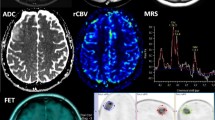
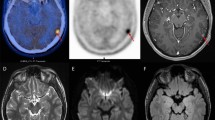
Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to conduct a systematic review of the published data about the current indications in clinical practice for the use of positron emission tomography (PET) or PET/computed tomography (PET/CT) using either Carbon-11 (11C) or Fluorine-18 (18F) choline tracer in brain tumours.
Methods
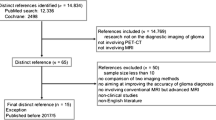
A comprehensive literature search of PubMed until April 30, 2016 with the Mesh terms: ‘‘positron emission tomography’’, ‘‘choline’’, and ‘‘brain neoplasm’’ was first performed. On a second step, the references of the retrieved articles were also screened, adding any relevant publications about the subject.
Results
A total of 15 articles corresponding to 453 patients with brain lesions (mostly gliomas) were included for the analysis, successfully imaging brain tumours for the following indications: diagnosis and tumour characterisation; biopsy guide; treatment planning; differential diagnosis of recurrence or radiation necrosis; and therapy response assessment and prognosis. In addition, other brain lesions have been imaged by PET choline, such as meningiomas and metastasis. PET or PET/CT with radiolabelled choline must be considered as an emerging procedure for the evaluation of brain tumours. Since choline has a low physiological uptake, it provides precise images with a very good tumour-to-background ratio, especially in lesions with disruption of the blood–brain barrier.
Conclusions
Even though the small population and heterogeneity of analyzed studies precluded performing a meta-analysis, the exposed results in this review support the use of choline in the aforementioned indications based on its availability, but larger studies are needed to better validate its use.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Galldiks N, Langen K-J, Pope WB (2015) From the clinician’s point of view—What is the status quo of positron emission tomography in patients with brain tumors? Neuro-Oncol 17:1434–1444. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nov118
Galldiks N, Langen KJ (2015) Applications of PET imaging of neurological tumors with radiolabeled amino acids. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 59:70–82
Fan GG, Deng QL, Wu ZH, Guo QY (2006) Usefulness of diffusion/perfusion-weighted MRI in patients with non-enhancing supratentorial brain gliomas: a valuable tool to predict tumour grading? Br J Radiol 79:652–658. doi:10.1259/bjr/25349497
Weber MA, Zoubaa S, Schlieter M, Jüttler E, Huttner HB, Geletneky K, Ittrich C, Lichy MP, Kroll A, Debus J, Giesel FL, Hartmann M, Essig M (2006) Diagnostic performance of spectroscopic and perfusion MRI for distinction of brain tumors. Neurology 66:1899–1906. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000219767.49705.9c
Braun V, Dempf S, Weller R, Reske S-N, Schachenmayr W, Richter HP (2002) Cranial neuronavigation with direct integration of (11)C methionine positron emission tomography (PET) data—results of a pilot study in 32 surgical cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 144:777–782. doi:10.1007/s00701-002-0942-5 (discussion 782)
Pirotte B, Goldman S, Massager N, David P, Wikler D, Lipszyc M, Salmon I, Brotchi J, Levivier M (2004) Combined use of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose and 11C-methionine in 45 positron emission tomography-guided stereotactic brain biopsies. J Neurosurg 101:476–483. doi:10.3171/jns.2004.101.3.0476
Herholz K, Langen K-J, Schiepers C, Mountz JM (2012) Brain tumors. Semin Nucl Med 42:356–370. doi:10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2012.06.001
Lam WW-C, Ng DC-E, Wong WY, Ong SC, Yu SW-K, See SJ (2011) Promising role of [18F] fluorocholine PET/CT vs [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT in primary brain tumors-early experience. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 113:156–161. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2010.09.012
Gulyás B, Halldin C (2012) New PET radiopharmaceuticals beyond FDG for brain tumor imaging. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 56:173–190
Herholz K, Hölzer T, Bauer B, Schröder R, Voges J, Ernestus RI, Mendoza G, Weber-Luxenburger G, Löttgen J, Thiel A, Wienhard K, Heiss WD (1998) 11C-methionine PET for differential diagnosis of low-grade gliomas. Neurology 50:1316–1322
Coope DJ, Cízek J, Eggers C, Vollmar S, Heiss W-D, Herholz K (2007) Evaluation of primary brain tumors using 11C-methionine PET with reference to a normal methionine uptake map. J Nucl Med 48:1971–1980. doi:10.2967/jnumed.107.043240
Nanni C, Fantini L, Nicolini S, Fanti S (2010) Non FDG PET. Clin Radiol 65:536–548. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2010.03.012
Albert NL, Weller M, Suchorska B, Galldiks N, Soffietti R, Kim MM, la Fougère C, Pope W, Law I, Arbizu J, Chamberlain MC, Vogelbaum M, Ellingson BM, Tonn JC (2016) Response assessment in Neuro-Oncology working group and European Association for Neuro-Oncology recommendations for the clinical use of PET imaging in gliomas. Neuro Oncol. doi:10.1093/neuonc/now058
Weber WA, Wester HJ, Grosu AL, Herz M, Dzewas B, Feldmann HJ, Molls M, Stöcklin G, Schwaiger M (2000) O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine and L-[methyl-11C]methionine uptake in brain tumours: initial results of a comparative study. Eur J Nucl Med 27:542–549
Kwee SA, DeGrado TR, Talbot JN, Gutman F, Coel MN (2007) Cancer imaging with fluorine-18-labeled choline derivatives. Semin Nucl Med 37:420–428. doi:10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2007.07.003
Calabria FF, Barbarisi M, Gangemi V, Grillea G, Cascini GL (2016) Molecular imaging of brain tumors with radiolabeled choline PET. Neurosurg Rev. doi:10.1007/s10143-016-0756-1
Zeisel SH (1981) Dietary choline: biochemistry, physiology, and pharmacology. Annu Rev Nutr 1:95–121. doi:10.1146/annurev.nu.01.070181.000523
Vallabhajosula S (2007) (18)F-labeled positron emission tomographic radiopharmaceuticals in oncology: an overview of radiochemistry and mechanisms of tumor localization. Semin Nucl Med 37:400–419. doi:10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2007.08.004
Podo F (1999) Tumour phospholipid metabolism. NMR Biomed 12:413–439
Nakagami K, Uchida T, Ohwada S, Koibuchi Y, Suda Y, Sekine T, Morishita Y (1999) Increased choline kinase activity and elevated phosphocholine levels in human colon cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res Gann 90:419–424
Ramírez de Molina A, Rodríguez-González A, Gutiérrez R, Martínez-Piñeiro L, Sánchez J, Bonilla F, Rosell R, Lacal J (2002) Overexpression of choline kinase is a frequent feature in human tumor-derived cell lines and in lung, prostate, and colorectal human cancers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 296:580–583
Swinnen JV, Brusselmans K, Verhoeven G (2006) Increased lipogenesis in cancer cells: new players, novel targets. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 9:358–365. doi:10.1097/01.mco.0000232894.28674.30
Jackowski S (1994) Coordination of membrane phospholipid synthesis with the cell cycle. J Biol Chem 269:3858–3867
Ackerstaff E, Pflug BR, Nelson JB, Bhujwalla ZM (2001) Detection of increased choline compounds with proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy subsequent to malignant transformation of human prostatic epithelial cells. Cancer Res 61:3599–3603
Swanson MG, Vigneron DB, Tabatabai ZL, Males RG, Schmitt L, Carroll PR, James JK, Hurd RE, Kurhanewicz J (2003) Proton HR-MAS spectroscopy and quantitative pathologic analysis of MRI/3D-MRSI-targeted postsurgical prostate tissues. Magn Reson Med 50:944–954. doi:10.1002/mrm.10614
Bhakoo KK, Williams SR, Florian CL, Land H, Noble MD (1996) Immortalization and transformation are associated with specific alterations in choline metabolism. Cancer Res 56:4630–4635
Roivainen A, Forsback S, Grönroos T, Lehikoinen P, Kähkönen M, Sutinen E, Minn H (2000) Blood metabolism of [methyl-11C]choline; implications for in vivo imaging with positron emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med 27:25–32
Hara T, Yuasa M, Yoshida H (1997) Automated synthesis of fluorine-18 labeled choline analogue 2-fluoroethyl-dimethyl-2-oxyethylammonium. J Nucl Med 38(suppl):44P
DeGrado TR, Coleman RE, Wang S, Baldwin SW, Orr MD, Robertson CN, Polascik TJ, Price DT (2001) Synthesis and evaluation of 18F-labeled choline as an oncologic tracer for positron emission tomography: initial findings in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 61:110–117
DeGrado TR, Baldwin SW, Wang S, Orr MD, Liao RP, Friedman HS, Reiman R, Price DT, Coleman RE (2001) Synthesis and evaluation of (18)F-labeled choline analogs as oncologic PET tracers. J Nucl Med 42:1805–1814
Mertens K, Slaets D, Lambert B, Acou M, De Vos F, Goethals I (2010) PET with (18)F-labelled choline-based tracers for tumour imaging: a review of the literature. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37:2188–2193. doi:10.1007/s00259-010-1496-z
Haroon A, Zanoni L, Celli M, Zakavi R, Beheshti M, Langsteger W, Fanti S, Emberton M, Bomanji J (2015) Multicenter study evaluating extraprostatic uptake of 11C-choline, 18F-methylcholine, and 18F-ethylcholine in male patients: physiological distribution, statistical differences, imaging pearls, and normal variants. Nucl Med Commun 36:1065–1075. doi:10.1097/MNM.0000000000000372
Calabria F, Gallo G, Schillaci O, Cascini GL (2015) Bio-distribution, imaging protocols and diagnostic accuracy of PET with tracers of lipogenesis in imaging prostate cancer: a comparison between 11C-Choline, 18FFluoroethylcholine and 18F-Methylcholine. Curr Pharm Des 21:4738–4747
Kirienko M, Sollini M, Lopci E, Versari A, Chiti A (2015) Applications of PET imaging with radiolabelled choline (11C/18F-choline). Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 59:83–94
Talbot J-N, Gutman F, Fartoux L, Grange J-D, Ganne N, Kerrou K, Grahek D, Montravers F, Poupon R, Rosmorduc O (2006) PET/CT in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma using [(18)F]fluorocholine: preliminary comparison with [(18)F]FDG PET/CT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 33:1285–1289. doi:10.1007/s00259-006-0164-9
Cassou-Mounat T, Balogova S, Nataf V, Calzada M, Huchet V, Kerrou K, Devaux J-Y, Mohty M, Talbot J-N, Garderet L (2016) 18F-fluorocholine versus 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose for PET/CT imaging in patients with suspected relapsing or progressive multiple myeloma: a pilot study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. doi:10.1007/s00259-016-3392-7
Spaeth N, Wyss MT, Pahnke J, Biollaz G, Lutz A, Goepfert K, Westera G, Treyer V, Weber B, Buck A (2006) Uptake of 18F-fluorocholine, 18F-fluoro-ethyl-L: -tyrosine and 18F-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose in F98 gliomas in the rat. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 33:673–682. doi:10.1007/s00259-005-0045-7
Wyss MT, Spaeth N, Biollaz G, Pahnke J, Alessi P, Trachsel E, Treyer V, Weber B, Neri D, Buck A (2007) Uptake of 18F-Fluorocholine, 18F-FET, and 18F-FDG in C6 gliomas and correlation with 131I-SIP(L19), a marker of angiogenesis. J Nucl Med 48:608–614
Geldenhuys WJ, Allen DD (2012) The blood–brain barrier choline transporter. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem 12:95–99
Spaeth N, Wyss MT, Weber B, Scheidegger S, Lutz A, Verwey J, Radovanovic I, Pahnke J, Wild D, Westera G, Weishaupt D, Hermann DM, Kaser-Hotz B, Aguzzi A, Buck A (2004) Uptake of 18F-fluorocholine, 18F-fluoroethyl-l-tyrosine, and 18F-FDG in acute cerebral radiation injury in the rat: implications for separation of radiation necrosis from tumor recurrence. J Nucl Med 45:1931–1938
Mertens K, Ham H, Deblaere K, Kalala J-PO, Van den Broecke C, Slaets D, De Vos F, Goethals I (2012) Distribution patterns of 18F-labelled fluoromethylcholine in normal structures and tumors of the head: a PET/MRI evaluation. Clin Nucl Med 37:e196–e203. doi:10.1097/RLU.0b013e31824c5dd0
Mertens K, Bolcaen J, Ham H, Deblaere K, Van den Broecke C, Boterberg T, De Vos F, Goethals I (2012) The optimal timing for imaging brain tumours and other brain lesions with 18F-labelled fluoromethylcholine: a dynamic positron emission tomography study. Nucl Med Commun 33:954–959. doi:10.1097/MNM.0b013e328355b6f5
Hara T (2002) 11C-choline and 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-d-glucose in tumor imaging with positron emission tomography. Mol Imaging Biol 4:267–273
Phillips B, Ball C, Sackett DL, Badenoch D, Straus S, Haynes B et al (1998) Levels of evidence and grades of recommendation. Centre for evidence-based medicine, Oxford-centre for evidence based medicine: GENERIC
Tian M, Zhang H, Higuchi T, Oriuchi N, Endo K (2004) Oncological diagnosis using (11)C-choline-positron emission tomography in comparison with 2-deoxy-2-[(18)F] fluoro-d-glucose-positron emission tomography. Mol Imaging Biol 6:172–179. doi:10.1016/j.mibio.2004.02.003
Hara T, Kosaka N, Shinoura N, Kondo T (1997) PET imaging of brain tumor with [methyl-11C]choline. J Nucl Med Off Publ Soc Nucl Med 38:842–847
Tian M, Zhang H, Oriuchi N, Higuchi T, Endo K (2004) Comparison of 11C-choline PET and FDG PET for the differential diagnosis of malignant tumors. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 31:1064–1072. doi:10.1007/s00259-004-1496-y
Shinoura N, Nishijima M, Hara T, Haisa T, Yamamoto H, Fujii K, Mitsui I, Kosaka N, Kondo T, Hara T (1997) Brain tumors: detection with C-11 choline PET. Radiology 202:497–503. doi:10.1148/radiology.202.2.9015080
Ohtani T, Kurihara H, Ishiuchi S, Saito N, Oriuchi N, Inoue T, Sasaki T (2001) Brain tumour imaging with carbon-11 choline: comparison with FDG PET and gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging. Eur J Nucl Med 28:1664–1670. doi:10.1007/s002590100620
Utriainen M, Komu M, Vuorinen V, Lehikoinen P, Sonninen P, Kurki T, Utriainen T, Roivainen A, Kalimo H, Minn H (2003) Evaluation of brain tumor metabolism with [11C]choline PET and 1H-MRS. J Neurooncol 62:329–338
Hara T, Kondo T, Hara T, Kosaka N (2003) Use of 18F-choline and 11C-choline as contrast agents in positron emission tomography imaging-guided stereotactic biopsy sampling of gliomas. J Neurosurg 99:474–479. doi:10.3171/jns.2003.99.3.0474
Kato T, Shinoda J, Nakayama N, Miwa K, Okumura A, Yano H, Yoshimura S, Maruyama T, Muragaki Y, Iwama T (2008) Metabolic assessment of gliomas using 11C-methionine, [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose, and 11C-choline positron-emission tomography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1176–1182. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1008
Takenaka S, Shinoda J, Asano Y, Aki T, Miwa K, Ito T, Yokoyama K, Iwama T (2011) Metabolic assessment of monofocal acute inflammatory demyelination using MR spectroscopy and (11)C-methionine-, (11)C-choline-, and (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose-PET. Brain Tumor Pathol 28:229–238. doi:10.1007/s10014-011-0027-3
Fraioli F, Shankar A, Hargrave D, Hyare H, Gaze MN, Groves AM, Alongi P, Stoneham S, Michopoulou S, Syed R, Bomanji JB (2015) 18F-fluoroethylcholine (18F-Cho) PET/MRI functional parameters in pediatric astrocytic brain tumors. Clin Nucl Med 40:e40–e45. doi:10.1097/RLU.0000000000000556
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JPA, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. J Clin Epidemiol 62:e1–e34. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.006
Roelcke U, Bruehlmeier M, Hefti M, Hundsberger T, Nitzsche EU (2012) F-18 choline PET does not detect increased metabolism in F-18 fluoroethyltyrosine-negative low-grade gliomas. Clin Nucl Med 37:e1–e3. doi:10.1097/RLU.0b013e3182336100
Huang Z, Zuo C, Guan Y, Zhang Z, Liu P, Xue F, Lin X (2008) Misdiagnoses of 11C-choline combined with 18F-FDG PET imaging in brain tumours. Nucl Med Commun 29:354–358. doi:10.1097/MNM.0b013e3282f4a21e
Kwee SA, Ko JP, Jiang CS, Watters MR, Coel MN (2007) Solitary brain lesions enhancing at MR imaging: evaluation with fluorine 18 fluorocholine PET. Radiology 244:557–565. doi:10.1148/radiol.2442060898
Li F-M, Nie Q, Wang R-M, Chang SM, Zhao W-R, Zhu Q, Liang Y-K, Yang P, Zhang J, Jia H-W, Fang H-H (2012) 11C-CHO PET in optimization of target volume delineation and treatment regimens in postoperative radiotherapy for brain gliomas. Nucl Med Biol 39:437–442. doi:10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2011.10.003
Tan H, Chen L, Guan Y, Lin X (2011) Comparison of MRI, F-18 FDG, and 11C-choline PET/CT for their potentials in differentiating brain tumor recurrence from brain tumor necrosis following radiotherapy. Clin Nucl Med 36:978–981. doi:10.1097/RLU.0b013e31822f68a6
Li W, Ma L, Wang X, Sun J, Wang S, Hu X (2014) (11)C-choline PET/CT tumor recurrence detection and survival prediction in post-treatment patients with high-grade gliomas. Tumour Biol J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med 35:12353–12360. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2549-x
Takenaka S, Asano Y, Shinoda J, Nomura Y, Yonezawa S, Miwa K, Yano H, Iwama T (2014) Comparison of (11)C-methionine, (11)C-choline, and (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose-PET for distinguishing glioma recurrence from radiation necrosis. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 54:280–289
Gómez-Río M, Testart Dardel N, Santiago Chinchilla A, Rodríguez-Fernández A, Olivares Granados G, Luque Caro R, Zurita Herrera M, Chamorro Santos CE, Lardelli-Claret P, Llamas-Elvira JM (2015) 18F-Fluorocholine PET/CT as a complementary tool in the follow-up of low-grade glioma: diagnostic accuracy and clinical utility. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 42:886–895. doi:10.1007/s00259-015-2997-6
Giovacchini G, Fallanca F, Landoni C, Gianolli L, Picozzi P, Attuati L, Terreni M, Picchio M, Messa C, Fazio F (2009) C-11 choline versus F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose for imaging meningiomas: an initial experience. Clin Nucl Med 34:7–10. doi:10.1097/RLU.0b013e31818f4369
Fallanca F, Giovacchini G, Picchio M, Bettinardi V, Messa C, Fazio F (2009) Incidental detection by [11C]choline PET/CT of meningiomas in prostate cancer patients. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging Off Publ Ital Assoc Nucl Med AIMN Int Assoc Radiopharmacol IAR Sect Soc Radiopharm Chem Biol 53:417–421
Schillaci O, Calabria F, Tavolozza M, Cicciò C, Carlani M, Caracciolo CR, Danieli R, Orlacchio A, Simonetti G (2010) 18F-choline PET/CT physiological distribution and pitfalls in image interpretation: experience in 80 patients with prostate cancer. Nucl Med Commun 31:39–45
Calabria F, Chiaravalloti A, Schillaci O (2014) (18)F-choline PET/CT pitfalls in image interpretation: an update on 300 examined patients with prostate cancer. Clin Nucl Med 39:122–130. doi:10.1097/RLU.0000000000000303
Bertagna F, Bosio G, Pinelli L, Treglia G, Giubbini R (2013) Incidental 11C-choline PET/CT brain uptake due to meningioma in a patient studied for prostate cancer: correlation with MRI and imaging fusion. Clin Nucl Med 38:e435–e437. doi:10.1097/RLU.0b013e31827a22f7
Rottenburger C, Hentschel M, Kelly T, Trippel M, Brink I, Reithmeier T, Meyer PT, Nikkhah G (2011) Comparison of C-11 methionine and C-11 choline for PET imaging of brain metastases: a prospective pilot study. Clin Nucl Med 36:639–642. doi:10.1097/RLU.0b013e3182175840
Morooka M, Ito K, Kubota K, Hasuo K, Okamoto K, Hara T (2011) 11C-choline and F-18 FDG PET/CT images of hemangioblastoma. Clin Nucl Med 36:143–144. doi:10.1097/RLU.0b013e318203bcaf
Ito S, Yokoyama J, Yoshimoto H, Yazawa M, Kazuo K, Hanaguri M, Ohba S, Fujimaki M, Ikeda K (2012) Usefulness of Choline-PET for the detection of residual hemangiopericytoma in the skull base: comparison with FDG-PET. Head Face Med 8:3. doi:10.1186/1746-160X-8-3
Parashar B, Wernicke AG, Rice S, Osborne J, Singh P, Nori D, Vallabhajosula S, Goldsmith S, Chao KSC (2012) Early assessment of radiation response using a novel functional imaging modality—[18F]fluorocholine PET (FCH-PET): a pilot study. Discov Med 14:13–20
Panagiotidis E, Shankar A, Afaq A, Bomanji J (2014) Assessing therapy response of secreting pineal germ cell tumor on simultaneous 18F-choline PET/MRI. Clin Nucl Med 39:e387–e388. doi:10.1097/RLU.0000000000000231
Cascini GL, Restuccia A, De Vincenti T, Manti F, Calabria F (2015) A vascular lesion mimicking a primitive brain tumour in a patient examined by (18)F-choline PET/CT and MRI. Rev Esp Med Nucl E Imagen Mol 34:335–336. doi:10.1016/j.remn.2015.02.003
Tsouana E, Stoneham S, Fersht N, Kitchen N, Gaze M, Bomanji J, Fraioli F, Hargrave D, Shankar A (2015) Evaluation of treatment response using integrated 18F-labeled choline positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging in adolescents with intracranial non-germinomatous germ cell tumours. Pediatr Blood Cancer 62:1661–1663. doi:10.1002/pbc.25538
Li L-F, Taw BB-T, Pu JK-S, Hwang GY-Y, Lui W-M, Leung GK-K (2015) Primary central nervous system natural killer cell lymphoma in a Chinese woman with atypical (11)C-Choline positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance spectrometry findings. World Neurosurg 84(1176):e5–e9. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2015.06.063
Jacob M, Delfort F, Heliette C, Renard D (2016) Brain 18F-choline PET/CT in primary diffuse leptomeningeal melanomatosis. Acta Neurol Belg. doi:10.1007/s13760-015-0586-x
Imperiale A, Bergerat J-P, Saussine C, Abu Eid M, Kehrli P, Namer I-J (2014) Isolated cerebellar metastasis from prostate adenocarcinoma diagnosed by 18F-fluorocholine PET/CT: a rare but not impossible complication. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 41:397–398. doi:10.1007/s00259-013-2577-6
Treglia G, Giovannini E, Di Franco D, Calcagni ML, Rufini V, Picchio M, Giordano A (2012) The role of positron emission tomography using carbon-11 and fluorine-18 choline in tumors other than prostate cancer: a systematic review. Ann Nucl Med 26:451–461. doi:10.1007/s12149-012-0602-7
Giovannini E, Lazzeri P, Milano A, Gaeta MC, Ciarmiello A (2015) Clinical applications of choline PET/CT in brain tumors. Curr Pharm Des 21:121–127
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No financial relationship exists. NT developed this review within the doctoral program of the Granada University (Spain) and was logistically supported by the “Instituto de Investigación Biosanitaria de Granada” (IBS), the FIS-Instituto de Salud Carlos III (PI 13/00539) (FEDER), and the “Fundación para la Investigación Biosanitaria de Andalucía Oriental Alejandro-Otero” (FIBAO), Spain. The authors thank Isabel Del Canto for language style support.
Conflict of interest
Nathalie Testart Dardel, Manuel Gómez-Río, Eva Triviño-Ibáñez, and José Manuel Llamas-Elvira declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Testart Dardel, N., Gómez-Río, M., Triviño-Ibáñez, E. et al. Clinical applications of PET using C-11/F-18-choline in brain tumours: a systematic review. Clin Transl Imaging 5, 101–119 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-016-0200-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-016-0200-0