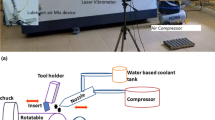
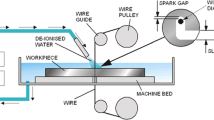
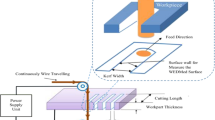
Abstract
In this present study, the effect of processing parameters on cutting width (kerf), material removal rate (MRR), Ra (arithmetic mean deviation), Rq (root mean square deviation) and Rz (maximum height) values as a result of wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) of Ti-6Al-4V alloy was investigated. It is aimed to determine the optimum values of the cutting parameters to obtain the highest MRR value with the lowest kerf, Ra, Rq, Rz. Cutting experiments were carried out using three different voltages (46, 56, 66 V), three different dielectric fluid pressures (10, 12, 14 kg/cm2) and three different wire feed rates (8, 10, 12 m/min). The parameters used in the experiments were designed according to the Taguchi L9 (33) orthogonal array in order to reduce the experimental cost. Gray Relational Analysis (GRA), one of the multi-criteria decision-making methods, has been applied to optimize the machining parameters in the cutting process with the wire erosion machine. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to determine the effect percentages of the processing parameters. By using the data obtained from the experiments, the prediction study of the experimental data was carried out with the Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) model. High correlation coefficients were obtained in the regression model created using the ANN technique, and it was observed that both models were suitable and usable to predict the answers. As a result of GRA, the most ideal sequence was determined as VG1LQ1WS1. Ideal conditions were determined as 46 V voltage, 10 kg/cm2 dielectric fluid pressure and 8 m/min wire feed rate. Using the optimum machining parameters, an improvement of 4.22%, 54.65%, 28.77%, 31.94% and 35.24% was obtained for kerf, MRR, Ra, Rq, and Rz, respectively. As for the results obtained from ANOVA the contribution rate of the voltage was 72.18%. However, the effect of wire feed rate and dielectric fluid pressure was not statistically significant.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pramanik A et al (2019) Optimizing dimensional accuracy of titanium alloy features produced by wire electrical discharge machining. Mater Manuf Process 34(10):1083–1090. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2019.1628259
Divya M, Sateesh N, Subbiah R (2020) Review on multi objective optimization of wire cut EDM process parameters using grey relational analysis. Mater Today Proc 26:3124–3130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.02.645
Datta S, Mahapatra S (2010) Modeling, simulation and parametric optimization of wire EDM process using response surface methodology coupled with grey-Taguchi technique. Int J Eng Sci Technol 2(5):162–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/10.4314/ijest.v2i5.60144
Manjaiah M, Narendranath S, Basavarajappa S (2014) A review on machining of titanium based alloys using EDM and WEDM. Rev Adv Mater Sci 36(2):89–111
Ishfaq K et al (2022) EDM of Ti6Al4V under nano-graphene mixed dielectric: a detailed roughness analysis. Int J Adv Manuf Technol:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09207-y
Ishfaq K et al (2022) EDM of Ti-6Al-4V under nano-graphene mixed dielectric: a detailed investigation on axial and radial dimensional overcuts. Nanomaterials 12(3):432. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030432
Rajhi W et al (2021) A contribution to numerical prediction of surface damage and residual stresses on die-sinking EDM of Ti6Al4V. J Manuf Process 68:1458–1484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.06.056
Ilani MA, Khoshnevisan M (2021) Study of surfactant effects on intermolecular forces (IMF) in powder-mixed electrical discharge machining (EDM) of Ti-6Al-4V. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 116(5):1763–1782. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07569-3
Ahmed N et al (2019) EDM of Ti-6Al-4V: electrode and polarity selection for minimum tool wear rate and overcut. Mater Manuf Process 34(7):769–778. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2019.1594278
Devarasiddappa D, Chandrasekaran M (2020) Experimental investigation and optimization of sustainable performance measures during wire-cut EDM of Ti-6Al-4V alloy employing preference-based TLBO algorithm. Mater Manuf Process 35(11):1204–1213. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2020.1762211
Ahmed N et al (2019) Machinability of titanium alloy through electric discharge machining. Mater Manuf Process 34(1):93–102. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2018.1532092
Ahmed N et al (2019) The potentiality of sinking EDM for micro-impressions on Ti-6Al-4V: keeping the geometrical errors (axial and radial) and other machining measures (tool erosion and work roughness) at minimum. Sci Rep 9(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52855-6
Ishfaq K et al (2020) A comprehensive analysis of the effect of graphene-based dielectric for sustainable electric discharge machining of Ti-6Al-4V. Materials 14(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010023
Banu A, Ali MY (2016) Electrical discharge machining (EDM): a review. Int J Eng Mater Manuf 1(1):3–10. https://doi.org/10.26776/ijemm.01.01.2016.02
Saedon J et al (2014) Multi-objective optimization of titanium alloy through orthogonal array and grey relational analysis in WEDM. Procedia Technol 15:832–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2014.09.057
Çaydaş U, Hasçalık A (2004) CNC tel erozyon tezgahlarında farklı malzemelerin işlenebilirliğinin araştırılması. Kutahya Dumlupınar University Journal of the Institute of Science and Technology 006:201–214
Boyer E, Gall L (1992) Nontraditional machining processes. Metals handbook, desk edition. American Society for Metals Park, Ohio, p 44073
Kuş A, Motorcu AR (2017) Nikel esaslı waspaloy alaşımının tel erozyon yöntemiyle işlenmesinde Taguchi metodu ile yüzey pürüzlülüğü için optimum kesme parametrelerinin tahmini. J Faculty Eng Archit Gazi Univ 32(1):195–204
Saini PK, Verma M (2014) Experimental investigation of wire-EDM process parameters on MRR of Ti-6al-4v alloy. Int J Innov Technol Explor Eng 4(5):16–20
Patel VD et al (2014) Review of wire-cut EDM process on titanium alloy. Int J Eng Res Appl 4(12):112–121
Sivaprakasam P, Hariharan P, Gowri S (2014) Modeling and analysis of micro-WEDM process of titanium alloy (Ti–6Al–4V) using response surface approach. Eng Sci Technoll 17(4):227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2014.06.004
Gong Y et al (2017) Experimental study on surface integrity of Ti-6Al-4V machined by LS-WEDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 88(1–4):197–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/10.1007/s00170-016-8784-0
Kuriakose S, Shunmugam M (2004) Characteristics of wire-electro discharge machined Ti6Al4V surface. Mater Lett 58(17–18):2231–2237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2004.01.037
Devarajaiah D, Muthumari C (2018) Evaluation of power consumption and MRR in WEDM of Ti–6Al–4V alloy and its simultaneous optimization for sustainable production. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 40(8):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-018-1318-y
Ramamurthy A et al (2015) Performance analysis of wire electrodes on machining Ti-6Al-4V alloy using electrical discharge machining process. Mach Sci Technol 19(4):577–592. https://doi.org/10.1080/10910344.2015.1085314
Mouralova K et al (2018) Analysis of surface and subsurface layers after WEDM for Ti-6Al-4V with heat treatment. Measurement 116:556–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2017.11.053
Aspinwall D et al (2008) Workpiece surface roughness and integrity after WEDM of Ti–6Al–4V and Inconel 718 using minimum damage generator technology. CIRP Ann 57(1):187–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2008.03.054
Pramanik A, Basak A, Prakash C (2019) Understanding the wire electrical discharge machining of Ti6Al4V alloy. Heliyon 5(4):e01473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01473
Devarasiddappa D, Chandrasekaran M, Arunachalam R (2020) Experimental investigation and parametric optimization for minimizing surface roughness during WEDM of Ti6Al4V alloy using modified TLBO algorithm. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42(3):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-2224-7
Manikandan N et al (2019) Influence of wire-EDM textured conventional tungsten carbide inserts in machining of aerospace materials (Ti–6Al–4V alloy). Mater Manuf Process 34(1):103–111. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2018.1544712
Farooq MU et al (2020) Curved profiles machining of Ti6Al4V alloy through WEDM: investigations on geometrical errors. J Mater Res Technol 9(6):16186–16201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.11.067
Khosrozadeh B, Shabgard M (2017) Effects of hybrid electrical discharge machining processes on surface integrity and residual stresses of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93(5):1999–2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0601-x
Kumar S, Dhanabalan S, Narayanan C (2019) Application of ANFIS and GRA for multi-objective optimization of optimal wire-EDM parameters while machining Ti–6Al–4V alloy. SN Appl Sci 1(4):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0195-z
Das S, Conceptualisation SNJ (2021) Measurement and analysis of molybdenum wire erosion and deformation during wire electric discharge machining of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Measurement:10e9440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109440
Vignesh M, Ramanujam R (2021) Numerical modelling and experimental validation of crater formation in WEDM hybrid turning of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Proc Inst Mech Eng E J Process Mech Eng 235(2):392–404. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954408920964687
Khan SA et al (2021) Exploring the feasibility of novel coated wires in wire EDM of Ti-6Al-4 V aerospace alloy: a case of multi-pass strategy. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 43(5):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-021-02994-7
Zhou Z et al (2021) Experimental study on short electric arc machining of Ti6Al4V in terms of power output characteristics. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 113(3):997–1008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-06683-6
Chakraborty S, Mitra S, Bose D (2021) Experimental investigation on enhancing die corner accuracy during powder mixed wire EDM of Ti6Al4V. Mater Today Proc 38:3097–3102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.09.491
Kumar VU, Raj DS (2021) Performance analysis of tools with rake face textures produced using wire-EDM in turning AISI4340. Mater Manuf Process:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2021.1905826
Prasad AR, Ramji K, Datta G (2014) An experimental study of wire EDM on Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Procedia Mater Sci 5:2567–2576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2014.07.517
Rao PS, Ramji K, Satyanarayana B (2014) Experimental investigation and optimization of wire EDM parameters for surface roughness, MRR and white layer in machining of aluminium alloy. Procedia Mater Sci 5:2197–2206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2014.07.426
Bhatia A, Kumar S, Kumar P (2014) A study to achieve minimum surface roughness in wire EDM. Procedia Mater Sci 5:2560–2566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2014.07.509
Tilekar S, Das SS, Patowari P (2014) Process parameter optimization of wire EDM on aluminum and mild steel by using taguchi method. Procedia Mater Sci 5:2577–2584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2014.07.518
Kuriachen B, Paul J, Mathew J (2012) Modeling of wire electrical discharge machining parameters using titanium alloy (Ti-6AL-4V). Int J Emerg Technol Adv Eng 2(4):377–381
Sharma N et al (2021) Machining of Ti-6Al-4V biomedical alloy by WEDM: investigation and optimization of MRR and Rz using grey-harmony search. World. J Eng
Sharma N et al (2019) Multi-quality characteristics optimisation on WEDM for Ti-6Al-4V using Taguchi-grey relational theory. Int J Mach Mach Mater 21(1–2):66–81
Motorcu AR, Ekici E, Kuş A (2016) Investigation of the WEDM of Al/B4C/gr reinforced hybrid composites using the Taguchi method and response surface methodology. Sci Eng Compos Mater 23(4):435–445
Chakraborty S, Mitra S, Bose D (2021) An investigation on dimensional accuracy and surface topography in powder mixed WEDM using RSM and GRA-PCA. Mater Today Proc 44:1524–1530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.11.734
Parameshwar K, Nandam SR, Thakur DG (2021) Performance evaluation of AE-pulse of wire EDM process on Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al alloy by Taguchi GRA technique. In: IOP conference series: materials science and engineering. IOP Publishing
Negemiya AA, Rajakumar S, Balasubramanian V (2019) Optimization of Ti-6Al-4V/AISI304 diffusion bonding process parameters using RSM and PSO algorithm. Multidiscipline Modeling in Materials and Structures 15(6):1037–1052. https://doi.org/10.1108/MMMS-07-2018-0134
Ram Prasad A et al (2019) Multi-response optimization of machining process parameters for wire electrical discharge machining of lead-induced Ti-6Al-4V alloy using AHP–TOPSIS method. J Adv Manuf Syst 18(02):213–236. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219686719500112
Fuse K et al (2021) Integration of fuzzy AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS methods for wire electric discharge machining of titanium (Ti6Al4V) alloy using RSM. Materials 14(23):7408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237408
Singh SK et al (2022) Multi-response optimization of EDMed parameters of Ti-6Al-4 V alloy using entropy integrated-VIKOR method. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.04.348
Ekici E, Motorcu AR, Kuş A (2016) Evaluation of surface roughness and material removal rate in the wire electrical discharge machining of Al/B4C composites via the Taguchi method. J Compos Mater 50(18):2575–2586. https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998315609788
Bilge T, Motorcu AR, Ivanov A (2017) Kompakt Laminatin Delinmesinde Boyutsal Tamlık için Delme Parametrelerinin Gri İlişkisel Analiz ile Optimizasyonu. Uluslararası Teknolojik Bilimler Dergisi 9(2):1–22
Abhilash P, Chakradhar D (2020) Prediction and analysis of process failures by ANN classification during wire-EDM of Inconel 718. Advances in Manufacturing 8(4):519–536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40436-020-00327-w
Gisario A et al (2020) Prediction model for determining the optimum operational parameters in laser forming of fiber-reinforced composites. Adv Manuf 8(2):242–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40436-020-00304-3
Markopoulos AP, Manolakos DE, Vaxevanidis NM (2008) Artificial neural network models for the prediction of surface roughness in electrical discharge machining. J Intell Manuf 19(3):283–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-008-0081-9
Ong P et al (2020) Intelligent approach for process modelling and optimization on electrical discharge machining of polycrystalline diamond. J Intell Manuf 31(1):227–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-018-1443-6
Maity K, Mishra H (2018) ANN modelling and elitist teaching learning approach for multi-objective optimization of μ-EDM. J Intell Manuf 29(7):1599–1616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-016-1193-2
Karatas MA, Gokkaya H, Nalbant M (2019) Optimization of machining parameters for abrasive water jet drilling of carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composite material using Taguchi method. Aircr Eng Aerosp Technol. https://doi.org/10.1108/AEAT-11-2018-0282
Akıncıoğlu G et al (2017) Taguchi optimization of machining parameters in drilling of AISI D2 steel using cryo-treated carbide drills. Sādhanā 42(2):213–222
Akıncıoğlu S, Gökkaya H, Uygur İ (2016) The effects of cryogenic-treated carbide tools on tool wear and surface roughness of turning of Hastelloy C22 based on Taguchi method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 82(1–4):303–314
Karataş MA (2022) Multi-criteria optimization of surface roughness in wire EDM of inconel 718 by Taguchi based gray relational analysis method. Pamukkale Univ J Eng Sci. https://doi.org/10.5505/pajes.2021.74501
Kumar P, Meenu M, Kumar V (2018) Optimization of process parameters for WEDM of Inconel 825 using grey relational analysis. Decis Sci Lett 7(4):405–416
Karataş MA, Motorcu AR, Gökkaya H (2020) Optimization of machining parameters for kerf angle and roundness error in abrasive water jet drilling of CFRP composites with different fiber orientation angles. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42(4):1–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-2261-2
Jahan MP (2014) Electrical discharge machining (EDM): types, technologies and applications. Nova Science Publishers, Incorporated
Majumder H, Maity K (2018) Prediction and optimization of surface roughness and micro-hardness using grnn and MOORA-fuzzy-a MCDM approach for nitinol in WEDM. Measurement 118:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.01.003
Sedlaček M, Podgornik B, Vižintin J (2009) Influence of surface preparation on roughness parameters, friction and wear. Wear 266(3–4):482–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2008.04.017
Munhoz MR et al (2020) Analysis of the surface roughness obtained by the abrasive flow machining process using an abrasive paste with oiticica oil. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 106(11):5061–5070. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04920-7
Svahn F, Kassman-Rudolphi Å, Wallén E (2003) The influence of surface roughness on friction and wear of machine element coatings. Wear 254(11):1092–1098. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(03)00341-7
Rao CM, Venkatasubbaiah K, Rao KJ (2016) Experimental investigation of surface roughness characteristics Ra, Rq and Rz. Int J Hybrid Inf Technol 9(7):373–388
Bobbili R, Madhu V, Gogia A (2013) Effect of wire-EDM machining parameters on surface roughness and material removal rate of high strength armor steel. Mater Manuf Process 28(4):364–368. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2012.736661
Canbolat A et al (2019) Performance optimization of absorption refrigeration systems using Taguchi, ANOVA and Grey relational analysis methods. J Clean Prod 229:874–885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.020
Raghuraman S et al (2013) Optimization of EDM parameters using Taguchi method and grey relational analysis for mild steel IS 2026. Int J Innov Res Sci Eng Technol 2(7):3095–3104
Devarasiddappa D, et al. (2019) Modified teaching learning based optimization for maximization of MRR in wire-cut EDM of Ti6Al4V alloy for sustainable production. in AIP Conference Proceedings. AIP Publishing LLC
Dobes J et al (2017) Effect of mechanical vibration on Ra, Rq, Rz, and Rt roughness parameters. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92(1):393–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0137-0
Lauwers B et al (2004) Investigation of material removal mechanisms in EDM of composite ceramic materials. J Mater Process Technol 149(1–3):347–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2004.02.013
Lodhi BK, Agarwal S (2014) Optimization of machining parameters in WEDM of AISI D3 steel using Taguchi technique. Procedia CIRP 14:194–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2014.03.080
Xu M et al (2009) Material removal mechanisms of cemented carbides machined by ultrasonic vibration assisted EDM in gas medium. J Mater Process Technol 209(4):1742–1746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.04.031
Örs A, Biberci MA, Aydın M, Çelik MB (2018) Prediction of Performance and Exhaust Emissions of a Motor Using Biodiesel and Butanol Mixture with Artificial Neural Network. INCOS2018 - 14th International Conference of Combustion
Çay Y, Korkmaz İ, Çiçek A, Kara F (2013) Prediction of engine performance and exhaust emissions for gasoline and methanol using artificial neural network. Energy. 50:177–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.10.052
Mukhopadhyay A et al (2019) Modeling and optimization of fractal dimension in wire electrical discharge machining of EN 31 steel using the ANN-GA approach. Materials 12(3):454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030454
Gökçe H, Biberci M (2021) Investigation of thrust force, Drill bit temperature and Burr height in the Drilling of Aluminum Alloy Used in ammunition wing drive systems. Exp Tech:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40799-021-00501-0
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Yeni Öztürk Kalıp A.Ş. who contributed to the realization of the experiments.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altin Karataş, M., Biberci, M. Statistical Analysis of WEDM Machining Parameters of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Using Taguchi-Based Grey Relational Analysis and Artificial Neural Network. Exp Tech 47, 851–870 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40799-022-00601-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40799-022-00601-5