Article contents
Buoyancy-driven flow in a confined aquifer with a vertical gradient of permeability
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 June 2018
Abstract
We examine the injection of fluid of one viscosity and density into a horizontal permeable aquifer initially saturated with a second fluid of different viscosity and density. The novel feature of the analysis is that we allow the permeability to vary vertically across the aquifer. This leads to recognition that the interface may evolve as either a rarefaction wave that spreads at a rate proportional to  $t$, a shock-like front of fixed length or a mixture of shock-like regions and rarefaction-wave-type regions. The classical solutions in which there is no viscosity ratio between the fluids and in which the formation has constant permeability lead to an interface that spreads laterally at a rate proportional to
$t$, a shock-like front of fixed length or a mixture of shock-like regions and rarefaction-wave-type regions. The classical solutions in which there is no viscosity ratio between the fluids and in which the formation has constant permeability lead to an interface that spreads laterally at a rate proportional to 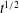 $t^{1/2}$. However, these solutions are unstable to cross-layer variations in the permeability owing to the vertical shear which develops in the flow, causing the structure of the interface to evolve to the rarefaction wave or shock-like structure. In the case that the viscosities of the two fluids are different, it is possible that the solution involves a mixture of shock-like and rarefaction-type structures as a function of the distance above the lower boundary. Using the theory of characteristics, we develop a regime diagram to delineate the different situations. We consider the implications of such heterogeneity for the prediction of front locations during
$t^{1/2}$. However, these solutions are unstable to cross-layer variations in the permeability owing to the vertical shear which develops in the flow, causing the structure of the interface to evolve to the rarefaction wave or shock-like structure. In the case that the viscosities of the two fluids are different, it is possible that the solution involves a mixture of shock-like and rarefaction-type structures as a function of the distance above the lower boundary. Using the theory of characteristics, we develop a regime diagram to delineate the different situations. We consider the implications of such heterogeneity for the prediction of front locations during 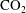 $\text{CO}_{2}$ sequestration. If we neglect the permeability fluctuations, the model always predicts rarefaction-type solutions, while even modest changes in the permeability across a layer can introduce shocks. This difference may be very significant since it leads to the
$\text{CO}_{2}$ sequestration. If we neglect the permeability fluctuations, the model always predicts rarefaction-type solutions, while even modest changes in the permeability across a layer can introduce shocks. This difference may be very significant since it leads to the  $\text{CO}_{2}$ plume occupying a greater fraction of the pore space between the injector and the leading edge of the
$\text{CO}_{2}$ plume occupying a greater fraction of the pore space between the injector and the leading edge of the 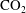 $\text{CO}_{2}$ front in a layer of the same mean permeability. This has important implications for estimates of the fraction of the pore space that the
$\text{CO}_{2}$ front in a layer of the same mean permeability. This has important implications for estimates of the fraction of the pore space that the 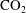 $\text{CO}_{2}$ may access.
$\text{CO}_{2}$ may access.
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2018 Cambridge University Press
References
- 27
- Cited by





