10.1002/cncr.29213.
Dickson MA, Tap WD, Keohan ML, et al. Phase II trial of the CDK4 inhibitor PD0332991 in patients with advanced CDK4-amplified well-differentiated or dedifferentiated liposarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(16):2024–8.
Niesvizky R, Ely S, Jayabalan DS, et al. A Phase I Trial of PD 0332991, a Novel, Orally-Bioavailable CDK4/6-Specific Inhibitor Administered in Combination with Bortezomib and Dexamethasone to Patients with Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma [abstract no. 1877]. In: 51st annual meeting and exposition of the American Society of Hematology. 2009.
Leonard JP, LaCasce AS, Smith MR, et al. Selective CDK4/6 inhibition with tumor responses by PD0332991 in patients with mantle cell lymphoma. Blood. 2012;119(20):4597–607.
Martin P, DiLiberto M, Mason CE, et al. The combination of palbociclib plus bortezomib is safe and active in patients with previously treated mantle cell lymphoma: final results of a phase I trial [abstract no. 4393]. In: 55th annual meeting and exposition of the American Society of Hematology. 2013.
Finn R, Crown J, Ettl J, et al. Clinical patterns of palbociclib associated neutropenia in the PALOMA-1/TRIO-18 trial [abstract no. 368P]. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(suppl 4):iv122.
Turner N, André F, Loibl S, et al. Phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of fulvestrant with or without PD-0332991 (palbociclib) ± goserelin in women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer (MBC) whose disease progressed after prior endocrine therapy [abstract no. OT3-2-10]. Cancer Res. 2013;73(24 Suppl).
Martin M, Beslija S, Carrasco E, et al. Phase III study of palbociclib in combination with exemestane vs. capecitabine, in hormonal receptor (HR) positive/HER2 negative metastatic breast cancer (MBC) patients with resistance to non-steroidal aromatase inhibitors (NSAI): PEARL study (geicam/2013-02_cecog/bc.1.3.006) [abstract no. 409TiP]. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(Suppl 4):iv134–iv5.
Malorni L, Sanna G, Pestrin M, et al. Phase 2 study of palbociclib (CDK 4/6 inhibitor) for ER positive, HER2- negative post-menopausal advanced breast cancer patients recurring after hormonal therapy (to reverse endocrine resistance - TREnd trial) [abstract no. Abstract OT2-6-01]. Cancer Res. 2013;73(24 Suppl).
Von Minckwitz G, Bear H, Bonnefoi H, et al. PENELOPE: Phase III study evaluating palbociclib (PD-0332991), a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitor in patients with hormone-receptor-positive, HER2-normal primary breast cancer with high relapse risk after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (GBG-78/BIG1-13) [abstract no. OT2-6-11]. Cancer Res. 2013;73(24 Suppl 1).
Mayer EL, Gropper AB, Tung NM, et al. Adjuvant palbociclib (P) plus endocrine therapy (ET) for hormone receptor positive (HR+) breast cancer: a phase II feasibility study [abstract no. TPS654]. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(15 Suppl 1).
Clark AS, O’Dwyer PJ, Heitjan D, et al. A phase I trial of palbociclib and paclitaxel in metastatic breast cancer [abstract no. 527]. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(5 Supp).
Foundation for the National Institutes of Health. Groundbreaking collaborative clinical trial launched [media release]. www.fnih.org. Accessed16 Jun 2014.
Littman S, Burkart A, Hyslop T, et al. The CD4/6 inhibitor, PD0332991, has activity in metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma: preliminary results of a phase II trial [abstract no. P-0119]. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(Suppl 4):iv69.
Disclosure
The preparation of this report was not supported by any external funding. During the peer review process the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on the article. Changes resulting from any comments received were made by the authors on the basis of scientific completeness and accuracy. S. Dhillon is a salaried employee of Adis, Springer SBM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This profile has been extracted and modified from the Adis R&D Insight drug pipeline database. Adis R&D Insight tracks drug development worldwide through the entire development process, from discovery, through pre-clinical and clinical studies to market launch.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhillon, S. Palbociclib: First Global Approval. Drugs 75, 543–551 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-015-0379-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-015-0379-9