Abstract
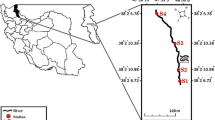
The current study was conducted to evaluate the impact of anthropogenic stresses on physico-chemical attributes and the abundance of macroinvertebrates during a period of one year from November 2017 to October 2018. Two important sampling sites (reference site S1; impacted site S2) characterized by various human activities were identified along the river. Anthropogenic activities were common at the impacted site (S2). High concentrations of TDS, phosphates, nitrates, sodium, turbidity, and conductivity were recorded at site S2. Based on Pearson’s correlation coefficient and canonical correspondence analysis, a few parameters including the dissolved oxygen, water velocity, TDS, turbidity, pH and nitrates shape the taxonomic order and species of macroinvertebrate in the Baldi River. The dominance of species under Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera, and Trichoptera orders at site S1 indicated the stress-free conditions, whereas an increase in the density of Oligochaeta and Diptera (Chrimonoids) at site S2 represented serious anthropogenic stress condition. Lower values of biotic indices (Shannon–Weiner diversity index, EPT %, BMWP, and ASPT) also indicated a disturbance at site S2. Degradation in water quality, decrease in the dominance of Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera, and Trichoptera, and an increase in Annelids and Chrimonoids are the key factors that reflect anthropogenic stress on the Baldi River.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data will be available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- WT:
-
Water temperature
- WV:
-
Water velocity
- Trans:
-
Transparency
- Cond:
-
Conductivity
- TU:
-
Turbidity
- TDS:
-
Total dissolved solids
- DO:
-
Dissolved oxygen
- AL:
-
Alkalinity
- CA:
-
Calcium
- HAR:
-
Hardness
- MG:
-
Magnesium
- NI:
-
Nitrates
- PHOS:
-
Phosphates
- NA:
-
Sodium
- K:
-
Potassium
- SUL:
-
Sulfates
- CM:
-
CPOM
- FM:
-
FPOM
- E:
-
Ephemeroptera
- P:
-
Plecoptera
- T:
-
Tricoptera
- D:
-
Diptera
- C:
-
Coleoptera
- O:
-
Odonata
- G:
-
Gastropoda
- Oi:
-
Oligochaeta
References
Aagaard KJ, Solem O, Bongard T, Hanseen O (2004) Studies of aquatic insects in the Atna River 1987–2002. Hydrobiologia 521:87–105
Aazami J, Esmaili-Sari A, Abdoli A, Sohrabi H, Brink PJV (2015) Monitoring and assessment of water health quality in the Tajan River, Iran using physicochemical, fish and macroinvertebrates indices. J Environ Health Sci Engineer 13:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40201-015-0186-y
Ahmed A (2004) Ecological studies of the River Padma at MawaGhat, Munshiganj I. Physicochemical Properties Pak J Biol Sci 7:1865–1869
Ali AL (2010) Seasonal variation in physico-chemical properties and zooplankton biomass in Greater Zab River-Iraq. Jordan J Biol Sci 3:115–120
APHA (American Public Health Association) (2005) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste Water, Washington DC 1–1368.
Armitage PD, Moss D, Wright JF, Furse M (1983) The performance of a new biological water quality score system based on macroinvertebrates over a wide range of unpolluted running-water sites. Water Res 17(3):333–347
Arslan N, Salur A, Kalyoncu H, Mercan D, Barisik B, Odabasi DA (2016) The use of BMWP and ASPT indices for evaluation of water quality according to macroinvertebrates in Küçük Menderes River (Turkey). Biologia 71:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2016-0005
Azrina MZ, Yap CK, Rahim-Ismail A, Ismail A, Tan SG (2006) Anthropogenic impacts on the distribution and biodiversity of benthic macroinvertebrates and water quality of the Langat River, Peninsular Malaysia. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64:337–347
Bawa U, Muhammad IA, Ibrahim H (2018) Assessment of water quality using biological monitoring working party (BMWP) and average score per taxon (ASPT) score at Kanye and Magaga dams. Kano Bayero J Pure Appl Sci 11(2):210–218. https://doi.org/10.4314/bajopas.v11i2.28
Beauger A, Lair N, Reyes-Marchant P, Peiry JL (2006) The distribution of macroinvertebrate assemblages in a reach of the river Allier (France), in relation to riverbed characteristics. Hydrobiologia 571(1):63–76
Bhatt LR, Lacoul P, Lekhak H, Jha PK (1999) Physicochemical characteristics and phytoplankton of Taudaha Lake. Kathmandu Pollution Research 18(14):353–358
Bisht S, Sharma RC, Rawat S, Kumar R (2018) Physico–chemical attributes and bacterial diversity of river water at Rudraprayag, Garhwal Himalaya. MOJ Eco Environ Sci. 3(4): 277‒282. https://doi.org/10.15406/mojes.2018.03.00100
Biswas S, Mukhopadhyay P, Saha SK (1995) Insecta: Coleoptera: Adephoga IV. Fam. Gyrinidae Fam Haliplidae. Zool. Surv. India, State Fauna Series 3. Fauna of West Bengal 64:77–220
Boulton AJ (2003) Parallels and contrasts in the effects of drought on stream macro-invertebrate assemblages. Freshw Biol 48:1173–1185
Carlisle DM, Meador MR (2007) A biological assessment of streams in the eastern United States using a predictive model for macroinvertebrate assemblages. J Am Water Resour Assoc 43:1194–1207
Chughtai MI, Mahmood K, Awan AR (2011) Assessment of planktonic diversity in River Chenab as affected by sewage of Multan city. Pak J Bot 43:2551–2555
Clews E, Low E, Belle CC, Todda PA, Eikaas HS, Ng PKL (2014) A pilot macroinvertebrate index of the water quality of Singapore’s reservoirs. Ecol Indic 38:90–103
Copatti CE, Copatti BR, Dal-Soler C, Barbosa S (2012) Macrodieta de trêsespécies de peixes do rio Cambará, bacia do rio Uruguai. Perspectiva 36(133):129–137
Czerniawska-Kusza I (2005) Comparing modified biological monitoring working party score system and several biological indices based on macroinvertebrates for water quality assessment. Limnologica 35:169–176
Death RG, Winterbourn MJ (1995) Diversity patterns in stream benthic invertebrate communities: The influence of habitat stability. Ecology 76:1446–1460
Den Van Brink FWB, Beljaards MJ, Boots NCA, Der Van VG (1994) Macrozoobenthos abundance and community composition in three lower Rhine floodplain lakes with varying inundation regimes. Regul Rivers 9(4):279–293
Disney RH (1975) A Key to British Dixidae. Freshwater Biological Association, The Ferry House, Ambleside, Cumbria, Scientific Publication No. 31
Dolisy D, Dohet A (2003) The use of Ephemeroptera to assess aquatic biodiversity in the rhithral part of the Luxembourgish rivers. In: Gaino E (ed) Research Update on Ephemeroptera & Plecoptera. Universitàdi Perugia, Perugia, Italy, pp 299–303
Edington JM, Hilldrew AG (1995) Caseless Caddis Larvae ofthe British Isles: A key with Ecological Notes. Scientific Publication No. 53. Freshwater Biological Association, The Ferry House, Ambleside, Cumbria.
Elliott JM, Humpesch UH, Macan TT (1988) Larvae of the British Ephemeroptera: a key with ecological notes. Freshwater Biological Association, The Ferry House, Ambleside, Cumbria, Scientific Publication 49: 1–145
Elósegui A, Pozo J (1994) Spatial versus temporal variability in the physical and chemical characteristics of the Agüera Stream (Northern Spain). Acta Oecol 15:543–559
Emmanuel AY, Jerry CS, Dzigbodi DA (2018) Review of Environmental and Health Impacts of Mining in Ghana. J Health Pollut 8(17):43–52. https://doi.org/10.5696/2156-9614-8.17.43
Enawgaw Y, Lemma B (2019) Ecological Conditions and Benthic Macroinvertebrates of Lake Tinishu Ababya, Ethiopia. Oceanogr Fish Open Access J. 10(2): 555782. https://doi.org/10.19080/OFOAJ.2019.10.555782
Goudie A (2000) The human impact on the natural environment, 5th edn. The MITPress, Cambridge
Grubh AR, Mitsch WJ (2004) Distribution and abundance of macroinvertebrates in created wetland ecosystems. In: Mitsch WJ, Zhang L, Tuttle C (eds) Olentangy river wetland research park annual report 2003. The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, pp 105–116
Gupta S (2013) Surface water quality monitoring of some selected fresh water environments in Durgapur, West Bengal, India in relation to macroinvertebrate diversity and ecological health status. Asian Acad Res J Multidisciplinary 1(14):342–363
Hammer Ø, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) Past: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electronica 4(1):1–9
Holomuzki JR, Biggs BJF (2000) Taxon-specific responses to high-flow disturbance in streams: implications for population persistence. J N Am Benthol Soc 19:670–679
Hwang SJ, Lee SW, Yoo B (2014) Ecological conservation and the restoration of freshwater environments in Korea. Paddy Water Environ 12:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-014-0457-8
Hynes HBN (1971) The Ecology of Running Waters. Liverpool University, Press Liverpool, pp 1–555
Hynes HBN (1977) Adults and nymphs of British stoneflies (Plecoptera): a key. Freshwater Biological Association, Ambleside, Cumbria. pp. 1–101.
Ishaq F, Khan A (2013a) Diversity pattern of macrozoobenthos and their relation with qualitative characteristics of River Yamuna in Doon Valley Uttarakhand. Am-Eur J Toxicol Sci 5(1):20–29
Ishaq F, Khan A (2013b) Seasonal limnological variation and macro benthic diversity of river Yamuna at Kalsi Dehradun of Uttarakhand. Asian J Plant Sci Res 3(2):133–144
Ishaq F, Khan A (2013c) Aquatic Biodiversity as an Ecological Indicators for Water Quality Criteria of River Yamuna in Doon Valley, Uttarakhand, India. World J Fish Marine Sci 5(3):322–334. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.wjfms.2013.05.03.72126
Jafari N, Nabavi SM, Akhavan M (2011) Ecological investigation of zooplankton abundance in the river Haraz Northeast Iran: Impact of environmental variables. Arch Biol Sci 63:785–798
Joshi PC, Negi RK, Negi T (2007) Seasonal variations in benthic macroinvertebrates and theircorrelation with the environmental variables in a freshwater stream in Garhwal Region (India). Life Sci 4(4):85–89
Kadam AD, Kishore G, Mishra DK, Arunachalam K (2020) Microalgal diversity as an indicator of the state of the environment of water bodies of Doon valley in Western Himalaya, India. Ecol. Indic. 112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106077
Karn SK, Harada H (2001) Surface water pollution inthree urban territories of Nepal, India, and Bangladesh. Environ Manage 28:483–496
Kannel PR, Lee S, Lee YS, Kanel SR, Pelletier GJ (2007) Application of automated QUAL2Kw for water quality modeling and management in the Bagmati River. Nepal Ecol Modell 202:503–517
Kumar R, Singh S, Sharma RC (2018) Application of WQI for assessment of water quality of high altitude lake Dodi Tal, Garhwal Himalaya, India. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 5(11). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-018-0281-1
Kumar R, Sharma RC (2019) Assessment of the water quality of Glacier-fed lake Neel Tal of Garhwal Himalaya. India Water Science 33(1):22–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/11104929.2019.1631554
Kumar R, Kumari R, Prasad C, Tiwari V, Singh N, Mohapatra S, Merugu R, Namtak S, Deep A (2020) Phytoplankton diversity in relation to physicochemical attributes and water quality of Mandakini River. Garhwal Himalaya Environ Monit Assess 192:799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08768-3
Kumar R, Kumari R, Prasad C, Deep A, Singh N, Namtak S, Tiwari V, Merugu R, Mohapatra S, Singh R (2021) Influence of water quality on the diversity of macroinvertebrates in the Mandakini River in India. Water Supply 21(4):1843–1860. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2021.020
Tampo L, Kaboré I, Alhassan EH, Ouéda A, Bawa LM, Djaneye-Boundjou G (2021) Benthic Macroinvertebrates as Ecological Indicators: Their Sensitivity to the Water Quality and Human Disturbances in a Tropical River. Front. water 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/frwa.2021.662765
Liang YL, Wang HZ (1999) Zoobenthos. In Advanced Hydrobiology, Liu JK (eds). Science Press: Beijing; 241–259. (in Chinese).
Liu C, Liu L, Shen H (2010) Seasonal variations of phytoplankton community structure in relation to physico-chemical factors in Lake Baiyangdian. China Procedia Environ Sci 2:1622–1631
Liu J, Zhang X, Xia J, Wu S, She D, Zou L (2016) Characterizing and explaining spatio-temporal variation of water quality in a highly disturbed river by multi-statistical techniques. Springer plus 5(1):1171. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-2815-z
LaBonte JR, Scott DW, McIver JD, Hayes JL (2001) Threatened, endangered and sensitive insects in Eastern Oregon and Washington forests and adjacent lands. Northwest Sci 75:185–198
Maddock I (1999) The importance of physical habitat assessment for evaluating river health.Freshwater Biology 41: 373–391.
Margalef R (1958) Information theory in ecology. General Systems 3: 36-71
Masson CF (1998) Biology of freshwater pollution, 3rd edn. Longman, Harlow (Essex)
Mehari AK, Wondie A, Mingist M, Vijverberg J (2014) Spatial and seasonal variation in the macro-invertebrates and physico-chemical parameters of the Enfranz River, Lake Tana sub-basin (Ethiopia). Ecohydrol Hydrobiol 14:304–312
Merritt RW, Cummins KW (1978) An introduction to the aquatic insects of North America. Kendall/Hunt Pub.Co.. Nature. pp. 1–441
Mitra A (1999) Studies on the Behavioural Patterns and SeasonalEcology of Some Species of Dragonflies (Odonata: Insecta) inAsan reservoir (Dehradun: India). D.Phil. Thesis, H.N.B. Garhwal University, Sringar-Garhwal.
Mitra RT (2003) Ecology and Biogeography of Odonata withspecial Reference to Indian Fauna, Part 202. ZoologicalSurvey of India, Kolkatta, pp. 1–41.
Mitra SC, Dey A, Ramkrishna C (2004) Pictoral Handbook-Indian Land Snails (Selected Species). Zoological Survey of India, Kolkata pp. 1–344.
Mophin-Kani K, Murugesan AG (2014) Assessment of river water quality using macroinvertebrate organisms as pollution indicators of Tamirabarani River Basin, Tamil Nadu. India Int J Environ Protection 4(1):1–14
Moskova G, Soufi R, Uzunov Y (2008) Application of the EPT-index for ecological status assessment of the riverine water bodies within the Basin of Kamchia River. Bioautomation 11:73–79
Moulton TP, Magalhães-Fraga SAP, Fraga SAP, Brito EF, Barbosa FAR (2010) Macroconsumers are more important than specialist macroinvertebrate shredders in leaf processing in urban forest streams of Rio de Janeiro. Brazil Hydrobiologia 638(1):55–66
Mustow SE (2002) Biological monitoring of rivers in Thailand: use and adaptation of the BMWP score. Hydrobiologia 479:191–229
Muylaert K, Sabbe K, Vyverman W (2000) Spatial and temporal dynamics of phytoplankton communities in a freshwater tidal estuary (Schelde, Belgium). Estuarine Coast Shelf Sci 50:673–687
Needham JG, Needham PR (1962) A guide to the study of freshwater biology, 5th edn. Holden Inc., San Francisco, USA
Nguyena HH, Everaertb G, Gabriels W, Hoangd TH, Goethals PLM (2014) A multimetric macroinvertebrate index for assessing the waterquality of the Cau river basin in Vietnam. Limnologica 45:16–23
Negi RK, Mamgain S (2013) Seasonal variation of benthic macro invertebrates from Tons River of Garhwal Himalaya Uttarakhand. Pak J Biol Sci 16(22):1510–1516. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjbs.2013.1510.1516
Ofenböck T, Moog O, Sharma S (2008) Development and application of the HKH Biotic Scoreto assess the river quality in the Hindu Kush-Himalaya. In: Moog O, Hering D, Sharma S, Stubauer I, Korte T (Eds.), ASSESS-HKH: Proceeding of the Scientific Conference ‘‘Rivers in the Hindu Kush-Himalaya-Ecology & Environmental Assessment’’, pp. 25–32.
Oliveira A, Callisto M (2010) Benthic macroinvertebrates as bioindicators of water quality in an Atlantic forest fragment. Iheringia, Sér. Zool., Porto Alegre 100(4): 291–300. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0073-47212010000400003
Ormerod SJ, Weatherley NS, Merrett WJ, Gee AS (1990) Restoring acidified streams in upland Wales: a modelling comparison of the chemical and biological effects of liming and reduced sulphate deposition. Environ Pollut 64:67–85
Payakka A, Prommi T (2014) The use of BMWP and ASPT biotic score as biological monitoring of streams in northern Thailand. J Appl Sci Environ Sanit 9(1):7–16
Pan BZ, Wang ZY, Xu MZ (2012) Macroinvertebrates in abandoned channels: assemblage characteristics and their indications for channel management. River Res Appl 28(8):1149–1160
Rani N, Sinha RK, Prasad K, Kedia DK (2011) Assessment of temporal variation in water quality of some important rivers in middle Gangetic plains. India Environ Monit Assess 174:401–415
Rawat H, Singh R, Namtak S, Deep A, Mamgain S, Sharma A, Tripathi N, Kirti V, Kumar R (2021) Water quality assessment of Garhwal Himalayan Lake Tarakund based on the application of WQI and mitigation measures for its conservation and management. Int J Energy Water Resources 5:73–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-020-00095-0
Rawat A, Gulati G, Maithani R, Sathyakumar S, Uniyal VP (2020) Bioassessment of Mandakini River with the help of aquatic macroinvertebrates in the vicinity of Kedarnath Wildlife Sanctuary. Appl Water Sci 10:36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-1115-5
Rawat S, Prasad C, Sharma RC, Bisht S, Kumar R (2018) Physicochemical Attributes and Bacterial Diversity of River Water at Deoprayag, Garhwal Himalaya, India. Journal of Aquatic Research and Marine Sciences 1(1): 1–6. https://doi.org/10.29199/ARMS.101017
Reynoldson TB, Schloessor DB, Manny BA (1989) Development of benthic invertebrate objective for mesotrophic great lakes waters. J Great Lakes Res 15:669–686
Rosenberg DM, Resh VH (1993) Fresh water biomonitoring and benthic macroinvertebrates. Chapman & Hall
Scarsbrook MR, Townsend CR (1993) Stream community structure in relation to spatial and temporal variation: a habitat templet study of two contrasting New Zealand streams. Freshw Biol 29:395–410
Semwal N, Akolkar P (2006) Water quality assessment of sacred Himalayan rivers of Uttaranchal. Curr Sci 91(4):486–496
Seth R, Mohan M, Singh P, Singh R, Dobhal R, Singh KP, Gupta S (2016) Water quality evaluation of Himalayan Rivers of Kumaun region, Uttarakhand, India. Appl Water Sci 6:137–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-014-0213-7
Sharma RC, Kumar R (2017) Water Quality Assessment of Sacred Glacial Lake Satopanth of Garhwal Himalaya. India Appl Water Sci 7(8):4757–4764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-017-0638-x
Sharma N, Kumar R, Sharma RC (2018) Microbiological water quality of the sacred River Bhagirathi, Garhwal Himalaya, India. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. https://doi.org/10.2166/washdev.2018.185
Shah RDT, Shah DN (2013) Evaluation of benthic macroinvertebrates assemblage for disturbance zonation in urban rivers using multivariate analysis: Implications for river management. J Earth Syst Sci 122(4):1125–1139
Shinde SE, Pathan TS, Raut KS, Sonawane DL (2011) Studies on the physico-chemical parameters and correlation coefficient of Harsool-savangi Dam, District Aurangabad, India. Middle-East J Sci Res 8:544–554
Shrestha M, Pradhan B, Shah DN, Tachamo RD, Sharma S, Moog O (2008) Water quality mapping of the Bagmati river basin, Kathmandu valley; In: Proceedingsof Scientific Conference on Rivers in the Hindu Kush Himalaya: Ecology and Environmental Assessment (eds) Moog O, Hering D, Sharma S, Stubauer I, Korte T. pp. 189–198.
Solimini AG, Gulia P, Monfrinotti M, Carchini G (2000) Performance of different biotic indices and sampling methods in assessing water quality in the lowland stretch of the Tiber River. Hydrobiologia 422(423):197–208
Søndergaard M, Jeppesen E (2007) Anthropogenic impacts on lake and stream ecosystems, and approaches to restoration. J Appl Ecol 44(6):1089–1094. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2664.2007.01426.x
Subbarao NV (1933) Freshwater molluscs of India. In: Rao KS (Ed.), Recent Advances in Freshwater Biology. ZoologicalSurvey of India, Kolkatta, pp. 182–202.
Thakur RK, Jindal R, Singh UB, Ahluwalia AS (2013) Plankton diversity and water quality assessment of three freshwater lakes of Mandi (Himachal Pradesh, India) with special reference to planktonic indicators. Environ Monit Assess 185:8355–8373
Todd LP (1995) Changes in biological characteristics of Daphnia magnafrom chronic action of copper and nickel at low concentrations. Hydrobiol J 5:59–62
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2005).Water Quality Standards Academy: Basic Course;Office of Water, Washington District of Columbia, USA,152p.
Varnosfaderany MN, Ebrahimi E, Mirghaffary N, Safyanian A (2010) Biological assessment of the ZayandehRud River, Iran, using benthic macroinvertebrates. Limnologica 40:226–232
Vinson MR, Hawkins CP (1998) Biodiversity of stream insects: variation at local, basin and regional scales. Annu Rev Entomol 43:193–271
Wallace JB, Webster JR (1996) The role of macroinvertebrates in stream ecosystem function. Annu Rev Entomol 41:115–139
Walley WJ, Hawkes HA (1996) A computer-based reappraisal of biological monitoring working party scores using data from the 1990 River Quality Survey of England and Wales. Water Res 30(9):2086–2094
Wang Y, Liu J, Li B, Liu W, Zuo Y, Kong D, Zhu J (2021) Relationships between characteristics of macrobenthic assemblages and environmental variables in the Heihe River Basin. China AQUA 70(5):710–730. https://doi.org/10.2166/aqua.2021.022
Ward JV, Stanford JA (1979) The Ecology of Regulated Streams. Plenum Press, New York, pp 1–398
Ward HB, Whipple GC (1992) Freshwater Biology, 2nd edn. John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp 1–1248
Wetzel RG, Likens GE (1991) Limnological Analyses, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 1–175p
Wilhm JL, Dorris TC (1968) Biological parameters of water quality criteria. Bioscience 18:477–481
Xu MZ, Wang ZY, Duan XH, Pan BZ (2013) Effects of pollution on aquatic ecology and water quality bio-assessment. Hydrobiologia 729(1):247–259
Yazdian H, Jaafarzadeh N, Zahraie B (2014) Relationship between benthic macroinvertebrate bio-indices and physicochemical parameters of water: a tool for water resources managers. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering. 12(1): Gale Academic OneFile, link.gale.com/apps/doc/A541261757/AONE?u=anon~89793b75&sid=googleScholar&xid=59bd9989
Zamora-Muňoz C, Sainz-Cantero C, Sanchez-Ortega A, Alba-Tercedor J (1995) Are biological indices BMWP and ASPT and their significance regarding water quality seasonally dependent? Factors Explaining Their Variations Water Res 29:285–290
Acknowledgements
Two of the authors (Neetu Singh and Rahul Kumar) thankfully acknowledge the University Grant Commission, New Delhi, and H.N.B. Garhwal University for providing financial support in the form of Central University Scholarship.
Funding
This study was solely funded by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study was conceived and designed by NS and RK. The study was performed by NS and RK. The laboratory work was conducted by NS and RK. The statistical design and data analyses by NS, BKC and SS. Manuscript was edited and approved for submission by NS, BKC, SS and RK.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Consent to participate
All authors voluntarily agree to participate in this research study.
Consent to publish
All authors voluntarily approved the publication of this research study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, N., Choudhary, B.K., Singh, S. et al. Monitoring and assessment of anthropogenic impacts on water quality by estimating the BMWP and ASPT indices for a headwater stream in Doon Valley, India. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 8, 108 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-022-00701-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-022-00701-5