Abstract
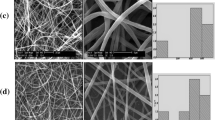
Although the healthcare market has billions of dollars in trade every year in this nano era, the nano products for healthcare remain limited. In this study, polyvinylpyrrolidone was used as a filament-forming matrix and drug carrier, and Phellinus igniarius (PI) was explored as a raw medicinal material. Coaxial electrospinning was implemented to transfer a traditional healthcare product (medicinal liquor) from PI into a nano healthcare product, that is, medicinal core–shell nanofibers. A homemade Teflon-coated concentric spinneret was utilized for setting up the coaxial electrospinning apparatus. The micro-formation mechanism of core–shell nanostructures from the spinneret was disclosed. The prepared core–shell nanofibers were characterized using scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, by which they were demonstrated to have a linear morphology with an evident core–shell structure. In addition, the active ingredients (primarily polysaccharides) from PI were presented in the nanofibers in an amorphous state, indicating good compatibility with the polymeric matrix. Homemade methods and ex vivo permeation tests were explored to evaluate the functional performance of medicinal core–shell nanofibers, which could be quickly dissolved to release the loaded active ingredients when they encountered water and ensured a rapid permeation effect. The present study pioneered a potential application to more people of electrospun core–shell healthcare nano products from traditional medicinal liquor.
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal A, Rao GK, Majumder S, Shandilya M, Rawat V, Purwar R, Verma M, Srivastava CM (2022) Natural protein-based electrospun nanofibers for advanced healthcare applications: progress and challenges. 3 Biotech 12(4):92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03152-z
Meftahi A, Samyn P, Geravand SA, Khajavi R, Alibkhshi S, Bechelany M, Barhoum A (2022) Nanocelluloses as skin biocompatible materials for skincare, cosmetics, and healthcare: formulations, regulations, and emerging applications. Carbohyd Polym 278:118956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118956
Liu ZQ, Ramakrishna S, Liu XL (2020) Electrospinning and emerging healthcare and medicine possibilities. APL Bioeng 4(3):030901. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0012309
Huesca-Uriostegui K, Garcia-Valderrama EJ, Gutierrez-Uribe JA, Antunes-Ricardo M, Guajardo-Flores D (2022) Nanofiber systems as herbal bioactive compounds carriers: current applications in healthcare. Pharmaceutics 14(1):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010191
Guo F, Zhou YF, Zhang F, Yuan F, Yuan YZ, Yao WY (2014) Idiopathic mesenteric phlebosclerosis associated with long-term use of medical liquor: two case reports and literature review. World J Gastroentero 20(18):5561–5566. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i18.5561
Chan TYK (2011) Causes and prevention of herb-induced aconite poisonings in Asia. Hum Exp Toxicol 30(12):2023–2026. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327111407224
Huang CY, Cheng YH, Chen SD (2022) Hot air-assisted radio frequency (HARF) drying on wild bitter gourd extract. Foods 11(8):1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11081173
Gao Y, Wu SM, Sun YQ, Cong RH, Xiao JY, Ma FL (2019) Effect of freeze dried, hot air dried and fresh onions on the composition of volatile sulfocompounds in onion oils. Dry Technol 37(11):1427–1440. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2018.1504062
Klaric M, Pervan S, Biosic M (2017) Influence of lyophilisation and oven-drying on extraction yield of oregonin from European black alder (Alnus glutinosa (L.) gaertn.) bark. Drvna Ind 68(3):205–210. https://doi.org/10.5552/drind.2017.1649
Hazarika U, Gosztola B (2020) Lyophilization and its effects on the essential oil content and composition of herbs and spices - a review. Acta Sci Polon-Techn 19(4):467–473. https://doi.org/10.17306/J.AFS.2020.0853
Sivan M, Madheswaran D, Valtera J, Kostakova EK, Lukas D (2022) Alternating current electrospinning: the impacts of various high-voltage signal shapes and frequencies on the spinnability and productivity of polycaprolactone nanofibers. Mater Design 213:110308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2021.110308
Salehipour M, Rezaei S, Haddad R, Mogharabi-Manzari M (2022) Preparation of electrospun hybrid polyacrylonitrile nanofibers containing TiO2/Fe3O4 and their capsaicinoids adsorption applications. Vietnam J Chem 60(3):267–280. https://doi.org/10.1002/vjch.202100105
Chen W, Zhao P, Yang YY, Yu DG (2022) Electrospun beads-on-the-string nanoproducts: preparation and drug delivery application. Curr Drug Deliv. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201819666220525095844
Pan D, Yang G, Abo-Dief HM, Dong JW, Su FM, Liu CT et al (2022) Vertically aligned silicon carbide nanowires/boron nitride cellulose aerogel networks enhanced thermal conductivity and electromagnetic absorbing of epoxy composites. Nano-Micro Lett 14(1):118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-022-00863-z
Wang M, Tan Y, Li D, Xu G, Yin D, Xiao Y, Xu T, Chen X, Zhu X, Shi X (2021) Negative isolation of circulating tumor cells using a microfluidic platform integrated with streptavidin-functionalized PLGA nanofibers. Adv Fiber Mater 3(3):192–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-021-00075-x
Kose MD, Ungun N, Bayraktar O (2021) Eggshell membrane based turmeric extract loaded orally disintegrating films. Curr Drug Deliv. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201818666210708123449
Feng XC, Hao JS (2021) Identifying new pathways and targets for wound healing and therapeutics from natural sources. Curr Drug Deliv 18(8):1052–1072. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201818666210111101257
Ji Y, Song W, Xu L, Yu DG, Annie-Bligh SW (2022) A review on electrospun poly(amino acid) nano-fibers and their applications of hemostasis and wound healing. Biomolecules 12:794. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12060794
Wang P, Song T, Abo-Dief HM, Song J, Alanazi AK, Fan BY et al (2022) Effect of carbon nanotubes on the interface evolution and dielectric properties of polylactic acid/ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer nanocomposites. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5(2):1100–1110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00489-0
Zhang CT, Sun JX, Lyu S, Lu ZY, Li T, Yang Y, Li B, Han H, Wu BY, Sun HY, Li DD, Huang JT, Sun DZ (2022) Poly(lactic acid)/artificially cultured diatom frustules nanofibrous membranes with fast and controllable degradation rates for air filtration. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00474-7
Cui Z, Marcelle SSA, Zhao M, Wu J, Liu X, Si J, Wang Q (2022) Thermoplastic polyurethane/titania/polydopamine (TPU/TiO2/PDA) 3-D porous composite foam with outstanding oil/water separation performance and photocatalytic dye degradation. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00503-5
Li JK, Guan SM, Su JJ, Liang JH, Cui LL, Zhang K (2021) The development of hyaluronic acids used for skin tissue regeneration. Curr Drug Deliv 18(7):836–846. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201817666201202094513
Yu DG, Wang M, Ge R (2021) Strategies for sustained drug release from electrospun multi-layer nanostructures. WIRES Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 14(3):e1772. https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1772
Kazsoki A, Palcso B, Alpar A, Snoeck R, Andrei G, Zelko R (2022) Formulation of acyclovir (core)-dexpanthenol (sheath) nanofibrous patches for the treatment of herpes labialis. Int J Pharma 611:121354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.121354
Omer S, Forgach L, Zelko R, Sebe I (2021) Scale-up of electrospinning: market overview of products and devices for pharmaceutical and biomedical purposes. Pharmaceutics 13(2):286. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13020286
Xu X, Lv H, Zhang M, Wang M, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Yu DG (2022) Recent progresses of electrospun nanofibers and their applications in treating heavy metal wastewater. Front Chem Sci Eng 2022(7):28
Liu Y, Chen X, Yu DG, Liu H, Liu Y, Liu P (2021) Electrospun PVP-core/PHBV-shell nanofibers to eliminate tailing off for an improved sustained release of curcumin. Mol Pharm 18(11):4170–4178. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.1c00559
Yuan Z, Sheng D, Jiang L, Shafifiq M, Khan AUR, Hashim R, Chen Y, Li B, Xie X, Chen J, Morsi Y, Mo XM, Chen SY (2022) Vascular endothelial growth factor-capturing aligned electrospun polycaprolactone/gelatin nanofibers promote patellar ligament regeneration. Acta Biomater 140:233–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2021.11.040
Zhou K, Wang M, Zhou Y, Sun M, Xie Y, Yu DG (2022) Comparisons of antibacterial performances between electrospun polymer@drug nanohybrids with drug-polymer nanocomposites. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00389-9
He H, Wu M, Zhu J, Yang Y, Ge R, Yu DG (2021) Engineered spindles of little molecules around electrospun nanofibers for biphasic drug release. Adv Fiber Mater 4(2):305–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-021-00112-9
Liu Y, Chen X, Gao Y, Liu YY, Yu DG, Liu P (2022) Electrospun core–sheath nanofibers with variable shell thickness for modifying curcumin release to achieve a better antibacterial performance. Biomolecules 2022:14
Lv H, Guo S, Zhang G, He W, Wu Y, Yu DG (2021) Electrospun structural hybrids of acyclovir-polyacrylonitrile at acyclovir for modifying drug release. Polymers 13(24):4286. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13244286
Huang C, Dong J, Zhang Y, Chai S, Wang X, Kang S (2022) Gold nanoparticles-loaded polyvinylpyrrolidone/ethylcellulose coaxial electrospun nanofibers with enhanced osteogenic capability for bone tissue regeneration. Mater Des 212:110240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2021.110240
Xu H, Zhang F, Wang M, Lv H, Yu DG, Liu X, Shen H (2022) Electrospun hierarchical structural films for effective wound healing. Biomater Adv 136:212795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioadv.2022.212795
Zhao K, Lu ZH, Zhao P, Kang SX, Yang YY, Yu DG (2021) Modified tri–axial electrospun functional core–shell nanofibrous membranes for natural photodegradation of antibiotics. Chem Eng J 425:131455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131455
Liu Y, Chen X, Gao Y, Yu DG, Liu P (2022) Elaborate design of shell component for manipulating the sustained release behavior from core–shell nanofibres. J Nanobiotechnol 20(1):244. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-022-01463-0
Liu H, Wang H, Lu X, Murugadoss V, Huang M, Yang H, Wan F, Yu DG, Guo Z (2022) Electrospun structural nanohybrids combining three composites for fast helicide delivery. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00478-3
Lv H, Zhang M, Wang P, Xu X, Liu Y, Yu DG (2022) Ingenious construction of Ni(DMG)2/TiO2-decorated porous nanofibers for the highly efficient photodegradation of pollutants in water. Colloid Surface A 650:129561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129561
Gao SL, Zhao XH, Fu Q, Zhang TC, Zhu J, Hou FH et al (2022) Highly transmitted silver nanowires-SWCNTs conductive flexible film by nested density structure and aluminum-doped zinc oxide capping layer for flexible amorphous silicon solar cells. J Mater Sci Technol 156:152–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2022.03.012
Du Y, Zhang X, Liu P, Yu DG, Ge R (2022) Electrospun nanofibers-based glucose sensors for glucose detection. Front Chem 10:944428. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2022.944428
Zhou Y, Liu Y, Zhang M, Feng Z, Yu DG, Wang K (2022) Electrospun nanofiber membranes for air filtration: a review. Nanomaterials 12(7):1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12071077
Xu X, Zhang M, Lv H, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Yu DG (2022) Electrospun polyacrylonitrile-based lace nanostructures and their Cu(II) adsorption. Sep Purif Technol 288:120643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120643
Xu L, Liu Y, Zhou W, Yu DG (2022) Electrospun medical sutures for wound healing: a review. Polymers 14(9):1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091637
Wang YB, Xu HX, Wu M, Yu DG (2022) Nanofibers-based food packaging. ES Food Agrof 7:1–24. https://doi.org/10.30919/esfaf598
Zhang X, Guo S, Qin Y, Li C (2021) Functional electrospun nanocomposites for efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Chem Res Chinese Universities 37(3):379–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40242-021-1123-5
Panthi G, Ranjit R, Khadka S, Gyawali KR, Kim HY, Park M (2020) Characterization and antibacterial activity of rice grain-shaped ZnS nanoparticles immobilized inside the polymer electrospun nanofibers. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 3(1):8–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-020-00141-9
Yu DG (2021) Preface—bettering drug delivery knowledge from pharmaceutical techniques and excipients. Curr Drug Deliv 18:2–3. https://doi.org/10.2174/156720181801201203091653
Zhang Y, Li S, Xu Y, Shi X, Zhang M, Huang Y, Liang Y, Chen Y, Ji W, Kim JR et al (2022) Engineering of hollow polymeric nanosphere-supported imidazolium-based ionic liquids with enhanced antimicrobial activities. Nano Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4160-6
Ma Y, Li D, Xiao Y, Ouyang Z, Shen M, Shi X (2021) LDH-doped electrospun short fibers enable dual drug loading and multistage release for chemotherapy of drug-resistant cancer cells. New J Chem 45(30):13421–13428. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1nj02159a
Liu X, Zhang M, Song W, Zhang Y, Yu DG, Liu Y (2022) Electrospun core (HPMC-acetaminophen)-shell (PVP-sucralose) nanohybrids as orodispersible drug delivery devices. Gels 8:357. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8060357
Tang Y, Varyambath A, Ding Y, Chen B, Huang X, Zhang Y et al (2022) Porous organic polymers for drug delivery: hierarchical pore structures, variable morphologies, and biological properties. Biomater. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2bm00719c
Yu DG, Lv H (2022) Preface-striding into nano drug delivery. Curr Drug Deliv 19(1):1–3
Zhang Y, Song W, Lu Y, Xu Y, Wang C, Yu DG, Kim I (2022) Recent advances in poly(α-L-glutamic acid)-based nanomaterials for drug delivery. Biomolecules 12(5):636. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12050636
Krysiak ZJ, Stachewicz U (2022) Electrospun fibers as carriers for topical drug delivery and release in skin bandages and patches for atopic dermatitis treatment. WIREs Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 14:e1829. https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1829
Mitragotri S, Burke P, Langer R (2014) Overcoming the challenges in administering biopharmaceuticals: formulation and delivery strategies. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13(9):655–672. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4363
Bakadia BM, Zhong A, Li X, e Boni1 BOO, Ahmed AAQ, Souho T, Zheng R, Shi Z, Shi D, Lamboni L, Yang G (2022) Biodegradable and injectable poly(vinyl alcohol) microspheres in silk sericin-based hydrogel for the controlled release of antimicrobials: application to deep full-thickness burn wound healing. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00467-6
Song Y, Huang H, He D, Yang M, Wang H, Zhang H, Li J, Li Y, Wang C (2021) Gallic acid/2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes electrospun nanofibrous webs: fast dissolution, improved aqueous solubility and antioxidant property of gallic acid. Chem Res Chinese Universities 37(3):450–455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40242-021-0014-0
Guo S, Jiang W, Shen L, Zhang G, Gao Y, Yang YY, Yu DG (2022) Electrospun hybrid films for fast and convenient delivery of active herbs extracts. Membranes 12(4):398. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040398
Kang S, Hou S, Chen X, Yu DG, Wang L, Li X, Williams GR (2020) Energy-saving electrospinning with a concentric Teflon-core rod spinneret to create medicated nanofibers. Polymers 12(10):2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102421
Ziyadi H, Baghali M, Bagherianfar M, Mehrali F, Faridi-Majidi R (2021) An investigation of factors affecting the electrospinning of poly (vinyl alcohol)/kefiran composite nanofibers. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4(3):768–779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00230-3
Ning T, Zhou Y, Xu H, Guo S, Wang K, Yu DG (2021) Orodispersible membranes from a modified coaxial electrospinning for fast dissolution of diclofenac sodium. Membranes 11(11):802. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110802
Liu H, Jiang W, Yang Z, Chen X, Yu DG, Shao J (2022) Hybrid films prepared from a combination of electrospinning and casting for offering a dual-phase drug release. Polymers 14(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14112132
Sun YQ, Huo JX, Zhong S, Zhu JX, Li YG, Li XJ (2021) Chemical structure and anti-inflammatory activity of a branched polysaccharide isolated from Phellinus baumii. Carbohyd Polym 268:118214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118214
Yang K, Zhang S, Ying YM, Li YG, Cai M, Guan RF, Hu JR, Sun PL (2020) Cultivated fruit body of Phellinus baumii: a potentially sustainable antidiabetic resource. ACS Omega 5(15):8596–8604. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b04478
Choi EH, Park KJ, Kang J, Lee SY (2020) The development of new functional ingredients for menopausal women and cardiovascular health. Food Sci Ind 53(4):374–381
Zhang HN, Chen RB, Zhang JS, Bu QT, Wang WH, Liu YF, Li Q, Guo Y, Zhang L, Yang Y (2019) The integration of metabolome and proteome reveals bioactive polyphenols and hispidin in ARTP mutagenized phellinus baumii. Sci Rep-Uk 9:16172. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52711-7
Zhang HN, Jiang FC, Qu DH, Wang WH, Dong YT, Zhang JS, Wu D, Yang Y (2019) Employment of ARTP to generate Phellinus baumii (agaricomycetes) strain with high flavonoids production and validation by liquid fermentation. Int J Med Mushrooms 21(12):1207–1221. https://doi.org/10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.2019032976
Min GJ, Bong-Sik Y, Kang HW (2020) Comparison of antioxidant activities and polyphenolic compounds of extracts from artificially cultivated Sanghwang mushroom species, Phellinus linteus and P. baumii. J Mushrooms 18(1): 29–36. https://doi.org/10.14480/JM.2020.18.1.29
Kim JH, Kwon KM, Yang JH, Ki B, Kim DK (2019) Antioxidative-activity of Phellinus baumii Pilat in Caenorhabditis elegans. Korean J Pharmacog 50(4):299–304
Yoon, KN, Soo LT (2020) Various physiological effects from fruiting body extracts of Phellinus baumii. J Mushrooms 18(3):260–267. https://doi.org/10.14480/JM.2020.18.3.260
Yang K, Zhang S, Geng Y, Tian BM, Cai M, Guan RF, Li YG, Ye BW, Sun PL (2021) Anti-inflammatory properties in vitro and hypoglycaemic effects of phenolics from cultivated fruit body of Phellinus baumii in type 2 diabetic mice. Molecules 26(8):2285. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082285
Yoo JH, Lee YS, Ku S, Lee HJ (2020) Phellinus baumii enhances the immune response in cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice. Nutr Res 75:15–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2019.12.005
Yang Y, Zhang L, Chen Q, Lu WL, Li N (2020) Antitumor effects of extract of the oak bracket medicinal mushroom, Phellinus baumii (Agaricomycetes), on human melanoma cells A375 in vitro and in vivo. Int J Med Mushrooms 22(2):197–209. https://doi.org/10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.2020033687
Gong L, Liu G, Bai J, Liu DL, He YH (2021) Optimization of extraction of Phellinus igniarius and antioxidant and antibacterial activities of lyophilized powder. Food Res Develop 42:143–149
Su Y, Li L (2020) Structural characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from four auriculariales. Carbohyd Polym 229:115407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115407
Chang C, Zhao JH, Yu WJ, Chen QH, Qin LW, Wu XL, Liu FX, Fan YG (2021) Extraction technology and determination of polysaccharide from Sanghuangporus vaninii. Chem Reagents 43:973–978
Ding Y (2017) Chemical constituents of the medicinal fungus Phellinus igniarius. PhD thesis, Anhui Medical University, Hefei, China
Wang YY, Ma HL, Ding ZC, Yang Y, Wang WH, Zhang HN, Yan JK (2019) Three-phase partitioning for the direct extraction and separation of bioactive exopolysaccharides from the cultured broth of Phellinus baumii. Int J Biol Macromol 123:201–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.065
Wang M, Yu DG, Williams GR, Annie Bligh SW (2022) Co-loading of inorganic nanoparticles and natural oil in the Electrospun Janus nanofibers for a synergetic antibacterial effect. Pharmaceutics 14:1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14061208
Brimo N, Serdaroglu DC, Uysal B (2021) Comparing antibiotic pastes with electrospun nanofibers as modern drug delivery systems for regenerative endodontics. Curr Drug Deliv 18:7. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201819666211216140947
Liu Y, Lv H, Liu Y, Gao Y, Kim HY, Ouyang Y, Yu DG (2022) Progresses on electrospun metal–organic frameworks nanofibers and their wastewater treatment applications. Mater Today Chem 25:100974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2022.100974
Zhan L, Deng J, Ke Q, Li X, Ouyang Y, Huang C, Liu X, Qian Y (2021) Grooved fibers: preparation principles through electrospinning and potential applications. Adv Fiber Mater 4(2):203–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-021-00116-5
Madheswaran D, Sivan M, Valtera J, Kostakova EK, Egghe T, Asadian M et al (2022) Composite yarns with antibacterial nanofibrous sheaths produced by collectorless alternating-current electrospinning for suture applications. J Appl Polym Sci 139(13):e51851. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.51851
Chen W, Wang C, Gao YY, Wu Y, Wu GM, Shi XW, Du YM, Deng HB (2020) Incorporating chitin derived glucosamine sulfate into nanofibers via coaxial electrospinning for cartilage regeneration. Carbohyd Polym 229:115544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115544
Ghazalian M, Afshar S, Rostami A, Rashedi S, Bahrami SH (2022) Fabrication and characterization of chitosan-polycaprolactone core-shell nanofibers containing tetracycline hydrochloride. Colloid Surface A 636:128163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.128163
Chen J, Zhang G, Zhao Y, Zhou M, Zhong A, Sun J (2022) Promotion of skin regeneration through co axial electrospun fibers loaded with basic fibroblast growth factor. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00439-w
Song X, Jiang Y, Zhang W, Elfawal G, Wang K, Jiang D, Hong H, Wu J, He C, Mo X et al (2022) Transcutaneous tumor vaccination combined with anti-programmed death-1 monoclonal antibody treatment produces a synergistic antitumor effect. Acta Biomater 140:247–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2021.11.033
Qi GY, Liu Y, Chen LL, Xie PT, Pan D, Shi ZC et al (2021) Lightweight Fe3C@Fe/C nanocomposites derived from wasted cornstalks with high-efficiency microwave absorption and ultrathin thickness. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4(4):1226–1238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00368-0
Xie PT, Shi ZC, Feng M, Sun K, Liu Y, Yan KL et al (2022) Recent advances in radio-frequency negative dielectric metamaterials by designing heterogeneous composites. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5(2):679–695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00479-2
Zhang Z, Liu MX, Ibrahim MM, Wu HK, Wu Y, Li Y et al (2022) Flexible polystyrene/graphene composites with epsilon-near-zero properties. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5(2):1054–1066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00486-3
Wu H, Zhong YM, Tang YX, Huang YQ, Liu G, Sun WT et al (2022) Precise regulation of weakly negative permittivity in CaCu3Ti4O12 metacomposites by synergistic effects of carbon nanotubes and grapheme. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5(1):419–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00378-y
Xie PT, Liu Y, Feng M, Niu M, Liu CZ, Wu NN et al (2021) Hierarchically porous Co/C nanocomposites for ultralight high-performance microwave absorption. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4(1):173–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-020-00202-z
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 81874034), Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (Nos. 20ZR1439000 and 21ZR1459500), Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning Foundation of Shanghai (No. 202140413), Medical Health Science and Technology Innovation Plan of Jinan (No.201805038, 201907085, and 202019182), Science and Technology Innovation Project of Medical Staff in Shandong province, Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No.ZR2020QH264), and Key Research and Development Project of Shandong Province (No. 2019GSF108002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, W., Zhang, X., Liu, P. et al. Electrospun healthcare nanofibers from medicinal liquor of Phellinus igniarius. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5, 3045–3056 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00551-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00551-x