Abstract
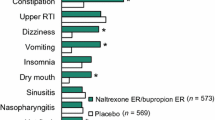
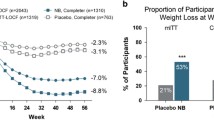
Oral naltrexone extended-release/bupropion extended-release (naltrexone ER/bupropion ER; Contrave®, Mysimba™) is available as an adjunct to a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity in adults with an initial body mass index (BMI) of ≥30 kg/m2 (i.e. obese) or a BMI of ≥27 kg/m2 (i.e. overweight) in the presence of at least one bodyweight-related comorbidity, such as type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension or dyslipidaemia. In 56-week phase III trials in these patient populations, oral naltrexone ER/bupropion ER 32/360 mg/day was significantly more effective than placebo with regard to percentage bodyweight reductions from baseline and the proportion of patients who achieved bodyweight reductions of ≥5 and ≥10 %. Significantly greater improvements in several cardiometabolic risk factors were also observed with naltrexone ER/bupropion ER versus placebo, as well as greater improvements in glycated haemoglobin levels in obese or overweight adults with type 2 diabetes. Naltrexone ER/bupropion ER was generally well tolerated in phase III trials, with nausea being the most common adverse event. Thus, naltrexone ER/bupropion ER 32/360 mg/day as an adjunct to a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity, is an effective and well tolerated option for chronic bodyweight management in obese adults or overweight adults with at least one bodyweight-related comorbidity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight: fact sheet no. 311. 2015. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets. Accessed 8 June 2015.
Jensen MD, Ryan DH, Apovian CM, et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(25 Pt B):2985–3023.
Apovian CM, Aronne LJ, Bessesen DH, et al. Pharmacological management of obesity: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(2):342–62.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Obesity: identification, assessment and management of overweight and obesity in children, young people and adults. NICE clinical guideline 189. 2014. http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance. Accessed 8 June 2015.
Takeda Pharmaceuticals America Inc. Contrave® (naltrexone HCl and bupropion HCl) extended-release tablets: US prescribing information. 2014. http://www.fda.gov. Accessed 8 June 2015.
Orexigen Therapeutics Ireland Ltd. Mysimba™ 8 mg/90 mg prolonged-release tablets: EU summary of product characteristics. 2015. http://www.ema.europe.eu. Accessed 8 June 2015.
Billes SK, Sinnayah P, Cowley MA. Naltrexone/bupropion for obesity: an investigational combination pharmacotherapy for weight loss. Pharmacol Res. 2014;84:1–11.
Sinnayah P, Wallingford N, Evans A, et al. Bupropion and naltrexone interact synergistically to decrease food intake in mice [abstract no. 567-P]. Obesity. 2007;15(Suppl.):A179.
Greenway FL, Whitehouse MJ, Guttadauria M, et al. Rational design of a combination medication for the treatment of obesity. Obesity. 2009;17(1):30–9.
Greenway FL, Dunayevich E, Tollefson G, et al. Comparison of combined bupropion and naltrexone therapy for obesity with monotherapy and placebo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94(12):4898–906.
Smith SR, Fujioka K, Gupta AK, et al. Combination therapy with naltrexone and bupropion for obesity reduces total and visceral adiposity. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15(9):863–6.
Wang GJ, Tomasi D, Volkow ND, et al. Effect of combined naltrexone and bupropion therapy on the brain’s reactivity to food cues. Int J Obes. 2014;38(5):682–8.
Greenway FL, Fujioka K, Plodkowski RA, et al. Effect of naltrexone plus bupropion on weight loss in overweight and obese adults (COR-I): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9741):595–605.
Apovian CM, Aronne L, Rubino D, et al. A randomized, phase 3 trial of naltrexone SR/bupropion SR on weight and obesity-related risk factors (COR-II). Obesity. 2013;21(5):935–43.
Wadden TA, Foreyt JP, Foster GD, et al. Weight loss with naltrexone SR/bupropion SR combination therapy as an adjunct to behavior modification: the COR-BMOD trial. Obesity. 2011;19(1):110–20.
Hollander P, Gupta AK, Plodkowski R, et al. Effects of naltrexone sustained-release/bupropion sustained-release combination therapy on body weight and glycemic parameters in overweight and obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(12):4022–9.
Plutzky J, Chilton R, Still C, et al. Weight loss, blood pressure, pulse and circadian patterns with naltrexone sustained-release/bupropion sustained-release combination therapy for obesity [abstract no. 1013-286]. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57(14 Suppl):E517.
GlaxoSmithKline. Zyban® (bupropion hydrochloride) sustained-release tablets, for oral use: US prescribing information. 2014. http://www.fda.gov. Accessed 8 June 2015.
Duramed Pharmaceuticals Inc. Revia® (naltrexone hydrochloride tablets USP) 50 mg: US prescribing information. 2013. http://www.fda.gov. Accessed 8 June 2015.
Kolotkin RL, Burns C, Walsh B, et al. Combination naltrexone/bupropion therapy resulted in clinically meaningful improvements in weight and quality of life (QoL): integrated analysis of four phase 3 trials [abstract no. 1056-P]. Diabetes. 2013;62(Suppl 1):A272.
Apovian C, Burns C, Walsh B, et al. An integrated analysis of weight loss with combination naltrexone/bupropion therapy by BMI (obesity) classification [abstract no. 1130-P]. Diabetes. 2013;62(Suppl 1):A293–4.
Crosby RD, Kolotkin RL, Williams GR. An integrated method to determine meaningful changes in health-related quality of life. J Clin Epidemiol. 2004;57(11):1153–60.
Fujioka K, Walsh B, Burns C, et al. Early improvement in control of eating is associated with long-term weight loss—integrated analysis of four phase 3 trials of combination naltrexone/bupropion treatment [abstract no. 1149-P]. Diabetes. 2013;62(Suppl. 1):A299.
Foreyt JP, Hill J, Maier H, et al. Naltrexone SR/bupropion SR-induced weight loss is independent of nausea [abstract no. 218-P]. Obesity. 2009;17(Suppl. 2):S109–10.
Pucci A, Finer N. New medications for treatment of obesity: metabolic and cardiovascular effects. Can J Cardiol. 2015;31(2):142–52.
Karmali S, Brar B, Shi X, et al. Weight recidivism post-bariatric surgery: a systematic review. Obes Surg. 2013;23(11):1922–33.
Cunningham JW, Wiviott SD. Modern obesity pharmacotherapy: weighing cardiovascular risk and benefit. Clin Cardiol. 2014;37(11):693–9.
Orexigen Therapeutics Inc. Orexigen announces successful interim analysis of Contrave Light Study: company will resubmit the Contrave NDA in the next few weeks—potential approval by June 2014 [media release]. 25 Nov 2013. http://www.orexigen.com.
US Food and Drug Administration. Contrave (application number 200063Orig1s000): summary review. 2014. http://www.fda.gov. Accessed 8 June 2015.
Orexigen Therapeutics Inc. Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Orexigen Therapeutics announce termination of the cardiovascular outcomes study (Light Study) of the obesity drug Contrave® (naltrexone HCl and bupropion HCl) [media release]. 12 May 2015. http://orexigen.com.
McElroy SL, Guerdjikova AI, Kim DD, et al. Naltrexone/bupropion combination therapy in overweight or obese patients with major depressive disorder: results of a pilot study. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2013. doi:10.4088/PCC.12m01494.
Verpeut JL, Bello NT. Drug safety evaluation of naltrexone/bupropion for the treatment of obesity. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2014;13(6):831–41.
Disclosure
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding. During the peer review process, the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on this article. Changes resulting from comments received were made by the authors on the basis of scientific and editorial merit. Sarah Greig and Gillian Keating are salaried employees of Adis/Springer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The manuscript was reviewed by: J. P. Mordes, Department of Medicine/Endocrinology, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA; A. P. Shukla, Division of Endocrinology, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, NY, USA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greig, S.L., Keating, G.M. Naltrexone ER/Bupropion ER: A Review in Obesity Management. Drugs 75, 1269–1280 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-015-0427-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-015-0427-5