Abstract
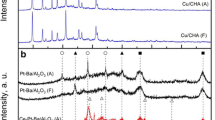
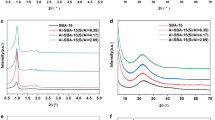
Nanoarray-based monolithic catalysts have been developed for various applications, including CO oxidation, hydrocarbon combustion, lean NOx trapping, and low-pressure CO2 hydrogenation. In this work, SO2 adsorption properties have been explored and evaluated on the cordierite honeycomb monoliths grown with zinc oxide nanoarray (ZnO), zinc oxide nanoarray washcoated by BaCO3 nanoparticles (ZnO/BaCO3), and manganese oxide nanowire array with cryptomelane structure (MnOx) at a temperature range from 50 to 425 °C. All samples show temperature-dependent SO2 adsorption behaviors. The adsorption results reveal the performance order: MnOx > ZnO/BaCO3 > ZnO, with ~ 90% SO2 adsorbed in MnOx at 425 °C. Washcoated BaCO3 contributes to the improvement of SO2 adsorption in ZnO nanoarray, and the best performance displayed in MnOx may be attributed to their high specific surface area. After regeneration, nanoarrays all exhibit good thermal stability during test-regeneration cycles. No additional phase is formed in regenerated ZnO nanoarrays (ZnO-R), while BaCO3 is converted to BaSO4 in the regenerated ZnO/BaCO3 nanoarrays (ZnO/BaCO3-R), and the sulfur species (possibly MnSO4) and Mn2O3 are found in regenerated MnOx nanoarrays (MnOx-R). It is noted that a small amount of sulfur species (possibly MnSO4) may promote the SO2 adsorption of MnOx-R at a lower temperature, while the formed Mn2O3 contributes to the deactivation of MnOx-R.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greenberg, N., Carel, R.S., Derazne, E., Bibi, H., Shpriz, M., Tzur, D., Portnov, B.A.: Different effects of long-term exposures to SO2 and NO2 air pollutants on asthma severity in young adults. J. Toxic. Environ. Health A. 79(8), 342–351 (2016)
Kan, H., Wong, C.-M., Vichit-Vadakan, N., Qian, Z.: Short-term association between sulfur dioxide and daily mortality: the public health and air pollution in Asia (PAPA) study. Environ. Res. 110(3), 258–264 (2010)
Weerasinghe, S.: A missing values imputation method for time series data: an efficient method to investigate the health effects of sulphur dioxide levels. Environmetrics. 21(2), 162–172 (2010)
Choi, J.-S., Partridge, W.P., Pihl, J.A., Daw, C.S.: Sulfur and temperature effects on the spatial distribution of reactions inside a lean NOx trap and resulting changes in global performance. Catal. Today. 136(1), 173–182 (2008)
Mathieu, Y., Tzanis, L., Soulard, M., Patarin, J., Vierling, M., Molière, M.: Adsorption of SOx by oxide materials: a review. Fuel Process. Technol. 114, 81–100 (2013)
Pineda, M., Palacios, J., Alonso, L., Garcıa, E., Moliner, R.: Performance of zinc oxide based sorbents for hot coal gas desulfurization in multicycle tests in a fixed-bed reactor. Fuel. 79(8), 885–895 (2000)
Sasaoka, E., Hirano, S., Kasaoka, S., Sakata, Y.: Stability of zinc oxide high-temperature desulfurization sorbents for reduction. Energy Fuel. 8(3), 763–769 (1994)
Siriwardane, R. V.; Cicero, D. C.; Jain, S.; Gupta, R. P.; Turk, B. S. Durable zinc oxide-based regenerable sorbents for desulfurization of syngas in a fixed-bed reactor; National Energy Technology Laboratory, Morgantown, WV; Research Triangle: 2002
Prades, J., Cirera, A., Morante, J.: Ab initio calculations of NO2 and SO2 chemisorption onto non-polar ZnO surfaces. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 142(1), 179–184 (2009)
Luo, S., Liu, J., Wu, Z.: Interaction of SO2 with ZnO nanoshapes: impact of surface polarity. J. Phys. Chem. C. (2019)
Wu, C.-M., Baltrusaitis, J., Gillan, E.G., Grassian, V.H.: Sulfur dioxide adsorption on ZnO nanoparticles and nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C. 115(20), 10164–10172 (2011)
Wang, J., Liang, B., Parnas, R.: Manganese-based regenerable sorbents for high temperature H2S removal. Fuel. 107, 539–546 (2013)
Wang, H. Q.; Ju, S. G.; Liu, L. P.; Zhao, X. W.; Mi, J. In The regeneration properties of manganese oxide sorbent under SO2 atmosphere, Materials Science Forum, Trans Tech Publ: 2016; pp 140–145
Li, L., King, D.L.: High-capacity sulfur dioxide absorbents for diesel emissions control. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 44(1), 168–177 (2005)
Li, L., King, D.L.: Cryptomelane as high-capacity sulfur dioxide absorbent for diesel emission control: a stability study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 44(19), 7388–7397 (2005)
Weng, J., Lu, X., Gao, P.X.: Nano-array integrated structured catalysts: a new paradigm upon conventional wash-coated monolithic catalysts? Catalysts. 7(9), 253 (2017)
Elmer, T. H.. Ultra-low expansion ceramic articles. Google Patents: 1976
Xiao, W., Guo, Y., Ren, Z., Wrobel, G., Ren, Z., Lu, T., Gao, P.-X.: Mechanical-agitation-assisted growth of large-scale and uniform ZnO nanorod arrays within 3D multichannel monolithic substrates. Cryst. Growth Des. 13(8), 3657–3664 (2013)
Liu, Z., Wu, D., Ren, S., Chen, X., Qiu, M., Wu, X., Yang, C., Zeng, G., Sun, Y.: Solvent-free synthesis of c-axis oriented ZSM-5 crystals with enhanced methanol to gasoline catalytic activity. ChemCatChem. 8(21), 3317–3322 (2016)
Wang, S., Wu, Y., Miao, R., Zhang, M., Lu, X., Zhang, B., Kinstler, A., Ren, Z., Guo, Y., Lu, T., Suib, S.L., Gao, P.X.: Scalable continuous flow synthesis of ZnO nanorod arrays in 3-D ceramic honeycomb substrates for low-temperature desulfurization. CrystEngComm. 19(34), 5128–5136 (2017)
Thongtem, T., Tipcompor, N., Phuruangrat, A., Thongtem, S.: Characterization of SrCO3 and BaCO3 nanoparticles synthesized by sonochemical method. Mater. Lett. 64(4), 510–512 (2010)
Koballa, T. E.; Dudukovic, M. In Sulfur dioxide adsorption on metal oxides supported on alumina, AIChE Symposium Series, 1977; pp 199–228
Cheng, S., Søgaard, M., Han, L., Zhang, W., Chen, M., Kaiser, A., Hendriksen, P.V.: A novel CO2- and SO2-tolerant dual phase composite membrane for oxygen separation. Chem. Commun. 51(33), 7140–7143 (2015)
Ostroff, A.G., Sanderson, R.T.: Thermal stability of some metal sulphates. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 9(1), 45–50 (1959)
Lietti, L., Forzatti, P., Nova, I., Tronconi, E.: NOx Storage reduction over Pt-Ba/γ-Al2O3 catalyst. J. Catal. 204(1), 175–191 (2001)
Yang, L., Jiang, X., Yang, Z.-S., Jiang, W.-J.: Effect of MnSO4 on the removal of SO2 by manganese-modified activated coke. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 54(5), 1689–1696 (2015)
Qu, Y.-F., Guo, J.-X., Chu, Y.-H., Sun, M.-C., Yin, H.-Q.: The influence of Mn species on the SO2 removal of Mn-based activated carbon catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 282, 425–431 (2013)
Funding
This work was sponsored by the US DOE Building Technologies Office, with Antonio Bouza as a program manager, the US National Science Foundation, and the University of Connecticut START PPOC Fund. J. Weng was partially supported by the Thermo Fisher Scientific Graduate Fellowship. The microscopy studies were performed using the facilities in the UConn/Thermo Fisher Scientific Center for Advanced Microscopy and Materials Analysis (CAMMA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weng, J., Gao, PX., Gao, Z. et al. Nanoarray-Based Monolithic Adsorbers for SO2 Removal. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 6, 315–323 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40825-020-00161-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40825-020-00161-3