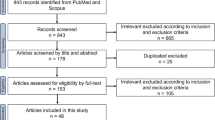
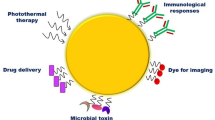
Abstract
Purpose of Review
For more than a century, cancer has been recognized as a fatal disease. Because current medicines are ineffective, certain modern therapeutic options are considered essential. This review provides a comprehensive outline of the biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles (Au-NPs) and their anti-cancer potentiality on cell lines. These gold nanoparticles are highly efficient, biocompatible, and eco-friendly.
Recent Findings
Due to the limitations of traditional cancer treatment, Au-NPs are being utilized. Owing to their unique optical and physical attributes, gold nanoparticles are widely used as promising materials in innumerable fields. Since it is target-specific, it had no undesirable effects. Au-NPs have been created utilizing various synthesis methods such as bottom-up and top-down approaches. Effective formulation of drugs has been a major challenge due to their instability and poor solubility in the vehicle. This issue can be combated by utilizing nano-particle mediated drug delivery. The enormous interfacial area of nano-particles furnishes targeted drug delivery.
Summary
This review gives an outlook on the various formulations of gold nanoparticles by physical, chemical, and biological methods, the mechanism of formation of nanoparticles, and the anticancer activity of gold nanoparticles. Papers from Google Scholar and PubMed Central have been used as references in this review. This paper reports a comparative study on the toxic effects of various nanoparticles in order to emphasize the non-toxicity of gold nanoparticles. Detailed research on gold nanoparticles will pave way for new avenues in cancer treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Jeevanandam J, Barhoum A, Chan YS, Dufresne A, Danquah MK. Review on nanoparticles and nanostructured materials: history, sources, toxicity and regulations. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2018;9(1):1050–74.
Lipomi DJ, Fenning DP, Ong SP, Shah NJ, Tao AR, Zhang L. Exploring Frontiers in Research and Teaching: NanoEngineering and Chemical Engineering at UC San Diego. ACS Nano. 2020;14(8):9203–16.
Nejati K, Dadashpour M, Gharibi T, Mellatyar H, Akbarzadeh A. Biomedical applications of functionalized gold nanoparticles: a review. J Cluster Sci. 2021;3:1–6.
Pratap D, Soni S. Review on the optical properties of nanoparticle aggregates towards the therapeutic applications. Plasmonics. 2021;16:1–9.
Peng J, Liang X. Progress in research on gold nanoparticles in cancer management. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(18):e15311.
Siddique S, Chow JC. Gold nanoparticles for drug delivery and cancer therapy. Appl Sci. 2020;10(11):3824.
Chakraborty T, Saini V, Govila D, Singh G. Four most life threatening urogenital cancer and its management. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2018;9:3166–74.
Roy PS, Saikia BJ. Cancer and cure: A critical analysis. Indian J Cancer. 2016;53(3):441–2.
Surgery,radiation,chemotherapy and immuno therapies are employed for the treatment of cancer. Wang J-J, Lei K-F, Han F. Tumor microenvironment: recent advances in various cancer treatments. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018; 22(12):3855–3864.
Mikelez-Alonso I, Aires A, Cortajarena AL. Cancer nano-immunotherapy from the injection to the target: the role of protein corona. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(2):519.
Chugh H, Sood D, Chandra I, Tomar V, Dhawan G, Chandra R. Role of gold and silver nanoparticles in cancer nano-medicine. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup1):1210–20.
Virmani I, Sasi C, Priyadarshini E, Kumar R, Sharma SK, Singh GP, Pachwarya RB, Paulraj R, Barabadi H, Saravanan M, Meena R. Comparative anticancer potential of biologically and chemically synthesized gold nanoparticles. J Cluster Sci. 2020;31(4):867–76.
Abdussalam-Mohammed W. Comparison of chemical and biological properties of metal nanoparticles (Au, Ag), with metal oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) and their applications. Adv. J. Chem. A 2020;3(2):192–210.
Pathak J, Ahmed H, Singh DK, Pandey A, Singh SP, Sinha RP. Recent developments ingreen synthesis of metal nanoparticles utilizing cyanobacterial cell factories. In Durgesh KT, editor. Nanomaterials in plants, algae and microorganisms. 2019;237–265.
Hamida RS, Ali MA, Redhwan A, Bin-Meferij MM. Cyanobacteria–a promising platform in green nanotechnology: a review on nanoparticles fabrication and their prospective applications. Int J Nanomed. 2020;15:6033.
Perera M, Wijenayaka LA, Siriwardana K, Dahanayake D, de Silva KN. Gold nanoparticle decorated titania for sustainable environmental remediation: green synthesis, enhanced surface adsorption and synergistic photocatalysis. RSC Adv. 2020;10(49):29594–602.
Singh RK, Behera SS, Singh KR, Mishra S, Panigrahi B, Sahoo TR, Parhi PK, Mandal D. Biosynthesized gold nanoparticles as photocatalysts for selective degradation of cationic dye and their antimicrobial activity. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem. 2020;400:112704.
Virgili AH, Laranja DC, Malheiros PS, Pereira MB, Costa TM, de Menezes EW. Nanocomposite film with antimicrobial activity based on gold nanoparticles, chitosan and aminopropylsilane. Surf Coat Technol. 2021;415:127086.
O’Connell KC, Monnier JR, Regalbuto JR. The curious relationship of sintering to activity in supported gold catalysts for the hydrochlorination of acetylene. Appl Catal B. 2018;225:264–72.
Wang X, Almoallim HS, Cui Q, Alharbi SA, Yang H. In situ decorated Au NPs on chitosan-encapsulated Fe3O4-NH2 NPs as magnetic nanocomposite: investigation of its anti-colon carcinoma, anti-gastric cancer and anti-pancreatic cancer. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;171:198–207.
Yu Y, Naik SS, Oh Y, Theerthagiri J, Lee SJ, Choi MY. Lignin-mediated green synthesis of functionalized gold nanoparticles via pulsed laser technique for selective colorimetric detection of lead ions in aqueous media. J Hazard Mater. 2021;420:126585. This article reports the production of functionalized gold nanoparticles can also be used as effective sensors for the rapid and selective detection of Pb2+ ions via the colorimetric analysis using the real environmental samples.
Zhao Y, Ye C, Liu W, Chen R, Jiang X. Tuning the composition of AuPt bimetallic nanoparticles for antibacterial application. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2014;53(31):8127–31.
Slepička P, Slepičková Kasálková N, Siegel J, Kolská Z, Švorčík V. Methods of gold and silver nanoparticles preparation. Materials. 2020;13(1):1.
Lu H, Tang SY, Yun G, Li H, Zhang Y, Qiao R, Li W. Modular and integrated systems for nanoparticle and microparticle synthesis—a review. Biosensors. 2020;10(11):165.
Swaminathan M, Sharma NK. Antimicrobial Activity of the engineered nanoparticles used as coating agents. Handbook of ecomaterials. Cham: Springer International Publishing. 2019: pp 549–63.
Elahi N, Kamali M, Baghersad MH. Recent biomedical applications of gold nanoparticles: a review. Talanta. 184:537–556.
Khan T, Ullah N, Khan MA, Nadhman A. Plant-based gold nanoparticles; a comprehensive review of the decade-long research on synthesis, mechanistic aspects and diverse applications. Adv Coll Interface Sci. 2019;272:102017.
Dong J, Carpinone PL, Pyrgiotakis G, Demokritou P, Moudgil BM. Synthesis of precision gold nanoparticles using Turkevich method. Kona Powder Part J. 2020;37:224–32.
Wang Y, Ge X, Zhang W. Effect of reference region size on strain measurements using geometrical phase analysis. J Microsc. 2020;278(1):49–56.
Tran M, DePenning R, Turner M, Padalkar S. Effect of citrate ratio and temperature on gold nanoparticle size and morphology. Mater Res Express. 2016;3(10):105027.
Ghosh S, Manna L. The many “facets” of halide ions in the chemistry of colloidal inorganic nanocrystals. Chem Rev. 2018;118(16):7804–64.
Chen W, Shen J, Chen S, Yan J, Zhang N, Zheng K, Liu X. Synthesis of graphene quantum dot-stabilized gold nanoparticles and their application. RSC Adv. 2019;9(37):21215–9.
Liu Y. Alkanethiolate-protected silver nanoparticles and clusters: characterization, synthesis optimization and formation mechanism investigation. Georgetown University; 2016. http://hdl.handle.net/10822/1043820.
Thangamani N, Bhuvaneshwari N. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Simarouba glauca leaf extract and their biological activity of micro-organism. Chem Phys Lett. 2019;732:136587.
• El-Batal AI, Abd Elkodous M, El-Sayyad GS, Al-Hazmi NE, Gobara M, Baraka A. Gum Arabic polymer-stabilized and Gamma rays-assisted synthesis of bimetallic silver-gold nanoparticles: powerful antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities against pathogenic microbes isolated from diabetic foot patients. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;165:169–86. This study proves that Ag-Au NPs exhibited the highest antimicrobial performance against B. subtilis (14.30 mm ZOI) followed by E. coli (12.50 mm ZOI) and C. tropicalis (11.90 mm ZOI). In addition, Ag-Au NPs were able to inhibit the biofilm formation by 99.64%, 94.15%, and 90.79% against B. subtilis, E. coli, and C. tropicalis, respectively.
Rajasekar T, Karthika K, Muralitharan G, Maryshamya A, Sabarika S, Anbarasu S, Revathy K, Prasannabalaji N, Kumaran S. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using extracellular metabolites of fish gut microbes and their antimicrobial properties. Braz J Microbiol. 2020;51:957–67.
Miyagawa Y, Tsatsuryan A, Haraguchi T, Shcherbakov I, Akitsu T. Photochemical reduction of Cr (VI) compounds by amino acid Schiff base copper complexes with a hydroxyl group and titanium oxide composites in aqueous solutions. New J Chem. 2020;44(38):16665–74.
Belloni J, Marignier JL, Mostafavi M. Mechanisms of metal nanoparticles nucleation and growth studied by radiolysis. Radiat Phys Chem. 2020;169:107952.
Moshkovich Y, Levy Y, Sher E. Experimental observations of the transition between heterogeneous to homogeneous nucleation regimes in flash-boiling atomization. Int J Multiphase Flow. 2021;134:103476.
Whitehead CB, Özkar S, Finke RG. LaMer’s 1950 model of particle formation: a review and critical analysis of its classical nucleation and fluctuation theory basis, of 10.1007/s40495-022-00290-z competing models and mechanisms for phase-changes and particle formation, and then of its application to silver halide, semiconductor, metal, and metal-oxide nanoparticles. Mater Adv. 2021: 1.
Bachheti RK, Sharma A, Bachheti A, Husen A, Shanka GM, Pandey DP. Nanomaterials from various forest tree species and their biomedical applications. In: Nanomaterials for Agriculture and Forestry Applications. Elsevier; 2020. p. 81–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-817852-2.00004-4.
Patil MP, Kim G. Eco-friendly approach for nanoparticles synthesis and mechanism behind antibacterial activity of silver and anticancer activity of gold nanoparticles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017;101(1):79–92.
Demirbas A, Büyükbezirci K, Celik C, Kislakci E, Karaagac Z, Gokturk E, Kati A, Cimen B, Yilmaz V, Ocsoy I. Synthesis of long-term stable gold nanoparticles benefiting from red raspberry (Rubus idaeus), strawberry (Fragaria ananassa), and blackberry (Rubus fruticosus) extracts–gold ion complexation and investigation of reaction conditions. ACS Omega. 2019;4(20):18637–44.
Wang Y, Xu J, Shi L, Yang H. Recent advances in the antilung cancer activity of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(12):8951–7.
Unal IS, Demirbas A, Onal I, Ildiz N, Ocsoy I. One step preparation of stable gold nanoparticle using red cabbage extracts under UV light and its catalytic activity. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2020;1(204):111800.
Wang L, Xu J, Yan Y, Liu H, Karunakaran T, Li F. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles from Scutellaria barbata and its anticancer activity in pancreatic cancer cell (PANC-1). Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):1617–27.
Akrami M, Samimi S, Alipour M, Bardania H, Ramezanpour S, Najafi N, Hosseinkhani S, Kamankesh M, Haririan I, Hassanshahi F. Potential anticancer activity of a new pro-apoptotic peptide–thioctic acid gold nanoparticle platform. Nanotechnology. 2021;32(14):145101.
Chen X, Han W, Zhao X, Tang W, Wang F. Epirubicin-loaded marine carrageenan oligosaccharide capped gold nanoparticle system for pH-triggered anticancer drug release. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1.
Rajeshkumar S. Anticancer activity of eco-friendly gold nanoparticles against lung and liver cancer cells. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2016;14(1):195–202.
Patil MP, Kang MJ, Niyonizigiye I, Singh A, Kim JO, Seo YB, Kim GD. Extracellular synthesis of gold nanoparticles using the marine bacterium Paracoccus haeundaensis BC74171T and evaluation of their antioxidant activity and antiproliferative effect on normal and cancer cell lines. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;183:110455.
Hussein SI, Sultan AS, Yaseen NY. Study the effect of gold nanoparticles on cancer and normal cells (in vitro study). J Med Genet. 2016;9(2):144–9.
Balashanmugam P, Durai P, Balakumaran MD, Kalaichelvan PT. Phytosynthesized gold nanoparticles from C. roxburghii DC. leaf and their toxic effects on normal and cancer cell lines. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol. 2016;165:163–73.
Yaqub A, Anjum KM, Munir A, Mukhtar H, Khan WA. Evaluation of acute toxicity and effects of sub-acute concentrations of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO-NPs) on hematology, selected enzymes and histopathology of liver and kidney in Mus musculus. Indian J Anim Res. 2018;52(1):92–8.
Majewski M, Ognik K, Juśkiewicz J. Copper nanoparticles modify the blood plasma antioxidant status and modulate the vascular mechanisms with nitric oxide and prostanoids involved in Wistar rats. Pharmacol Rep. 2019;71(3):509–16.
Zhang CH, Wang Y, Sun QQ, Xia LL, Hu JJ, Cheng K, Wang X, Fu XX, Gu H. Copper nanoparticles show obvious in vitro and in vivo reproductive toxicity via ERK mediated signaling pathway in female mice. Int J Biol Sci. 2018;14(13):1834.
Luo J, Hao S, Zhao L, Shi F, Ye G, He C, Lin J, Zhang W, Liang H, Wang X, Guo H. Oral exposure of pregnant rats to copper nanoparticles caused nutritional imbalance and liver dysfunction in fetus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020;206:111206.
Bahadar H, Maqbool F, Niaz K, Abdollahi M. Toxicity of nanoparticles and an overview of current experimental models. Iran Biomed J. 2016;20(1):1.
Fadda LM, Ali HM, Mohamed AM, Hagar H. Prophylactic administration of carnosine and melatonin abates the incidence of apoptosis, inflammation, and DNA damage induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in rat livers. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2020;27(16):19142–50.
Wani MR, Shadab GG. Titanium dioxide nanoparticle genotoxicity: a review of recent in vivo and in vitro studies. Toxicol Ind Health. 2020;36(7):514–30.
Smallcombe CC, Harford TJ, Linfield DT, Lechuga S, Bokun V, Piedimonte G, Rezaee F. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles exaggerate respiratory syncytial virus-induced airway epithelial barrier dysfunction. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020;319(3):L481–96.
Subhan F, Aslam S, Yan Z, Ahmad A, Etim UJ. Fabrication of 3-D confined spaces with Au NPs: superior dispersion and catalytic activity. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019;540:371–81.
Karimi-Maleh H, Fallah Shojaei A, Karimi F, Tabatabaeian K, Shakeri S. Au nanoparticle loaded with 6-thioguanine anticancer drug as a new strategy for drug delivery. J Nanostruct. 2018;8(4):217–424.
Nasrollahzadeh M, Sajadi SM. Preparation of Au nanoparticles by Anthemis xylopoda flowers aqueous extract and their application for alkyne/aldehyde/amine A 3-type coupling reactions. RSC Adv. 2015;5(57):46240–6.
Sumesh KR, Kanthavel K. Green synthesis of aluminium oxide nanoparticles and its applications in mechanical and thermal stability of hybrid natural composites. J Polym Environ. 2019;27(10):2189–200.
Temple TL, Bagnall DM. Optical properties of gold and aluminium nanoparticles for silicon solar cell applications. J Appl Phys. 2011;109(8):084343.
Mukherjee A, Sadiq IM, Prathna TC, Chandrasekaran N. Antimicrobial activity of aluminium oxide nanoparticles for potential clinical applications. In book Science against microbial pathogens: communicating current research and technological advances. Publisher: Formatex Research Center 2011;1:245–251.
Barron AR. The interaction of carboxylic acids with aluminium oxides: Journeying from a basic understanding of alumina nanoparticles to water treatment for industrial and humanitarian applications. Dalton Trans. 2014;43(22):8127–43.
Zhang S, Liang X, Gadd GM, Zhao Q. A sol–gel based silver nanoparticle/polytetrafluorethylene (AgNP/PTFE) coating with enhanced antibacterial and anti-corrosive properties. Appl Surf Sci. 2021;535:147675.
Vijayakumar S, Divya M, Vaseeharan B, Chen J, Biruntha M, Silva LP, Durán-Lara EF, Shreema K, Ranjan S, Dasgupta N. Biological compound capping of silver nanoparticle with the seed extracts of blackcumin (Nigella sativa): a potential antibacterial, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater. 2021;31(2):624–35.
Sadowski Z. Biosynthesis and application of silver and gold nanoparticles. Silver Nanoparticles. 2010;1:257–76.
Amirsadeghi A, Jafari A, Hashemi SS, Kazemi A, Ghasemi Y, Derakhshanfar A, Shahbazi MA, Niknezhad SV. Sprayable antibacterial Persian gum-silver nanoparticle dressing for wound healing acceleration. Mater Today Commun. 2021;27:102225. This article reports the high potential of dressings that were developed by in situ formation of Ag-nanoparticles using Persian gum as a carbohydrate polymer for wound repair.
Dnyanmote S, Alio J, Dnyanmote A. Nano silver coated surgical apparels and phaco needles for safety of ophthalmic surgeons in view of COVID-19 pandemic. Open J. Opthalmol. 2021;15:1874–3641.
Pinheiro MC, Carneiro JA, Pithon MM, Martinez EF. Thermopolymerized acrylic resin immersed or incorporated with silver nanoparticle: microbiological, cytotoxic and mechanical Effect. Mater Res. 2021;5:24.
Lin HC, Ho MY, Tsen CM, Huang CC, Wu CC, Huang YJ, Hsiao IL, Chuang CY. From the cover: comparative proteomics reveals silver nanoparticles alter fatty acid metabolism and amyloid beta clearance for neuronal apoptosis in a triple cell coculture model of the blood–brain barrier. Toxicol Sci. 2017;158(1):151–63.
Tang J, Xiong L, Wang S, Wang J, Liu L, Li J, Wan Z, Xi T. Influence of silver nanoparticles on neurons and blood-brain barrier via subcutaneous injection in rats. Appl Surface Sci. 2008;255(2):502–4.
Lin HC, Ho MY, Tsen CM, Huang CC, Wu CC, Huang YJ, Hsiao IL, Chuang CY. From the cover: comparative proteomics reveals silver nanoparticles alter fatty acid metabolism and amyloid beta clearance for neuronal apoptosis in a triple cell coculture model of the blood–brain barrier. Toxicol Sci. 2017;158(1):151–63.
Vergara-Llanos D, Koning T, Pavicic MF, Bello-Toledo H, Díaz-Gómez A, Jaramillo A, Melendrez-Castro M, Ehrenfeld P, Sánchez-Sanhueza G. Antibacterial and cytotoxic evaluation of copper and zinc oxide nanoparticles as a potential disinfectant material of connections in implant provisional abutments: an in-vitro study. Arch Oral Biol. 2021;122:105031. This study evaluates the antibacterial activity against mono and multispecies bacterial models and the cytotoxic effects of zinc oxide and copper nanoparticles in cell cultures of human gingival fibroblasts.
Valdiglesias V, Fernández-Bertólez N, Lema-Arranz C, Rodríguez-Fernández R, Pásaro E, Reis AT, Teixeira JP, Costa C, Laffon B. Salivary leucocytes as in vitro model to evaluate nanoparticle-induced DNA damage. Nanomaterials. 2021;11(8):1930.
Marino M, Gigliotti L, Møller P, Riso P, Porrini M, Del Bo C. Impact of 12-month cryopreservation on endogenous DNA damage in whole blood and isolated mononuclear cells evaluated by the comet assay. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):1–1. This study evaluates the impact of storage at different time-points on the levels of strand breaks and formamidopyrimidine DNA glycosylase sensitive sites in isolated PBMCs and whole blood.
Vangijzegem T, Stanicki D, Laurent S. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for drug delivery: applications and characteristics. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019;16(1):69–78.
Dadfar SM, Roemhild K, Drude NI, von Stillfried S, Knüchel R, Kiessling F, Lammers T. Iron oxide nanoparticles: diagnostic, therapeutic and theranostic applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;138:302–25.
Bietenbeck M, Florian A, Faber C, Sechtem U, Yilmaz A. Remote magnetic targeting of iron oxide nanoparticles for cardiovascular diagnosis and therapeutic drug delivery: where are we now? Int J Nanomed. 2016;11:3191.
Tong S, Zhu H, Bao G. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for disease detection and therapy. Mater Today. 2019;1(31):86–99.
Marcu A, Pop S, Dumitrache F, Mocanu M, Niculite CM, Gherghiceanu M, Lungu CP, Fleaca C, Ianchis R, Barbut A, Grigoriu C. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as drug delivery system in breast cancer. Appl Surf Sci. 2013;15(281):60–5.
Mahmoudi M, Sant S, Wang B, Laurent S, Sen T. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): development, surface modification and applications in chemotherapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63(1–2):24–46.
Martinkova P, Brtnicky M, Kynicky J, Pohanka M. Iron oxide nanoparticles: innovative tool in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(5):1700932.
Morovati A, Ahmadian S, Jafary H. Cytotoxic effects and apoptosis induction of cisplatin-loaded iron oxide nanoparticles modified with chitosan in human breast cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep. 2019;46(5):5033–9.
Ansari MO, Parveen N, Ahmad MF, Afrin S, Rahman Y, Jameel S, Khan YA, Siddique HR, Tabish M, Shadab GG. Evaluation of DNA interaction, genotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by iron oxide nanoparticles both in vitro and in vivo: attenuation by thymoquinone. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1–4.
Fatehbasharzad P, Fatehbasharzad P, Sillanpää M, Shamsi Z. Investigation of bioimpacts of metallic and metallic oxide nanostructured materials: size, shape, chemical composition, and surface functionality: a review. Part Part Syst Charact. 2021:2100112. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppsc.202100112.
Podila R, Brown JM. Toxicity of engineered nanomaterials: a physicochemical perspective. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2013;27(1):50–5.
Iswarya V, Manivannan J, De A, Paul S, Roy R, Johnson JB, Kundu R, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A, Mukherjee A. Surface capping and size-dependent toxicity of gold nanoparticles on different trophic levels. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2016;23(5):4844–58.
Katsumiti A, Arostegui I, Oron M, Gilliland D, Valsami-Jones E, Cajaraville MP. Cytotoxicity of Au, ZnO and SiO2 NPs using in vitro assays with mussel hemocytes and gill cells: relevance of size, shape and additives. Nanotoxicology. 2016;10(2):185–93.
Khan MY, Roy M. Synthesis, Limitation and application of gold nanoparticles in treatment of cancerous cell. Int J Sci Res Multidiscip Stud. 2019;5(9):8–14.
Hamed MM, Abdelftah LS. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using marine Streptomyces griseus isolate (M8) and evaluating its antimicrobial and anticancer activity. Egypt J Aquat Biol Fish. 2019;23(1):173–84.
Munawer U, Raghavendra VB, Ningaraju S, Krishna KL, Ghosh AR, Melappa G, Pugazhendhi A. Biofabrication of gold nanoparticles mediated by the endophytic Cladosporium species: photodegradation, in vitro anticancer activity and in vivo antitumor studies. Int J Pharm. 2020;588:119729.
Govindaraju K, Vasantharaja R, Uma Suganya KS, Anbarasu S, Revathy K, Pugazhendhi A, Karthickeyan D, Singaravelu G. Unveiling the anticancer and antimycobacterial potentials of bioengineered gold nanoparticles. Process Biochem. 2020;96:213–9.
Balasubramanian S, Kala SMJ, Pushparaj TL. Biogenic synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Jasminum auriculatum leaf extract and their catalytic, antimicrobial and anticancer activities. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2020;57:101620.
Sunderam V, Thiyagarajan D, Lawrence AV, Mohammed SSS, Selvaraj A. In-vitro antimicrobial and anticancer properties of green synthesized gold nanoparticles using Anacardium occidentale leaves extract. Saudi J Boil Sci. 2019;26(3):455–9.
Wu T, Duan X, Hu C, Wu C, Chen X, Huang J, Liu J, Cui S. Synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles from Abies spectabilis extract and its anticancer activity on bladder cancer T24 cells. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):512–23.
Lokina S, Narayanan V. Antimicrobial and anticancer activity of gold nanoparticles synthesized from grapes fruit extract. Chem Sci Trans. 2013;2(S1):S105–10.
Wang L, Xu J, Yan Y, Liu H, Li F. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles from leaf Panaxnotoginseng and its anticancer activity in pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cell lines. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):1216–23.
Mmola M, Roes-Hill ML, Durrell K, Bolton JJ, Sibuyi N, Meyer ME, Beukes DR, Antunes E. Enhanced Antimicrobial and anticancer activity of silver and gold nanoparticles synthesised using sargassum incisifolium aqueous extracts. Molecules. 2016;21(12):1633.
Yarramala DS, Doshi S, Rao CP. Green synthesis, characterization and anticancer activity of luminescent gold nanoparticles capped with apo-α-lactalbumin. RSC Adv. 2015;5(41):32761–7.
Shah M, Badwaik V, Kherde Y, Waghwani HK, Modi T, Aguilar ZP, Rodgers H, Hamilton W, Marutharaj T, Webb C, Lawrenz MB. Gold nanoparticles: various methods of synthesis and antibacterial applications. Front Biosci. 2014;19(8):1320–44.
Jadoun S, Arif R, Jangid NK, Meena RK. Green synthesis of nanoparticles using plant extracts: a review. Environ Chem Lett. 2021;19(1):355–74.
Malik P, Mukherjee TK. Recent advances in gold and silver nanoparticle based therapies for lung and breast cancers. Int J Pharm. 2018;553(1–2):483–509.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology for facilitating this study.
Funding
This work was funded by ICMR (35/14/2020-NAN/BMS) and DST WOS-B (2020–4964), the Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Naturopathy, Nanotechnology, Nutraceuticals, and Immunotherapy in Cancer Research
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akif S, M., Unnikrishnan, S. & Ramalingam, K. Gold Nanoparticles: Potential Tool for the Treatment of Human Cancer Cells. Curr Pharmacol Rep 8, 300–311 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40495-022-00290-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40495-022-00290-z